Abstract
Larval metamorphosis of the veined rapa whelk (Rapana venosa) is a pelagic to benthic transition that involves considerable structural and physiological changes. Because metamorphosis plays a pivotal role in R. venosa commercial breeding and natural populations, the endogenous proteins that drive this transition attract considerable interest. This study is the first to perform a comprehensive and quantitative proteomic analysis related to metamorphosis in a marine gastropod. We analyzed the proteomes of competent R. venosa larvae and post-larvae, resulting in the identification of 5312 proteins, including 470 that were downregulated and 668 that were upregulated after metamorphosis. The differentially expressed proteins reflected multiple processes involved in metamorphosis, including cytoskeleton and cell adhesion, ingestion and digestion, stress response and immunity, as well as specific tissue development. Our data improve understanding of the physiological traits controlling R. venosa metamorphosis and provide a solid basis for further study.
Keywords: transcriptome, Rapana venosa, gastropod, larva, digital gene expression
1. Introduction
The veined rapa whelk (Rapana venosa) is an economically important sea snail in China, and since 1992, there has been interest in its commercial aquaculture [1]. However, sea-ranching efforts have been hampered by difficulties cultivating larvae during the settlement and metamorphosis stages. In countries that do not consume R. venosa, such as the United States, Argentina, and France, this predatory species has become an invasive pest due to unintended worldwide transport and severely disrupts the survival of native bivalves [2,3,4,5,6]. Because R. venosa population dynamics and spatial expansion are dominated by recruitment and survival rate during metamorphosis, which is a vital process in the species’ biphasic life cycle, understanding the mechanisms behind this process is necessary for both successful aquaculture and invasion control. Moreover, the metamorphosis of R. venosa is unusual compared with other lifelong phytophagous gastropods for exhibiting considerable developmental specificity; the planktonic, pelagic larvae go from filter-feeding on microalgae to carnivorous juveniles that prey on bivalves [7]. This transition occurs rapidly, despite fundamental changes in morphology including velum degeneration and reabsorption, foot reorientation and elongation, as well as secondary-shell growth [7]. Thus, clarifying R. venosa metamorphosis is also of theoretical interest to gastropod researchers.
However, information about R. venosa metamorphosis is relatively scarce. A previous study had documented the morphological changes that occur during this process [7]. Additionally, CaCl2 and acetylcholine chloride were found to be effective and low-toxicity inducers of metamorphosis in R. venosa pelagic larvae [8], suggesting these compounds might be suitable for applying to its artificial seeding. Finally, a comprehensive transcriptomic profile has been constructed from R. venosa planktonic larvae and post-larvae [9], which paves the way for studies on metamorphosis-related gene activity. However, because complex gene regulation occurs during post-transcription and post-translation [10,11], proteomic data are required to provide more concrete support for conclusions based on transcriptome data. Indeed, proteomic analysis has been successfully applied to identify a number of metamorphosis-related proteins in marine-invertebrates, specifically in bryozoans [12], polychaetes [13,14], and barnacles [12,15]. To our knowledge, no proteomic study has been conducted to investigate gastropod metamorphosis.
Although two-dimensional electrophoresis (2DE) is the most common proteomic approach, the method lacks the sensitivity to identify low-abundance proteins or those not amenable to gels [16]. Moreover, 2DE’s accuracy is potentially compromised by the phenomenon of protein co-migration [17]. The recently developed, high-throughput isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) has therefore become increasingly popular. This method labels peptides with isobaric (same-mass) reagents consisting of reporter ions and their equalizing balance groups. During mass spectrometry (e.g., collision-induced dissociation (CID)), the reporter ions are then separated from the labelled peptides, allowing for determination of ion intensity and thus peptide quantity. Therefore, iTRAQ differs from other quantitative proteomics technologies, which tend to measure precursor (pre-fragmentation) ion intensities. The difference allows for greater accuracy and reliability [18]. In this current study, we chose iTRAQ to assess proteomic changes during metamorphosis via a comparative proteomic analysis on competent larvae and juveniles of R. venosa. We were able to identify and annotate over 5000 proteins through searching the R. venosa transcriptome with protein sequences [9]; 1138 of the identified proteins were differentially expressed, during metamorphosis, suggesting that they are responsible for the process. Our results showed that these differentially expressed proteins function in diverse biological processes, including cytoskeleton and cell adhesion, ingestion and digestion, stress response and immunity, as well as specific tissue development. These findings provide a proteomic overview of gastropod metamorphosis and facilitate future research on protein function during the transitions of a biphasic life cycle.
2. Results
2.1. General Characterization of Proteomic Data
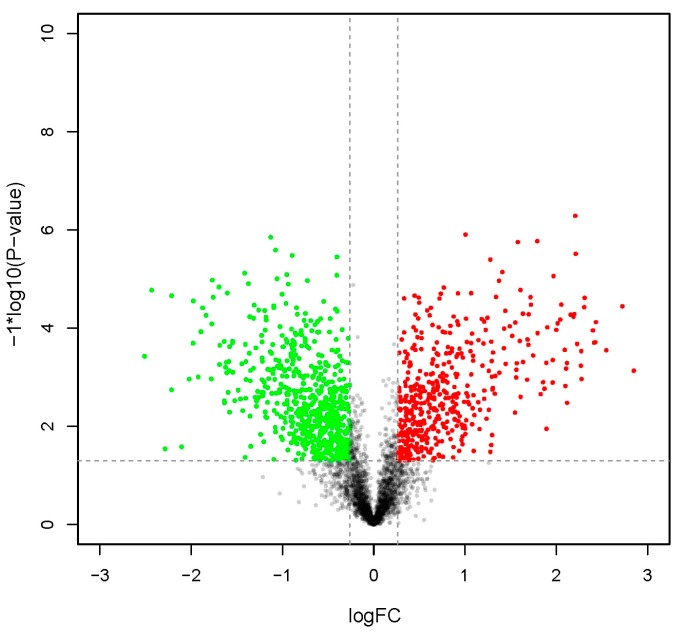
Raw data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Database (accession number: PXD004119). As shown in Table 1, of the 224,473 detected spectra, 46,485 were considered unique. Moreover, 5321 proteins were identified. Figure 1 displays the overall changes to protein abundance before and after metamorphosis. More detailed information on these 5321 proteins is available in Table S1, while variation in expression during metamorphosis is shown in Table S2: 470 proteins were upregulated and 668 were downregulated after metamorphic transition (Table S2). Homologous sequence analysis of these differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) revealed four functional groups of interest (Table 2): cytoskeleton and cell adhesion, ingestion and digestion, stress response and immunity, as well as specific tissue development.
Table 1.
