Abstract
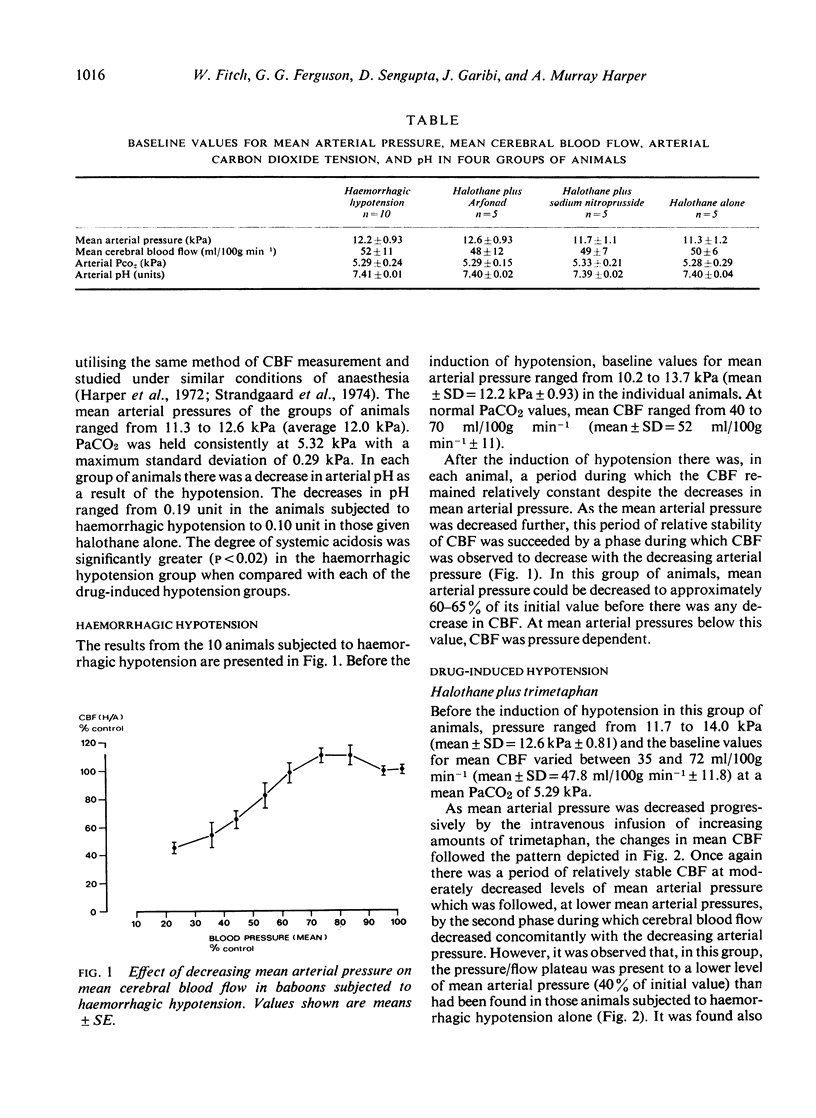
The effect of graded, progressive hypotension on the autoregulation of cerebral blood flow was studied in anaesthetised baboons. Progressive hypotension was produced over a period of four to five hours, either by graded haemorrhage or by the administration of increasing concentrations of hypotensive drugs. During haemorrhagic hypotension autoregulation was maintained until the mean arterial pressure had decreased to 65% of its baseline value, below which cerebral blood flow was pressure passive. In those animals subjected to drug-induced hypotension, autoregulation persisted to lower levels of mean arterial pressure (35-40% of baseline). It is postulated that under conditions of haemorrhagic hypotension, constriction of the extraparenchymal cerebral vessels in response to sympathetic stimulation decreases the possible range of autoregulation in the anaesthetised baboon.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. H., Brierley J. B., Connor R. C., Treip C. S. The effects of systemic hypotension upon the human brain. Clinical and neuropathological observations in 11 cases. Brain. 1966 Jun;89(2):235–268. doi: 10.1093/brain/89.2.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken R. R., Drake C. G. A technique of anesthesia with induced hypotension for surgical correction of intracranial aneurysms. Clin Neurosurg. 1974;21:107–114. doi: 10.1093/neurosurgery/21.cn_suppl_1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BESSMAN A. N., ALMAN R. W., FAZEKAS J. F. Effect of acute hypotension on cerebral hemodynamics and metabolism of elderly patients. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1952 Jun;89(6):893–898. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1952.00240060036004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIERLEY J. B., COOPER J. E. Cerebral complications of hypotensive anaesthesia in a healthy adult. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1962 Feb;25:24–30. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.25.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter L. P., Atkinson J. R. Cortical blood flow in controlled hypotension as measured by thermal diffusion. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Dec;36(6):906–913. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.6.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON M. H. A. The disadvantages of controlled hypotension in surgery. Br Med Bull. 1958 Jan;14(1):52–53. