Abstract
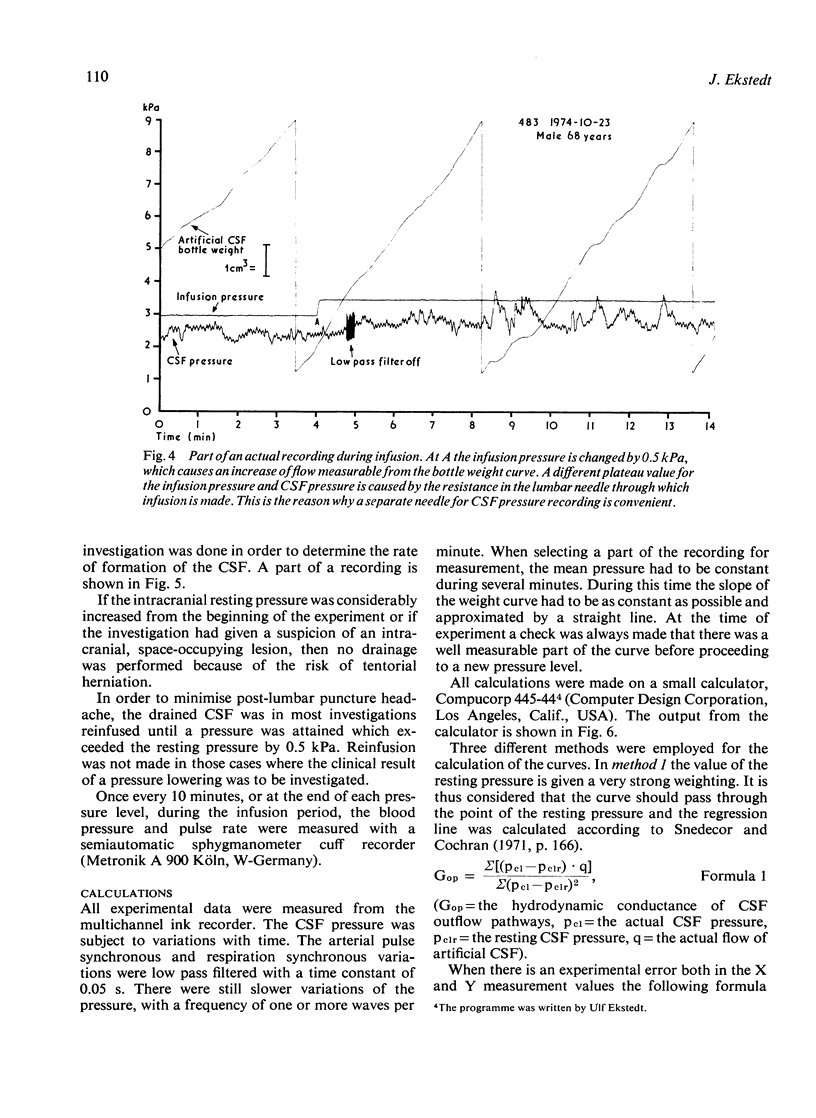
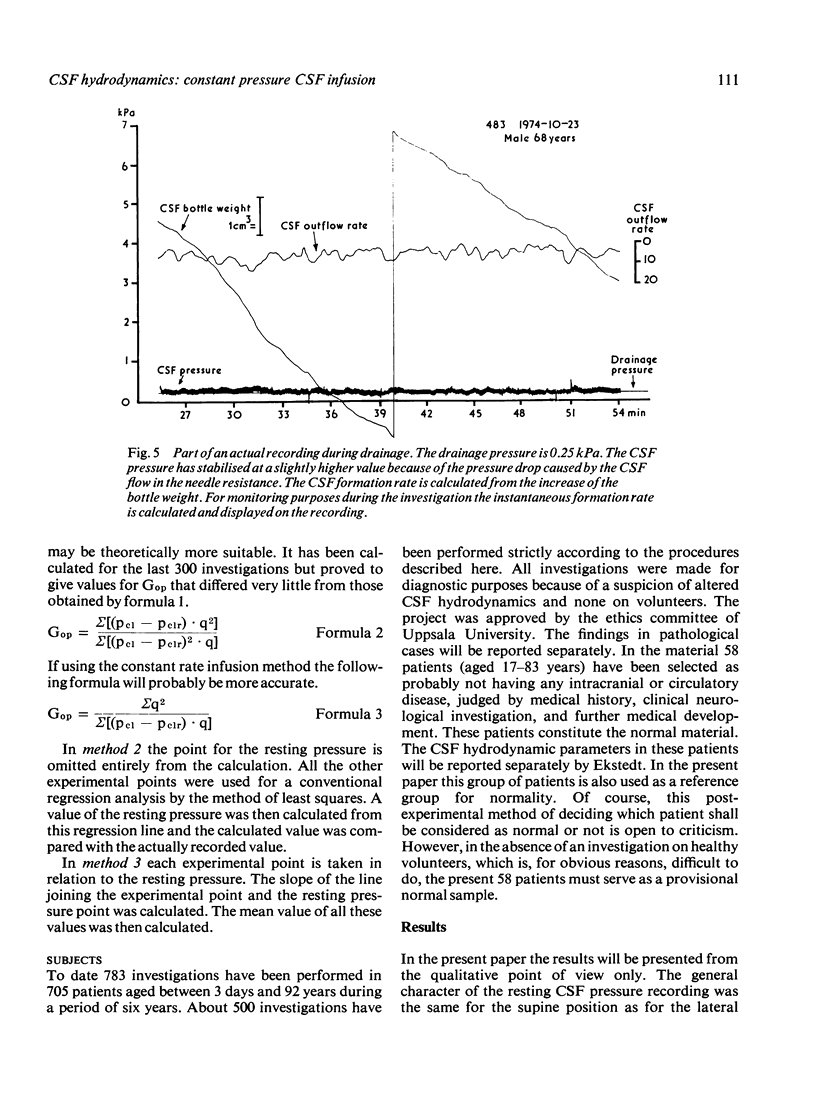
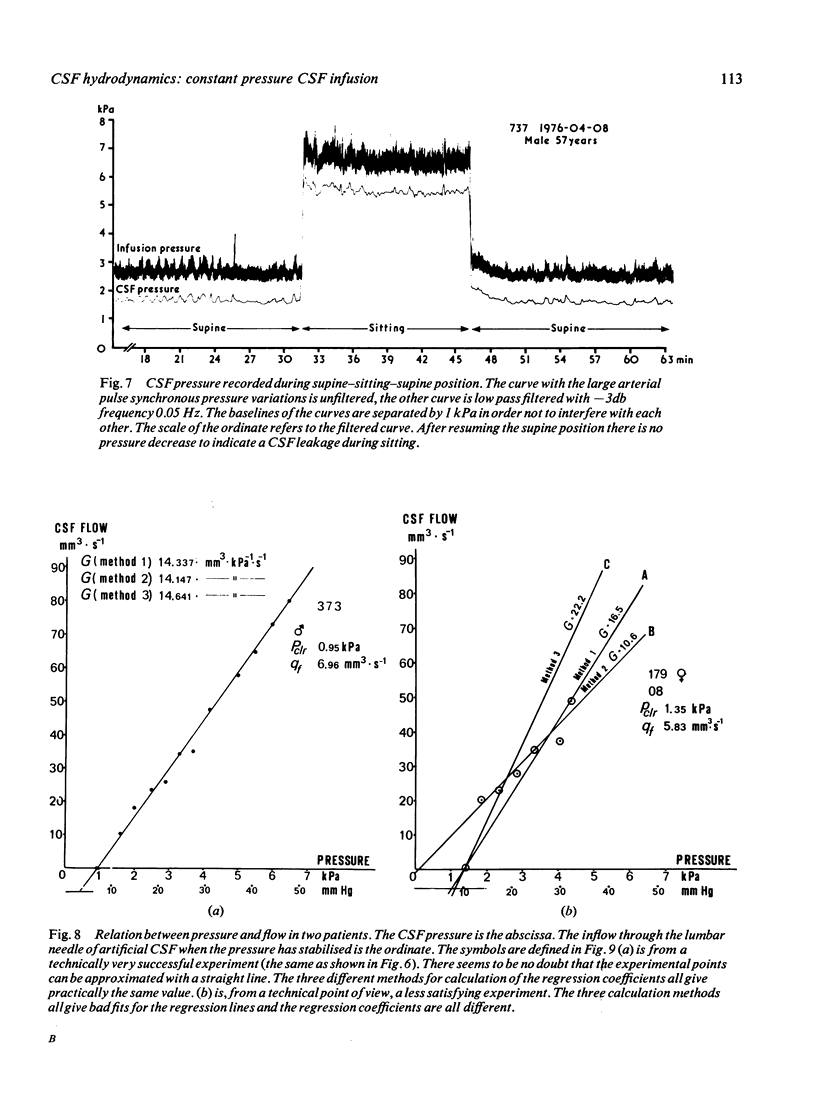
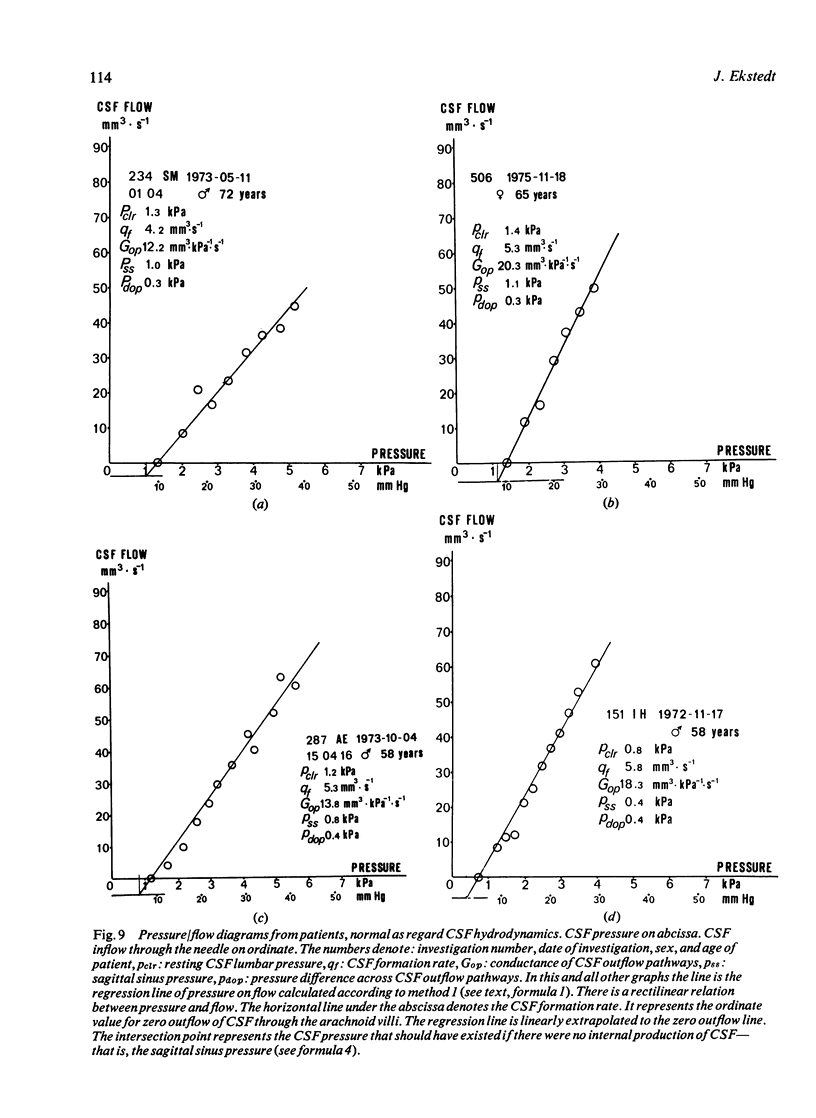
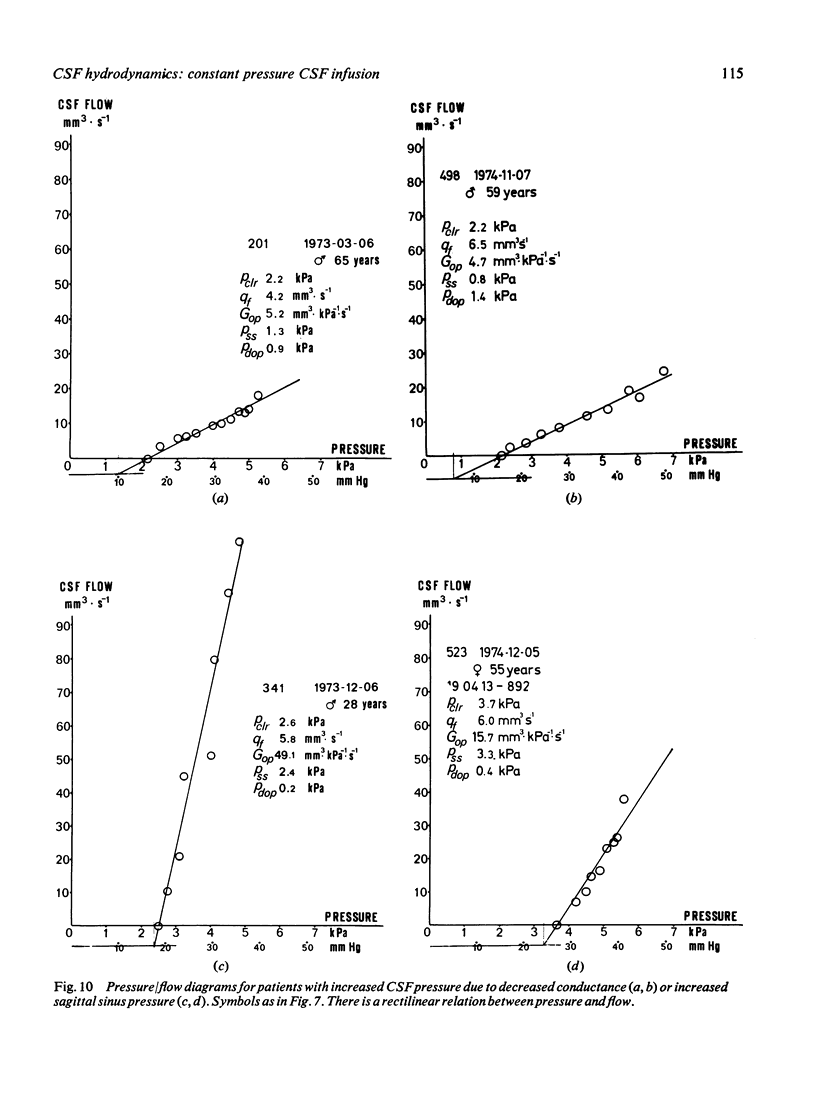
