Abstract
ATP modulates voltage- and ligand-gated channels in the CNS via the activation of ionotropic P2X and metabotropic P2Y receptors. While P2Y receptors are expressed in retinal neurons, the function of these receptors in the retina is largely unknown. Using whole-cell patch-clamp techniques in rat retinal slice preparations, we demonstrated that ATP suppressed glycine receptor-mediated currents of OFF type ganglion cells (OFF-GCs) dose-dependently, and the effect was in part mediated by P2Y1 and P2Y11, but not by P2X. The ATP effect was abolished by intracellular dialysis of a Gq/11 protein inhibitor and phosphatidylinositol (PI)-phospholipase C (PLC) inhibitor, but not phosphatidylcholine (PC)-PLC inhibitor. The ATP effect was accompanied by an increase in [Ca2+]i through the IP3-sensitive pathway and was blocked by intracellular Ca2+-free solution. Furthermore, the ATP effect was eliminated in the presence of PKC inhibitors. Neither PKA nor PKG system was involved. These results suggest that the ATP-induced suppression may be mediated by a distinct Gq/11/PI-PLC/IP3/Ca2+/PKC signaling pathway, following the activation of P2Y1,11 and other P2Y subtypes. Consistently, ATP suppressed glycine receptor-mediated light-evoked inhibitory postsynaptic currents of OFF-GCs. These results suggest that ATP may modify the ON-to-OFF crossover inhibition, thus changing action potential patterns of OFF-GCs.
As a neurotransmitter in the CNS, ATP functions by acting on two distinct subfamilies of P2 purinoceptors: seven ionotropic P2X receptors (P2X1-7) and eight metabotropic mammalian P2Y receptors (P2Y1,2,4,6,11,12,13,14)1,2. These receptors are involved in regulating voltage-gated Ca2+, K+ channels, ligand-gated NMDA channels3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 and neurotransmitter release11,12,13. Moreover, ATP may be hydrolyzed to adenosine by ecto-ATPases and ectonucleotidases14, which regulates neuronal activity by activating neuronal adenosine receptors (P1 purinoceptors)15,16.
Expression of P2 receptors has been described in rat retinal neurons and Müller cells17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25. In the retina, ATP released by Müller cells may act on both neurons and Müller cells15,16. In the inner retina, another source of ATP is cholinergic amacrine cells (ACs)26,27. In addition, the enzymes required for deactivating extracellular ATP are also found in the synaptic layers of the rat retina19. It is therefore highly possible that ATP may modulate the activity of retinal neurons.
Ganglion cells (GCs) are output neurons in the retina. Functionally, GCs are classified into ON and OFF subtypes according to distinct features of their light responses28,29. While ON and OFF pathways process visual signals in a relatively independent manner, their signals may interact with each other at multiple levels30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39. For instance, in the inner retina cumulative evidence suggests that the so-called ON-to-OFF pathway crossover inhibition, mediated by glycinergic ACs, including AII ACs, plays a crucial role in the interplay between ON and OFF pathways30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39. It is known that AII ACs modulate the firing rates of OFF type GCs (OFF-GCs) by sending direct glycinergic signal to these cells32,35,36,40. ATP has been found to modulate the activity of GCs. ATP released from Müller cells evokes hyperpolarizing responses and outward currents in a subset of GCs, thus providing an inhibition of the firing rate of these cells15,16. Of interest, ATP-induced modulatory actions on the activity of GCs differ between the ON and OFF pathways41.
Because of the importance of OFF-GCs in the ON-to-OFF crossover inhibition and the essential role of glycinergic signal in shaping temporal features of OFF-GC responses, the present work focused on ATP-induced modulation of glycine-receptor mediated responses of OFF-GCs. By using whole-cell patch-clamp techniques in rat retinal slice preparations, we characterized how ATP modulated glycine currents of OFF-GCs, by activating P2Y receptors and explored the intracellular signaling pathway mediating such a modulation. Our results clearly show that a distinct Gq/11/phosphatidylinostiol (PI)-phospholipase C (PLC)/inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3)/Ca2+/protein kinase C (PKC) signaling pathway is responsible for the ATP effect. Consistent with this, we also found that ATP suppressed light-evoked glycine receptor-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic currents (L-IPSCs) of OFF-GCs via P2Y receptors.
Results
ATP suppresses glycine currents of OFF-GCs
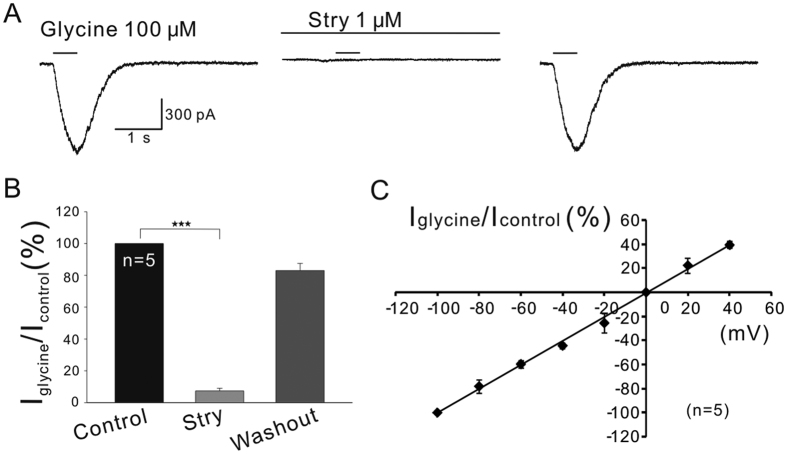
We first characterized glycine-induced currents in rat GCs. Glycine receptor-mediated currents were pharmacologically isolated by adding D-AP5, CNQX, bicuculline and TTX to bath Ringer’s (see Methods for details). Figure 1A shows that the current of a GC clamped at −60 mV, which was induced by local puff of 100 μM glycine to the dendrites of the cell in Ringer’s containing the above antagonists. The current was almost completely abolished by 1 μM strychnine, a specific antagonist of glycine receptors42 (7.36 ± 1.62% of control, n = 5, P < 0.001; Fig. 1B). The current response returned to the control level after washout with Ringer’s (83.0 ± 4.42% of control, P > 0.05). The current-voltage relationship of the currents was linear, with a reversal potential of 0.15 ± 1.4 mV (n = 5; Fig. 1C), which is very close to ECl- (0 mV), calculated according to the Nernst equation.