Overview of proteomics sequencing results.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Total Spectra | 224,473 |
| Spectra | 53,723 |
| Unique Spectra | 46,485 |
| Peptide | 21,626 |
| Unique Peptide | 20,175 |
| Protein | 5312 |
| Upregulated protein | 470 |
| Downregulated protein | 668 |
Figure 1.
Change in global protein abundance between the post-larval stage (PL) and the competent larval stage (CL). LogFC represents log2Ratio (PL/CL); proteins with log2Ratio (PL/CL) >0.26 or <−0.26 are colored (red for fold changes >1.20 and green for <0.83).
Table 2.
Selected differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) between competent larvae and post-larvae. “FC” represents Log2 (competent larvae /post larvae).
| Accession | FC | p-Value | Annotation | Organism Species | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cytoskeleton and Cell Adhesion | |||||
| c111395_g1 | 0.49 | 8.22 × 10−3 | Paramyosin | Mytilus galloprovincialis | cytoskeleton component |
| c119060_g1 | 1.01 | 6.45 × 10−5 | Paramyosin | Mytilus galloprovincialis | cytoskeleton component |
| c67246_g1 | 0.80 | 1.29 × 10−3 | Paramyosin | Mytilus galloprovincialis | cytoskeleton component |
| c128871_g1 | 0.30 | 3.16 × 10−2 | Tropomyosin-2 | Biomphalaria glabrata | cytoskeleton component |
| c128871_g1 | 0.30 | 3.16 × 10−2 | Tropomyosin-2 | Biomphalaria glabrata | cytoskeleton component |
| c64757_g1 | 1.42 | 1.03 × 10−4 | Tubulin α chain | Plasmodium falciparum | cytoskeleton component |
| c144449_g1 | −0.63 | 1.02 × 10−2 | Tubulin α-1 chain | Paracentrotus lividus | cytoskeleton component |
| c19674_g1 | −0.46 | 1.08 × 10−2 | Tubulin α-2 chain | Gossypium hirsutum | cytoskeleton component |
| c65878_g1 | 0.60 | 5.21 × 10−3 | Tubulin α-8 chain (Fragment) | Gallus gallus | cytoskeleton component |
| c129550_g1 | −0.52 | 2.78 × 10−2 | Tubulin β chain (Fragment) | Haliotis discus | cytoskeleton component |
| c52663_g1 | −0.59 | 3.64 × 10−3 | Tubulin β-2 chain | Drosophila melanogaster | cytoskeleton component |
| c91498_g1 | −0.52 | 1.39 × 10−3 | Tubulin β-4B chain | Mesocricetus auratus | cytoskeleton component |
| c154903_g1 | −0.46 | 2.80 × 10−4 | Collagen α-1(XV) chain | Homo sapiens | extracellular matrix |
| c136294_g1 | −1.19 | 5.14 × 10−3 | Collagen α-1(XXI) chain | Xenopus laevis | extracellular matrix |
| c156326_g1 | −1.23 | 1.42 × 10−4 | Collagen α-1(XXII) chain | Homo sapiens | extracellular matrix |
| c155801_g1 | −0.56 | 1.18 × 10−3 | Collagen α-4(VI) chain | Crassostrea gigas | extracellular matrix |
| c156014_g6 | −0.85 | 1.72 × 10−2 | Collagen α-5(VI) chain | Crassostrea gigas | extracellular matrix |
| c154603_g1 | −0.91 | 2.20 × 10−4 | Collagen α-6(VI) chain | Homo sapiens | extracellular matrix |
| c156014_g2 | −1.06 | 9.95 × 10−6 | Collagen α-6(VI) chain | Homo sapiens | extracellular matrix |
| c169434_g1 | 0.81 | 1.38 × 10−2 | Extracellular matrix protein 3 | Lytechinus variegatus | extracellular matrix |
| c215931_g1 | 0.87 | 2.65 × 10−2 | FRAS1-related extracellular matrix protein 2 | Homo sapiens | extracellular matrix |
| c157006_g5 | −0.61 | 2.06 × 10−2 | Laminin subunit alpha-2 | Mus musculus | extracellular matrix |
| c155563_g1 | −0.87 | 2.04 × 10−4 | Laminin-like protein epi-1 | Crassostrea gigas | extracellular matrix |
| c154307_g2 | −0.79 | 4.65 × 10−2 | Matrix metalloproteinase-19 | Homo sapiens | extracellular matrix |
| c147589_g2 | −0.89 | 1.45 × 10−2 | Cadherin-89D | Drosophila melanogaster | involved in adhesion |
| c149462_g1 | 0.42 | 9.10 × 10−3 | Kinectin | Mus musculus | involved in adhesion |
| c104353_g1 | −0.55 | 2.02 × 10−2 | Lactadherin | Rattus norvegicus | involved in adhesion |
| c156870_g1 | 0.64 | 8.39 × 10−4 | Macrophage mannose receptor 1 | Homo sapiens | involved in adhesion |
| c156842_g1 | −0.36 | 1.64 × 10−3 | Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 | Bos taurus | involved in adhesion |
| c151606_g1 | −0.40 | 6.31 × 10−3 | Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 | Rattus norvegicus | involved in adhesion |
| c136200_g1 | −0.31 | 2.49 × 10−2 | Neuroglian | Drosophila melanogaster | involved in adhesion |
| c154303_g4 | 0.68 | 2.35 × 10−2 | Non-neuronal cytoplasmic intermediate filament protein | Helix aspersa | involved in adhesion |
| c135777_g1 | −1.18 | 5.99 × 10−5 | Periostin | Mus musculus | involved in adhesion |
| c157397_g1 | −1.38 | 1.25 × 10−5 | Protocadherin Fat 4 | Homo sapiens | involved in adhesion |
| c142570_g1 | −1.11 | 2.18 × 10−4 | Protocadherin-like wing polarity protein stan | Drosophila melanogaster | involved in adhesion |
| Ingestion and Digestion | |||||
| c128401_g2 | −0.78 | 2.31 × 10−2 | Beta-galactosidase-1-like protein 2 | Homo sapiens | involved in carbohydrates hydrolysis |
| c135558_g1 | −1.78 | 1.09 × 10−3 | Endo-1,4-β-xylanase Z | Clostridium thermocellum | involved in carbohydrates hydrolysis |
| c96519_g1 | −1.58 | 5.17 × 10−3 | Endoglucanase | Mytilus edulis | involved in carbohydrates hydrolysis |
