Abstract
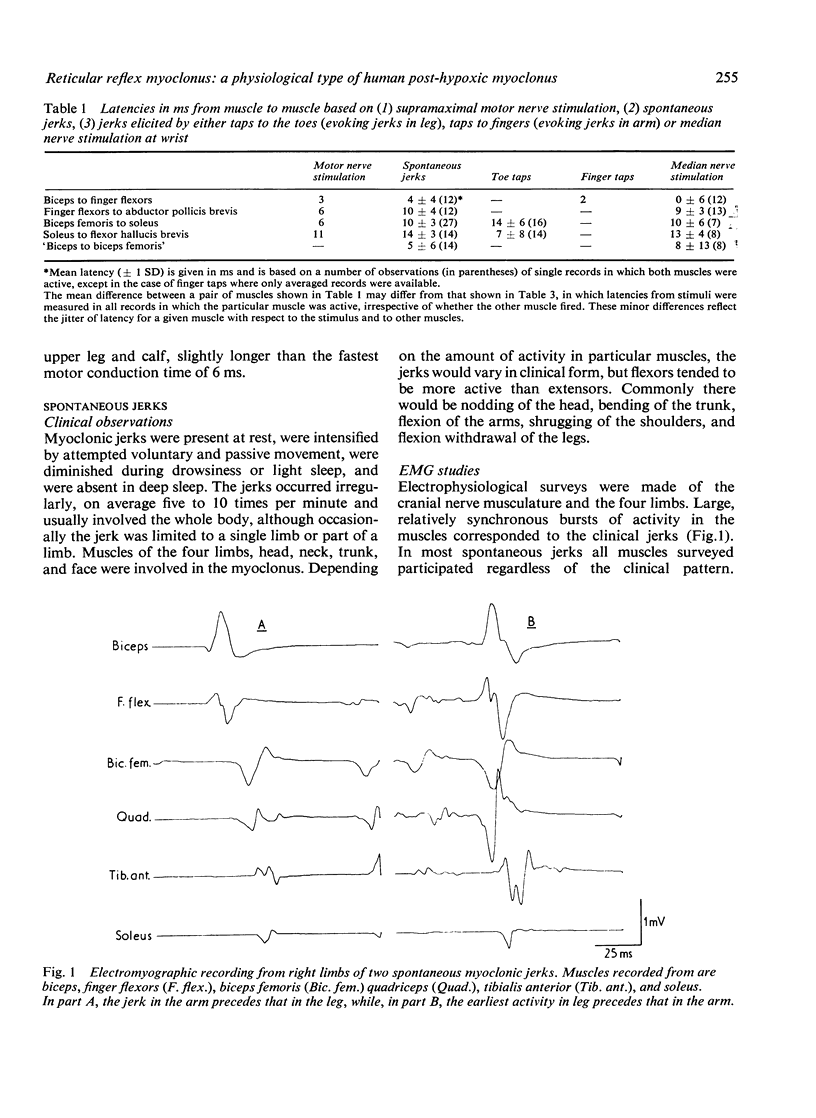
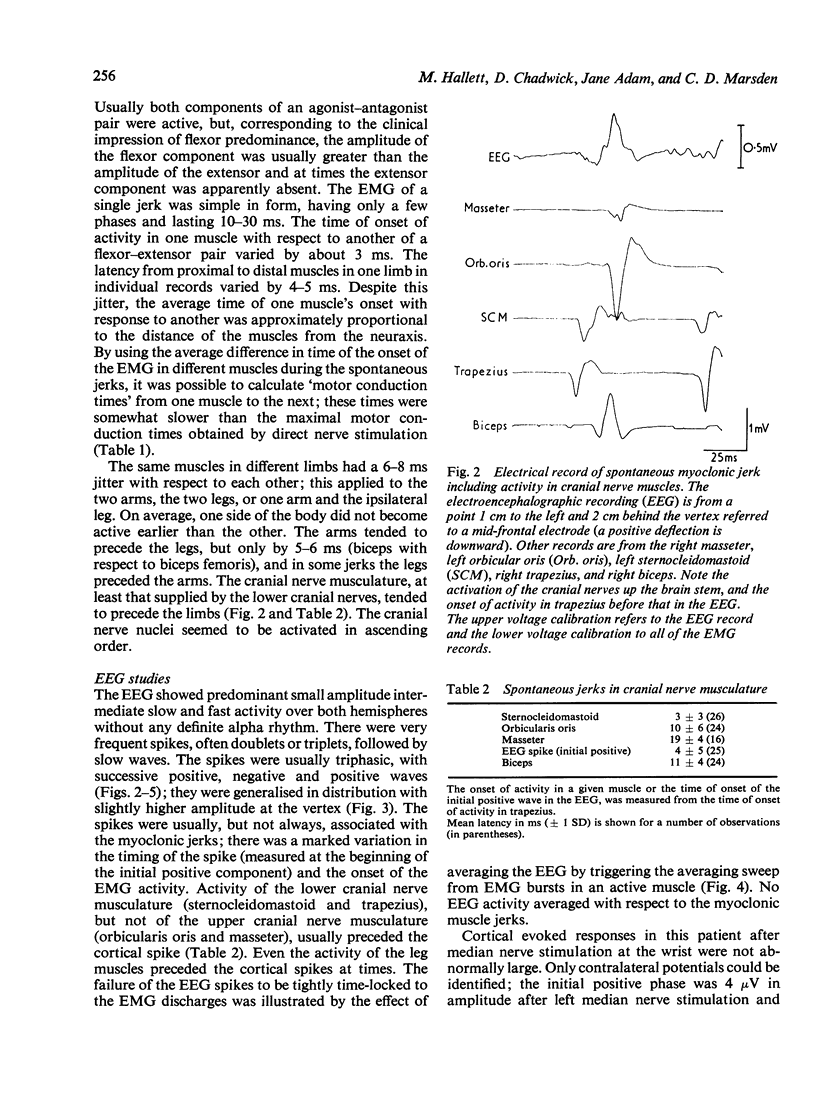
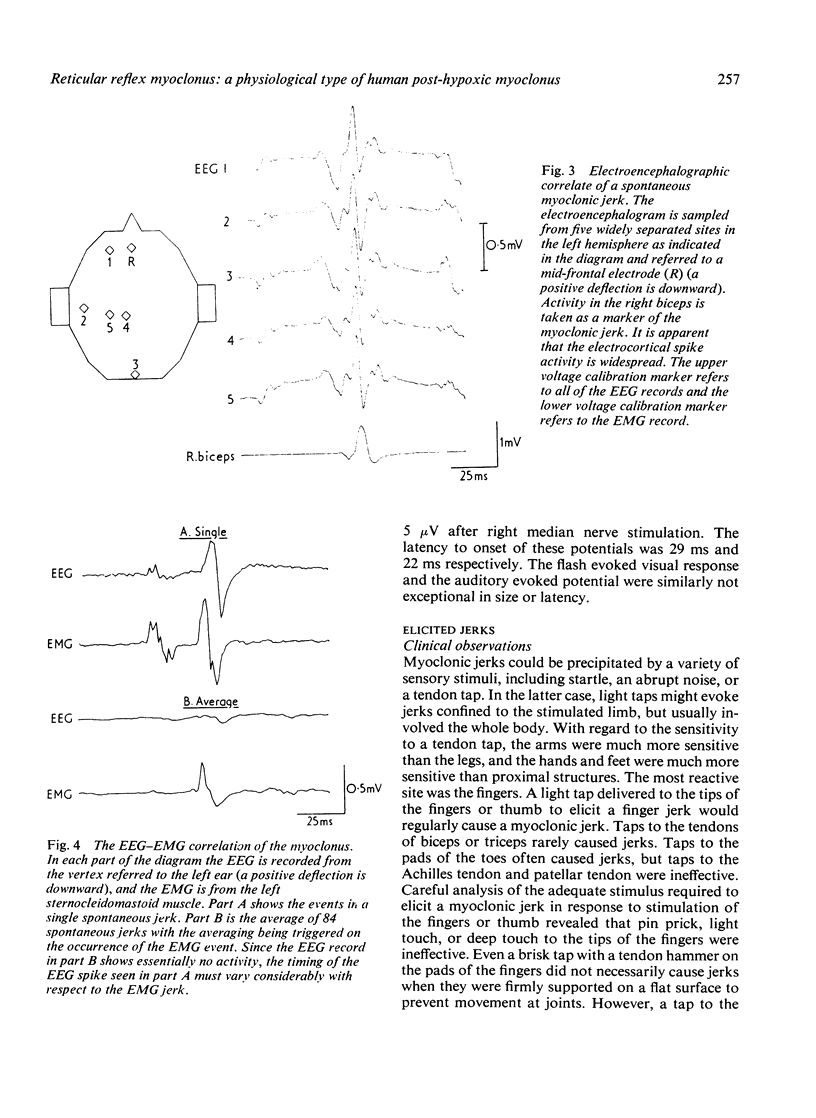
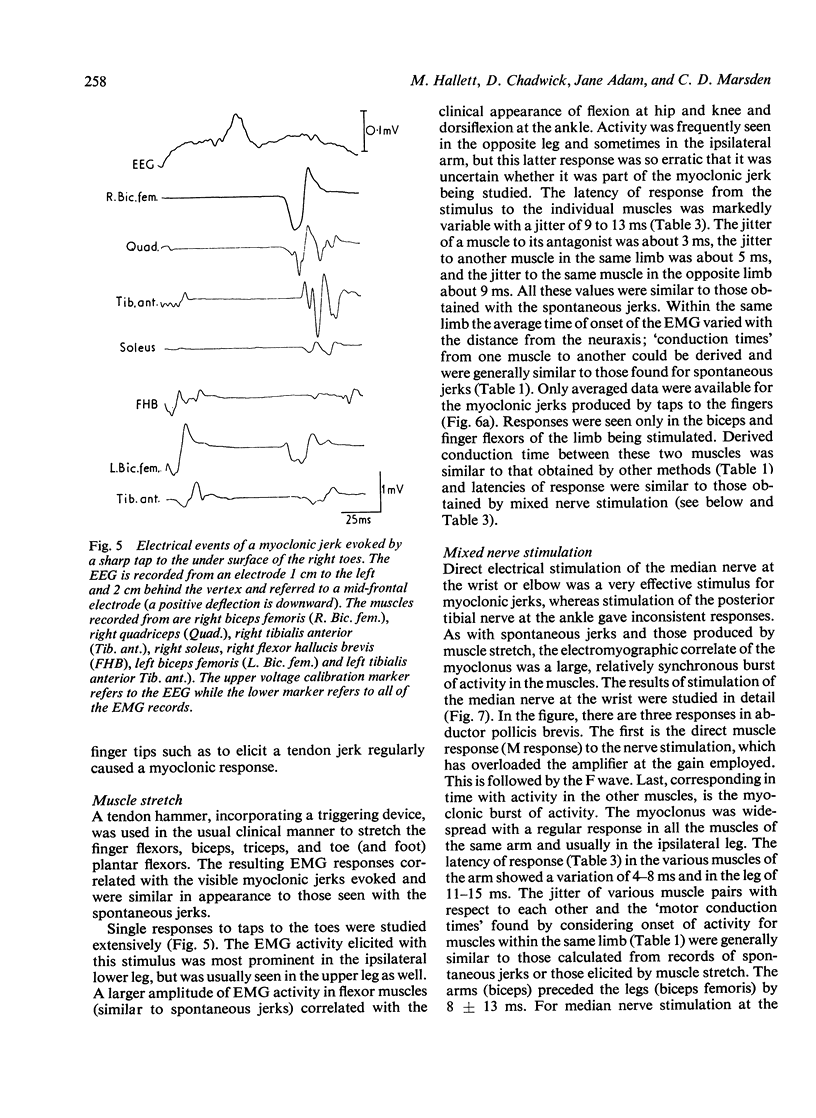
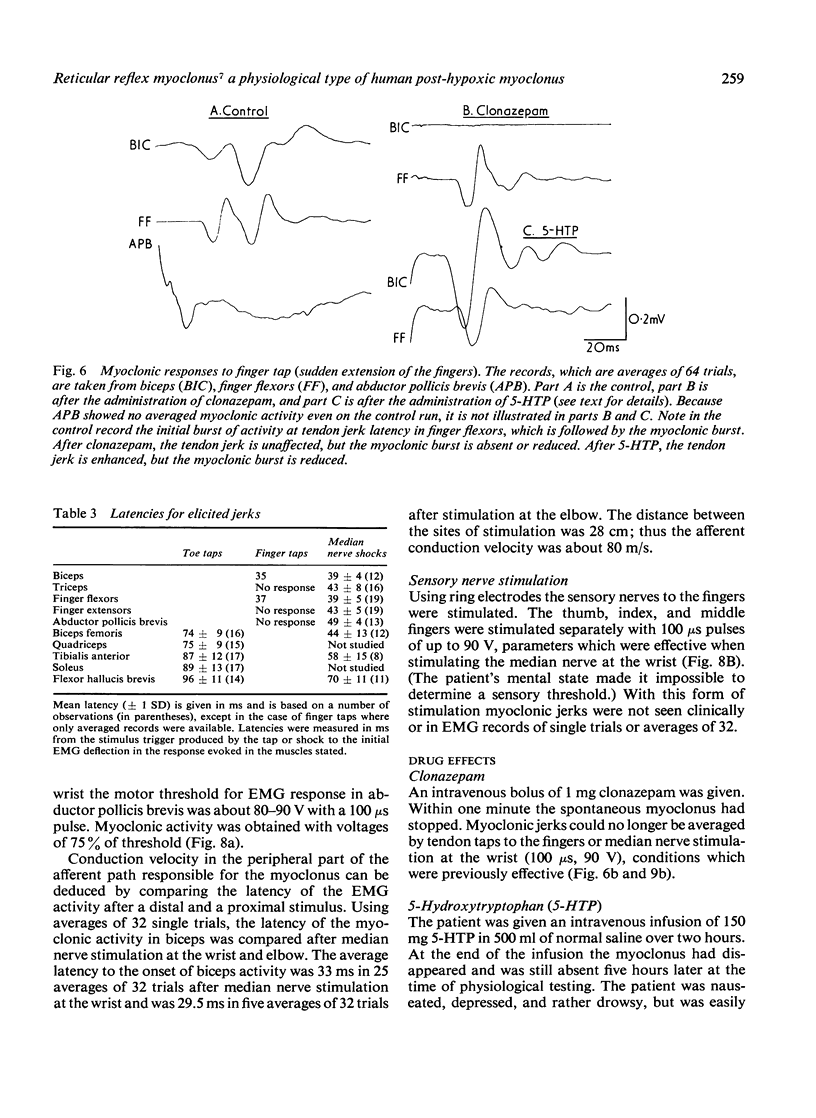
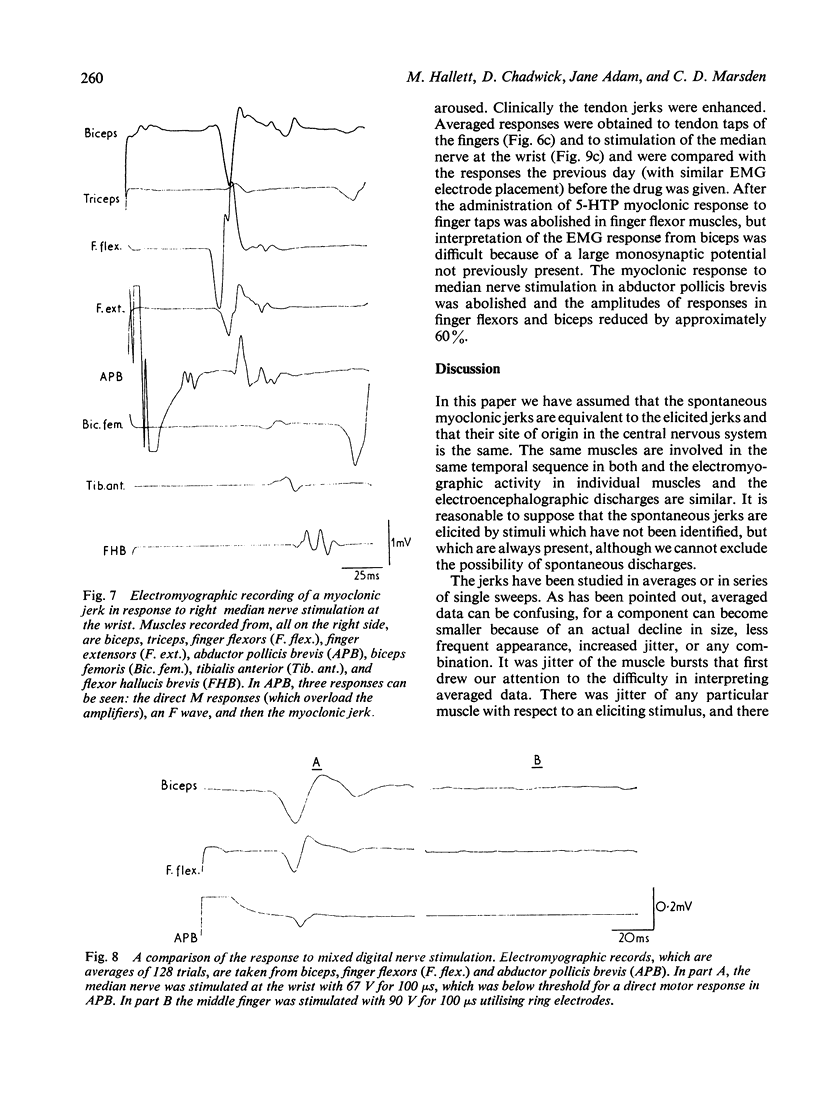
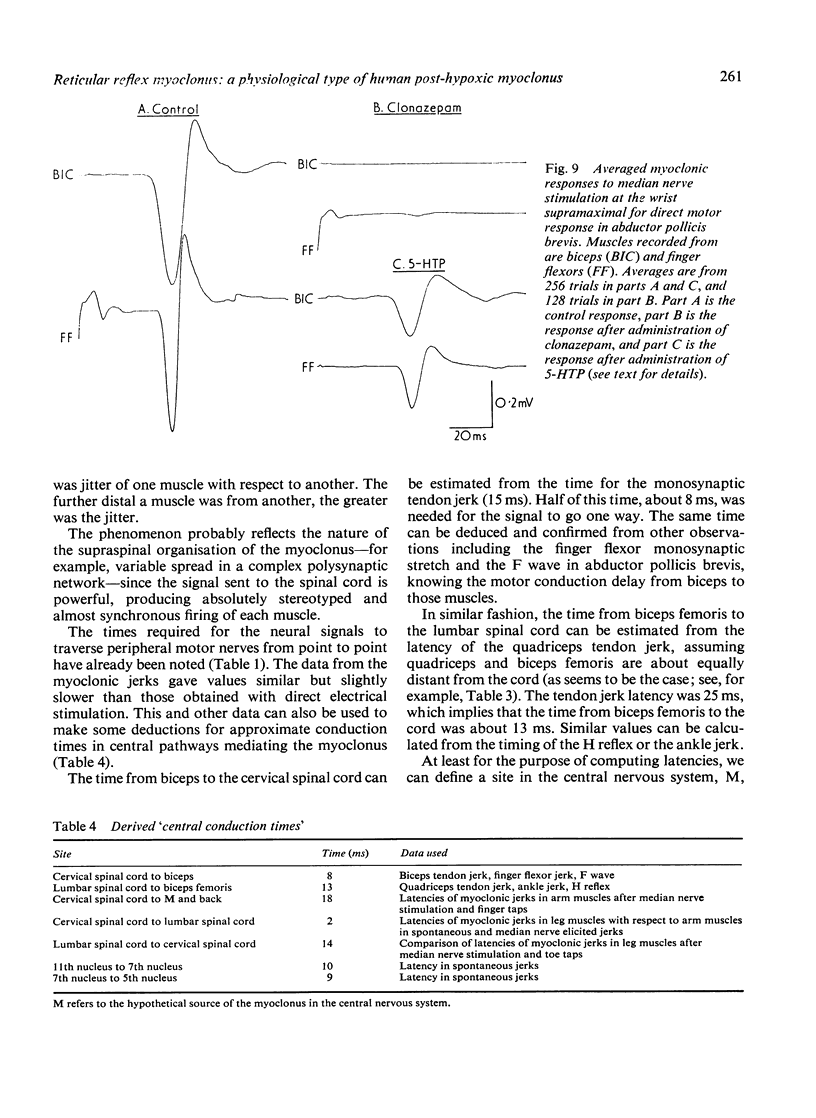
A patient with post-hypoxic myoclonus, sensitive to therapy with 5-hydroxytryptophan and clonazepam, was subjected to detailed electrophysiological investigation. Brief generalised jerks followed the critical stimulus of muscle stretch. The electroencephalogram showed generalised spikes that were associated with, but not time locked to, the myoclonus. The cranial nerve nuclei were activated upward. Analysis of the findings suggests that the mechanism of the myoclonus is hyperactivity of a reflex mediated in the reticular formation of the medulla oblongata.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gottfries C. G., Roos B. E., Winblad B. Determination of 5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid and homovanillic acid in brain tissue from an autopsy material. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1974;50(5):496–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1974.tb09711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier-Ewert K., Hümme U., Dahm J. New evidence favouring long loop reflexes in man. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr (1970) 1972;215(2):121–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00342529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIMAMURA M., MORI S., MATSUSHIMA S., FUJIMORI B. ON THE SPINO-BULBO-SPINAL REFLEX IN DOGS, MONKEYS AND MAN. Jpn J Physiol. 1964 Aug 15;14:411–421. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.14.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton G. G. Receptors in focal reflex myoclonus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 May;38(5):505–507. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.5.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