Figure 1. Characterization of glycine receptor-mediated currents recorded in rat GCs.
(A) Representative current response of a GC clamped at −60 mV, which was elicited by local puff (500 ms) of 100 μM glycine at intervals of 2 min to the dendrites in a rat retinal slice. The current was reversibly suppressed by 1 μM strychnine (Stry). The time- and amplitude-scale bars shown below the current trace are for the current responses. Durations of drug applications are indicated by horizontal lines above the current traces. (B) Bar chart summarizing the effects of 1 μM strychnine on glycine currents of GCs (n = 5). ***P < 0.001 vs. control. (C) Average current-voltage relationship of glycine-induced currents from 5 GCs. Current responses for each cell at different holding potentials were normalized to the response obtained at −100 mV. The data are presented as means ± SEM in all figures.
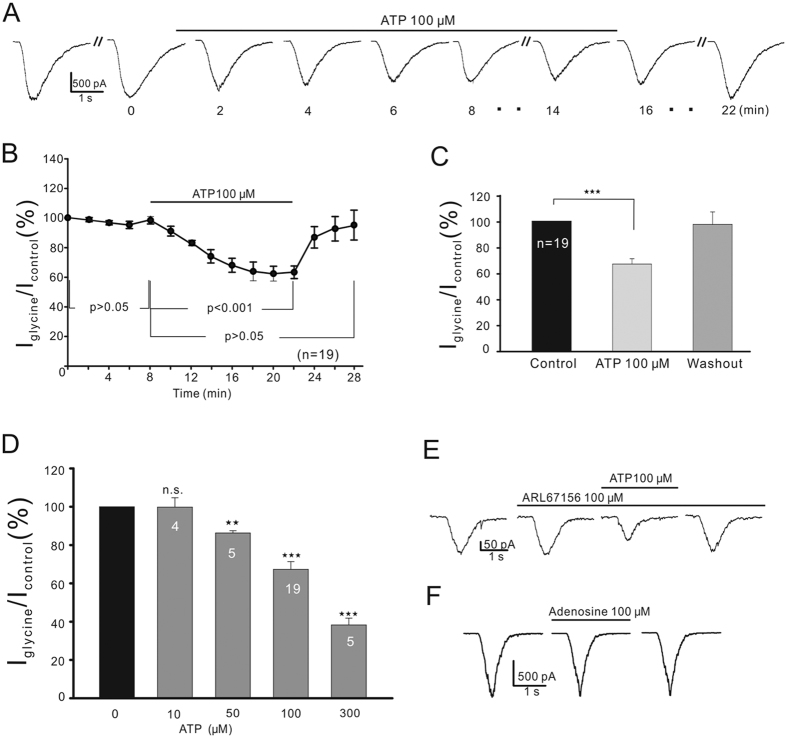
Application of 100 μM ATP elicited no detectable current in OFF-GCs (data not shown). When 100 μM ATP was bath-applied, as shown in Fig. 2A, the current induced by 100 μM glycine was suppressed in a progressive manner during the first 6 min after ATP application, and the current became stable in about 8 min and was kept at a similar level thereafter. ATP-induced suppression of glycine currents was observed in most of the OFF-GCs tested (19 out of 23, 82.61%). The average current amplitudes, following 14 min perfusion of 100 μM ATP, were reduced to 67.3 ± 4.05% of control (n = 19, P < 0.001; Fig. 2B,C). In the remaining four cells, ATP had no effects on the glycine currents (4/23, 17.39%).
Figure 2. ATP suppresses glycine currents of OFF-GCs.
(A) Representative recordings, showing the effect of 100 μM ATP on glycine currents of an OFF-GC. Drug application is indicated by the horizontal line above the current traces and the times, at which the current traces were recorded, are marked below (min). (B) Average peak amplitudes of glycine currents are plotted as a function of time, showing that ATP suppressed the glycine currents. (C) Bar chart showing the effect of 100 μM ATP on glycine current amplitudes of OFF-GCs (n = 19). (D) ATP suppressed the glycine currents in a dose-dependent manner. Cell numbers are indicated inside the bars. (E) ATP persisted to suppress the glycine current in the presence of 100 μM ARL67156. (F) Adenosine of 100 μM did not change the glycine current. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. control. n.s., represents no significant difference.
We further examined the concentration dependence of the ATP effect. For these experiments, data were pooled only from the cells, in which peak amplitudes to 100 μM glycine applied at intervals of 2 min were altered less than 5% during a period of 8 min prior to the experiment. For each cell, only a single concentration of ATP was tested, and the response amplitude obtained after 14-min incubation of ATP was normalized to the level recorded prior to the incubation (control). Following the 8-min washout, the response commonly returned to the control level (Fig. 2C). The data were discarded in case the response amplitudes (after 8-min washout) were changed by more than 5% of control. Figure 2D shows how the ATP effect depended upon ATP concentration. No suppression was seen with 10 μM ATP (104.2 ± 4.67%, n = 4, P > 0.05), but the glycine currents were respectively reduced to 86.3 ± 1.18% (n = 5, P < 0.01), 67.3 ± 4.05% (n = 19, P < 0.001) and 38.3 ± 3.53% (n = 5, P < 0.001) of control following ATP incubation at concentrations of 50 μM, 100 μM and 300 μM. Based on these data, ATP of 100 μM was chosen for all experiments to be subsequently described.
