Abstract
Ingestion of staphylococcal enterotoxins preformed by Staphylococcus aureus in food leads to staphylococcal food poisoning, the most prevalent foodborne intoxication worldwide. There are five major staphylococcal enterotoxins: SEA, SEB, SEC, SED, and SEE. While variants of these toxins have been described and were linked to specific hosts or levels or enterotoxin production, data on sequence variation is still limited. In this study, we aim to extend the knowledge on promoter and gene variants of the major enterotoxins SEB, SEC, and SED. To this end, we determined seb, sec, and sed promoter and gene sequences of a well-characterized set of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus strains originating from foodborne outbreaks, human infections, human nasal colonization, rabbits, and cattle. New nucleotide sequence variants were detected for all three enterotoxins and a novel amino acid sequence variant of SED was detected in a strain associated with human nasal colonization. While the seb promoter and gene sequences exhibited a high degree of variability, the sec and sed promoter and gene were more conserved. Interestingly, a truncated variant of sed was detected in all tested sed harboring rabbit strains. The generated data represents a further step towards improved understanding of strain-specific differences in enterotoxin expression and host-specific variation in enterotoxin sequences.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus, enterotoxin, sequence variation, seb, sec, sed, promoter
1. Introduction
Staphylococcal food poisoning (SFP) is the most prevalent foodborne intoxication worldwide. The Centers for Disease Control estimate that 240,000 cases per year occur in the US alone, leading to 1000 hospitalizations and six deaths [1]. Upon ingestion, staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs) secreted by Staphylococcus (S.) aureus during growth in the food matrix elicit symptoms of acute gastroenteritis such as violent vomiting and diarrhea [2]. S. aureus strains can produce one or several of the five major SEs (SEA, SEB, SEC, SED, SEE).
Pronounced strain-specific variation of SE mRNA and protein levels has been reported, in particular under conditions of environmental stress encountered in the food matrix [3,4,5,6]. Expression of the phage-encoded SEA was shown to be linked to the life cycle of the phage [7,8] and to nucleotide sequence variation in the sea gene and upstream promoter region [9].
There is some data on the variation of the enterotoxin gene and promoter sequences of SEB, SEC, and SED. Previous studies characterizing the seb and sed promoters have shown that the region from −98 to −59 is required for the expression and regulation of seb [10] and that the region from −34 to +18 is required for sed promoter function [11].
The seb gene resides in one of seven different S. aureus pathogenicity islands (SaPIs) [12,13,14]. Strains harboring different SaPIs carrying seb were reported to vary in SEB levels produced [13]. To date, five different allelic variants of SEB have been described that vary in biological activity [15].
The sec gene can also be located in different SaPIs, including SaPIn1, SaPIm1, SaPImw2, and SaPIbov1. Four variants of SEC (SEC1-4) associated with human S. aureus strains have been described, as well as the host-specific variants SEC-bovine and SEC-ovine [16,17,18,19].
The sed gene and reporter sequences seem to be highly conserved and are located on a pIB485-related 27.6 kb plasmid [20]. However, strains harboring a single base deletion in various locations in the sed sequence have been reported in S. aureus isolates obtained from human hosts [21,22,23,24].
The aim of this study was to analyze promoter and gene sequences of seb, sec, and sed from S. aureus strains originating from different sources. Data on the variability of enterotoxin nucleotide sequences in strains from different hosts can represent an important further step in understanding strain-specific variation in SE expression, and in monitoring the evolution of S. aureus pathogenicity and host adaptation.
2. Results
2.1. Seb Promoter and Gene Sequences
The seb promoter and gene sequences of 12 strains were determined and alignments of all sequences are provided as a supplementary file (Figure S1). Five variants of the seb promoter (sebp v1–v5) were detected that differed at several nucleotide positions. While −35 (TGAATA) and −10 (TATATT) seb promoter elements were identical in all tested strains, sequence variation was detected in the region essential for seb expression that is located between 59 and 93 nucleotides upstream of the transcription start site. The seb promoter variants sebp v1, v2, and v5 exhibited nucleotides GT (positions −47, −46), AT (positions −23, −22), and A (position −18), while sebp v3 and v4 exhibited nucleotides AA (position −47, −46), GA (positions −23, −22), and G (position −18). Promoter variant sebp v4 and v5 did not correspond to any known seb promoter sequences in GenBank.
