Abstract
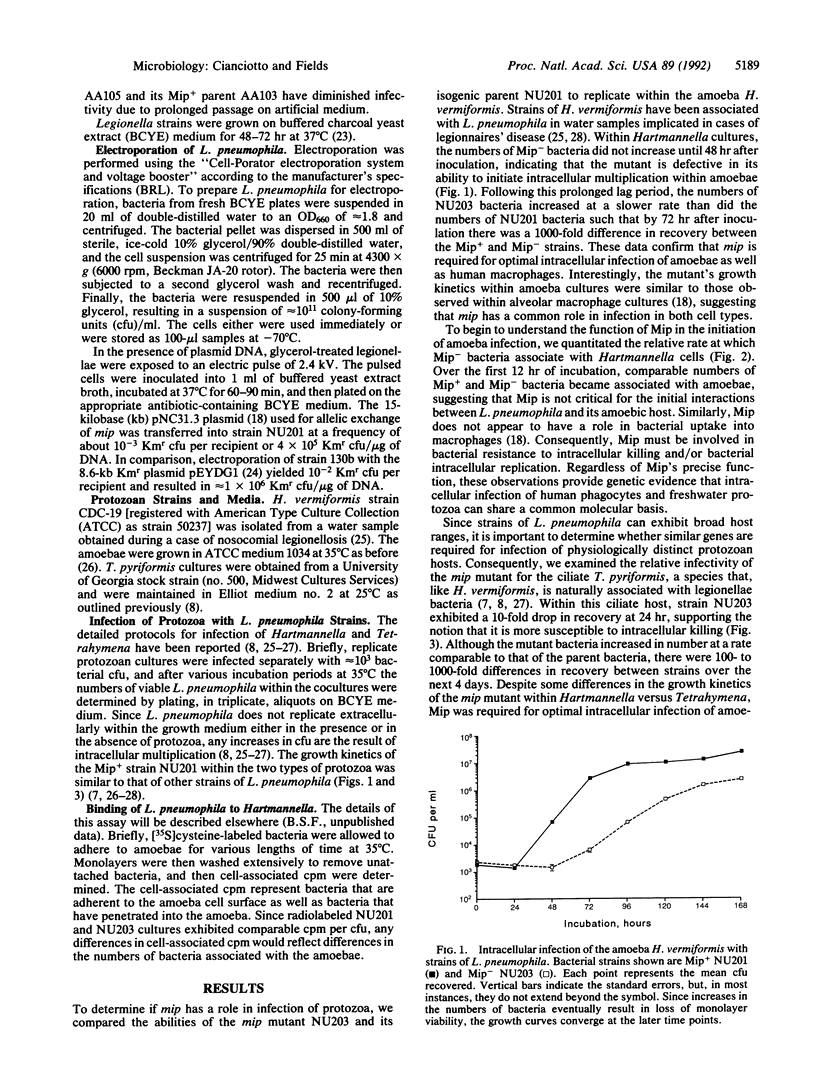
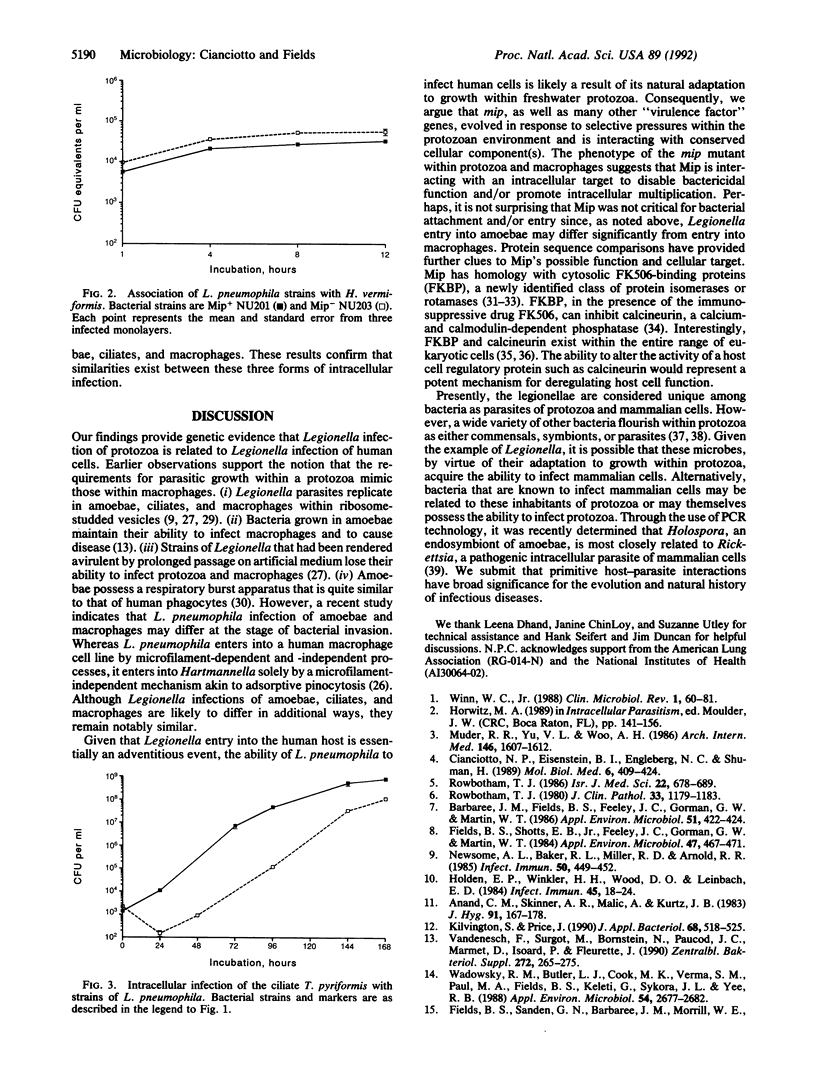
Legionella pneumophila is an intracellular parasite of freshwater protozoa and human macrophages. Recent studies determined that the macrophage infectivity potentiator (Mip) surface protein, a prokaryotic homolog of the FK506-binding proteins, is required for optimal infection of macrophages. To determine whether Mip is also involved in L. pneumophila infection of protozoa, we examined the ability of a strain lacking Mip to parasitize Hartmannella amoebae and Tetrahymena ciliates. After 3 days of incubation, approximately 1000-fold fewer bacteria were recovered from protozoan cocultures infected with the Mip- strain than from those cocultures infected with an isogenic Mip+ strain. The mip mutant was, however, not impaired in its ability to bind to amoebae cell surfaces, indicating that Mip is involved in bacterial resistance to intracellular killing and/or intracellular multiplication. These data suggest that L. pneumophila employs similar genes and mechanisms to infect human cells and protozoa. Furthermore, they support the hypothesis that the ability of L. pneumophila to parasitize macrophages and hence to cause human disease is a consequence of its prior adaptation to intracellular growth within protozoa.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann R., Springer N., Ludwig W., Görtz H. D., Schleifer K. H. Identification in situ and phylogeny of uncultured bacterial endosymbionts. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):161–164. doi: 10.1038/351161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anand C. M., Skinner A. R., Malic A., Kurtz J. B. Interaction of L. pneumophilia and a free living amoeba (Acanthamoeba palestinensis). J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Oct;91(2):167–178. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangsborg J. M., Cianciotto N. P., Hindersson P. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the Legionella micdadei mip gene, encoding a 30-kilodalton analog of the Legionella pneumophila Mip protein. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3836–3840. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3836-3840.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbaree J. M., Fields B. S., Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Martin W. T. Isolation of protozoa from water associated with a legionellosis outbreak and demonstration of intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):422–424. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.422-424.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breiman R. F., Fields B. S., Sanden G. N., Volmer L., Meier A., Spika J. S. Association of shower use with Legionnaires' disease. Possible role of amoebae. JAMA. 1990 Jun 6;263(21):2924–2926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N. P., Bangsborg J. M., Eisenstein B. I., Engleberg N. C. Identification of mip-like genes in the genus Legionella. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2912–2918. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2912-2918.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N. P., Eisenstein B. I., Mody C. H., Engleberg N. C. A mutation in the mip gene results in an attenuation of Legionella pneumophila virulence. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):121–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N. P., Eisenstein B. I., Mody C. H., Toews G. B., Engleberg N. C. A Legionella pneumophila gene encoding a species-specific surface protein potentiates initiation of intracellular infection. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1255–1262. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1255-1262.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N., Eisenstein B. I., Engleberg N. C., Shuman H. Genetics and molecular pathogenesis of Legionella pneumophila, an intracellular parasite of macrophages. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Oct;6(5):409–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleberg N. C., Carter C., Weber D. R., Cianciotto N. P., Eisenstein B. I. DNA sequence of mip, a Legionella pneumophila gene associated with macrophage infectivity. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1263–1270. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1263-1270.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleberg N. C., Drutz D. J., Eisenstein B. I. Cloning and expression of Legionella pneumophila antigens in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):222–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.222-227.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. S., Barbaree J. M., Shotts E. B., Jr, Feeley J. C., Morrill W. E., Sanden G. N., Dykstra M. J. Comparison of guinea pig and protozoan models for determining virulence of Legionella species. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):553–559. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.553-559.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. S., Nerad T. A., Sawyer T. K., King C. H., Barbaree J. M., Martin W. T., Morrill W. E., Sanden G. N. Characterization of an axenic strain of Hartmannella vermiformis obtained from an investigation of nosocomial legionellosis. J Protozool. 1990 Nov-Dec;37(6):581–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1990.tb01269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. S., Shotts E. B., Jr, Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Martin W. T. Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as an intracellular parasite of the ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena pyriformis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):467–471. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.467-471.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitman J., Movva N. R., Hiestand P. C., Hall M. N. FK 506-binding protein proline rotamase is a target for the immunosuppressive agent FK 506 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1948–1952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden E. P., Winkler H. H., Wood D. O., Leinbach E. D. Intracellular growth of Legionella pneumophila within Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):18–24. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.18-24.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Formation of a novel phagosome by the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1319–1331. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilvington S., Price J. Survival of Legionella pneumophila within cysts of Acanthamoeba polyphaga following chlorine exposure. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 May;68(5):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb02904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. H., Fields B. S., Shotts E. B., Jr, White E. H. Effects of cytochalasin D and methylamine on intracellular growth of Legionella pneumophila in amoebae and human monocyte-like cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):758–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.758-763.