Since extracellular ATP can be converted into adenosine by ectonucleotidases14, we tested whether ATP or adenosine induced the suppression. ARL67156 (100 μM), an ectonucleotidase antagonist, which blocks the degradation of ATP43, did not change the glycine currents of OFF-GCs (105.1 ± 2.33% of control, n = 7, P > 0.05). In the presence of ARL67156, application of ATP still suppressed the glycine currents to an extent (67.5 ± 5.0% of control, n = 7, P < 0.001; Fig. 2E), comparable to that obtained in Ringer’s. Moreover, perfusion of adenosine (100 μM) had no effect on the glycine currents of OFF-GCs (98.4 ± 0.48% of control, n = 6, P > 0.05; Fig. 2F). These results indicate that it was ATP, but not the hydrolysed products of ATP, suppressed glycine currents of OFF-GCs.
ATP effect is mediated by P2-purinoceptors
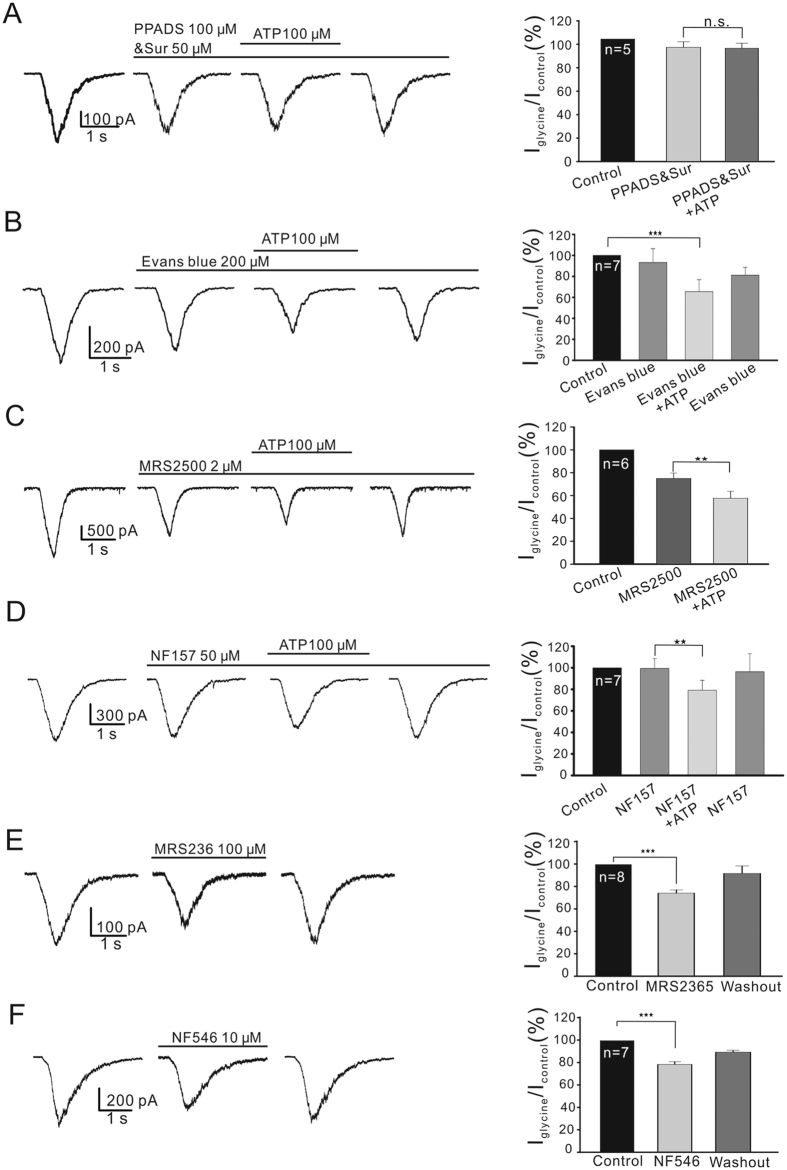
Figure 3A shows that, in the presence of PPADS (a relatively selective antagonist of homomeric P2X1,7, P2Y1,2,4) and suramin (a relative selective antagonist of P2X1,2,3,5,7, P2Y2,4,11)41,44,45, ATP application for 8 min failed to affect the glycine currents with an average being 94.2 ± 4.27% of control (P > 0.05). To explore which P2-receptor subtype(s) (P2X, P2Y) was (were) involved, we first perfused Evans blue (200 μM), a broad spectrum antagonist of P2X receptors44,46, which exerted no effect on glycine currents (93.1 ± 3.22% of control, P > 0.05), but co-application of ATP suppressed the currents to 65.5 ± 1.36% of control (n = 7, P < 0.001; Fig. 3B). This result is suggestive of no involvement of P2X receptors in the ATP effect.
Figure 3. ATP-induced suppression of glycine currents in OFF-GCs is mediated by P2 receptors.
(A) Representative current traces, taken from an OFF-GC, showing that during perfusion of PPADS (100 μM) and suramin (Sur) (50 μM), application of ATP (100 μM) no longer suppressed the glycine current. (B) Current traces of an OFF-GC, showing that in the presence of Evans blue (200 μM), 100 μM ATP still suppressed the glycine current. (C,D) Representative recordings obtained from two different OFF-GCs, showing that in the presence of 2 μM MRS2500 (C) or 50 μM NF157 (D), ATP persisted to suppress the glycine currents. Note that extracellular application of 2 μM MRS2500 per se suppressed the current (C), and the ATP-induced suppression of glycine currents was partially attenuated by MRS2500/NF157. (E,F) Current traces of two different OFF-GCs, showing that application of 100 μM MRS2365 (E) or 10 μM NF546 (F) suppressed the glycine currents. Each bar chart in A-F shows the statistical analysis of the data. ***P < 0.001 vs. control (B,E,F); **P < 0.01, as compared to the current amplitudes before ATP application (C,D).