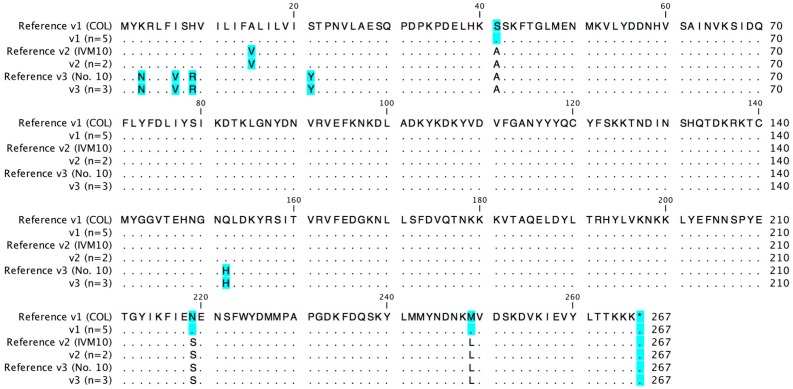
The seb gene ORF exhibited a length of 801 bp in all 12 strains. Nucleotide sequence variation was found at numerous positions (9, 19, 26, 44, 52, 62, 84, 87, 121, 162, 165, 351, 393, 405, 456, 484, 513, 522, 543, 621, 656, 738, 745), leading to the identification of four different variants (seb v1–v4). Two strains (RKI4 and SAI33) harbored the novel variant v3. The different seb nucleotide sequences resulted in three different amino acid variants (266 amino acid precursor), which were identical to known amino acid variants of reference strains (COL, IVM10, No. 10). An alignment of the respective amino acid sequences and reference sequences is provided in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Amino acid variants of SEB. Amino acid exchanges compared to the most common amino acid detected are highlighted in blue (n = number of strains representing each variant).
Screening of strains representing the different seb variants for production of SEB using SET-RPLA (Oxoid, Pratteln, Switzerland) showed that all variants are expressed.
2.2. Sec Promoter and Gene Sequences
The sec promoter and gene sequences were determined in 10 strains and alignments of all sequences are provided as a supplementary file (Figure S2). The −35 (TTGAA) and −10 (TATATTT) sec promoter elements were identical in all tested strains.
The sec ORF exhibited a length of 801 bp in all strains. Isolates obtained from nasal colonization and foodborne outbreaks harbored a sec variant (v1) identical to the previously described SEC-2 subtype. All bovine strains exhibited sec v2 identical with the SEC-bovine subtype. For SAI3, a human infection isolate, a sec variant (sec v3) identical to subtype SEC-1 was found. For SAI48, a strain also linked to an infection in a human patient, a novel nucleotide sequence similar to SEC-2, with the exception of a point mutation at position 87 (T -> C), was identified. The four nucleotide sequence variants resulted in three different predicted variants of the 266-amino-acid precursor. Nucleotide sequence variants v1 and the novel variant v4 both resulted in the amino acid variant secaa v1 (SEC-2), while v2 resulted in secaa v2 (SEC-bovine), and v3 resulted in secaa v3 (SEC-1), respectively. An alignment of the respective amino acid sequences and reference sequences is provided as Figure 2.
Figure 2.
Amino acid variants of SEC. Amino acid exchanges compared to the most common amino acid detected are highlighted in blue (n = number of strains representing each variant).
Screening the strains exhibiting sec for SEC production using SET-RPLA led to detection of SEC in all strains, showing that all sec variants are expressed.
2.3. Sed Promoter and Gene Sequences
The sequences of the sed promoter and gene were determined in 12 strains and alignments of all sequences are provided as a supplementary file (Figure S3). The −35 (ATGAAA) and −10 (TATAA) promoter elements were identical in all tested strains.
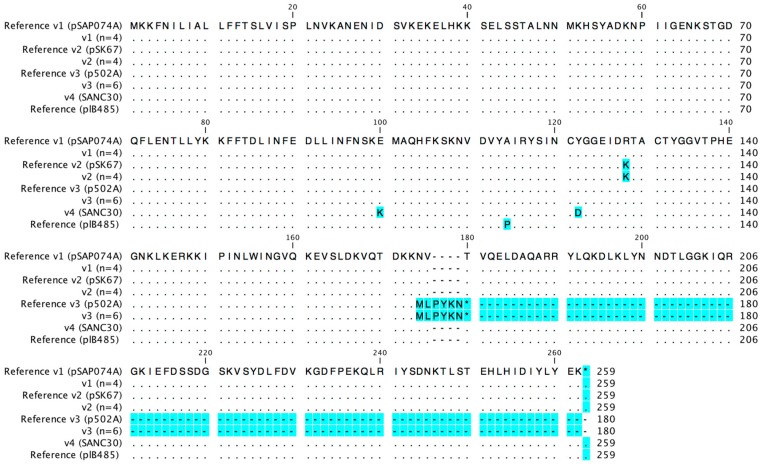
The sed sequences were also highly conserved. However, point mutations were observed in strain SANC30 (position 198 G -> A, position 364 T -> G) and in strains BW10, RKI1, RKI2, and SAR35 (position 383 G -> A). In total, four different amino acid variants were detected, none of which was 100% identical to the common sed plB485 reference sequence (Genbank accession number M28521.1). SANC30 exhibited a novel amino acid sequence (variant 4) with two amino acid changes (position 100 E -> K, position 121 Y -> D) that did not correspond to any sequence in the GenBank database. An alignment of the respective amino acid sequences and reference sequences is provided in Figure 3.