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Boulay G., Symon L., Shah S., Dorsch N., Ackerman R. Cerebral arterial reactivity and spasm after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Proc R Soc Med. 1972 Jan;65(1):80–82. doi: 10.1177/003591577206500135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECKENHOFF J. E., ENDERBY G. E., LARSON A., DAVIES R., JUDEVINE D. E. HUMAN CEREBRAL CIRCULATION DURING DELIBERATE HYPOTENSION AND HEAD-UP TILT. J Appl Physiol. 1963 Nov;18:1130–1138. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1963.18.6.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENDERBY G. E. H. The advantages of controlled hypotension in surgery. Br Med Bull. 1958 Jan;14(1):49–51. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklöf B., Ingvar D. H., Kågström E., Olin T. Persistence of cerebral blood flow autoregulation following chronic bilateral cervical sympathectomy in the monkey. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Jun;82(2):172–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAZEKAS J. F., KLEH J., PARRISH A. E. Renal and cerebral hemodynamics with hypotension. Am J Med Sci. 1957 Jan;233(1):35–39. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195701000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINNERTY F. A., Jr, WITKIN L., FAZEKAS J. F. Cerebral hemodynamics during cerebral ischemia induced by acute hypotension. J Clin Invest. 1954 Sep;33(9):1227–1232. doi: 10.1172/JCI102997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W., MacKenzie E. T., Harper A. M. Effects of decreasing arterial blood pressure on cerebral blood flow in the baboon. Influence of the sympathetic nervous system. Circ Res. 1975 Nov;37(5):550–557. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.5.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths D. P., Cummins B. H., Greenbaum R., Griffith H. B., Staddon G. E., Wilkins D. G., Zorab J. S. Cerebral blood flow and metabolism during hypotension induced with sodium nitroprusside. Br J Anaesth. 1974 Sep;46(9):671–679. doi: 10.1093/bja/46.9.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. M. Autoregulation of cerebral blood flow: influence of the arterial blood pressure on the blood flow through the cerebral cortex. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Oct;29(5):398–403. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.5.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. M., Deshmukh V. D., Rowan J. O., Jennett W. B. The influence of sympathetic nervous activity on cerebral blood flow. Arch Neurol. 1972 Jul;27(1):1–6. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490130003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. M. General physiology of cerebral circulation. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 1969 Fall;7(3):473–506. doi: 10.1097/00004311-196907030-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoedt-Rasmussen K., Sveinsdottir E., Lassen N. A. Regional cerebral blood flow in man determined by intra-arterial injection of radioactive inert gas. Circ Res. 1966 Mar;18(3):237–247. doi: 10.1161/01.res.18.3.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häggendal E., Johansson B. Effects of arterial carbon dioxide tension and oxygen saturation on cerebral blood flow autoregulation in dogs. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1965;258:27–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb03234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
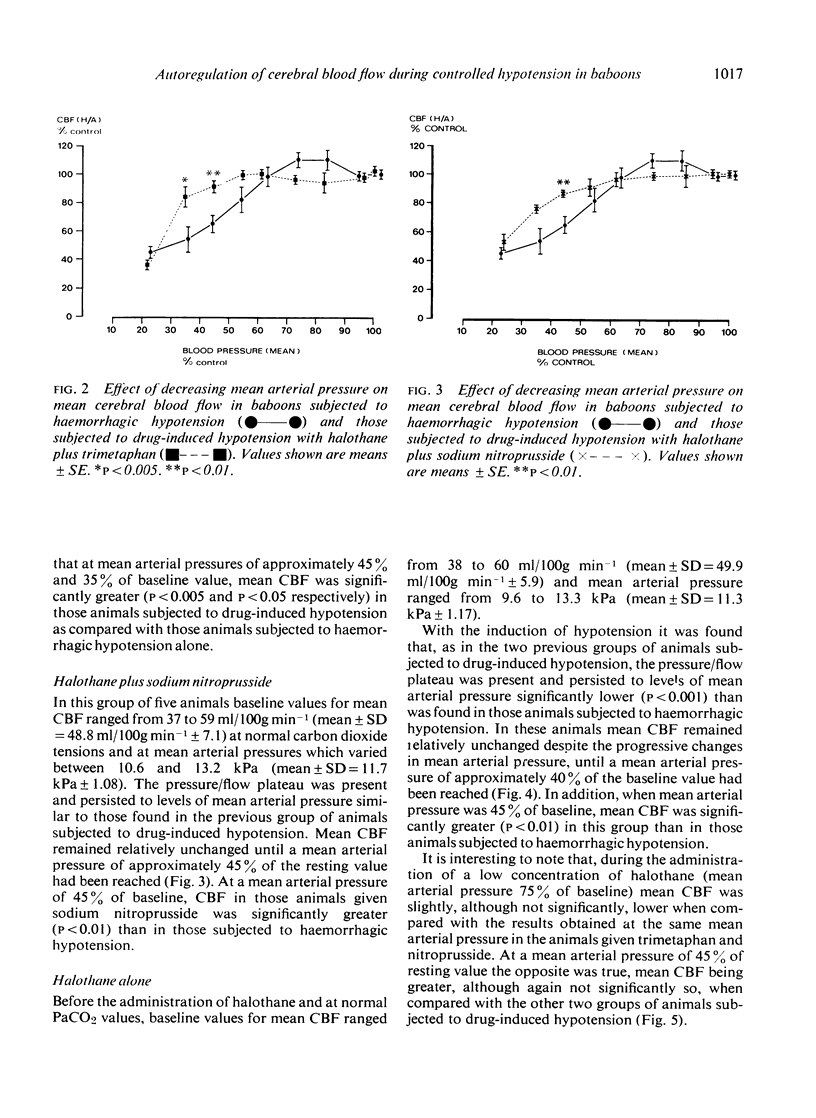
- James I. M., Millar R. A., Purves M. J. Observations on the extrinsic neural control of cerebral blood flow in the baboon. Circ Res. 1969 Jul;25(1):77–93. doi: 10.1161/01.res.25.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keaney N. P., Pickerodt V. W., McDowall D. G., Coroneos N. J., Turner J. M., Shah Z. P. Cerebral circulatory and metabolic effects of hypotension produced by deep halothane anaesthesia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Dec;36(6):898–905. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.6.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kety S. S., Schmidt C. F. THE NITROUS OXIDE METHOD FOR THE QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW IN MAN: THEORY, PROCEDURE AND NORMAL VALUES. J Clin Invest. 1948 Jul;27(4):476–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI101994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSEN N. A. AUTOREGULATION OF CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW. Circ Res. 1964 Aug;15:SUPPL–SUPPL:204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSEN N. A. Cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption in man. Physiol Rev. 1959 Apr;39(2):183–238. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1959.39.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen L. V., Johansson G. G., Tarkkanen L. The effect of nitrous oxide on pulsatile cerebral impedance and cerebral blood flow. Br J Anaesth. 1967 Oct;39(10):781–785. doi: 10.1093/bja/39.10.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYER J. H., MORRIS G. Cerebral hemodynamics during controlled hypotension induced by the continuous infusion of ganglionic blocking agents (hexamethonium, pendiomide and arfonad). J Clin Invest. 1954 Aug;33(8):1081–1088. doi: 10.1172/JCI102980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
