Abstract
A patient with clinical features of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus, who responded dramatically to shunting, was found a necropsy to have a severe hypertensive and arteriosclerotic vasculopathy with multiple lacunar infarcts. There was no pathological evidence of thickened leptomeninges, fibrosis of the arachnoid villi, or Alzheimer's disease. An abnormal absorption mechanism was demonstrated with cisternography and by an increase in the concentration of homovanillic acid in the cerebrospinal fluid. It is suggested that vascular changes may play an important role in the pathophysiology in some cases of normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Full text
PDF
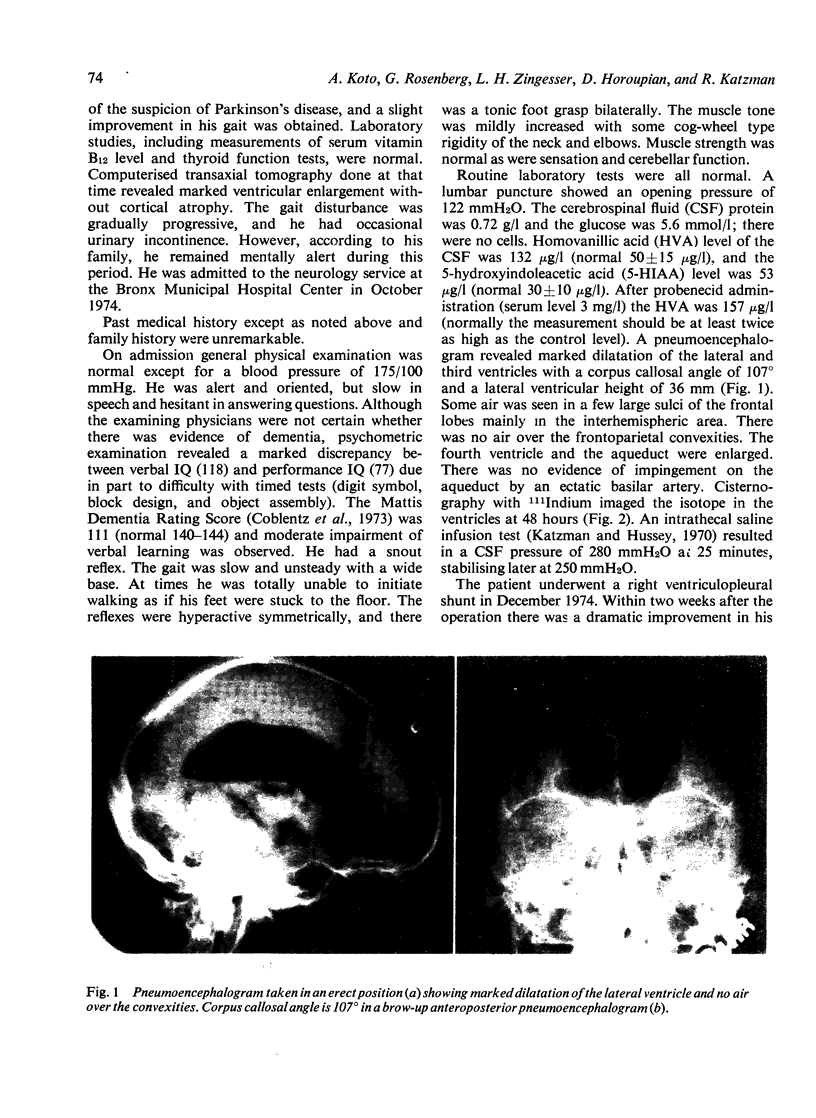


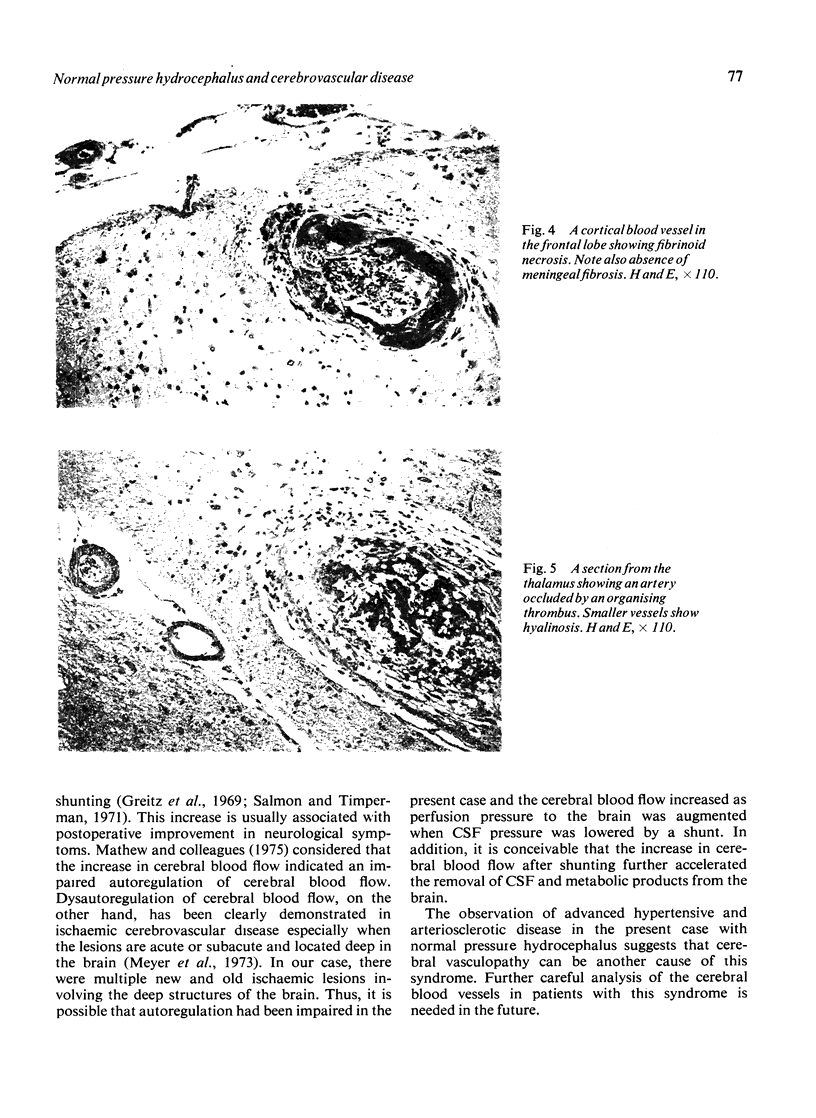


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS R. D., FISHER C. M., HAKIM S., OJEMANN R. G., SWEET W. H. SYMPTOMATIC OCCULT HYDROCEPHALUS WITH "NORMAL" CEREBROSPINAL-FLUID PRESSURE.A TREATABLE SYNDROME. N Engl J Med. 1965 Jul 15;273:117–126. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196507152730301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson H., Roos B. E. 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in cerebrospinal fluid of hydrocephalic children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1969 Nov;58(6):601–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1969.tb04768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belloni G., di Rocco C., Focacci C., Galli G., Maira G., Rossi G. F. Surgical indications in normotensive hydrocephalus. A retrospective analysis of the relations of some diagnostic findings to the results of surgical treatment. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1976;33(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01405737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson D. F., LeMay M., Patten D. H., Rubens A. B. Diagnosis of normal-pressure hydrocephalus. N Engl J Med. 1970 Sep 17;283(12):609–615. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009172831201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coblentz J. M., Mattis S., Zingesser L. H., Kasoff S. S., Wiśniewski H. M., Katzman R. Presenile dementia. Clinical aspects and evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics. Arch Neurol. 1973 Nov;29(5):299–308. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490290039003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowell R. M., Tew J. M., Jr, Mark V. H. Aggressive dementia associated with normal pressure hydrocephalus. Report of two unusual cases. Neurology. 1973 May;23(5):461–464. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.5.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLand F. H., James A. E., Jr, Ladd D. J., Konigsmark B. W. Normal pressure hydrocephalus: a histologic study. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jul;58(1):58–63. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/58.