Figure 3.
Amino acid variants of SED. Amino acid exchanges compared to the most common amino acid detected are highlighted in blue (n = number of strains representing each variant).
All three tested rabbit isolates harbored the same sed nucleotide sequence variant (v3), which exhibits a deletion in sed at nucleotide position 521, resulting in a premature stop codon at amino acid position 180. To confirm the possibility of a host-specific variant, an additional three sed+ rabbit strains were sequenced, which harbored the same truncated variant.
Screening of strains representing the different sed variants for production of SED by SET-RPLA showed that not only the complete sed variants but also the truncated sed v3 were expressed. However, for the strains harboring the truncated sed variant, SED levels were far lower, with only the first dilution in the dilution series yielding a weakly positive test result. Four rabbit strains harboring the truncated sed v3 variant were screened. While SED was detected in three of these strains (SAK8, SAK11, SAK13), one strain (SAK64) did not yield a positive result for SED production. While all sed+ rabbit strains represent the same clonal complex (CC5), SAK64 was the only rabbit strain of spa type t160.
3. Discussion
In this study, several new variants of seb, sec, and sed enterotoxin genes and promoters were detected. Sequencing of seb, sec, and sed promoter regions revealed that promoter sequences were highly conserved in sec and sed. In contrast, several variable positions were observed in the seb promoter region, including the region required for seb transcription and expression. This is consistent with findings by Sato’o et al. [13], reporting high variability in seb upstream sequences from different strains. In the same study, several novel SaPIs carrying seb were identified and linked to differences in SEB production levels. However, the differences in seb promoter regions did not correlate with SEB production in a statistically significant manner [13].
Comparative analysis of the nucleotide sequences of the seb, sec, and sed genes showed that sed sequences were more conserved than seb and sec sequences. The length of the seb and sec coding sequences determined in this study was consistent with previous reports [18,25,26].
Most of the residues that are conserved throughout all SEs are either centrally located or can be found at the C-terminal end [27]. This is also consistent with the findings in this study for the amino acid prediction of seb, and sec variants, indicating that amino acid exchanges were more likely to occur at the N-terminus. However, for SED, the highest degree of amino acid variability detected in this study was centrally located.
Predicting altered functionality based on the detected amino acid exchanges is challenging, as emetic activity is still poorly understood. While lack of the disulfide loop was suggested to result in no or lower emetic activity, it has been shown that the disulfide bond is not a prerequisite for emetic activity [28]. Concerning superantigenic activity, ovine and bovine SEC variants were reported to be strongly altered in function due to only three amino acid changes resulting in host-dependent superantigenicity [27]. With regard to antigenicity, it was shown that SE variants differing in several residues, such as the SEC variants identified in FRI909 and FRI913 (9 differing residues), can still be antigenetically indistinguishable [27].
For SEC, four variants (SEC1-4) associated with human S. aureus isolates have been reported, as well as the host-specific variants SEC-bovine and SEC-ovine [16,17,18,19]. In contrast, subtypes of seb and the different SaPIs associated with these subtypes have only recently gained attention [13,15]. Kohler et al. demonstrated the existence of multiple SEB variants that differed in their ability to activate subsets of T cells and in their effects on the proliferation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and rabbit splenocytes [15].
In this study, a novel seb nucleotide sequence variant (seb v3) was identified in two of the tested strains (RKI4 and SAI33). However, the seb v3 nucleotide sequence variant results in a known SEB amino acid sequence identical to reference strain No. 10. For sec, one novel sec nucleotide sequence (sec v4) was detected in one strain (SAI48). Amino acid sequence prediction showed that sec v4 results in an amino acid sequence identical to the one of sec v1, which is also known as SEC-2 (reference strain 79_S10). For sed, one novel nucleotide sequence (sed v4) was determined in a strain associated with human nasal colonization (SANC30). The novel sed v4 nucleotide sequence variant results in a novel amino acid sequence variant of SED that was not previously described elsewhere (sedaa v4).