| c137870_g1 | −1.17 | 1.63 × 10−3 | Endoglucanase E-4 | Thermobifida fusca | involved in carbohydrates hydrolysis |
| c154739_g1 | −0.98 | 7.49 × 10−4 | Endoglucanase E-4 | Thermobifida fusca | involved in carbohydrates hydrolysis |
| c150903_g1 | −1.78 | 1.09 × 10−3 | Exoglucanase XynX | Clostridium thermocellum | involved in carbohydrates hydrolysis |
| c145604_g1 | 1.18 | 6.57 × 10−5 | Inactive pancreatic lipase-related protein 1 | Rattus norvegicus | involved in fat hydrolysis |
| c71768_g2 | 2.20 | 5.20 × 10−7 | Pancreatic triacylglycerol lipase | Myocastor coypus | involved in fat hydrolysis |
| c141966_g1 | 1.21 | 2.76 × 10−3 | Chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 3B | Mus musculus | involved in proteins hydrolysis |
| c140662_g1 | 0.74 | 3.47 × 10−3 | Chymotrypsin-like serine proteinase | Haliotis rufescens | involved in proteins hydrolysis |
| c141241_g2 | 0.33 | 2.94 × 10−2 | Glutamate carboxypeptidase 2 | Rattus norvegicus | involved in proteins hydrolysis |
| c150838_g1 | 1.44 | 4.46 × 10−5 | Prolyl endopeptidase | Mus musculus | involved in proteins hydrolysis |
| c153823_g1 | 0.43 | 3.91 × 10−3 | Trypsin | Sus scrofa | involved in proteins hydrolysis |
| c149315_g1 | 1.96 | 4.51 × 10−4 | Zinc carboxypeptidase A 1 | Anopheles gambiae | involved in proteins hydrolysis |
| c150282_g1 | 2.22 | 2.11 × 10−4 | Zinc metalloproteinase nas-13 | Caenorhabditis elegans | involved in proteins hydrolysis |
| c146629_g1 | 1.74 | 3.63 × 10−4 | Zinc metalloproteinase nas-14 | Caenorhabditis elegans | involved in proteins hydrolysis |
| c149138_g1 | −0.45 | 3.15 × 10−3 | Zinc metalloproteinase nas-30 | Caenorhabditis elegans | involved in proteins hydrolysis |
| c128907_g1 | 1.87 | 1.72 × 10−3 | Zinc metalloproteinase nas-38 | Caenorhabditis elegans | involved in proteins hydrolysis |
| c153700_g1 | 1.79 | 1.27 × 10−4 | Zinc metalloproteinase nas-6 | Caenorhabditis elegans | involved in proteins hydrolysis |
| c156669_g2 | 2.30 | 3.77 × 10−5 | Zinc metalloproteinase nas-8 | Caenorhabditis elegans | involved in proteins hydrolysis |
| c131553_g1 | 0.83 | 4.63 × 10−3 | Conotoxin Cl14.12 | Conus californicus | involved in secretory venom for predation |
| c147316_g1 | 1.33 | 9.47 × 10−4 | Cysteine-rich venom protein | Conus textile | involved in secretory venom for predation |
| c143655_g1 | 2.27 | 2.96 × 10−4 | Cysteine-rich venom protein Mr30 | Conus marmoreus | involved in secretory venom for predation |
| Stress Response and Immunity | |||||
| c122242_g1 | 1.59 | 1.84 × 10−4 | Myeloperoxidase | Mus musculus | anti-oxidant protein |
| c88819_g1 | 1.68 | 1.13 × 10−3 | Peroxidase-like protein 3 (Fragment) | Lottia gigantea | anti-oxidant protein |
| c156674_g2 | 0.49 | 1.21 × 10−2 | Peroxidasin homolog | Mus musculus | anti-oxidant protein |
| c140657_g1 | −0.38 | 1.54 × 10−2 | Peroxiredoxin-2 | Rattus norvegicus | anti-oxidant protein |
| c142245_g1 | −0.37 | 1.23 × 10−2 | Peroxiredoxin-6 | Gallus gallus | anti-oxidant protein |
| c156482_g1 | 0.30 | 1.01 × 10−2 | Probable deferrochelatase/peroxidase YfeX | Escherichia coli | anti-oxidant protein |
| c130129_g1 | −0.69 | 3.65 × 10−3 | Thioredoxin-T | Drosophila melanogaster | anti-oxidant protein |
| c152296_g4 | −0.85 | 1.93 × 10−3 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme (Fragment) | Gallus gallus | immune-related protein |
| c154571_g1 | −2.22 | 1.81 × 10−3 | Uncharacterized protein C1orf194 homolog | Danio rerio | immune-related protein |
| c120194_g1 | 2.15 | 5.35 × 10−5 | Hemocyanin A-type, units Ode to Odg (Fragment) | Enteroctopus dofleini | oxygen supply, immune-related protein |
| c147531_g1 | 2.31 | 2.43 × 10−5 | Hemocyanin A-type, units Ode to Odg (Fragment) | Enteroctopus dofleini | oxygen supply, immune-related protein |
| c153812_g1 | 2.41 | 2.00 × 10−4 | Hemocyanin G-type, units Oda to Odg | Enteroctopus dofleini | oxygen supply, immune-related protein |
| c146636_g1 | 2.42 | 1.95 × 10−4 | Hemocyanin G-type, units Oda to Odg | Enteroctopus dofleini | oxygen supply, immune-related protein |
| c156294_g1 | 2.43 | 7.60 × 10−5 | Hemocyanin G-type, units Oda to Odg | Enteroctopus dofleini | oxygen supply, immune-related protein |
| c153794_g2 | 1.02 | 1.50 × 10−3 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin | Pongo abelii | proteolysis, immune-related protein |
| c155750_g1 | 0.45 | 5.33 × 10−5 | 60 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial | Cricetulus griseus | response to stress |
| c155284_g2 | 0.42 | 7.02 × 10−3 | Heat shock protein 75 kDa, mitochondrial | Mus musculus | response to stress |
| Particular Tissue Development | |||||
| c157271_g1 | −0.73 | 2.29 × 10−2 | Dynein heavy chain 10, axonemal | Strongylocentrotus purpuratus | cilia-specific protein |
| c156807_g2 | −0.76 | 1.09 × 10−2 | Dynein heavy chain 12, axonemal | Xenopus laevis | cilia-specific protein |