P2Y1,2,4,618,21,22,23,24,25 and P2Y11 (Zhang and Zhong, unpublished data) are expressed in rat GCs. There are two P2Y antagonists now commercially available, MRS2500, a selective P2Y1 antagonist47 and NF157, a selective P2Y11 antagonist48. Perfusion of 2 μM MRS2500 reduced the glycine currents, and the currents became stable in about 8 min (74.9 ± 4.78% of control, n = 6; Fig. 3C). During the perfusion of MRS2500, addition of ATP further suppressed the currents (Fig. 3C) and the current amplitudes obtained after an 8-min perfusion of ATP were 76.9 ± 2.35% of those obtained before ATP perfusion (P < 0.01 vs. ATP), which were less than the results obtained in normal Ringer’s (67.3 ± 4.05%). No significant change in suppression was seen with a higher concentration (20 μM) of MRS2500 (data not shown). NF157 (50 μM), while applied alone, produced no change in glycine currents (99.3 ± 9.12%, n = 7, P > 0.05), and co-application of ATP suppressed the currents to 79.1 ± 9.28% of those obtained before ATP perfusion (P < 0.05 vs. ATP; Fig. 3D), which were also less than the results obtained in normal Ringer’s (67.3 ± 4.05%). It is likely that blockade of P2Y1 or P2Y11 partially attenuated the ATP-induced suppression of glycine currents. Consistently, application of 100 μM MRS2365, an agonist of P2Y149, and 10 μM NF546, an agonist of P2Y1150, respectively suppressed the glycine currents of OFF-GCs to 74.2 ± 2.91% (for MRS2365) (n = 8, P < 0.001; Fig. 3E) or to 78.5 ± 2.35% (for NF546) (n = 7, P < 0.001; Fig. 3F), thus mimicking the ATP effect. All these results imply that both P2Y1 and P2Y11 partially mediated the ATP effect.
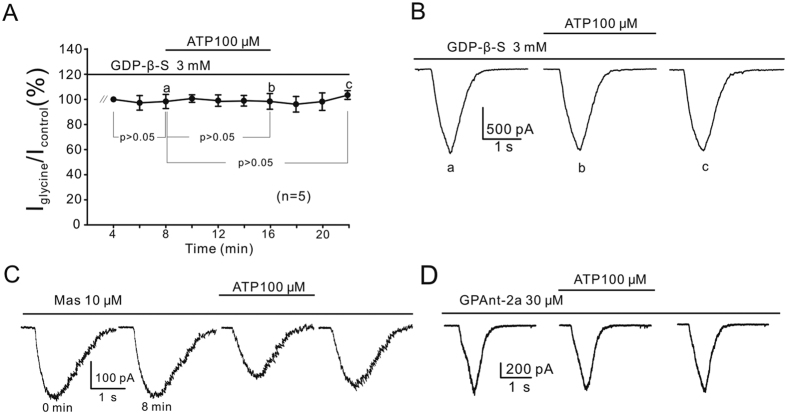
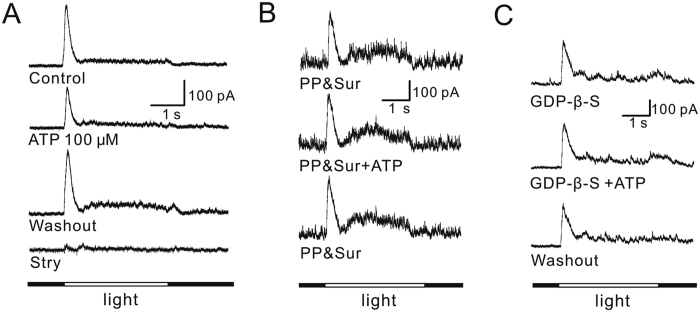
Given P2Y receptors being G-protein-coupled44,45, the ATP effect should be eliminated when G-protein activity is inhibited. This was experimentally demonstrated. ATP did not suppress glycine currents recorded from OFF-GCs which were intracellularly dialyzed with the G-protein inhibitor GDP-β-S (3 mM) for more than 8 min (98.4 ± 6.25% of control, n = 5, P > 0.05; Fig. 4A,B). Recent evidence suggests that P2Y1,2,4,6,11 and P2Y12-14 are mainly coupled to Gq/11 and Gi/o proteins, respectively51,52. We further examined which subtype(s) of G-proteins may mediate the ATP effect. Internal dialysis with 10 μM mastoparan, a peptide activator of Gi and Go53, for 8 min appeared to slow down the decay phases of the glycine currents of OFF-GCs, but did not change glycine current amplitudes (100.7 ± 3.69% of control, n = 5, P > 0.05), and addition of ATP persisted to suppress the currents to 63.7 ± 7.66% of control (P < 0.001; Fig. 4C). In contrast, during internal infusion of 30 μM GPAnt-2a, a specific Gq/11 protein inhibitor51, application of ATP no longer suppressed the glycine currents of OFF-GCs (95.3 ± 2.48% of control, n = 9, P > 0.05; Fig. 4D).
Figure 4. G-protein mediates the suppression of glycine currents by ATP.
