Abstract
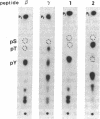
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAP kinases) are activated by dual tyrosine and threonine phosphorylations in response to various stimuli, including phorbol esters. To define the mechanism of activation, recombinant wild-type 42-kDa MAP kinase (p42mapk) and a kinase-defective mutant of p42mapk (K52R) were used to assay both activator activity for p42mapk and kinase activity toward K52R in stimulated EL4.I12 mouse thymoma cells. Phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate (10 min, 650 nM) stimulated a single peak of MAP kinase activator that was coeluted from Mono Q at pH 7.5 and 8.9 with K52R kinase activity. Both activities were inactivated by the serine/threonine-specific phosphatase 2A but not by the tyrosine-specific phosphatase CD45. Phosphorylation of K52R occurred specifically on Thr-183 and Tyr-185, as determined by tryptic phosphopeptide mapping in comparison with synthetic marker phosphopeptides. These findings indicate that phorbol ester-stimulated MAP kinase kinase can activate p42mapk by threonine and tyrosine phosphorylations, and that p42mapk thus does not require an autophosphorylation reaction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. D., Parker P. J. TPA-induced activation of MAP kinase. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 23;290(1-2):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn N. G., Weiel J. E., Chan C. P., Krebs E. G. Identification of multiple epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein serine/threonine kinases from Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11487–11494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Boulton T. G., Robbins D. J. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases: ERKs in progress. Cell Regul. 1991 Dec;2(12):965–978. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.12.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A. A., Erikson R. L. Mouse Erk-1 gene product is a serine/threonine protein kinase that has the potential to phosphorylate tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8845–8849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. K., Payne D. M., Martino P. A., Rossomando A. J., Shabanowitz J., Weber M. J., Hunt D. F., Sturgill T. W. Identification by mass spectrometry of threonine 97 in bovine myelin basic protein as a specific phosphorylation site for mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19728–19735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Cohen P. Dissection of the protein kinase cascade by which nerve growth factor activates MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):170–173. doi: 10.1038/353170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Krebs E. G. Consensus sequences as substrate specificity determinants for protein kinases and protein phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15555–15558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Rossomando A. J., Martino P., Erickson A. K., Her J. H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):885–892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A. J., Payne D. M., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Evidence that pp42, a major tyrosine kinase target protein, is a mitogen-activated serine/threonine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6940–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A. J., Sanghera J. S., Marsden L. A., Weber M. J., Pelech S. L., Sturgill T. W. Biochemical characterization of a family of serine/threonine protein kinases regulated by tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylations. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20270–20275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scimeca J. C., Ballotti R., Nguyen T. T., Filloux C., Van Obberghen E. Tyrosine and threonine phosphorylation of an immunoaffinity-purified 44-kDa MAP kinase. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9313–9319. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Ahn N. G., Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Panayotatos N., Radziejewska E., Ericsson L., Bratlien R. L., Cobb M. H., Krebs E. G. Microtubule-associated protein 2 kinases, ERK1 and ERK2, undergo autophosphorylation on both tyrosine and threonine residues: implications for their mechanism of activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6142–6146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Wu J. Recent progress in characterization of protein kinase cascades for phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 17;1092(3):350–357. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(97)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Rossomando A. J., Her J. H., Del Vecchio R., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Autophosphorylation in vitro of recombinant 42-kilodalton mitogen-activated protein kinase on tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9508–9512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]