In this study, a variant of sed was identified which was present in all tested rabbit isolates (n = 6). This variant sed v3 exhibited a deletion that resulted in a premature stop codon and a truncated sed amino acid precursor. In foodborne outbreak isolates, deletions at nucleotide positions 150 [21] and 514 [22] resulting in a premature stop codon have been reported. A deletion in sed identical to the one seen in the rabbit isolates in this study (nucleotide position 521) has been reported in S. aureus isolates originating from humans and from food [23,24]. While Lis et al. confirmed transcription of sed by qPCR, they could not detect SED protein by ELISA or Western blotting [24]. In contrast, in this study, three of four rabbit strains tested with truncated sed variants yielded a weak, but positive result for SED in the SET-RPLA assay. The deletion in sed may impair the functionality of the protein and recognition by various detection methods.
4. Conclusions
The sequence data generated in this study extends the current knowledge on sequence variation in enterotoxin genes of S. aureus strains isolated from various sources. Several novel variants of enterotoxin promoter and gene nucleotide sequences were described, and a novel amino acid sequence variant of SED was identified in a strain obtained from a nasal carrier. In addition, the results presented in this study confirm previous reports of host-specific enterotoxin variants such as SEC-bovine. Interestingly, all sed+ rabbit strains tested in this study harbored a sed variant that exhibited a deletion in sed leading to a premature stop codon.
The data generated represents a further step towards improved understanding of strain-specific differences in enterotoxin expression and host-specific variation in enterotoxin sequences.
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Bacterial Strains
The S. aureus isolates used in this study originated from SFP outbreaks, asymptomatic nasal colonization or cases of infections in humans, as well as rabbit carcasses and bovine mastitis milk. Isolates were selected from a large collection of well-characterized S. aureus strains, for which DNA microarray enterotoxin hybridization patterns, spa types, and clonal complexes had been previously determined and published [14,28,29,30,31]. Detailed information on all S. aureus strains used in this study is provided in Table 1.
Table 1.
Detailed overview of sequence variants of enterotoxin promoters and genes of all S. aureus strains used in this study. In addition, information on other major enterotoxin genes harbored by each strain, the source of the strain, and its assignment to a spa type and clonal complex are provided.
| Gene | Strain ID | Identical Reference 1 | Promoter Variant 2 (Reference) | Gene Variant 2 (Reference) | Amino Acid Variant (Reference) | Source | Clonal Complex/spa Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| seb | KLT6 | COL | sebp v1 | seb v1 | sebaa v1 | SFP 3 | CC12/t160 | [29] |
| SANC31 | COL | sebp v1 | seb v1 | sebaa v1 | Human nasal colonization | CC59/t216 | [30] | |
| SANC49 | COL | sebp v1 | seb v1 | sebaa v1 | Human nasal colonization | CC59/t216 | [30] | |
| SAK9 | COL | sebp v1 | seb v1 | sebaa v1 | Rabbit | CC5/t8456 | [31] | |
| SAK18 | COL | sebp v1 | seb v1 | sebaa v1 | Rabbit | CC5/t8456 | [31] | |
| SAI10 | COL | sebp v1 | seb v1 | sebaa v1 | Human infection | CC59/t216 | [30] | |
| SAI50 | COL | sebp v1 | seb v1 | sebaa v1 | Human infection | CC59/t015 | [30] | |
| SANC14 | IVM10 | sebp v2 | seb v2 | sebaa v2 | Human nasal colonization | CC45/t630 | [30] | |
| RKI4 | novel 4 | sebp v3 (No. 10) | seb v3 (novel) 4 | sebaa v3 (No. 10) | SFP | CC9/t733 | [14] | |