(A) Changes in glycine currents of OFF-GCs caused by ATP are plotted as a function of time during internal infusion of 3 mM GDP-β-S. The data obtained for each cell were normalized to the amplitudes obtained at 8 min after GDP-β-S infusion when the currents became stable. (B) Representative current responses recorded at times indicated by a, b and c shown in (A). (C) Representative recordings of an OFF-GC, showing that during the internal infusion of 10 μM mastoparan (Mas), application of ATP still suppressed the glycine current. (D) Current traces of an OFF-GC, showing that in the presence of 30 μM GPAnt-2a, ATP failed to suppress the glycine current.
PI-PLC, but not PC-PLC, signaling pathway mediates ATP-induced suppression of glycine currents
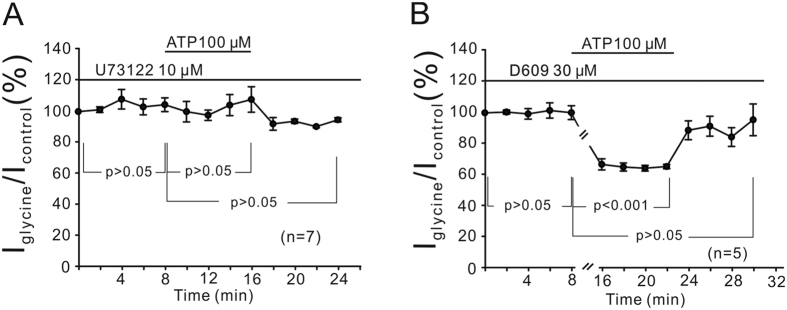
Activation of P2Y receptors could regulate several second messengers, and the PLC-PKC signaling pathway is a major downstream effector following P2Y receptor activation52,54,55,56. To test whether the PLC pathway may be involved, we investigated how U73122 (PI-PLC inhibitor) or D609 (PC-PLC inhibitor)57 changed the ATP effect. Figure 5A shows that internal infusion of 10 μM U73122 for 8 min did not change glycine currents of OFF-GCs (104.4 ± 4.40%, n = 7, P > 0.05), then addition of ATP for 8 min no longer reduced the currents (107.6 ± 8.18%, P > 0.05). In contrast, during internal infusion of 30 μM D609, application of ATP reduced the currents to 65.5 ± 1.42% (n = 5, P < 0.001; Fig. 5B) of those obtained before the ATP application. These results suggest the involvement of the PI-PLC pathway, but not the PC-PLC one.
Figure 5. PI-PLC, but not PC-PLC, is involved in modulation by ATP of glycine currents.
(A) Average peak amplitudes of glycine currents are plotted as a function of time, showing that the effective inhibition of endogenous PI-PLC by U73122 eliminated ATP-induced suppression of glycine currents. (B) Plot of average peak glycine current amplitudes as a function of time, showing that ATP-induced suppression of glycine currents was still seen in the presence of 30 μM D609.
Intracellular Ca2+ is involved in ATP-induced suppression of glycine currents
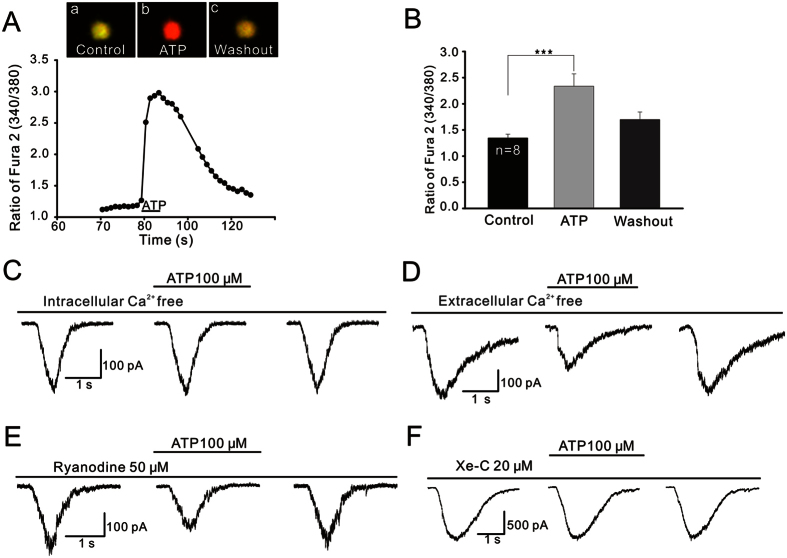
As Ca2+ is considered to be a mediator between PI-PLC and PKC58, whether the ATP effect is dependent on [Ca2+]i was further examined. We first monitored ATP-induced changes in [Ca2+]i in isolated GCs via calcium imaging. Because it is impossible to make a distinction between ON- and OFF-GC when they were isolated, the cells on which calcium imaging was performed should contain both the types. As shown in a representative result (Fig. 6A), application of ATP induced a significant increase in [Ca2+]i of the GC in a reversible manner, represented as the ratio of fura-2 (340/380). The CCD images (Fig. 6a–c) show the changes in [Ca2+]i induced by ATP in the soma of a GC. In eight GCs tested the averaged peak ratio value of fura-2 (340/380) obtained with the perfusion of ATP was 2.34 ± 0.23, which was significantly higher compared with the value obtained in Ringer’s (1.25 ± 0.07, P < 0.001; Fig. 6B). Consistently, internal infusion of Ca2+-free solution containing 10 mM BAPTA, a calcium chelator59, the application of ATP for 8 min no longer suppressed the glycine currents (95.9 ± 2.49% of control, n = 5, P > 0.05; Fig. 6C). ATP-induced increase in [Ca2+]i may be induced by an increase in extracellular Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane via Ca2+ channels and/or an increase in Ca2+ release from intracellular calcium stores. When OFF-GCs were bathed in Ca2+-free extracellular solution containing 1 mM EGTA, a calcium chelator60, ATP still suppressed the glycine currents to 62.1 ± 1.56% of control (n = 6, P < 0.001; Fig. 6D), suggesting that the ATP effect was independent of changes in extracellular calcium levels ([Ca2+]o).