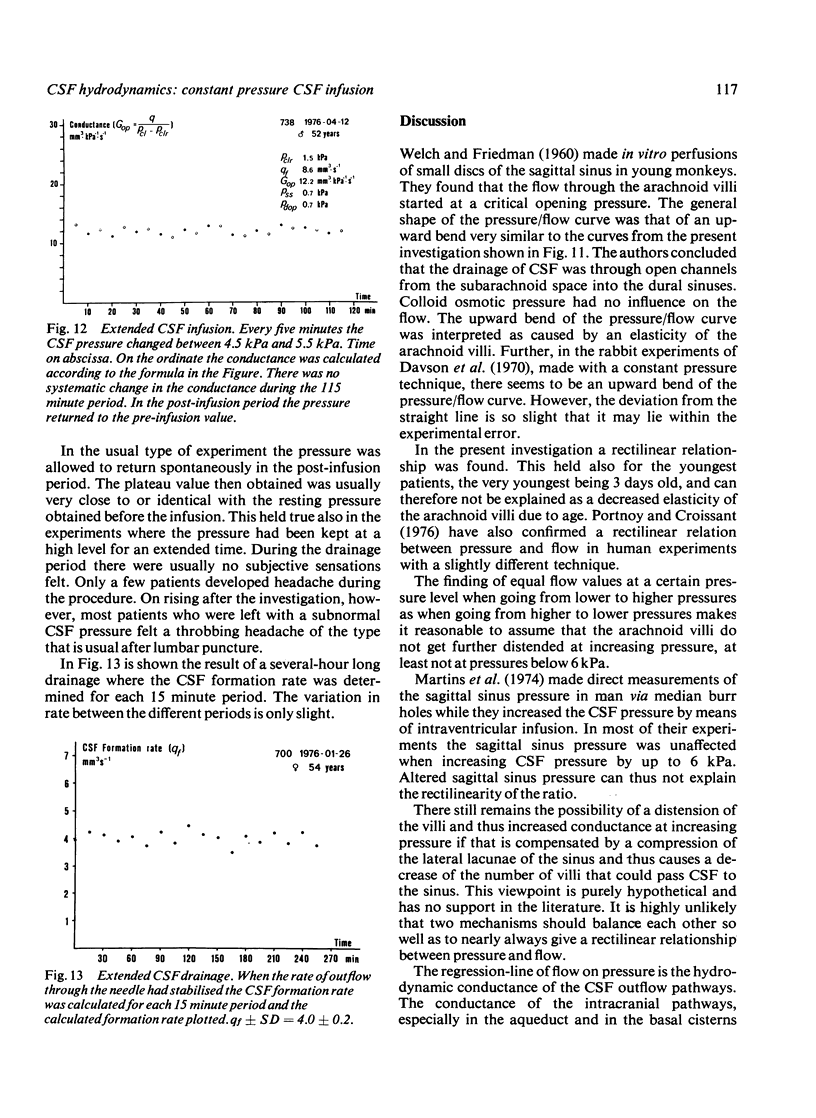
The constant pressure method for the study of the hydrodynamics of CSF is presented. By infusing artificial CSF at constant pressures and recording the resultant flow, it is possible to obtain information about the hydrodynamic conductance of the CSF outflow pathways. By lowering the infusion pressure below the pressure of the sagittal sinus all CSF produced can be collected and the CSF formation rate may thus be calculated. There is a rectilinear relationship between CSF pressure and the flow necessary to maintain the pressure. It is thus concluded that the arachnoidal villi, when once opened, are not further distended by pressure. This method makes possible indirect calculation of the pressure of the sagittal sinus and the pressure difference between the subarachnoid space and the sagittal sinus.
