Abstract
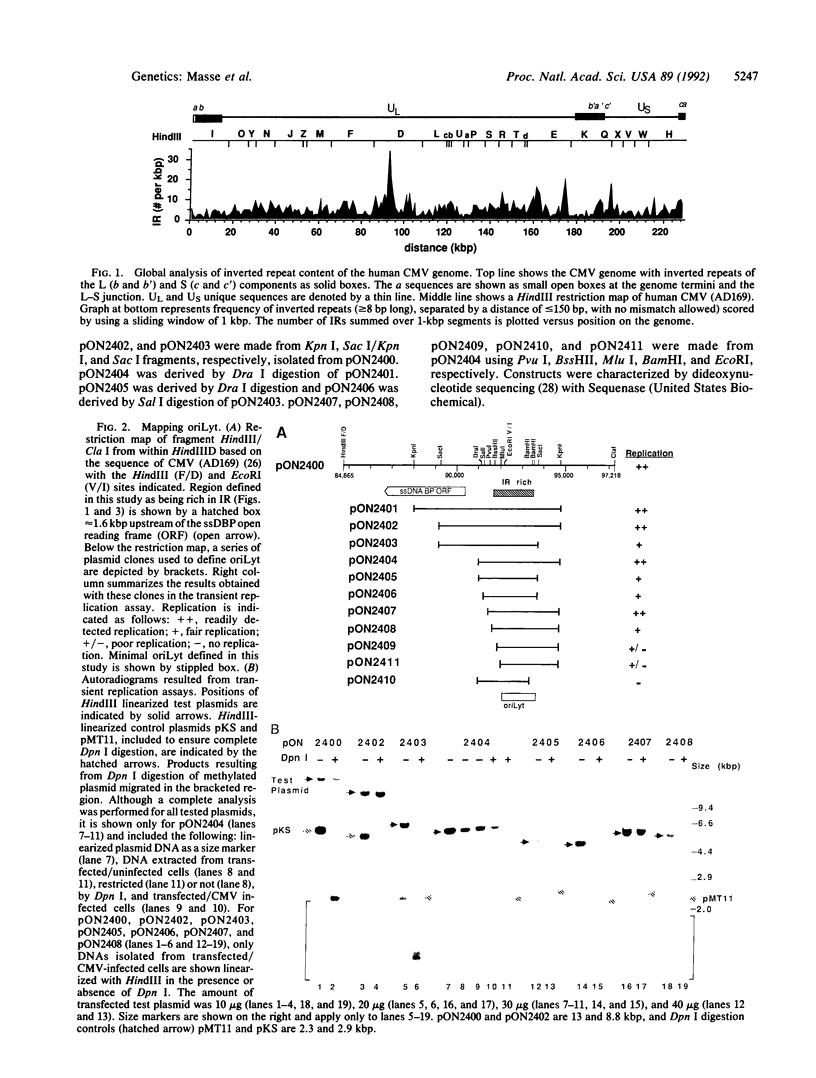
A global analysis of the 230-kilobase-pair (kbp) human cytomegalovirus genome revealed three regions that were very rich in repeated sequences. The region with the highest content of inverted and direct repeats lies between 92,100 and 93,500 bp, upstream of the gene encoding the single-stranded DNA binding protein. Cloned restriction fragments containing this region were able to replicate when trans-acting factors were provided by virus infection in a transient replication assay. With this assay, the region between 92,210 and 93,715 bp on the viral genome was defined as the minimal replication origin, oriLyt. The sequence composition and repeats within oriLyt were used to divide the region into two domains that may be important in origin function. Sequences flanking either the left or right side of the minimal oriLyt contributed to efficient replication; however, these sequences were not essential for origin function. Thus, the region of the viral genome with the most striking concentration of direct and inverted repeats corresponds to the oriLyt of human cytomegalovirus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akrigg A., Wilkinson G. W., Oram J. D. The structure of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virus Res. 1985 Mar;2(2):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders D. G., Punturieri S. M. Multicomponent origin of cytomegalovirus lytic-phase DNA replication. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):931–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.931-937.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann R. P., Yalamanchili V. R., O'Callaghan D. J. Functional mapping and DNA sequence of an equine herpesvirus 1 origin of replication. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1275–1283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1275-1283.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camp H. S., Coussens P. M., Silva R. F. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of a Marek's disease virus origin of DNA replication. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6320–6324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6320-6324.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Doelberg M. A 67-base-pair segment from the Ori-S region of herpes simplex virus type 1 encodes origin function. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2516–2519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2516-2519.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleckenstein B., Müller I., Collins J. Cloning of the complete human cytomegalovirus genome in cosmids. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. DNA replication of herpesviruses during the lytic phase of their life-cycles. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Feb;7(1):45–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Identification and characterization of oriLyt, a lytic origin of DNA replication of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamzeh F. M., Lietman P. S., Gibson W., Hayward G. S. Identification of the lytic origin of DNA replication in human cytomegalovirus by a novel approach utilizing ganciclovir-induced chain termination. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6184–6195. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6184-6195.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Gompels U. A., Barrell B. G., Craxton M., Cameron K. R., Staden R., Chang Y. N., Hayward G. S. Deviations from expected frequencies of CpG dinucleotides in herpesvirus DNAs may be diagnostic of differences in the states of their latent genomes. J Gen Virol. 1989 Apr;70(Pt 4):837–855. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-4-837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Bucher P., Brendel V., Altschul S. F. Statistical methods and insights for protein and DNA sequences. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:175–203. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S. Significant potential secondary structures in the Epstein-Barr virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6915–6919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J. DNA replication in mammalian cells: insights from the SV40 model system. Harvey Lect. 1989;85:173–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupershmidt S., DeMarchi J. M., Lu Z. Q., Ben-Porat T. Analysis of an origin of DNA replication located at the L terminus of the genome of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6283–6291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6283-6291.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton T., Gahn T. A., Martin J. M., Sugden B. Immortalizing genes of Epstein-Barr virus. Adv Virus Res. 1991;40:19–55. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60276-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Yates J., Sugden B. A putative origin of replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus is composed of two cis-acting components. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1822–1832. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus gene expression: alpha and beta promoters are trans activated by viral functions in permissive human fibroblasts. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):135–143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.135-143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Davison A. J. Identification of a varicella-zoster virus origin of DNA replication and its activation by herpes simplex virus type 1 gene products. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1613–1623. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Promoter-regulatory region of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal L. P. Relationship of eukaryotic DNA replication to committed gene expression: general theory for gene control. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):512–542. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.512-542.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Spadaro A., Schaffer J. E., Murray A. W., Maxam A. M., Schaffer P. A. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of oriL, a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):930–942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K. An enhancer element in the short unique region of human cytomegalovirus regulates the production of a group of abundant immediate early transcripts. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):406–416. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. W., Schaffer P. A. Elements in the transcriptional regulatory region flanking herpes simplex virus type 1 oriS stimulate origin function. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2601–2611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2601-2611.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Li R., Mohr I. J., Clark R., Botchan M. R. Activation of BPV-1 replication in vitro by the transcription factor E2. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):628–632. doi: 10.1038/353628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