Figure 6. Calcium relevance of ATP-induced suppression of glycine currents.
(A) A continuous recording of [Ca2+]i in a GC, represented by the ratio of fura-2 AM fluorescence at 340 nm and 380 nm (340/380). Application of ATP dramatically increased [Ca2+]i in a reversible manner. Three CCD images of an another GC loaded with fura-2 AM were taken before (a) and 10 s following ATP perfusion (b), and after washout (c). (B) Bar chart showing the ATP-caused changes in [Ca2+]i in GCs. ***P < 0.001 vs. control. (C) Representative recordings from an OFF-GC, showing that during internal infusion of Ca2+-free solution (containing 10 mM BAPTA), ATP failed to suppress the glycine current. (D) Representative recordings from an OFF-GC, showing that ATP still suppressed the glycine current in Ca2+-free extracellular solution (containing 1 mM EGTA). (E,F) Current traces of two OFF-GCs, showing that during the internal infusion of ryanodine (50 μM) (E), but not Xe-C (20 μM) (F), the ATP suppression effect on glycine current was seen.
Ca2+ release from intracellular calcium stores could be mediated by ryanodine- and/or IP3-sensitive pathways. With intracellular dialysis of 50 μM ryanodine, which depletes ryanodine-sensitive calcium sites61, ATP still significantly suppressed the currents (64.1 ± 3.64% of control, n = 6, P < 0.001; Fig. 6E). In contrast, during internal infusion of 20 μM xestospongin-C (Xe-C), an IP3 receptor antagonist, addition of ATP no longer suppressed the glycine currents of OFF-GCs (97.9 ± 5.81% of control, n = 5, P > 0.05; Fig. 6F). Similar results were obtained with internal infusion of heparin (5 mg/ml), another IP3 receptor antagonist (data not shown).
Role of PKC activity
Changes in [Ca2+]i are known to modulate the activity of PKC62. The effects of two PKC inhibitors on ATP-induced suppression of glycine currents in OFF-GCs were examined. None of the seven cells, tested with pipette solution containing 10 μM bisindolylmaleimide IV (Bis-IV), a general inhibitor of PKC, responded to application of ATP (99.3 ± 1.83% of control, P > 0.05; Fig. 7). Internal infusion of 2 μM Gö6976, an inhibitor of conventional Ca2+-dependent PKCα and β1 isozymes, yielded a similar result. That is, in the presence of Gö6976 the mean current amplitude during ATP perfusion was hardly changed (102.7 ± 2.61% of control, n = 6, P > 0.05; Fig. 7). Moreover, perfusion of 1 μM PMA, a PKC activator, suppressed the glycine currents in a progressive manner, with the amplitudes at 8 min being 62.8 ± 4.68% of control (n = 8, P < 0.001; Fig. 7), thus mimicking the ATP effect. During the perfusion of PMA, ATP did not cause a further suppression of the currents (103.9 ± 2.59% of the currents obtained before ATP application, P > 0.05 vs. ATP).
Figure 7. ATP-induced suppression of glycine currents in OFF-GCs is PKC-dependent.
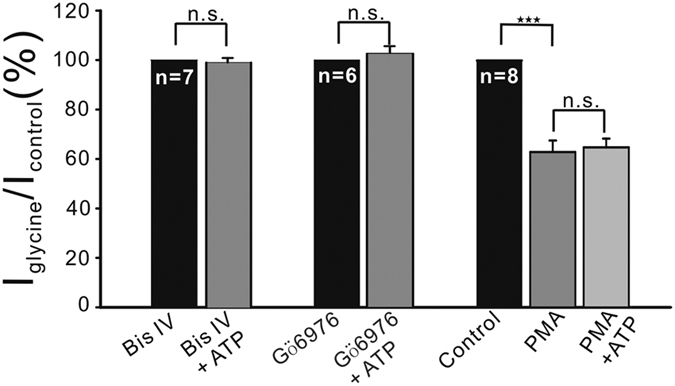
Bar charts, showing that ATP failed to suppress the glycine currents during internal infusion of 10 μM Bis-IV or 30 μM Gö6976. Extracellular application of 1 μM PMA decreased the glycine currents and in the presence of PMA ATP application did not further suppress the currents.
No involvement of cAMP-PKA and cGMP-PKG signaling pathways in the action of ATP
Finally, we tested whether cAMP-PKA and cGMP-PKG signaling pathways may be involved in the ATP effect on OFF-GCs. During intracellular application of 3 mM cAMP or 4 mM cGMP, ATP still suppressed the glycine currents in all OFF-GCs tested (65.7 ± 2.38% of control, n = 5, P < 0.001 for cAMP; 64.3 ± 9.21% of control, n = 5, P < 0.001 for cGMP). Furthermore, internal infusion of Rp-cAMP (50 μM), a PKA inhibitor or KT5823 (30 μM), a PKG inhibitor, did not change the ATP effect on glycine currents respectively (62.1 ± 5.09% for Rp-cAMP, n = 6, P < 0.001; 65.1 ± 3.42% for KT5823, n = 5, P < 0.001). These results suggest the involvement of neither cAMP-PKA nor cGMP-PKG pathway.