Full text
PDF
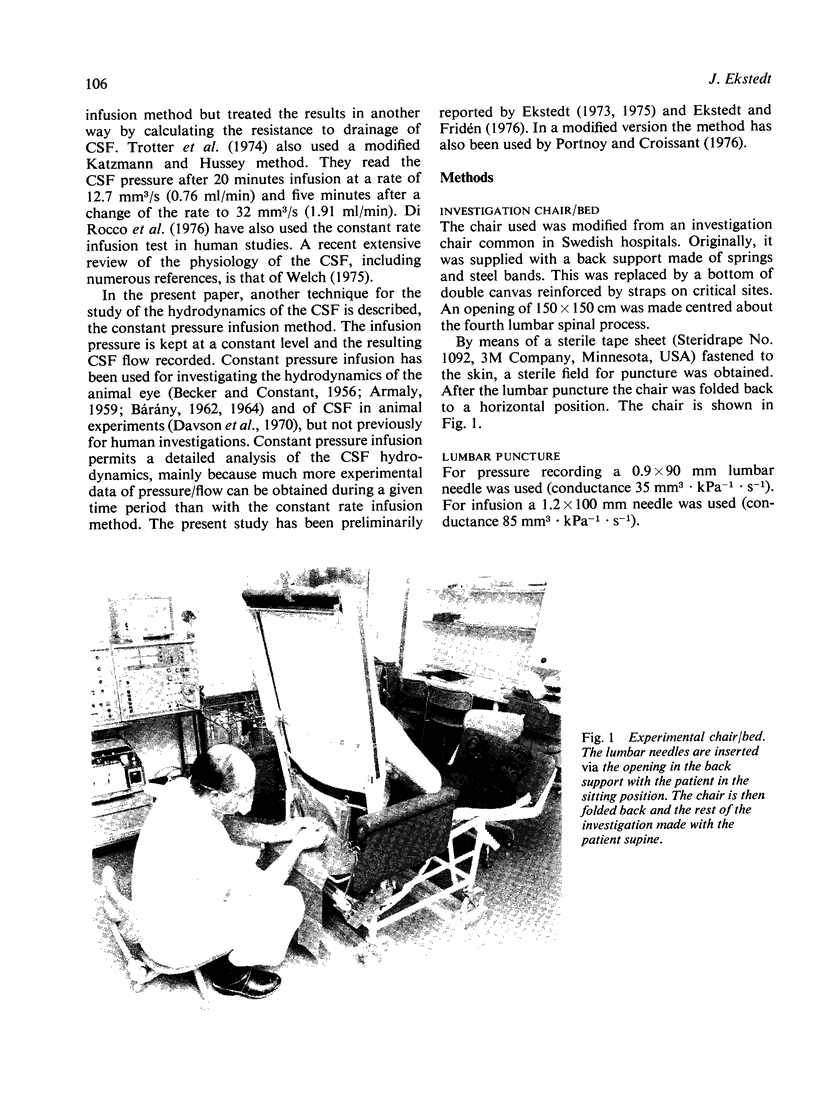

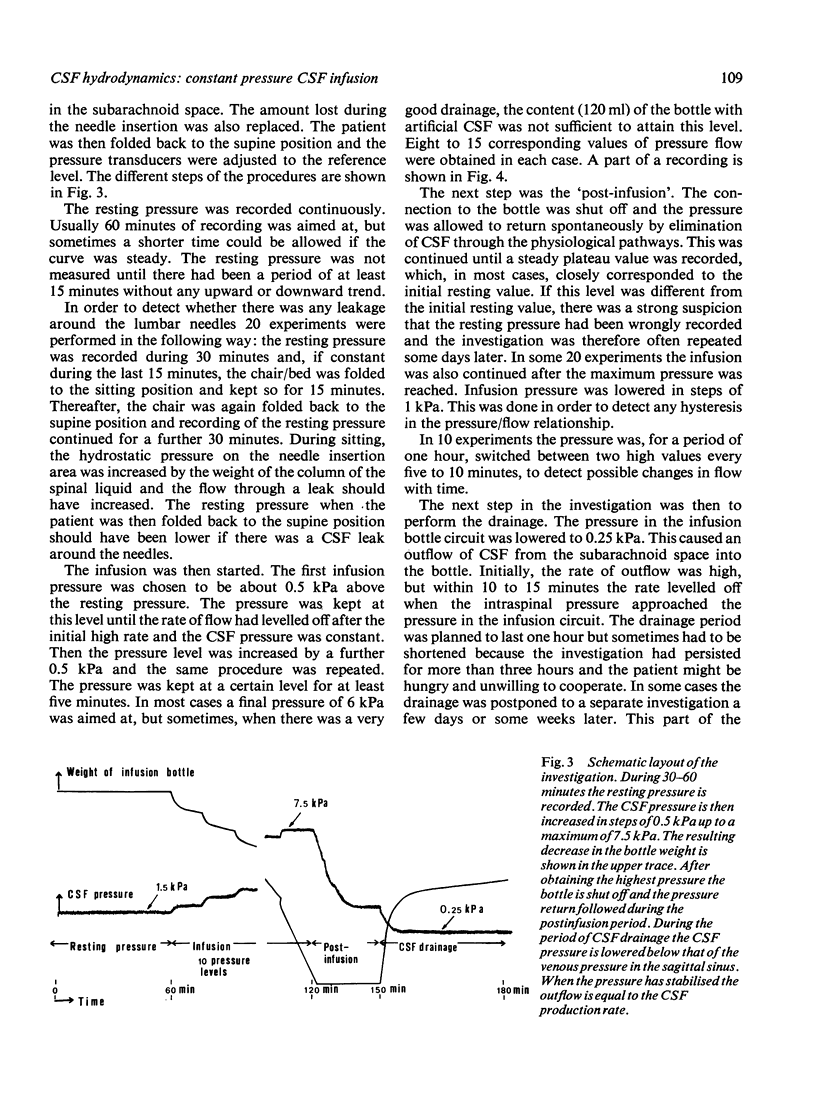



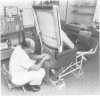
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMALY M. F. Studies on intraocular effects of the orbital parasympathetic pathway. III. Effect on steady-state dynamics. Arch Ophthalmol. 1959 Nov;62:817–827. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1959.04220050079013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARANY E. H. SIMULTANEOUS MEASUREMENT OF CHANGING INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE AND OUTFLOW FACILITY IN THE VERVET MONKEY BY CONSTANT PRESSURE INFUSION. Invest Ophthalmol. 1964 Apr;3:135–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARANY E. H. The mode of action of pilocarpine on outflow resistance in the eye of a primate (Cercopithecus ethiops). Invest Ophthalmol. 1962 Dec;1:712–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler R. W., Page L., Galicich J., Watters G. V. Formation and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid in man. Brain. 1968;91(4):707–720. doi: 10.1093/brain/91.4.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
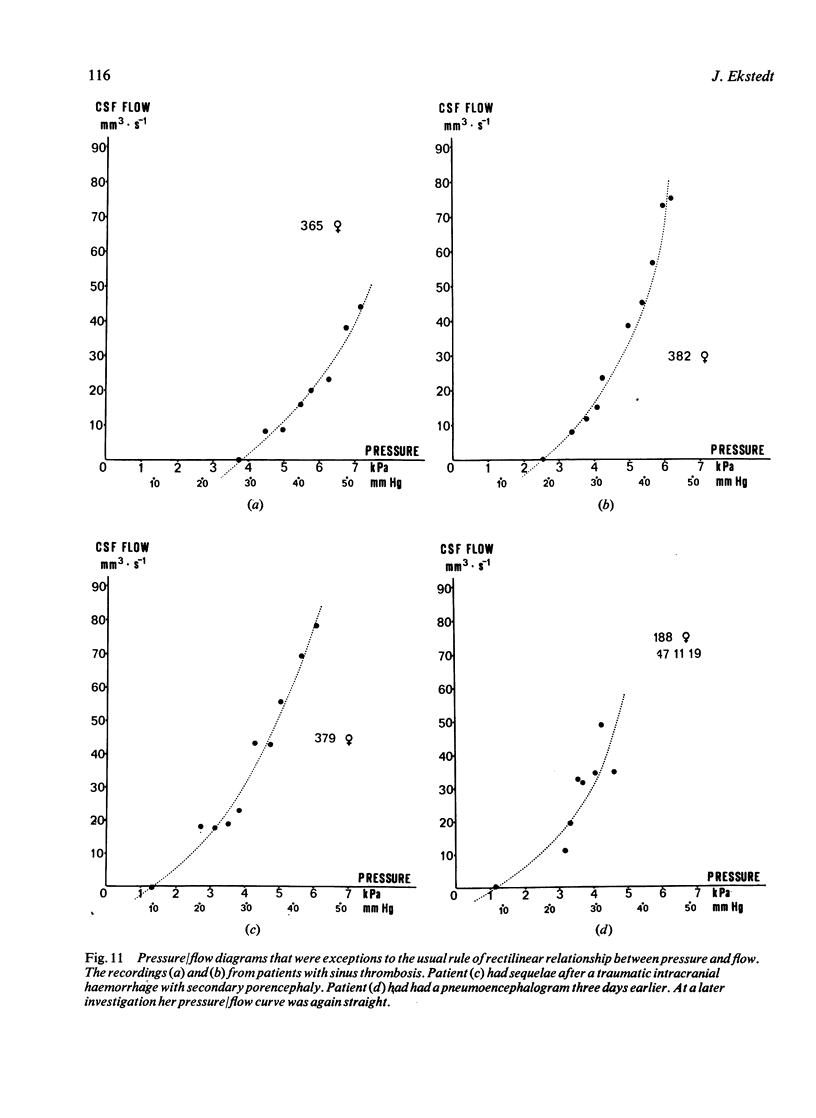
- Davson H., Hollingsworth G., Segal M. B. The mechanism of drainage of the cerebrospinal fluid. Brain. 1970;93(4):665–678. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.4.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Rocco C., Maira G., Rossi G. F., Vignati A. Cerebrospinal fluid pressure studies in normal pressure hydrocephalus and cerebral atrophy. Eur Neurol. 1976;14(2):119–128. doi: 10.1159/000114734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foldes F. F., Arrowood J. G. CHANGES IN CEREBROSPINAL FLUID PRESSURE UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF CONTINUOUS SUBARACHNOIDAL INFUSION OF NORMAL SALINE. J Clin Invest. 