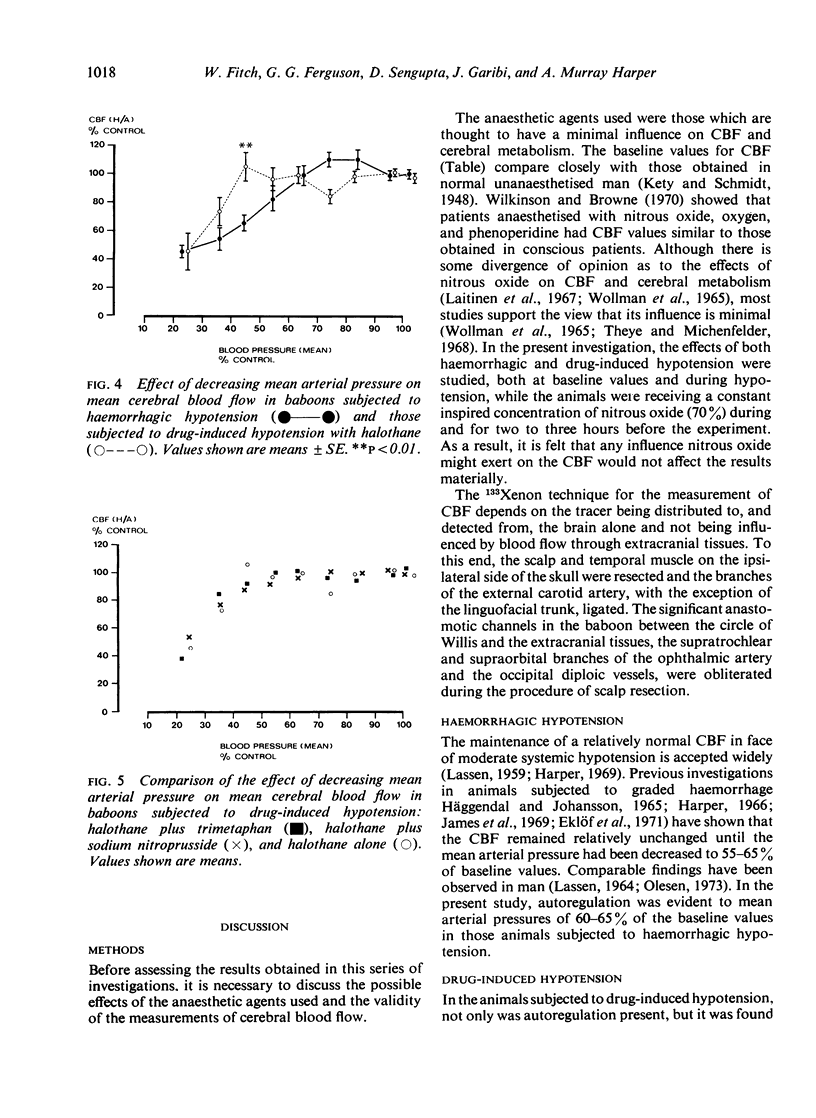
- McDowall D. G., Keaney N. P., Turner J. M., Lane J. R., Okuda Y. The toxicity of sodium nitroprusside. Br J Anaesth. 1974 May;46(5):327–332. doi: 10.1093/bja/46.5.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowall D. G. The effects of clinical concentrations of halothane on the blood flow and oxygen uptake of the cerebral cortex. Br J Anaesth. 1967 Mar;39(3):186–196. doi: 10.1093/bja/39.3.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olesen J. Quantitative evaluation of normal and pathologic cerebral blood flow regulation to perfusion pressure. Changes in man. Arch Neurol. 1973 Mar;28(3):143–149. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490210023001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olesen J. The effect of intracarotid epinephrine, norepinephrine, and angiotensin on the regional cerebral blood flow in man. Neurology. 1972 Sep;22(9):978–987. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.9.978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prys-Roberts C., Lloyd J. W., Fisher A., Kerr J. H., Patterson T. J. Deliberate profound hypotension induced with halothane: studies of haemodynamics and pulmonary gas exchange. Br J Anaesth. 1974 Feb;46(2):105–116. doi: 10.1093/bja/46.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLACK W. K., WALTHER W. W. CEREBRAL CIRCULATION IN INDUCED HYPOTENSION. Anaesthesia. 1964 Oct;19:494–500. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1964.tb00417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STONE H. H., MACKRELL T. N., WECHSLER R. L. The effect on cerebral circulation and metabolism in man of acute reduction in blood pressure by means of intravenous hexamethonium bromide and head-up tilt. Anesthesiology. 1955 Mar;16(2):168–176. doi: 10.1097/00000542-195503000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinghaus J. W. Blood gas calculator. J Appl Physiol. 1966 May;21(3):1108–1116. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.3.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Neigh J. L., Hoffman J. C., Wollman H. Effects of general anesthesia on autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in man. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Nov;29(5):665–669. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.29.5.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoica E., Meyer J. S., Kawamura Y., Hiromoto H., Hashi K., Aoyagi M., Pascu I. Central neurogenic control of cerebral circulation. Effects of intravertebral injection of pyrithioxin on cerebral blood flow and metabolism. Neurology. 