ATP suppresses glycine receptor-mediated L-IPSCs of OFF-GCs through P2Y receptors
To further explore physiological implication of the ATP-induced suppression of glycine currents in OFF-GCs, we examined the effects of ATP on glycine receptor-mediated L-IPSCs in retinal slice preparations. Whole cell light responses were recorded from 48 OFF-GCs. In 22 of these cells light-induced responses were completely blocked by co-application of bicuculline and TTX (see Methods for details) and no glycine receptor-mediated L-IPSCs could be recorded. In the remaining 26 GCs, glycine receptor-mediated L-IPSCs were recorded, which were abolished by co-application of 1 μM strychnine. As shown in Fig. 8A, perfusion of 100 μM ATP significantly suppressed the glycine receptor-mediated L-IPSC and the response returned to the control level after washout. Similar results obtained in 8 out 9 OFF-GCs tested, and the average peak amplitudes of the L-IPSCs following ATP application were reduced to 61.8 ± 2.19% of control (P < 0.001). For the remaining one cell, ATP had no effect on the currents.
Figure 8. ATP suppresses glycine receptor-mediated L-IPSCs of OFF-GCs via P2Y receptor activation.
(A) L-IPSCs from an OFF-GC, clamped at 0 mV, were elicited by a 3-second, full-field light stimulus in the presence of bicuculline and TTX. Application of 100 μM ATP suppressed the L-IPSC reversibly. The L-IPSC was completely eliminated by 1 μM strychnine (Stry). (B) L-IPSCs from an OFF-GC, showing that, in the presence of PPADS (PP) (100 μM) and suramin (Sur) (50 μM), application of 100 μM ATP no longer suppressed the current. (C) ATP did not change the L-IPSC of an OFF-GC during internal infusion of 3 mM GDP-β-S.
We also tested whether P2Y receptors mediated the ATP-induced suppression of glycine receptor-mediated L-IPSCs in OFF-GCs. Bath application of PPADS (100 μM) and suramin (50 μM) hardly changed L-IPSCs (90.4 ± 11.1%, n = 6, P > 0.05), as illustrated by a representative example from an OFF-GC (Fig. 8B). In the presence of PPADS and suramin, the current peak amplitudes obtained after an 8-min perfusion of ATP were 97.1 ± 9.97% of those obtained before ATP perfusion. Moreover, during internal infusion of 3 mM GDP-β-S, ATP did not change the L-IPSCs (100.0 ± 4.23%, n = 5, P > 0.05; Fig. 8C).
Discussion
ATP has been found to regulate both voltage- and ligand-gated channels in central neurons4,5,6,7,8,9,10. As far as ligand-gated channels are concerned, NMDA receptors are the only ones which are reported to be modulated by ATP. In the layer V pyramidal neurons of rat prefrontal cortex, for instance, ATP enhances NMDA responses via P2Y2 activation6.
In the retina it has been previously reported that ATP released from Müller cells and retinal neurons modulates the activity of GCs. Newman (2003, 2004) shows that ATP released from rat Müller cells could mediate interaction between these cells and GCs, suggesting that Müller cells contribute to information processing in the inner retina. Such neuromodulatory actions of ATP on GCs, however, are not due to the activation of P2 receptors, but may be resulted when neuronal adenosine receptors (P1 receptors) are activated by adenosine, which is hydrolyzed from ATP. In the mouse retina Kaneda et al.41 show that ATP differentially modulates ON-GCs and OFF-GCs, but these authors did not identify the P2 receptor subtypes mediating this modulation of ATP. This work demonstrated, for the first time, that ATP suppresses glycine currents via P2Y receptors. This effect of ATP is neither mediated by P2X receptors (Fig. 3B) nor by P1 receptors (Fig. 2D,E), which is quite different from the effect of ATP released from Müller cells on a subset of GCs that is mediated by P1 receptors. Among the P2Y subtypes, it seems likely that P2Y1,11 may be involved, as evidenced by the fact that MRS2365/NF546 induced suppression of glycine currents (Fig. 3E,F). The involvement of P2Y1,11 was further suggested by the partial blockade of the ATP effect by the antagonists (MRS2500 and NF157) of these receptor subtypes (Fig. 3C,D). Furthermore, the partial blockade due to either MRS2500 (2 μM) or NF157 (50 μM) raises a possibility that the subtypes (P2Y2,4,6) other than P2Y1,11 could be also involved. In fact, P2Y2,4,6, just like P2Y1,11, are also mainly coupled to Gq/1157. The involvement of the P2Y6 subtype seems unlikely since it only responds to UDP and UTP, but not ATP44,45. Whether P2Y2,4 may work together with P2Y1,11 to mediate the ATP effect remains to be further explored when antagonists for these subtypes are available. Modulation by ATP of glycine responses of retinal GCs observed in this work should be the first report about purinoceptor-mediated modulation of strychnine-sensitive glycine receptors, not only in the retina, but also in the CNS. In the inner retina cholinergic ACs may most likely be the cell type that releases ATP acting on OFF-GCs26,27.
By pharmacological dissections, we provided evidence showing that a distinct PI-PLC/PKC signaling pathway, following P2Y receptor activation, may be responsible for the ATP effect on glycine responses of OFF-GCs. Actually, this signaling pathway in P2Y1,2,4,6,11 receptor-mediated effects has been demonstrated in both neurons and non-neuronal cells46,52,55,56,63. Furthermore, the ATP effect on glycine currents is dependent on calcium released from intracellular stores via the IP3-sensitive pathway. This is consistent with the observation that activation of P2Y receptors by ATP induces IP3-mediated calcium release in astrocytes and spinal dorsal horn44,64,65. Consistently, Ca2+-dependent PKC (possibly PKCα and β1 isozymes) was involved in the ATP effect (Fig. 7). This is the first work reporting the intracellular signaling pathway, which is schematically depicted in Fig. S1, responsible for the modulation of ligand-gated channels caused by the activation of P2Y receptors.
