Abstract
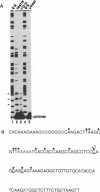
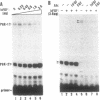
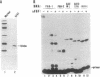
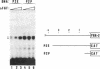
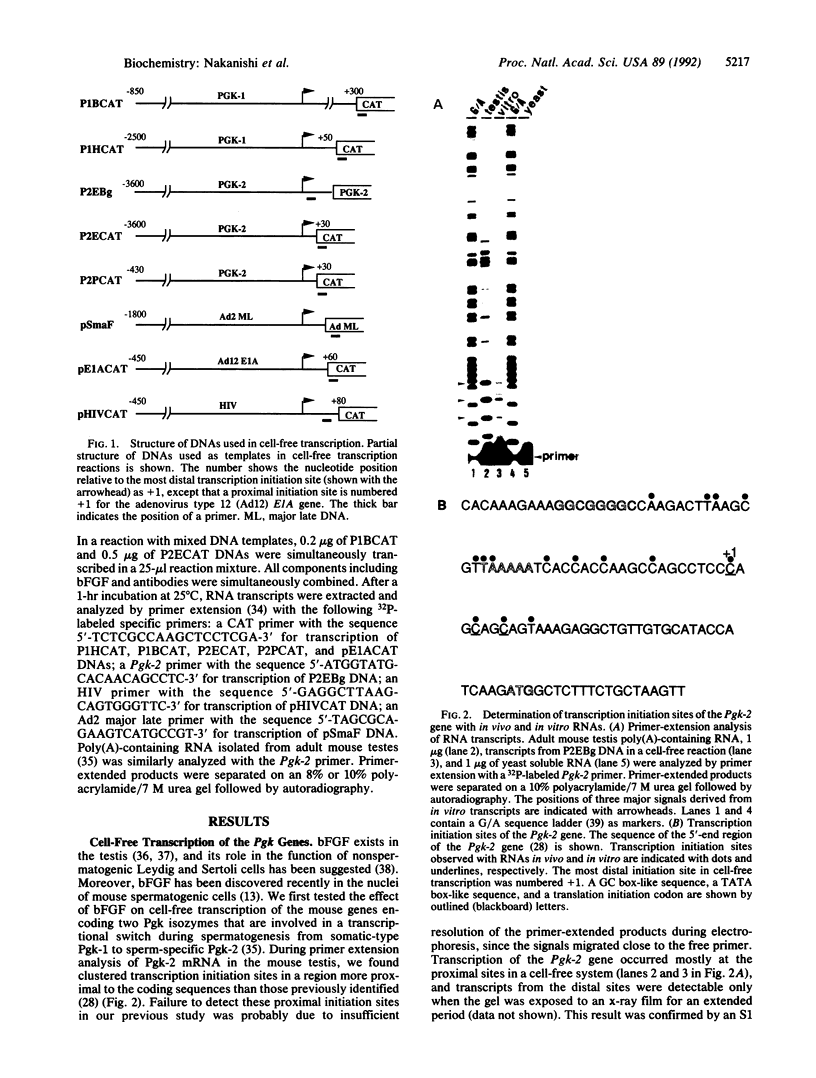
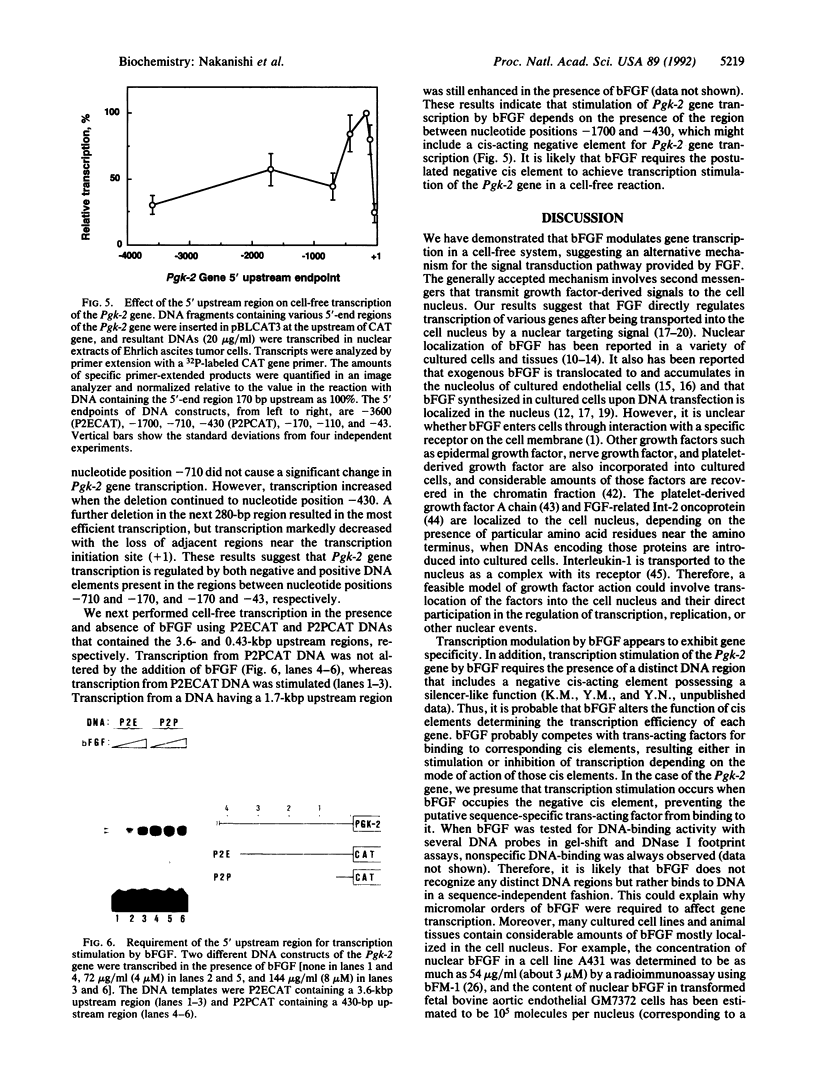
Recent findings on the translocation of intact fibroblast growth factor (FGF) into the cell nucleus suggest that it functions directly in nuclear events. We examined the effect of human basic FGF (bFGF) on gene transcription in a cell-free system. When mouse genes encoding phosphoglycerate kinases 1 and 2 (Pgk-1 and Pgk-2) were transcribed by using nuclear extracts of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells, FGF affected transcription in different ways: in the presence of bFGF, transcription of the Pgk-1 gene was inhibited, whereas that of the Pgk-2 gene was enhanced. When viral genes were tested, transcription of the adenovirus major late DNA was slightly stimulated but that of the adenovirus early E1A DNA or the human immunodeficiency virus DNA was not changed by the addition of bFGF. Moreover, the presence of a distinct 5' upstream region of the Pgk-2 gene, which includes a negative cis-acting element, was required for transcription stimulation by bFGF. These results suggest that bFGF can regulate transcription directly in the nucleus in a gene-specific manner.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acland P., Dixon M., Peters G., Dickson C. Subcellular fate of the int-2 oncoprotein is determined by choice of initiation codon. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):662–665. doi: 10.1038/343662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adra C. N., Boer P. H., McBurney M. W. Cloning and expression of the mouse pgk-1 gene and the nucleotide sequence of its promoter. Gene. 1987;60(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldin V., Roman A. M., Bosc-Bierne I., Amalric F., Bouche G. Translocation of bFGF to the nucleus is G1 phase cell cycle specific in bovine aortic endothelial cells. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1511–1517. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boer P. H., Adra C. N., Lau Y. F., McBurney M. W. The testis-specific phosphoglycerate kinase gene pgk-2 is a recruited retroposon. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3107–3112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouche G., Gas N., Prats H., Baldin V., Tauber J. P., Teissié J., Amalric F. Basic fibroblast growth factor enters the nucleolus and stimulates the transcription of ribosomal genes in ABAE cells undergoing G0----G1 transition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6770–6774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigstock D. R., Sasse J., Klagsbrun M. Subcellular distribution of basic fibroblast growth factor in human hepatoma cells. Growth Factors. 1991;4(3):189–196. doi: 10.3109/08977199109104815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugler B., Amalric F., Prats H. Alternative initiation of translation determines cytoplasmic or nuclear localization of basic fibroblast growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):573–577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Widmer M. B., deRoos P., Qwarnstrom E. E. IL-1 and its receptor are translocated to the nucleus. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1295–1303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dell'Era P., Presta M., Ragnotti G. Nuclear localization of endogenous basic fibroblast growth factor in cultured endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Feb;192(2):505–510. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90070-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florkiewicz R. Z., Baird A., Gonzalez A. M. Multiple forms of bFGF: differential nuclear and cell surface localization. Growth Factors. 