Abstract
We propose a new species, Christensenella timonensis, strain Marseille-P2437T (CSUR P2437T), which was isolated from gut microbiota of a 66-year-old patient as a part of culturomics study. C. timonensis represents the second species isolated within the Christensenella genus.
Keywords: Christensenella timonensis, culturomics, emerging bacterium, gut microbiota, taxonomy
In January 2016, we isolated a bacterial strain that could not be identified by our systematic matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) screening on a Microflex spectrometer (Bruker Daltonics, Leipzig, Germany) [1] as part of study of the human microbiome by culturomics [2]. The strain came from the stool sample of a 66-year-old diabetic patient hospitalized in November 2015 at the Timone Hospital in Marseilles, France, for a malignant blood disease. This study had been previously approved by the local ethics committee of the IFR48 (Marseille, France) under agreement 09-022.
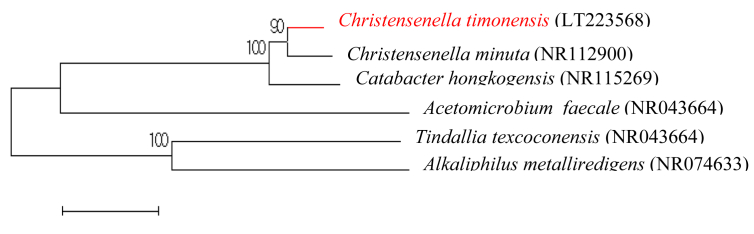
After receiving signed informed consent, the stool specimen was preincubated in anaerobic conditions at 37°C in a culture bottle containing a blood-enriched Columbia agar liquid medium (bioMérieux, Marcy l’Etoile, France). After 7 days of preincubation, the sample was seeded on 5% sheep's blood agar (bioMérieux), and the initial growth was obtained after 4 days under anaerobic generated by AnaeroGen (bioMérieux). The colonies are beige and about 0.1 to 0.2 mm in diameter. Cells are Gram-negative bacilli (0.3–0.5 × 1.2–1.5 μm), strictly anaerobic, nonmotile and non–spore forming. The strain Marseille-P2437 presents no catalase and oxidase activities. The 16S rRNA gene of the strain Marseille-P2437 was sequenced using fD1-rP2 primers (Eurogentec, Angers, France) as previously described [3], and the obtained amplicon showed a similarity of 97.4% with Christensenella minuta strain YIT 12065 (GenBank accession no. NR112900), the phylogenetically closest species with standing in nomenclature (Fig. 1), which classifies it as a member within the genus Christensenella in the Firmicutes phylum [4]. To date, Christensenella minuta is the only species published and validated name within the Christensenella genus, and was also isolated from human faeces.
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic tree showing position of Christensenella timonensis strain Marseille-P2437T relative to other phylogenetically close members of family Christensenellaceae. GenBank accession numbers are indicated in parentheses. Sequences were aligned using CLUSTALW, and phylogenetic inferences were obtained using maximum-likelihood method within MEGA software. Numbers at nodes are percentages of bootstrap values obtained by repeating analysis 500 times to generate majority consensus tree. Only values greater than 95% are displayed. Scale bar indicates 2% nucleotide sequence divergence.
The 16S rRNA gene sequencing of strain Marseille-P2437 (DSM 102800) yielded divergence of more 1.3% with its phylogenetically closest species with a validly published name standing in nomenclature [5]. On the basis of these results, strain Marseille-P2437 (DSM 102800) is proposed as a novel species of the genus Christensenella, namely Christensenella timonensis sp. nov. (ti.mo.nen'sis. L. masc. adj., timonensis, pertaining to Timone, named after Hôpital de la Timone, the hospital in Marseilles, France, where the type strain was isolated).
MALDI-TOF MS spectrum
The MALDI-TOF MS spectrum of C. timonensis is available at http://www.mediterranee-infection.com/article.php?laref=256&titre=urms-database.
Nucleotide sequence accession number
The 16S rRNA gene sequence was deposited in GenBank under accession number LT223568.
Deposit in a culture collection
Strain Marseille-P2437T was deposited in the Collection de Souches de l’Unité des Rickettsies (CSUR) under number P2437.
Acknowledgement
This study was funded by the Fondation Méditerranée Infection.
Conflict of Interest
None declared.
References
- 1.Seng P., Abat C., Rolain J.M., Colson P., Lagier J.C., Gouriet F. Identification of rare pathogenic bacteria in a clinical microbiology laboratory: impact of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51:2182–2194. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00492-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lagier J.C., Hugon P., Khelaifia S., Fournier P.E., La Scola B., Raoult D. The rebirth of culture in microbiology through the example of culturomics to study human gut microbiota. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015;28:237–264. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00014-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Drancourt M., Bollet C., Carlioz A., Martelin R., Gayral J.P., Raoult D. 16S ribosomal DNA sequence analysis of a large collection of environmental and clinical unidentifiable bacterial isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:3623–3630. doi: 10.1128/jcm.38.10.3623-3630.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Morotomi M., Nagai F., Watanabe Y. Description of Christensenella minuta gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human faeces, which forms a distinct branch in the order Clostridiales, and proposal of Christensenellaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2012;62:144–149. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.026989-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kim M., Oh H.S., Park S.C., Chun J. Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2014;64:346–351. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.059774-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]