| c123013_g1 | −0.56 | 3.64 × 10−2 | Dynein heavy chain 5, axonemal | Bos taurus | cilia-specific protein |
| c155384_g3 | −0.64 | 2.82 × 10−3 | Dynein heavy chain 6, axonemal | Rattus norvegicus | cilia-specific protein |
| c154803_g2 | −0.76 | 4.90 × 10−3 | Dynein heavy chain 7, axonemal | Homo sapiens | cilia-specific protein |
| c157287_g2 | −0.79 | 2.31 × 10−4 | Dynein heavy chain 8, axonema | Mus musculus | cilia-specific protein |
| c154991_g1 | −1.02 | 5.78 × 10−4 | Dynein intermediate chain 2, ciliary | Heliocidaris crassispina | cilia-specific protein |
| c122667_g1 | −0.87 | 1.98 × 10−3 | Dynein light chain 1, axonemal | Homo sapiens | cilia-specific protein |
| c156053_g3 | 0.89 | 2.24 × 10−3 | Myosin essential light chain, striated adductor muscle | Homo sapiens | cilia-specific protein |
| c85433_g2 | 0.89 | 8.64 × 10−4 | Myosin heavy chain, striated muscle | Homo sapiens | cilia-specific protein |
| c151606_g1 | −0.40 | 6.31 × 10−3 | Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 | Homo sapiens | cilia-specific protein |
| c136200_g1 | −0.31 | 2.49 × 10−2 | Neuroglian | Homo sapiens | cilia-specific protein |
| c150230_g2 | −1.42 | 7.67 × 10−6 | Tektin-1 | Homo sapiens | cilia-specific protein |
| c153806_g1 | −1.58 | 2.39 × 10−4 | Tektin-2 | Homo sapiens | cilia-specific protein |
| c155866_g1 | −1.30 | 2.54 × 10−4 | Tektin-3 | Rattus norvegicus | cilia-specific protein |
| c28062_g1 | −0.89 | 1.80 × 10−4 | Tektin-4 | Tripneustes gratilla | cilia-specific protein |
| c153806_g3 | −1.19 | 1.10 × 10−4 | Tektin-B1 | Heliocidaris crassispina | cilia-specific protein |
| c131813_g1 | −1.08 | 1.05 × 10−2 | Dynein beta chain, ciliary | Argopecten irradians | muscle-specific protein |
| c95355_g1 | −0.93 | 4.43 × 10−3 | Dynein beta chain, ciliary | Argopecten irradians | muscle-specific protein |
| c157057_g1 | −0.68 | 1.06 × 10−2 | Dynein heavy chain 1, axonemal | Drosophila melanogaster | neuron-specific protein |
| c155993_g1 | −0.64 | 4.95 × 10−3 | Dynein heavy chain 10, axonemal | Rattus norvegicus | neuron-specific protein |
2.2. Functional Analysis of DEPs with Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)
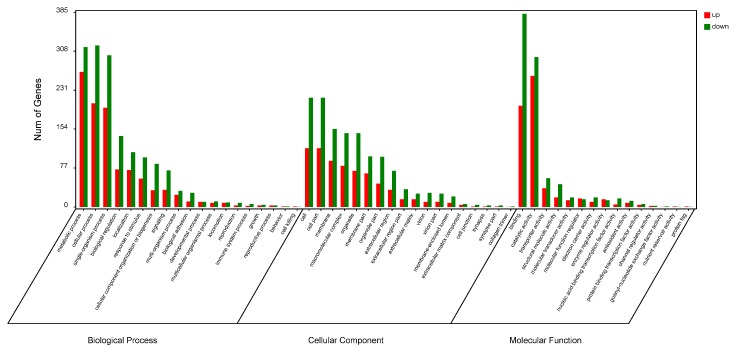
Under GO analysis, significant enrichment (p < 0.05) was found for 77, 27, and 63 categories in the biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF) domains, respectively (Table S3). The most enriched GO terms were metabolic, cellular, and single-organism processes in BPs; cell and cell part in CCs; as well as binding and catalytic activity secondary items in MFs (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Enriched gene ontology (GO) analysis of differentially expressed proteins after metamorphosis. The most enriched GO terms (based on gene number) in “Cellular component,” “Molecular function,” and “Biological process” are shown.
Of the 38 significantly enriched pathways under KEGG analysis (p < 0.05; Table S4), seven were reliably enriched after adjustment (q < 0.05; Table 3). The high representation of phototransduction, pentose and glucuronate, olfactory transduction, and salivary secretion pathways suggest changes to ingestion and digestion characteristics during metamorphosis. Additionally, enrichment in glycerolipid metabolism and galactose metabolism pathways illustrate differing energy strategies between competent larvae and post-larvae.
Table 3.
Seven enriched pathways identified with KEGG analysis of differentially expressed proteins.
| # | Pathway | Differential Proteins with Pathway Annotation (347) | All Proteins with Pathway Annotation (2056) | p-Value | q-Value | Pathway ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Phototransduction | 7 (2.02%) | 11 (0.54%) | 0.000655 | 0.039412 | ko04744 |
| 2 | Caprolactam degradation | 7 (2.02%) | 11 (0.54%) | 0.000655 | 0.039412 | ko00930 |
| 3 | Pentose and glucuronate Interconversions | 12 (3.46%) | 27 (1.31%) | 0.000685 | 0.039412 | ko00040 |
| 4 | Olfactory transduction | 9 (2.59%) | 18 (0.88%) | 0.001175 | 0.039412 | ko04740 |
| 5 | Glycerolipid metabolism | 11 (3.17%) | 25 (1.22%) | 0.001275 | 0.039412 | ko00561 |
| 6 | Galactose metabolism | 11 (3.17%) | 25 (1.22%) | 0.001275 | 0.039412 | ko00052 |
| 7 | Salivary secretion | 17 (4.9%) | 48 (2.33%) | 0.001326 | 0.039412 | ko04970 |
2.3. Association Analysis of Transcriptome and Proteome Data
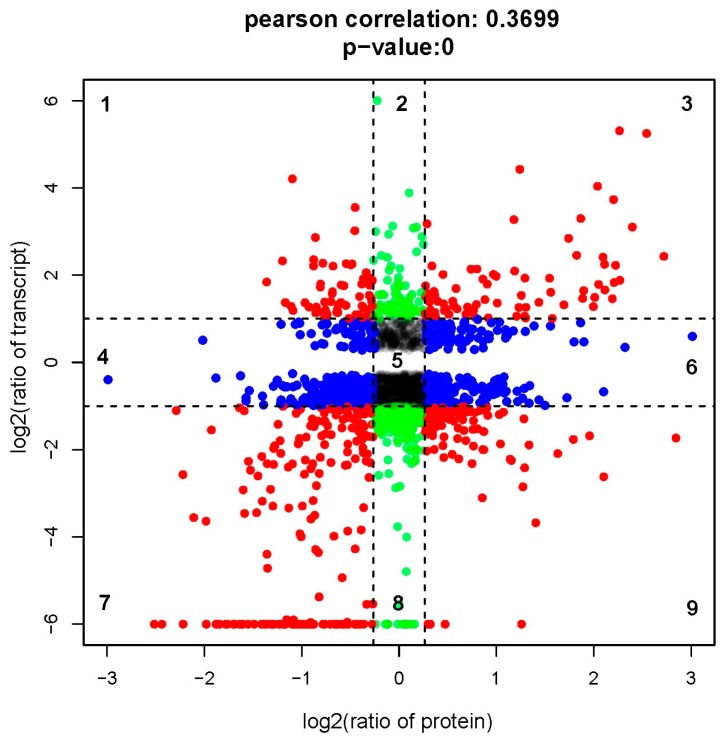
We performed a direct comparison of transcriptome and proteome abundance during metamorphosis. Concordance tests revealed a significant relationship between mRNA and protein ratios (Pearson’s correlation, r = 0.3699; Figure 3). We observed 458 concordant dots, representing a correspondence of protein abundance with transcript accumulation (red dots in Figure 3). We also found 282 green dots and 592 blue dots, respectively, indicating differential expression only on the transcript or the protein levels. Detailed quantitation and annotation on the points in Figure 3 are provided in Table S5.