| SAI40 | novel 4 | sebp v4 (novel) 4 | seb v3 (No. 10) | sebaa v3 (No. 10) | Human infection | CC15/t084 | [30] | |
| SAI33 | novel 4 | sebp v4 (novel) 4 | seb v3 (novel) 4 | sebaa v3 (No. 10) | Human infection | CC20/t164 | [30] | |
| SAI45 | novel 4 | sebp v5 (novel) 4 | seb v4 (IVM10) | sebaa v2 (IVM10) | Human infection | CC121/t272 | [30] | |
| sec | BW10 | 79_S10 | secp v1 | sec v1 = SEC-2 | secaa v1 = SEC-2 | SFP | CC45/t383 | Medical Department of the German Federal Armed Forces, Germany |
| LRA1 | 79_S10 | secp v1 | sec v1 = SEC-2 | secaa v1 = SEC-2 | SFP | CC73/t015 | Bavarian State Office of Health and Food Safety, Germany | |
| SANC23 | 79_S10 | secp v1 | sec v1 = SEC-2 | secaa v1 = SEC-2 | Human nasal colonization | CC8/t8016 | [30] | |
| SANC48 | 79_S10 | secp v1 | sec v1 = SEC-2 | secaa v1 = SEC-2 | Human nasal colonization | CC45/t015 | [30] | |
| NB6 | 79_S10 | secp v1 | sec v1 = SEC-2 | secaa v1 = SEC-2 | SFP | CC45/t6969 | Bavarian State Office of Health and Food Safety, Germany | |
| SAR1 | RF122 | secp v2 | sec v2 = SEC-bovine | secaa v2 = SEC-bovine | Bovine mastitis milk | CC151/t529 | [32] | |
| SAR38 | RF122 | secp v2 | sec v2 = SEC-bovine | secaa v2 = SEC-bovine | Bovine mastitis milk | CC151/t529 | [32] | |
| SAR50 | RF122 | secp v2 | sec v2 = SEC-bovine | secaa v2 = SEC-bovine | Bovine mastitis milk | CC151/t529 | [32] | |
| SAI3 | novel 4 | secp v3 (H-EMRSA-15) | sec v3 = SEC-1 (B1085) | secaa v3 = SEC-1 (B1085) | Human infection | CC8/t148 | [30] | |
| SAI48 | novel 4 | secp v1 (79_S10) | sec v4 (novel) 4 | secaa v1 = SEC-2 (79_S10) | Human infection | CC5/t002 | [30] | |
| sed | KLT8 | pSAP074A | sedp v1 | sed v1 | sedaa v1 | SFP | CC5/t8017 | Cantonal Laboratory Thurgau, Switzerland |
| SAI8 | pSAP074A | sedp v1 | sed v1 | sedaa v1 | Human infection | CC5/t954 | [30] | |
| SAI41 | pSAP074A | sedp v1 | sed v1 | sedaa v1 | Human infection | CC5/t8017 | [30] | |
| SAI48 | novel 4 | sedp v3 (novel) 4 | sed v1 (pSAP074A) | sedaa v1 (pSAP074A) | Human infection | CC5/t002 | [30] | |
| BW10 | pSK67 | sedp v2 | sed v2 | sedaa v2 | SFP | CC45/t383 | Medical Department of the German Federal Armed Forces, Germany | |
| RKI1 | pSK67 | sedp v2 | sed v2 | sedaa v2 | SFP | CC8/t648 | Robert Koch Institute, Germany | |
| RKI2 | pSK67 | sedp v2 | sed v2 | sedaa v2 | SFP | CC8/t008 | Robert Koch Institute, Germany | |
| SAR35 | novel 4 | sedp v1 (pSAP074A) | sed v2 (pSK67) | sedaa v2 (pSK67) | Bovine mastitis milk | CC8/t2953 | [32] | |
| SAK8 | novel 4 | sedp v1 (pSAP074A) | sed v3 (p502A) | sedaa v3 (p502A) | Rabbit | CC5/t179 | [31] | |
| SAK9 | novel 4 | ND 5 | sed v3 (p502A) | sedaa v3 (p502A) | Rabbit | CC5/t8456 | [31] | |
| SAK11 | novel 4 | sedp v1 (pSAP074A) | sed v3 (p502A) | sedaa v3 (p502A) | Rabbit | CC5/t179 | [31] | |
| SAK13 | novel 4 | sedp v1 (pSAP074A) | sed v3 (p502A) | sedaa v3 (p502A) | Rabbit | CC5/t179 | [31] | |
| SAK18 | novel 4 | ND 5 | sed v3 (p502A) | sedaa v3 (p502A) | Rabbit | CC5/t8456 | [31] | |
| SAK64 | novel 4 | ND 5 | sed v3 (p502A) | sedaa v3 (p502A) | Rabbit | CC5/t160 | [31] | |
| SANC30 | novel 4 | sedp v1 (pSAP074A) | sed v4 (novel)4 | sedaa v4 (novel) 4 | Human nasal colonization | CC5/t002 | [30] |
1 Reference sequences were obtained from GenBank. Accession numbers: CP000046.1 (strain COL), AB716349.1 (strain IVM10), AB716351.1 (strain No. 10), CP010952.1 (strain 93b_S9), CP010944.1 (strain 79_S10), AJ938182.1 (strain RF122), KF386012.1 (strain B1085), CP007659.1 (strain H-EMRSA-15), GQ900426.1, (plasmid pSAP074A), CP007455.1 (plasmid p502A), GQ900447.1 (plasmid pSK67); 2 Nucleotide sequence; 3 SFP = Staphylococcal Food Poisoning; 4 Novel variant with no identical reference sequence available in GenBank; 5 Not determined.
