Abstract
The motor unit content and the dimensions of individual motor unit action potentials were studied in 17 patients with acute idiopathic polyneuritis from one week to 9 1/2 years after the onset of the illness. An initial decrease in motor unit numbers is followed by a progressive increase with the passage of time from the onset of the illness. The latencies, areas, amplitudes, and durations of individual motor unit potentials were increased above normal values. The results suggest the presence of significant axonal damage in the majority of cases of acute idiopathic polyneuritis. The intramuscular nerve fibres are the site of most severe electrophysiological dysfunction in this study.
Full text
PDF

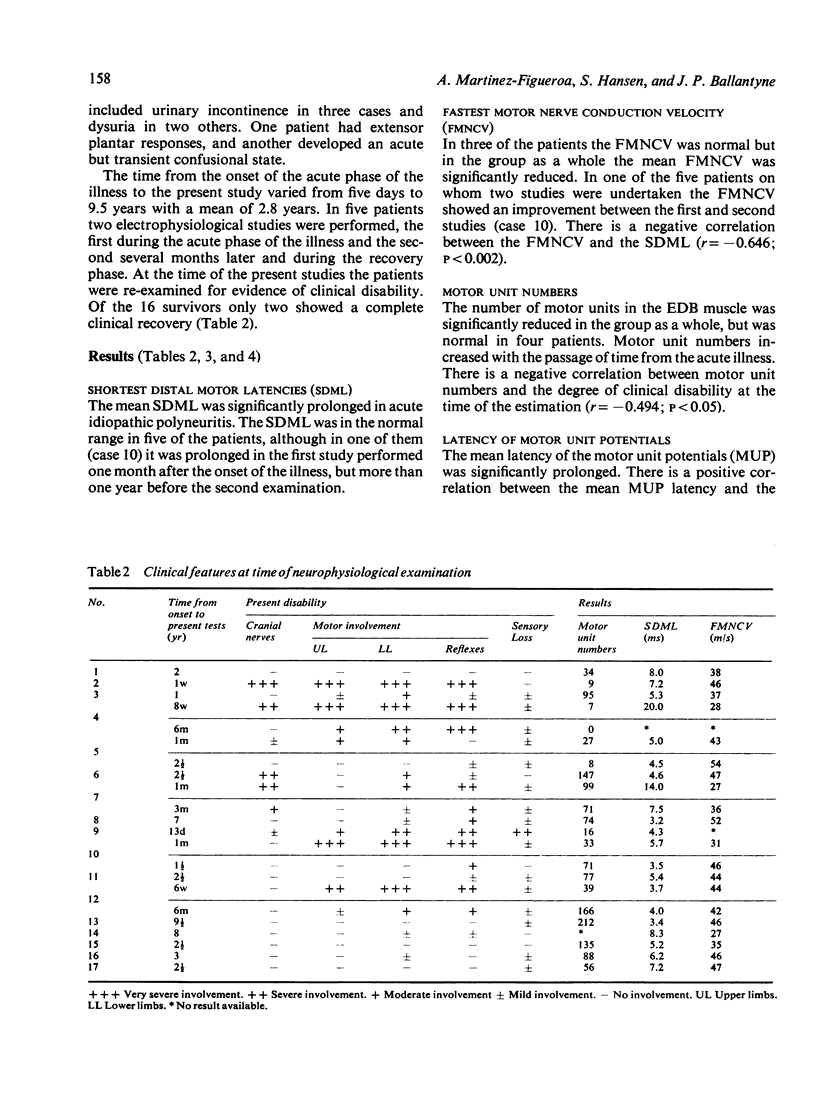
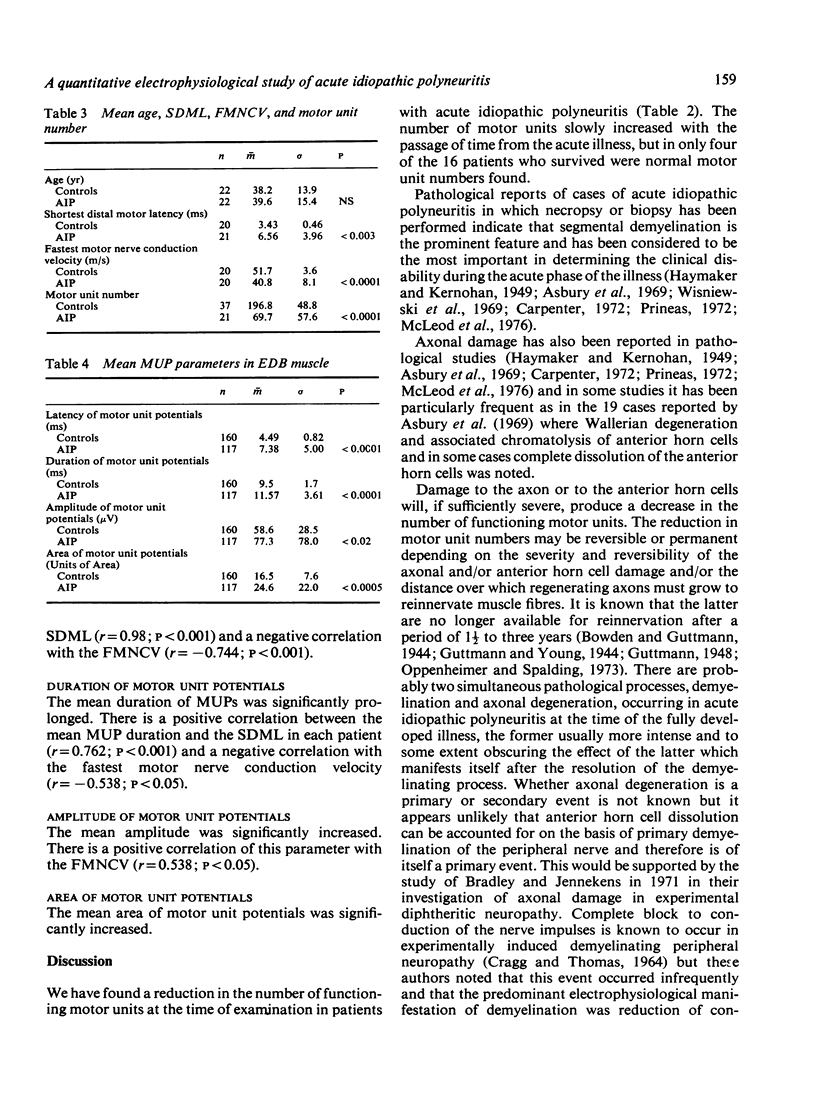


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbury A. K., Arnason B. G., Adams R. D. The inflammatory lesion in idiopathic polyneuritis. Its role in pathogenesis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 May;48(3):173–215. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196905000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne J. P., Hansen S. A new method for the estimation of the number of motor units in a muscle. I. Control subjects and patients with myasthenia gravis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Aug;37(8):907–915. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.8.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne J. P., Hansen S. Computer method for the analysis of evoked motor unit potentials. 2. Duchenne, limb-girdle, facioscapulohumeral and myotonic muscular dystrophies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 May;38(5):417–428. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.5.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne J. P., Hansen S. Computer method for the analysis of evoked motor unit potentials. I. Control subjects and patients with myasthenia gravis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Nov;37(11):1187–1194. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.11.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergamini L., Gandiglio G., Fra L. Motor and afferent nerve conduction in the Guillain-Barré-Sthrol syndrome: a longitudinal study in five cases with different clinical features. Electromyography. 1966 Aug-Oct;6(3):205–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley W. G., Jennekens F. G. Axonal degeneration in diphtheritic neuropathy. J Neurol Sci. 1971 Aug;13(4):415–430. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(71)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAGG B. G., THOMAS P. K. CHANGES IN NERVE CONDUCTION IN EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC NEURITIS. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1964 Apr;27:106–115. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.27.2.