Figure 3.
Comparison of expression ratios from transcriptomic (y-axis) and proteomic (x-axis) profiling. Log2 expression ratios were calculated from competent larvae versus post-larvae. Significant changes in expression are color-coded: blue, proteins only; green, transcripts only; red, both.
3. Discussion
In this study, we performed a proteomic analysis to identify DEPs before and after R. venosa metamorphosis. Based on the reference transcriptome, we identified 470 upregulated proteins and 668 downregulated proteins. These DEPs were generally associated with cytoskeleton and cell adhesion, ingestion and digestion, immunity and stress response, transcription and translation, specific tissue development, and signal transduction. Additionally, their differential expression patterns reflect life-stage transitions in R. venosa (Table 2). We discuss the implications of our results in the following sections.
3.1. Cytoskeleton and Cell Adhesion
The intracellular cytoskeleton, transmembrane cell-adhesion components, and extracellular matrices (ECMs) comprise a complex “skeleton” network, which is critical for cell motility processes, including proliferation, differentiation, migration, and apoptosis. In this study, active cell motility during metamorphosis is indicated by the abundance of proteins involved in cytoskeleton, cell adhesion, and ECMs.
Tubulins (tubulin α-1 chain, tubulin α-2 chain, tubulin β-2 chain, and tubulin β-4B chain) were highly expressed in larvae but declined in post-larvae. As components of microtubules, alpha and beta tubulins function in essential cellular processes, including cell division, proliferation, and migration [19]. Any temporal variation in tubulin expression is likely related to various physiological functions and post-translational modifications [20,21]. Thus, the expression patterns that we observed are consistent with the suggestion that protein degradation and apoptosis during metamorphosis mediate the loss of larval organs, as well as the morphogenesis of juvenile characteristics [22,23]. Furthermore, our results conformed with studies in marine invertebrates (e.g., the spionid polychaete Pseudopolydora vexillosa [24] and polychaete Hydroides elegans [13]) that demonstrated a decline of tubulin isoforms during metamorphosis.
Proteins associated with ECMs were also differentially expressed. Specifically, we observed downregulation in collagen α-1 (XV, XXI, and XXII chain), collagen α-6 (VI chain), and matrix metalloproteinase-19. The ECM is the cell base and participates in tissue remodeling, as well as cell migration and differentiation; convincing evidence exists to show that ECMs are remodeled during metamorphic transition [25,26], and, in fact, the process is considered essential in the metamorphosis of amphibians [26,27], insects [28], and mollusks [29]. Thus, the observed expression patterns suggest that ECM remodeling—specifically involving the identified proteins—functions in R. venosa metamorphosis. Although this hypothesis requires further validation for our study species, we note that collagenase (a matrix-metalloprotease) was first discovered in the tail of a tadpole undergoing metamorphosis [30]. Additionally, matrix metalloprotease was highly expressed during the metamorphosis of the lepidopteran Galleria mellonella, causing collagen degradation [31].
3.2. Ingestion and Digestion
Morphological and functional changes in the digestive system clearly play a vital role in the metamorphic transition of R. venosa from a diet of microalgae to one of bivalve mollusks [7]. It follows that proteins associated with food intake and digestion will be differentially expressed between the larval and post-larval stages. Indeed, we found that post-metamorphosis, carnivorous digestive enzymes clearly increased, whereas phytophagous digestive enzymes were downregulated. Our study provides novel molecular data on the dietary shift that occurs with metamorphic transition.
In larval R. venosa, we detected several enzymes involved in the breakdown of cellulose and hemi-cellulose, both plant cell-wall components. Specifically, we observed two important cellulase components, endoglucanase and exoglucanase, as well as endo-1,4-β-xylanase, important in the hydrolysis of hemicellulose. Next, we also observed the presence of β-galactosidase, a key enzyme in the hydrolysis of lactose into galactose and glucose. Together, these data indicated that larval whelks were able to completely digest and absorb microalgae. High levels of cellulases have been reported in the pre-competent and competent larvae of the spotted babylon snail Babylonia areolata, which also has a pre-metamorphosis diet of microalgae [32], suggesting that the two species may have similar digestive mechanisms.
In R. venosa post-larvae, we observed higher levels of proteolytic enzymes, illustrating the capacity to exploit varied protein diets post-metamorphosis. For example, serine proteases (trypsin and chymotrypsin), as well as zinc carboxypeptidase, are major proteolytic enzymes in the gastropod digestive glands and were all highly expressed. Additionally, we observed an upregulation of pancreatic triacylglycerol lipase in post-larvae. Through hydrolysis, lipases prepare fatty acids for absorption through membranes [33]. Our results are corroborated by previous findings of high lipase expression in B. areolata juveniles [32]. Taken together, we suggest that cellulase downregulation and protease/lipase upregulation are primarily responsible for the transition from herbivores to carnivores in R. venosa with biphasic life history.
Unexpectedly, we found high expression of conotoxin and cysteine-rich venom protein in the post-larvae. The former is a neurotoxic peptide that was first isolated from the venom of the predatory marine cone snail (Conus spp.) [34]. The latter has also been found in a particular species of cone snail, Conus textile, where it exhibits protease activity and functions in pro-conotoxin processing of C. textile venom [35]. Our results suggest that R. venosa may possess predation mechanisms homologous to Conus. As little information is available regarding the composition and toxicity of R. venosa venom, the presence of conotoxin observed here warrants further research.
In summary, the diverse suite of proteins associated with ingestion and digestion illustrates the capacity of R. venosa to exploit different diets that suit the shifting nutritional requirements in a biphasic life cycle.
3.3. Stress Response and Immunity
Proteins involved in stress response and immunity tend to be upregulated during metamorphosis [36]. In the present study, we found that anti-oxidant enzymes, such as thioredoxin-T and peroxiredoxin-2, were highly expressed in the competent larval stage. Similarly, significant upregulation of peroxiredoxin has been documented in Crassostrea gigas post-metamorphosis [29]. These patterns suggest that competent larvae may experience considerable oxidative stress from reactive oxygen species (ROS) [29]. Indeed, amphibian studies have shown that when endogenous thyroid hormone induces metamorphosis, it also enhances mitochondrial respiration, which leads to higher ROS content [37,38]. Similar mechanisms may be at work in R. venosa, and the observed anti-oxidant enzymes are likely essential for protection against ROS-induced cell damage and maintenance of cell redox homeostasis during the metamorphosis.