5.2. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
Frozen stock cultures (−80 °C) of S. aureus strains were resuscitated by plating on 5% sheep blood agar and incubation at 37 °C over night. Bacterial DNA was extracted using the DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer′s instructions.
PCR was performed using the Phusion High-Fidelity System (Thermo Scientific, Reinach, Switzerland) using a total reaction volume of 50 μL. All primers and primer-pair specific annealing temperatures are provided as supplemental material (Table S1). For each reaction, 5 μL buffer, 2 μL DMSO, 1 μL dNTP mix, 2 μL of each primer (c = 10 μM), 0.5 μL Phusion High-Fidelity DNA polymerase, 36.5 μL Aq.B., and 1 μL DNA template were used. PCR cycling conditions included: 5 min hot start at 95 °C, followed by 30 amplification cycles (denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at the primer-specific annealing temperature for 30 s, elongation at 72 °C for 75 s), a final elongation step at 72 °C for 10 min, and a cooling step. Target-specific amplification was confirmed by electrophoresis using a 1% agarose gel.
5.3. PCR Purification and Sequencing
PCR amplicons were purified using the MinElute PCR Purification Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and sequencing was outsourced (Microsynth, Balgach, Switzerland). The acquired sequences were analyzed using CLC Main Workbench software (Version 6.9, CLC Bio/Qiagen, Aarhus, Denmark, 2012) and were compared to reference nucleotide sequences imported from GenBank (NCBI). Novel variants of enterotoxin promoter or gene sequences were subsequently submitted to GenBank.
5.4. Toxin Detection by SET-RPLA
Expression of different seb, sec, and sed variants was assessed in selected strains using the SET-RPLA kit (Oxoid). Enterotoxins were detected using bacterial culture filtrates (0.2 μm filter, Whatman, Sigma-Aldrich, Buchs, Switzerland) from stationary phase cultures of each strain in Luria Bertrani (LB, Becton Dickinson, Allschwil, Switzerland) broth (37 °C, 225 rpm shaking, 20 h of incubation) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Culture filtrates were diluted in a five-fold dilution series for semi-quantitative detection of SEB, SEC, and SED. For seb, strains KLT6, SANC49, SANC14, SAI45, RKI4, and SAI40 were tested for SEB expression. All sec strains were assayed for SEC expression. For sed, strains BW10, RKI1, RKI2, KLT8, SAK8, SAK11, SAK13, and SAK64 were tested for SED expression.
5.5. Amino Acid Identity
A pairwise amino acid identity comparison between all SEB, SEC, and SED enterotoxin variants is provided in Table 2.
Table 2.
Overview of pairwise amino acid identity of the different SEB, SEC, and SED variants. The novel variant 4 of SED (sedaa v4) was detected in a strain isolated from a nasal carrier and has not been previously described.