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S. An ultrastructural study of an acute fatal case of the Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 1972 Feb;15(2):125–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(72)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann E., Young J. Z. The re-innervation of muscle after various periods of atrophy. J Anat. 1944 Jan;78(Pt 1-2):15–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J., Butzer J. F. F-wave conduction velocity in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Assessment of nerve segment between axilla and spinal cord. Arch Neurol. 1975 Aug;32(8):524–529. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490500044004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masucci E. F., Kurtzke J. F. Diagnostic criteria for the Guillain-Barré syndrome. An analysis of 50 cases. J Neurol Sci. 1971 Aug;13(4):483–501. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(71)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComas A. J., Fawcett P. R., Campbell M. J., Sica R. E. Electrophysiological estimation of the number of motor units within a human muscle. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Apr;34(2):121–131. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. G., Walsh J. C., Prineas J. W., Pollard J. D. Acute idiopathic polyneuritis. A clinical and electrophsiological follow-up study. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Feb;27(2):145–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuillen M. P. Idiopathic polyneuritis: serial studies of nerve and immune functions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Oct;34(5):607–615. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.5.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer D. R., Spalding J. M. Late residua of acute idiopathic polyneuritis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Dec;36(6):978–988. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.6.978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J. W. Acute idiopathic polyneuritis. An electron microscope study. Lab Invest. 1972 Feb;26(2):133–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raman P. T., Taori G. M. Prognostic significance of electrodiagnostic studies in the Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Feb;39(2):163–170. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert E. D., Oester Y. T. Nerve impulses and trophic effect. Absence of fibrillation after prolonged and reversible conduction block. Arch Neurol. 1970 Jan;22(1):57–63. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480190061010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfalck A., Buchthal F. Demyelination and axonal degeneration. Acta Neurol Scand. 1970;46(Suppl):199–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1970.tb02183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H., Terry R. D., Whitaker J. N., Cook S. D., Dowling P. C. Landry-Guillain-Barré syndrome. A primary demyelinating disease. Arch Neurol. 1969 Sep;21(3):269–276. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480150059008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