We also noticed that R. venosa hemocyanin (RvH) A-type and RvH G-type were significantly upregulated after metamorphosis. Hemocyanin was first identified in the snail Helix pomatia; the protein has two copper atoms that reversibly bind with oxygen and acts as an oxygen transport molecule similar to hemoglobin. Under cold environments with low oxygen pressure, hemocyanin is more efficient at oxygen transportation than its vertebrate counterpart [39]. However, hemocyanin also plays important roles in innate immunity, exhibiting antiviral, antimicrobial, and antitumor activities [40,41]. Further evidence supporting this role in immune function includes the identification of four novel proline-rich peptides from RvH that exhibit antimicrobial activities against Gram-positive Klebsiella pneumonia and Gram-negative Staphylococcus aureus [42]. Moreover, the structural subunits RvH-1 and RvH2 exert strong antiviral effects upon the Herpes simplex virus [43,44]. Thus, two complementary levels of explanation could account for abundant RvH expression in juvenile R. venosa: on the evolutionary level, it is an adaptation to hypoxia stress at the benthic life stage, and on the developmental level, it reflects immune-system maturation post-metamorphosis. In support of the latter concept, proteins such as α-2macroglobulin and myeloperoxidase were also elevated in post-larvae. α-2-macroglobulins are selective protease inhibitors and major components of the eukaryotic innate immune system [45], while myeloperoxidase is highly expressed in neutrophil granulocytes, where it produces antimicrobial hypohalous acids [46].
3.4. Specific Tissue Development
Tissue-specific or tissue-preferential DEPs likely reflect physiological changes in those tissues [29]. For example, fluctuations in tropomyosin and myosin abundance are closely associated with muscle development during the metamorphosis of red abalone Haliotis rufescens [47,48]. Here, we demonstrated that larvae and post-larvae exhibit differential expression of neuron- and muscle-specific proteins, including myosin heavy chain, myosin light chain, and neuroglian proteins. All of these proteins are closely involved with transitions in nervous and muscular systems during molluscan metamorphosis [36,48].
As described earlier (see Section 3.1), tubulins were downregulated after metamorphosis. These proteins are cilia-specific, along with tektin, dynein heavy chain, and dynein beta chain, all of which experienced downregulation. The decline of proteins that comprise core cilial structure and function in cilia movement accords with post-metamorphic degradation of the velum, a conspicuous, ciliated organ in larvae used for swimming and filter-feeding.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Larvae Culture and Sample Collection
Egg capsules of Rapana venosa were obtained from rocks in Laizhou Bay (37°11′4.78″ N, 119°41′3.75″ E), Laizhou, China. Larvae were cultivated at Blue Ocean Co. Limited (Laizhou, China) following previously published methods [7]: pelagic larvae were cultured in 2.5 m × 2.5 m × 1.5 m tanks with a density range of 0.3–0.05 ind/mL, depending on developmental stage. Diets were a mixture of microalgae Platymonas subcordiformis, Isochrysis galbana, and Chlorella vulgaris; larvae were fed 13.0 × 104 cell/mL daily. Seawater used for culturing was filtered with sand and radiosterilized with UV light. Water temperature was maintained below 25 ± 1 °C. Larvae samples from four spiral-whorl stages (competent larva) and post-larval stages were collected and examined under a microscope to guarantee developmental synchronies. Samples were immediately washed with dH2O, snap frozen in liquid nitrogen, stored at −80 °C till use.
4.2. Protein Extraction, Digestion, and iTRAQ Labelling
Three biological replicates (each containing approximately 500 mg larvae) were prepared for the iTRAQ analysis. Total proteins were extracted using the cold acetone method. Samples were ground to powder in liquid nitrogen before the addition of 2 mM EDTA and 1 mM PMSF, then dissolved in lysis buffer. After 5 min, DTT (10 mM) was added to the samples, which were centrifuged at 4 °C and 25,000× g for 20 min. All subsequent centrifugation steps described in this section occurred at 4 °C and 25,000× g. The precipitate was then discarded and the supernatant was mixed with 10 mM DTT in 5× volume of cold acetone, followed by incubation at −20 °C for 12 h. After a second round of centrifugation for 20 min, the supernatant was discarded. Pellets were washed in 1.5 mL cold acetone (containing 10 mM DTT), then centrifuged a third time for 15 min, to discard the supernatant. This final step was repeated three times. The precipitate was then air-dried and resuspended in 1 mL extraction buffer (10 mM DTT, 4% (w/v) CHAPS, 30 mM HEPES, 8 M urea, 1 mM PMSF and 2 mM EDTA), sonicated for 10 min, and centrifuged for 15 min. The resulting supernatant was transferred to a new tube, mixed with 10 mM DDT, and incubated at 56 °C for 1 h. The solution was incubated in a dark room for another hour after the addition of iodacetamide (55 mM), then precipitated in cold acetone at −20 °C overnight. Finally, the precipitate was centrifuged for 15 min, air-dried, and dissolved in 1 mL extraction buffer under ultrasound. Protein quality and concentrations were examined with SDS-PAGE and the 2-D Quant Kit (General Electric Company, Fairfield, CT, USA), respectively.
Protein digestion was performed with Trypsin Gold (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) for 16 h at 37 °C, and peptides were dried in a centrifugal vacuum concentrator. Competent-larvae samples were labeled with iTRAQ tags 113, 114, and 115, whereas post-larvae samples were labeled with tags 118, 119, and 121, following manufacturer protocol in the iTRAQ 8-plex labelling kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA).
4.3. Strong Cation Exchange (SCX) Fractionation and Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) Analysis
Labeled samples were pooled and subjected to the SCX fractionation column connected with an HPLC system (LC-20ab, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). Peptides were eluted using buffer-1 (25 mM NaH2PO4 in 25% ACN, pH 2.7) and a gradient of buffer-2 (25 mM NaH2PO4, 1 M KCl in 25% ACN, pH 2.7). The fractionating procedure was as follows: 100% buffer A for 10 min, 5%–35% buffer B for 20 min, 35%–80% buffer-2 for 1 min. Flow rate was kept at 1 mL/min. Fractions were desalted using a Strata X 33-μm Polymeric Reversed Phase column (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA) and vacuum-dried.
Peptide fractions were analyzed using Nano HPLC (LC-20AD Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) and a 10-cm eluting C18 column (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). A Triple TOF 5600 instrument (AB SCIEX, Concord, ON, Canada), fitted with Nanospray III (AB SCIEX) and a pulled quartz-tip emitter (New Objectives, Woburn, MA, USA), was used for mass spectrometry [49]. This procedure was carried out by Guangzhou Gene denovo Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China).