1991;4(4):265–275. doi: 10.3109/08977199109043912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Koji T., Mizuno K., Tamaru M., Koikeda S., Nakane P. K., Mori N., Masamune Y., Nakanishi Y. Transcription switch of two phosphoglycerate kinase genes during spermatogenesis as determined with mouse testis sections in situ. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Feb;186(2):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90306-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Growth factors: mechanism of action and relation to oncogenes. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura T., Engleka K., Zhan X., Tokita Y., Forough R., Roeder D., Jackson A., Maier J. A., Hla T., Maciag T. Recovery of mitogenic activity of a growth factor mutant with a nuclear translocation sequence. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1567–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.1699274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kardami E., Fandrich R. R. Basic fibroblast growth factor in atria and ventricles of the vertebrate heart. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1865–1875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan A. Intracrine regulation at the nucleus--a further mechanism of growth factor activity? J Endocrinol. 1990 Jun;125(3):339–343. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1250339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher D. W., Lee B. A., Donoghue D. J. The alternatively spliced exon of the platelet-derived growth factor A chain encodes a nuclear targeting signal. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2251–2253. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda Y., Yoshitake Y., Nishikawa K. Growth control of A431 cells in protein-free medium: secretory products do not affect cell growth. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1988 Sep;24(9):893–899. doi: 10.1007/BF02623899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T. In vitro accurate initiation of transcription on the adenovirus type 2 IVa2 gene which does not contain a TATA box. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7089–7101. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki K., Yoshitake Y., Matuo Y., Sasaki H., Nishikawa K. Monoclonal antibodies against heparin-binding growth factor II/basic fibroblast growth factor that block its biological activity: invalidity of the antibodies for tumor angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9911–9915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki K., Yoshitake Y., Miyagiwa M., Minemura M., Tanaka M., Sasaki H., Nishikawa K. Production of basic fibroblast growth factor-like factor by cultured human cholangiocellular carcinoma cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1990 Apr;81(4):345–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1990.tb02574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayerhofer A., Russell L. D., Grothe C., Rudolf M., Gratzl M. Presence and localization of a 30-kDa basic fibroblast growth factor-like protein in rodent testes. Endocrinology. 1991 Aug;129(2):921–924. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-2-921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi Y., Shibata H., Hase T., Masamune Y. Analysis of promoters of adenovirus type 12 E1A gene in a cell-free transcription system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 31;146(2):783–790. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90598-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarto N., Finger F. P., Rifkin D. B. The NH2-terminal extension of high molecular weight bFGF is a nuclear targeting signal. J Cell Physiol. 