| Variant | SEB v1 | SEB v2 | SEB v3 | SEC-1 | SEC-2 | SEC-3 | SEC-4 | SEC-bovine | SEC-ovine | SED v1 | SED v2 | SED v3 | SED v4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEB v1 | 100 | 99 | 97 | 68 | 67 | 69 | 67 | 69 | 67 | 36 | 35 | 25 | 36 |
| SEB v2 | - | 100 | 98 | 67 | 66 | 67 | 66 | 68 | 67 | 36 | 36 | 25 | 36 |
| SEB v3 | - | - | 100 | 67 | 66 | 67 | 66 | 68 | 67 | 36 | 35 | 24 | 35 |
| SEC-1 | - | - | - | 100 | 97 | 94 | 97 | 99 | 98 | 32 | 32 | 22 | 32 |
| SEC-2 | - | - | - | - | 100 | 96 | 99 | 97 | 96 | 33 | 32 | 22 | 32 |
| SEC-3 | - | - | - | - | - | 100 | 96 | 94 | 93 | 33 | 33 | 23 | 33 |
| SEC-4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 100 | 97 | 96 | 33 | 33 | 22 | 33 |
| SEC-bovine | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 100 | 99 | 32 | 32 | 22 | 32 |
| SEC-ovine | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 100 | 32 | 32 | 21 | 32 |
| SED v1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 100 | 99 | 66 | 99 |
| SED v2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 100 | 66 | 99 |
| SED v3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 100 | 65 |
| SED v4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 100 |
5.6. Accession Numbers
All variants of promoter and gene sequences were submitted to GenBank and can be accessed using accession numbers KX168612–KX168635. Promoter sequence variants are available for seb variants (sebp v1 = KX168623, sebp v2 = KX168624, sebp v3 = KX168625, sebp v4 = KX168626, sebp v5 = KX168627), sec variants (secp v1 = KX168633, secp v2 = KX168634, secp v3 = KX168635), and sed variants (sedp v1 = KX168616, sedp v2 = KX168617, sedp v3 = KX168618). Sequence variants are available for the seb gene (seb v1 = KX168628, seb v2 = KX168629, seb v3 = KX168630, seb v4 = KX168631, seb v5 = KX168632), the sec gene (sec v1 = KX168612, sec v2 = KX168613, sec v3 = KX168614, sec v4 = KX168615), and the sed gene (sed v1 = KX168619, sed v2 = KX168620, sed v3 = KX168621, sed v4 = KX168622).
Acknowledgments
We thank Mirjam Moser for laboratory work. This study was supported by the Swiss National Research Program 69 (40690_145211/1) and the Forschungskredit of the University of Zurich (grant no. FK-13-059 and FK-15-055).
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/2072-6651/8/6/169/s1, Figure S1: Sequence alignments for seb. Figure S2: Sequence alignments for sec. Figure S3: Sequence alignments for sed. Table S1: Primers used in this study.
Author Contributions
S.J. and R.S. conceived and designed the study. H.-M.S., G.M. and S.J. performed the experiments and analyzed the data. S.J. and H.-M.S. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Scallan E., Hoekstra R.M., Angulo F.J., Tauxe R.V., Widdowson M.-A., Roy S.L., Jones J.L., Griffin P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—Major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011;17:7–15. doi: 10.3201/eid1701.P11101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tranter H.S. Foodborne staphylococcal illness. Lancet. 1990;336:1044–1046. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92500-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sihto H.M., Tasara T., Stephan R., Johler S. Growth behavior and temporal enterotoxin D expression of Staphylococcus aureus strains under glucose and lactic acid stress. Food Control. 2016;62:69–73. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.10.008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sihto H.-M., Budi Susilo Y., Tasara T., Rådström P., Stephan R., Schelin J., Johler S. Effect of sodium nitrite and regulatory mutations Δagr, ΔsarA, and ΔsigB on the mRNA and protein levels of staphylococcal enterotoxin D. Food Control. 2016;65:37–45. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.01.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sihto H.-M., Tasara T., Stephan R., Johler S. Temporal expression of the staphylococcal enterotoxin D gene under NaCl stress conditions encountered during food production and preservation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015 doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnv024. submitted for publication. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wallin-Carlquist N., Cao R., Márta D., da Silva A.S., Schelin J., Rådström P. Acetic acid increases the phage-encoded enterotoxin A expression in Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Microbiol. 2010;10 doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cao R., Zeaki N., Wallin-Carlquist N., Skandamis P.N., Schelin J., Rådström P. Elevated enterotoxin A expression and formation in Staphylococcus aureus and its association with prophage Induction. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012;78:4942–4948. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00803-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sumby P., Waldor M.K. Transcription of the toxin genes present within the staphylococcal phage φSa3ms is intimately linked with the phage’s life cycle. J. Bacteriol. 2003;185:6841–6851. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.23.6841-6851.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Borst D.W., Betley M.J. Phage-associated differences in staphylococcal enterotoxin A gene (sea) expression correlate with sea allele class. Infect. Immun. 1994;62:113–118. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.1.113-118.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mahmood R., Khan S.A. Role of upstream sequences in the expression of the staphylococcal enterotoxin B gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;265:4652–4656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhang S., Stewart G.C. Characterization of the promoter elements for the staphylococcal enterotoxin D gene. J. Bacteriol. 2000;182:2321–2325. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.8.2321-2325.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shafer W.M., Iandolo J.J. Chromosomal locus for staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Infect. Immun. 1978;20:273–278. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.273-278.