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Farmer J. D., Jr, Lane W. S., Friedman J., Weissman I., Schreiber S. L. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muder R. R., Yu V. L., Woo A. H. Mode of transmission of Legionella pneumophila. A critical review. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Aug;146(8):1607–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome A. L., Baker R. L., Miller R. D., Arnold R. R. Interactions between Naegleria fowleri and Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):449–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.449-452.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham T. J. Current views on the relationships between amoebae, legionellae and man. Isr J Med Sci. 1986 Sep;22(9):678–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham T. J. Preliminary report on the pathogenicity of Legionella pneumophila for freshwater and soil amoebae. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(12):1179–1183. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.12.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standaert R. F., Galat A., Verdine G. L., Schreiber S. L. Molecular cloning and overexpression of the human FK506-binding protein FKBP. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):671–674. doi: 10.1038/346671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tropschug M., Wachter E., Mayer S., Schönbrunner E. R., Schmid F. X. Isolation and sequence of an FK506-binding protein from N. crassa which catalyses protein folding. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):674–677. doi: 10.1038/346674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall R. L., Domingue E. L. Cocultivation of Legionella pneumophila and free-living amoebae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):954–959. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.954-959.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenesch F., Surgot M., Bornstein N., Paucod J. C., Marmet D., Isoard P., Fleurette J. Relationship between free amoeba and Legionella: studies in vitro and in vivo. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1990 Mar;272(3):265–275. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadowsky R. M., Butler L. J., Cook M. K., Verma S. M., Paul M. A., Fields B. S., Keleti G., Sykora J. L., Yee R. B. Growth-supporting activity for Legionella pneumophila in tap water cultures and implication of hartmannellid amoebae as growth factors. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2677–2682. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2677-2682.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadowsky R. M., Wilson T. M., Kapp N. J., West A. J., Kuchta J. M., States S. J., Dowling J. N., Yee R. B. Multiplication of Legionella spp. in tap water containing Hartmannella vermiformis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jul;57(7):1950–1955. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.7.1950-1955.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr Legionnaires disease: historical perspective. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):60–81. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakobson E. A., Guiney D. G., Jr Conjugal transfer of bacterial chromosomes mediated by the RK2 plasmid transfer origin cloned into transposon Tn5. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):451–453. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.451-453.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