4.4. Protein Identification and Quantification
Raw data from LC-MS/MS were transformed into MGF files with Proteome Discovery 1.2 (Thermo, Pittsburgh, PA, USA). In the Mascot search engine (version 2.3.02, Matrix, Science, London, UK), proteins were identified using the R. venosa reference transcriptome [9]. Mascot search results were then normalized and quantified. Proteins with fold changes significantly (p < 0.05) >1.2 or <0.83 were considered differentially expressed [49].
4.5. Enrichment of GO and KEGG Pathways
We searched against the GO and KEGG databases to classify and identify differentially expressed proteins [50,51]. Significant pathway enrichment was examined with the hypergeometric test, and significance was set at p < 0.05.
4.6. Correlation Analysis of Transcriptomic and Proteomic Data
Previously, we had constructed an RNA-seq library of competent larvae and post-larvae (raw data available in NCBI GEO, accession number GSE70548). To investigate the concordance between transcript and protein levels, we calculated the Pearson’s correlation for these data and created scatterplots with the expression ratios of competent larvae versus post-larvae.
5. Conclusions
Using iTRAQ, we constructed a comprehensive and quantitative proteomic profile of R. venosa larvae and post-larvae. To our knowledge, this work is the first proteomic study focused on gastropod metamorphosis. We identified over a thousand differentially expressed proteins that reflected physiological processes occurring in metamorphosis, including changes to cytoskeleton and cell adhesion, ingestion and digestion, stress response and immunity, as well as tissue development. Our data contributed to a better understanding of the regulatory mechanisms underlying R. venosa development through identifying major participating proteins. Therefore, this study should provide a sound basis for future studies aiming to investigate specific metamorphosis-related proteins in greater depth.
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31572636), the National Natural Science Foundation of China-Shandong Joint Fund for Marine Science Research Centers (Grant No. U1406403), the National Key Technology R & D Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology (Grant No. 2011BAD13B01), and the Agricultural Major Application Technology Innovation Project of Shandong Province. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Abbreviations
| 2DE | Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis |
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| CHAPS | 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]propanesulfonate |
| DEPs | Differentially Expressed Proteins |
| DTT | DL-Dithiothreitol |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| EDTA | Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| HEPES | 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic Acid |
| HPLC | High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| iTRAQ | isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantitation |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LC–MS/MS | Fractionation and Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| PMSF | Phenylmethanesulfonyl Fluoride |
| SCX | Strong Cation Exchange |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be found at http://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/17/6/924/s1.
Author Contributions
Tao Zhang and Hai-Yan Wang conceived and designed the experiments. Hao Song performed the experiments and analyzed the data. Tao Zhang and Hai-Yan Wang contributed reagents, materials, and analysis tools. Hao Song wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
References
- 1.Yuan C.-Y. Primary exploration on aquaculture of Rapana venosa. Fish. Sci. 1992;11:16–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mann R., Harding J.M. Salinity tolerance of larval Rapana venosa: Implications for dispersal and establishment of an invading predatory gastropod on the North American Atlantic coast. Biol. Bull. 2003;204:96–103. doi: 10.2307/1543499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mann R., Harding J.M., Westcott E. Occurrence of imposex and seasonal patterns of gametogenesis in the invading veined rapa whelk Rapana venosa from Chesapeake Bay, USA. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006;310:129–138. doi: 10.3354/meps310129. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Giberto D.A., Bremec C.S., Schejter L., Schiariti A., Mianzan H., Acha E.M. The invasive Rapa Whelk Rapana venosa (Valenciennes 1846): status and potential ecological impacts in the Río de la Plata estuary, Argentina-Uruguay. J. Shellfish Res. 2006;25:919–924. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Leppäkoski E., Gollasch S., Olenin S. Invasive Aquatic Species of Europe. Distribution, Impacts and Management. Springer Science & Business Media; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Çulha M., Bat L., Doğan A., Dağlı E. Ecology and distribution of the veined rapa whelk Rapana venosa (Valenciennes, 1846) in Sinop peninsula (Southern Central Black Sea), Turkey. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2009;8:51–58. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pan Y., Qiu T., Zhang T., Wang P., Ban S. Morphological studies on the early development of Rapana venosa. J. Fish. China. 2013;37:1503–1512. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231.2013.38690. (In Chinese) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yang Z., Yu H., Yu R., Li Q. Induced metamorphosis in larvae of the veined rapa whelk Rapana venosa using chemical cues. Mar. Biol. Res. 2015;11:1–8. doi: 10.1080/17451000.2015.1062518. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Song H., Yu Z.L., Sun L.N., Gao Y., Zhang T., Wang H.Y. De novo transcriptome sequencing and analysis of Rapana venosa from six different developmental stages using Hi-seq 2500. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D-Genom. Proteom. 2016;17:48–57. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2016.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Glisovic T., Bachorik J.L., Yong J., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins and post-transcriptional gene regulation. FEBS Lett. 2008;582:1977–1986. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.03.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Deribe Y.L., Pawson T., Dikic I. Post-translational modifications in signal integration. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010;17:666–672. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vengatesen T., Tim W., Pei-Yuan Q. 2D gel-based proteome and phosphoproteome analysis during larval metamorphosis in two major marine biofouling invertebrates. J. Proteome Res. 2009;8:2708–2719. doi: 10.1021/pr800976u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mok F.S., Thiyagarajan V., Qian P.Y. Proteomic analysis during larval development and metamorphosis of the spionid polychaete Pseudopolydora vexillosa. Proteome Sci. 2009;7:178–183. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-7-44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Huoming Z., Him W.Y., Hao W., Zhangfan C., Arellano S.M., Timothy R., Pei-Yuan Q. Quantitative proteomics identify molecular targets that are crucial in larval settlement and metamorphosis of Bugula neritina. J. Proteome Res. 2011;10:349–360. doi: 10.1021/pr100817v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Thiyagarajan V., Qian P. Proteomic analysis of larvae during development, attachment, and metamorphosis in the fouling barnacle, Balanus amphitrite. Proteomics. 2008;8:3164–3172. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200700904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zieske L.R. A perspective on the use of iTRAQ reagent technology for protein complex and profiling studies; Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits & Systems; Nice, France. 10–13 December 2006; pp. 1501–1508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wu W.W., Guanghui W., Seung Joon B., Rong-Fong S. Comparative study of three proteomic quantitative methods, DIGE, cICAT, and iTRAQ, using 2D gel- or LC-MALDI TOF/TOF. J. Proteome Res. 2006;5:651–658. doi: 10.1021/pr050405o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Karp N.A., Huber W., Sadowski P.G., Charles P.D., Hester S.V., Lilley K.S. Addressing accuracy and precision issues in iTRAQ quantitation. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010;9:1885–1897. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900628-MCP200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hammond J.W., Cai D., Verhey K.J. Tubulin modifications and their cellular functions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2008;20:71–76. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2007.11.