1973 Jul;23(7):687–698. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.7.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoyka W. W., Schutz H. The cerebral response to sodium nitroprusside and trimethaphan controlled hypotension. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1975 May;22(3):275–283. doi: 10.1007/BF03004836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandgaard S., MacKenzie E. T., Sengupta D., Rowan J. O., Lassen N. A., Harper A. M. Upper limit of autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in the baboon. Circ Res. 1974 Apr;34(4):435–440. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.4.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theye R. A., Michenfelder J. D. The effect of nitrous oxide on canine cerebral metabolism. Anesthesiology. 1968 Nov-Dec;29(6):1119–1124. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196811000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLLMAN H., ALEXANDER C., COHEN P. J., SMITH T. C., CHASE P. E., VANDERMOLEN R. CEREBRAL CIRCULATION DURING GENERAL ANESTHESIA AND HYPERVENTILATION IN MAN.: THIOPENTAL INDUCTION TO NITROUS OXIDE AND D-TUBOCURARINE. Anesthesiology. 1965 May-Jun;26:329–334. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196505000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLLMAN H., ALEXANDER S. C., COHEN P. J., CHASE P. E., MELMAN E., BEHAR M. G. CEREBRAL CIRCULATION OF MAN DURING HALOTHANE ANESTHESIA: EFFECTS OF HYPOCARBIA AND OF D-TUBOCURARINE. Anesthesiology. 1964 Mar-Apr;25:180–184. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196403000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltz A. G. Effect of blood pressure on blood flow in ischemic and in nonischemic cerebral cortex. The phenomena of autoregulation and luxury perfusion. Neurology. 1968 Jul;18(7):613–621. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.7.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson I. M. Browne DR: The influence of anaesthesia and of arterial hypocapnia on regional blood flow in the normal human cerebral hemisphere. Br J Anaesth. 1970 Jun;42(6):472–482. doi: 10.1093/bja/42.6.472-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yashon D., Locke G. E., Bingham W. G., Jr, Wiederholt W. C., Hunt W. E. Cerebral function during profound oligemic hypotension in the dog. J Neurosurg. 1971 Apr;34(4):494–499. doi: 10.3171/jns.1971.34.4.0494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