1948 May;27(3 Pt 1):346–351. doi: 10.1172/JCI101965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussey F., Schanzer B., Katzman R. A simple constant-infusion manometric test for measurement of CSF absorption. II. Clinical studies. Neurology. 1970 Jul;20(7):665–680. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.7.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janny P. La surveillance de la pression intra-cranienne en neuro-chirurgie. Neurochirurgie. 1974 Nov;20(6):521–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman R., Hussey F. A simple constant-infusion manometric test for measurement of CSF absorption. I. Rationale and method. Neurology. 1970 Jun;20(6):534–544. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.6.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo A. V., Page L. K., Watters G. V. Relationship between cerebrospinal fluid formation, absorption and pressure in human hydrocephalus. Brain. 1970;93(4):679–692. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.4.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg N., West K. A. Leakage as a source of error in measurement of the cerebrospinal fluid pressure by lumbar puncture. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1965;13(Pt 1):115–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1965.tb01865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martins A. N., Kobrine A. I., Larsen D. F. Pressure in the sagittal sinus during intracranial hypertension in man. J Neurosurg. 1974 May;40(5):603–608. doi: 10.3171/jns.1974.40.5.0603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martins A. N. Resistance to drainage of cerebrospinal fluid: clinical measurement and significance. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Apr;36(2):313–318. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. R., Goodman S. J. An evaluation of the cerebrospinal fluid infusion test for hydrocephalus. Neurology. 1971 Oct;21(10):1037–1053. doi: 10.1212/wnl.21.10.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy H. D., Croissant P. D. A practical method for measuring hydrodynamics of cerebrospinal fluid. Surg Neurol. 1976 May;5(5):273–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. C., Henderson E. S., Ommaya A. K., Walker M. D., Rall D. P. The production of cerebrospinal fluid in man and its modification by acetazolamide. J Neurosurg. 1966 Oct;25(4):430–436. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.25.4.0430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolowski S. J. A new quantitative technique for the assessement of cerebrospinal fluid absorption in man. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Sep;23(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter J. L., Luzecky M., Siegel B. A., Gado M. Cerebrospinal fluid infusion test. Identification of artifacts and correlation with cisternography and pneumoencephalography. Neurology. 1974 Feb;24(2):181–186. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.2.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELCH K., FRIEDMAN V. The cerebrospinal fluid valves. Brain. 1960 Sep;83:454–469. doi: 10.1093/brain/83.3.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch K. The principles of physiology of the cerebrospinal fluid in relation to hydrocephalus including normal pressure hydrocephalus. Adv Neurol. 1975;13:247–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]