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnest M. P., Fahn S., Karp J. H., Rowland L. P. Normal pressure hydrocephalus and hypertensive cerebrovascular disease. Arch Neurol. 1974 Oct;31(4):262–266. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490400076009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greitz T. V., Grepe A. O., Kalmér M. S., Lopez J. Pre- and postoperative evaluation of cerebral blood flow in low-pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg. 1969 Dec;31(6):644–651. doi: 10.3171/jns.1969.31.6.0644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakim S., Adams R. D. The special clinical problem of symptomatic hydrocephalus with normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Observations on cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics. J Neurol Sci. 1965 Jul-Aug;2(4):307–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(65)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz E. R., Davis D. O., Karp H. R. Abnormal isotope cisternography in sympatomatic occult hydrocephalus. A correlative isotopic-neuroradiological study in 130 subjects. Radiology. 1970 Apr;95(1):109–120. doi: 10.1148/95.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs L., Conti D., Kinkel W. R., Manning E. J. "Normal-pressure" hydrocephalus. Relationship of clinical and radiographic findings to improvement following shunt surgery. JAMA. 1976 Feb 2;235(5):510–512. doi: 10.1001/jama.235.5.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman R., Hussey F. A simple constant-infusion manometric test for measurement of CSF absorption. I. Rationale and method. Neurology. 1970 Jun;20(6):534–544. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.6.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo A. V., Bresnan M. J., Barlow C. F. Cerebrospinal fluid absorption deficit in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Arch Neurol. 1974 May;30(5):387–393. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490350045007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maira G., Bareggi S. R., Di Rocco C., Calderini G., Morselli P. L. Monoamine acid metabolites and cerebrospinal fluid dynamics in normal pressure hydrocephalus: preliminary results. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Feb;38(2):123–128. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.2.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew N. T., Meyer J. S., Hartmann A., Ott E. O. Abnormal cerebrospinal fluid-blood flow dynamics. Implications in diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Arch Neurol. 1975 Oct;32(10):657–664. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490520027003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messert B., Wannamaker B. B. Reappraisal of the adult occult hydrocephalus syndrome. Neurology. 1974 Mar;24(3):224–231. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.3.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. S., Shimazu K., Fukuuchi Y., Ouchi T., Okamoto S., Koto A. Impaired neurogenic cerebrovascular control and dysautoregulation after stroke. Stroke. 