1991 May;147(2):311–318. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041470217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakowicz-Szulczynska E. M., Rodeck U., Herlyn M., Koprowski H. Chromatin binding of epidermal growth factor, nerve growth factor, and platelet-derived growth factor in cells bearing the appropriate surface receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3728–3732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renko M., Quarto N., Morimoto T., Rifkin D. B. Nuclear and cytoplasmic localization of different basic fibroblast growth factor species. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jul;144(1):108–114. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041440114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiurba R. A., Jing N., Sakakura T., Godsave S. F. Nuclear translocation of fibroblast growth factor during Xenopus mesoderm induction. Development. 1991 Oct;113(2):487–493. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.2.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kamel T., Hakamata Y., Kikukawa K., Shiota K., Takahashi M. Basic fibroblast growth factor-like substance in nuclei of male germ cells undergoing meiosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1991 Nov;198(2):728–731. doi: 10.3181/00379727-198-43310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaru M., Nagao Y., Taira M., Tatibana M., Masamune Y., Nakanishi Y. Selective activation of testis-specific genes in cultured rat spermatogenic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 30;1049(3):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90106-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessler S., Neufeld G. Basic fibroblast growth factor accumulates in the nuclei of various bFGF-producing cell types. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Nov;145(2):310–317. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041450216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. A., Protter A. A., Bitting L., Fiddes J. C., Abraham J. A. Cloning, recombinant expression, and characterization of basic fibroblast growth factor. Methods Enzymol. 1991;198:96–116. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)98012-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno N., Baird A., Esch F., Ling N., Guillemin R. Isolation and partial characterization of basic fibroblast growth factor from bovine testis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Feb;49(2-3):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90212-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Melton D. A. Growth factors in early embryogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:93–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitake Y., Matsuzaki K., Nishikawa K. Derivation of monoclonal antibody to basic fibroblast growth factor and its application. Methods Enzymol. 1991;198:148–157. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)98016-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitake Y., Nishikawa K. Production of monoclonal antibodies with specificity for different epitopes on the human epidermal growth factor molecule. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jun;263(2):437–446. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90656-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng W. X., Butwell T. J., Heckert L., Griswold M. D., Bellvé A. R. Pleiotypic actions of the seminiferous growth factor on two testicular cell lines: comparisons with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Growth Factors. 1990;3(1):73–82. doi: 10.3109/08977199009037504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]