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sato’o Y., Omoe K., Ono H.K., Nakane A., Hu D.-L. A novel comprehensive analysis method for Staphylococcus aureus pathogenicity islands. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013;57:91–99. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Stevens M.J.A., Stephan R., Johler S. Complete and assembled genome sequence of Staphylococcus aureus RKI4, a food-poisoning strain exhibiting a novel S. aureus pathogenicity island carrying seb. Genome Announc. 2015;3 doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00769-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kohler P.L., Greenwood S.D., Nookala S., Kotb M., Kranz D.M., Schlievert P.M. Staphylococcus aureus isolates encode variant staphylococcal enterotoxin B proteins that are diverse in superantigenicity and lethality. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Couch J.L., Betley M.J. Nucleotide sequence of the type C3 staphylococcal enterotoxin gene suggests that intergenic recombination causes antigenic variation. J. Bacteriol. 1989;171:4507–4510. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4507-4510.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Marr J.C., Lyon J.D., Roberson J.R., Lupher M., Davis W.C., Bohach G.A. Characterization of novel type C staphylococcal enterotoxins: biological and evolutionary implications. Infect. Immun. 1993;61:4254–4262. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.10.4254-4262.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bohach G.A., Schlievert P.M. Nucleotide sequence of the staphylococcal enterotoxin C1 gene and relatedness to other pyrogenic toxins. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1987;209:15–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00329830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fitzgerald J.R., Monday S.R., Foster T.J., Bohach G.A., Hartigan P.J., Meaney W.J., Smyth C.J. Characterization of a putative pathogenicity island from bovine Staphylococcus aureus encoding multiple superantigens. J. Bacteriol. 2001;183:63–70. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.1.63-70.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bayles K.W., Iandolo J.J. Genetic and molecular analyses of the gene encoding staphylococcal enterotoxin D. J. Bacteriol. 1989;171:4799–4806. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4799-4806.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kauffman N.M., Roberts R.F. Staphylococcal enterotoxin D production by Staphylococcus aureus FRI 100. J. Food Prot. 2006;69:1448–1451. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-69.6.1448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Suzuki Y., Kobayashi M., Matsushita S., Uehara S., Kato R., Sato’o Y., Ono H.K., Sadamasu K., Kai A., Kamata Y. Detection of the staphylococcal enterotoxin D-like gene from staphylococcal food poisoning isolates over the last two decades in Tokyo. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015;77:905–911. doi: 10.1292/jvms.15-0028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Parker D., Narechania A., Sebra R., Deikus G., Larussa S., Ryan C., Smith H., Prince A., Mathema B., Ratner A.J., et al. Genome sequence of bacterial interference strain Staphylococcus aureus 502A. Genome Announc. 2014;2:5–6. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00284-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lis E., Podkowik M., Schubert J., Bystroń J., Stefaniak T., Bania J. Production of staphylococcal enterotoxin R by Staphylococcus aureus strains. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012;9:762–766. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2012.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jones C.L., Khan S.A. Nucleotide sequence of the enterotoxin B gene from Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 1986;166:29–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.29-33.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Johns M.B., Jr., Khan S.A. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B gene is associated with a discrete genetic element. J. Bacteriol. 1988;170:4033–4039. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4033-4039.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dinges M.M., Orwin P.M., Schlievert P.M. Exotoxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000;13:16–34. doi: 10.1128/CMR.13.1.16-34.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hovde C., Marr C., Hoffmann M., Hackett S., Chi Y., Crum K., Stevens D., Stauffacher C., Bohach G. Investigation of the role of the disulphide bond in the activity and structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin C1. Mol. Microbiol. 1994;15:897–909. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tobes R., Manrique M., Brozynska M., Stephan R., Pareja E., Johler S. Noncontiguous finished genome sequence of Staphylococcus aureus KLT6, a staphylococcal enterotoxin B-positive strain involved in a food poisoning outbreak in Switzerland. Genome Announc. 2013;1 doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00214-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wattinger L., Stephan R., Layer F., Johler S. Comparison of Staphylococcus aureus isolates associated with food intoxication with isolates from human nasal carriers and human infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012;31:455–464. doi: 10.1007/s10096-011-1330-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Merz A., Stephan R., Johler S. Genotyping and DNA microarray based characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from rabbit carcasses. Meat Sci. 2016;112:86–89. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2015.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Johler S., Layer F., Stephan R. Comparison of virulence and antibiotic resistance genes of food poisoning outbreak isolates of Staphylococcus aureus with isolates obtained from bovine mastitis milk and pig carcasses. J. Food Prot. 2011;74:1852–1859. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-11-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.