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Erck C., Peris L., Andrieux A., Meissirel C., Gruber A.D., Vernet M., Schweitzer A., Saoudi Y., Pointu H., Bosc C. A vital role of tubulin-tyrosine-ligase for neuronal organization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:7853–7858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409626102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ikegami K., Heier R.L., Taruishi M., Takagi H., Mukai M., Shimma S., Taira S., Hatanaka K., Morone N., Yao I. Loss of α-tubulin polyglutamylation in ROSA22 mice is associated with abnormal targeting of KIF1A and modulated synaptic function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:3213–3218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611547104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Blake J.A., Woodwick K.H. Reproduction and larval development of Pseudopolydora paucibranchiata (Okuda) and Pseudopolydora kempi (Southern) (Polychaeta: Spionidae) Biol. Bull. 1975;149:109–127. doi: 10.2307/1540483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jacobson M.D., Weil M., Raff M.C. Programmed cell death in animal development. Cell. 1997;88:347–354. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81873-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhang Y., Sun J., Xiao K., Arellano S.M., Thiyagarajan V., Qian P.-Y. 2D gel-based multiplexed proteomic analysis during larval development and metamorphosis of the biofouling polychaete tubeworm Hydroides elegans. J. Proteome Res. 2010;9:4851–4860. doi: 10.1021/pr100645z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Timpl R., Brown J.C. Supramolecular assembly of basement membranes. Bioessays. 1996;18:123–132. doi: 10.1002/bies.950180208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shi Y.-B., Fu L., Hasebe T., Ishizuya-Oka A. Regulation of extracellular matrix remodeling and cell fate determination by matrix metalloproteinase stromelysin-3 during thyroid hormone-dependent post-embryonic development. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007;116:391–400. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.07.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fujimoto K., Nakajima K., Yaoita Y. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase genes in regressing or remodeling organs during amphibian metamorphosis. Dev. Growth Differ. 2007;49:131–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2007.00916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Royer V., Hourdry A., Fraichard S., Bouhin H. Characterization of a putative extracellular matrix protein from the beetle Tenebrio molitor: Hormonal regulation during metamorphosis. Dev. Genes Evol. 2004;214:115–121. doi: 10.1007/s00427-004-0389-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Huan P., Wang H., Liu B. A label-free proteomic analysis on competent larvae and juveniles of the pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:506–509. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Visse R., Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ. Res. 2003;92:827–839. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000070112.80711.3D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Altincicek B., Vilcinskas A. Identification of a lepidopteran matrix metalloproteinase with dual roles in metamorphosis and innate immunity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008;32:400–409. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2007.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wei Y., Huang B., Ke C., Xu Y., Wang D. Activities of several digestive enzymes of Babylonia areolata (Gastropoda: Buccinidae) during early development. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2006;26:55–59. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jensen R.G. Detection and determination of lipase (acylglycerol hydrolase) activity from various sources. Lipids. 1983;18:650–657. doi: 10.1007/BF02534677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Olivera B.M., Cruz L.J., Gray W.R., Rivier J.E.F. Conotoxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:22067–22137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Milne T.J., Abbenante G., Tyndall J.D., Halliday J., Lewis R.J. Isolation and characterization of a cone snail protease with homology to CRISP proteins of the pathogenesis-related protein superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:31105–31110. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304843200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Heyland A., Moroz L.L. Signaling mechanisms underlying metamorphic transitions in animals. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2006;46:743–759. doi: 10.1093/icb/icl023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Inoue M., Sato E.F., Nishikawa M., Hiramoto K., Kashiwagi A., Utsumi K. Free radical theory of apoptosis and metamorphosis. Redox Rep. 2004;9:238–248. doi: 10.1179/135100004225006010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Johnson J., Manzo W., Gardner E., Menon J. Reactive oxygen species and anti-oxidant defenses in tail of tadpoles, Xenopus laevis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C-Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013;158:101–108. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2013.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Strobel A., Hu M.Y.A., Gutowska M.A., Lieb B., Lucassen M., Melzner F., Pörtner H.O., Mark F.C. Influence of temperature, hypercapnia, and development on the relative expression of different hemocyanin isoforms in the common cuttlefish sepia officinalis. J. Exp. Zool. Part A. 2012;317:511–523. doi: 10.1002/jez.1743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Coates C.J., Nairn J. Diverse immune functions of hemocyanins. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014;45:43–55. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2014.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Olga A., Lilia Y., Rada S., Stefan S., Pavlina D., Draga T. Changes in the gene expression profile of the bladder cancer cell lines after treatment with Helix lucorum and Rapana venosa hemocyanin. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2015;20:180–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dolashka P., Moshtanska V., Borisova V., Dolashki A., Stevanovic S., Dimanov T., Voelter W. Antimicrobial proline-rich peptides from the hemolymph of marine snail Rapana venosa. Peptides. 2011;32:1477–1483. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2011.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Velkova L., Todorov D., Dimitrov I., Shishkov S., Beeumen J.V., Dolashkaangelova P. Rapana Venosa hemocyanin with antiviral activity. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2014;23:606–610. doi: 10.1080/13102818.2009.10818498. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pavlina D., Ludmyla V., Stoyan S., Kalina K., Aleksander D., Ivan D., Boris A., Bart D., Wolfgang V., Jozef V.B. Glycan structures and antiviral effect of the structural subunit RvH2 of Rapana hemocyanin. Carbohydr. Res. 2010;345:2361–2367. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2010.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wong S.G., Dessen A. Structure of a bacterial α2-macroglobulin reveals mimicry of eukaryotic innate immunity. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:4917–4917. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Klebanoff S.J. Myeloperoxidase: Friend and foe. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005;77:598–625. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1204697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Degnan B.M., Groppe J.C., Morse D.E. Chymotrypsin mRNA expression in digestive gland amoebocytes: Cell specification occurs prior to metamorphosis and gut morphogenesis in the gastropod, Haliotis rufescens. Dev. Genes Evol. 1995;205:97–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00188848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Degnan B., Degnan S.M., Morse D.E. Muscle-specific regulation of tropomyosin gene expression and myofibrillogenesis differs among muscle systems examined at metamorphosis of the gastropod Haliotis rufescens. Dev. Genes Evol. 1997;206:464–471. doi: 10.1007/s004270050076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Xu D., Sun L., Liu S., Zhang L., Yang H. Understanding the heat shock response in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus, using iTRAQ-based proteomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016;17:150. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gene Ontology Consortium. [(accessed on 1 March 2015)]. Available online: http://www.geneontology.org/
- 51.KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. [(accessed on 1 March 2015)]. Available online: http://www.genome.jp/kegg/
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.