1973 Mar-Apr;4(2):169–186. doi: 10.1161/01.str.4.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojemann R. G., Fisher C. M., Adams R. D., Sweet W. H., New P. F. Further experience with the syndrome of "normal" pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg. 1969 Sep;31(3):279–294. doi: 10.3171/jns.1969.31.3.0279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. H., Timperman A. L. Effect of intracranial hypotension on cerebral blood flow. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Dec;34(6):687–692. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenkin H. A., Greenberg J. O., Grossman C. B. Ventricular size after shunting for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Sep;38(9):833–837. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.9.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singounas E. G., Krasanakis C., Karvounis P. C. Observations on the pathogenesis of low pressure hydrocephalus. Analysis of 25 cases. Neurochirurgia (Stuttg) 1976 Jan;19(1):22–25. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1090384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohn R. S., Siegel B. A., Gado M., Torack R. M. Alzheimer's disease with abnormal cerebrospinal fluid flow. Neurology. 1973 Oct;23(10):1058–1065. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.10.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S. C., Langfitt T. W. Normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Predicting the results of cerebrospinal fluid shunting. J Neurosurg. 1974 Oct;41(4):463–470. doi: 10.3171/jns.1974.41.4.0463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sypert G. W., Leffman H., Ojemann G. A. Occult normal pressure hydrocephalus manifested by parkinsonism-dementia complex. Neurology. 1973 Mar;23(3):234–238. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.3.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torack R. M. Congophilic angiopathy complicated by surgery and massive hemorrhage. A light and electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1975 Nov;81(2):349–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vessal K., Sperber E. E., James A. E., Jr Chronic communicating hydrocephalus with normal CSE pressures: a cisternographic-pathologic correlation. Ann Radiol (Paris) 1974 Dec;17(8):785–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson L. I., Katzman R., Escriva A. Clearance of amine metabolites from the cerebrospinal fluid: the brain as a "sink". Neurology. 1974 Aug;24(8):772–779. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.8.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. H., Bartlet D., James A. E., Jr, Udvarhelyi G. B. Normal-pressure hydrocephalus: diagnosis and patient selection for shunt surgery. Neurology. 1974 Jun;24(6):517–526. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.6.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]