It is of interest that glycine responses of rat GCs could be modulated due to activation of other G-protein-coupled receptors via a totally different signaling pathway. In isolated rat retinal GCs melatonin activates the Gi/o protein-coupled MT2 receptor, thus potentiating glycine responses of rat GCs through a PC-PLC/Ca2+-independent PKC signaling pathway66.
Glycine is predominantly released by narrow-field ACs, including AII ACs, and these glycinergic ACs mediate the crossover inhibition between ON and OFF pathways30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39, initiated in the ON pathway, that provides an inhibitory conductance to OFF-GCs by controlling glutamate release from presynaptic OFF cone bipolar cells and directly shapes temporal properties of light-evoked responses of OFF-GCs32,35,36,40. The suppression by ATP of glycine responses of OFF-GCs suggests that ATP weakens the crossover inhibition, thus resulting in a regulation of spike patterns in OFF-GCs.
There is evidence, showing that ligand-gated receptors may interact with each other, which is mediated either through direct protein-protein interaction8,67 or via protein phosphorylation60,66. This direct interaction occurs between P2X and GABAA receptors in neurons in the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus67 and between P2Y and NMDA receptors in layer V pyramidal neurons of the prefrontal and parietal cortex8. The ATP effect on glycine responses of OFF-GCs should not be a consequence of such a direct crosstalk between P2Y and glycine receptors, as the effect was abolished by G-protein inhibitors (Fig. 4). Nevertheless, the possibility that a direct crosstalk between P2X and GABAA receptors in OFF-GCs could not be ruled out. If this were the case, it would provide a sophisticated way in that the ATP-induced modulation of inhibitory inputs from ACs, mediated respectively by glycine and GABA receptors, comes into play in two different manners, by activating two distinct purinoceptor subtypes: P2Y and P2X.
Methods
Ethical approval
All animal protocols were performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by Animal Care and Use Committee of Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University. Male albino rats (Sprague-Dawley, 15–18 days of age) were used in this study. During this study, all efforts were made to minimize the number of animals used and their pain and discomfort.
Retinal slice preparations
Retinal slices were prepared following the procedures described previously68, with minor modifications. Briefly, following deep anesthesia with 25 mg/ml urethane, the eyes were enucleated, and the retinas were removed. The isolated retinas were vertically cut into 200 μm-thick slices in Ringer’s using a manual cutter (ST-20, Narishige, Tokyo, Japan). The slices were transferred into a recording chamber with the cut side up and held mechanically in place by a grid of parallel nylon strings glued onto a U-shape frame of platinum wire. They were then viewed through a fixed-stage upright microscope (BX51WI, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a 60X water-immersion ceramic objective and DIC optics. Unless described otherwise, retinal slices were perfused continuously with oxygenated and carbogen-bubbled Ringer’s, which contained (in mM) NaCl 125, KCl 2.5, CaCl2 2, MgCl2 1, NaH2PO4 1.25, NaHCO3 25, and glucose 15. While recording glycine-induced currents, the extracellular solution was supplemented with CNQX (10 μM), D-AP5 (50 μM), bicuculline (10 μM) and TTX (0.5 μM) to block AMPA-, NMDA-, GABAA-receptor-mediated components and voltage-gated sodium channels, respectively. These preparations were used for all the experiments except for calcium imaging.
Preparation of isolated retinal GCs
The GCs were acutely dissociated from rat retinas by enzymatic and mechanical methods as previously described69 with minor modifications. In brief, animals were deeply anaesthetized and the retinas were removed quickly and incubated in oxygenated Hanks’ solution containing (in mM): NaCl 137, NaHCO3 0.5, NaH2PO4 1, KCl 3, CaCl2 2, MgSO4 1, HEPES 20, sodium pyruvate 1 and glucose 16, adjusted to pH 7.4 with NaOH. The retinas were then digested in 5–7 mg/ml papain (Worthington Biochemical, Freehold, NJ, USA) containing Hanks’ solution, supplemented with L-cysteine and bovine serum albumin (0.2 mg/ml for each) for 30 min at 33 °C. The solution was bubbled continuously with 100% O2. After several rinses in Hanks’ solution, the retinas were mechanically dissociated by gently triturating with fire-polished Pasteur pipettes, and cell suspension was plated onto a culture dish mounted on an inverted microscope (IX 70, Olympus). Isolated GCs were only used for calcium imaging experiments.
Whole-cell patch-clamp recording
Whole-cell membrane currents of GCs, clamped at −60 mV, were recorded with pipettes of 6–8 MΩ resistance in voltage-clamp modes filled with the internal solution containing (in mM) CsCl 120, CaCl2 1, MgCl2 2, EGTA 10, HEPES 10, ATP-Mg 2, GTP-Na 0.4, NaCl 5 and phosphocreatine 10; adjusted to pH 7.2 with CsOH. Pipettes were mounted on a motor-driven micromanipulator (MP-285, Sutter, Novato, CA, USA), and connected to an EPC10 patch clamp amplifier (HEKA, Lambrecht, Germany). Fast capacitance was fully cancelled and cell capacitance was partially cancelled by the circuits of the amplifier as much as possible. Sixty percent of the series resistance was compensated. Data were acquired at a sampling rate of 5 kHz, and then stored for further analysis. Drug-containing extracellular Ringer’s was either locally applied through a puff pipette (tip diameter ~2 μm), using a pressure micro-injector (PMI-100, DAGAN, Minneapolis, MN, USA), which applied a pressure of 35 kPa (5 p.s.i.) to the top of the pipette, or administrated in bath medium through another inlet by gravity, depending on the purpose of an experiment. Some drugs (GDP-β-S, GPAnt-2a, U73122, D609, mastoparan, BAPTA, heparin, xestospongin-C, ryanodine, Bis IV, Gö6976, cAMP, cGMP, Rp-cAMP and KT5823) were dialyzed into neurons after membrane rapture by including them into the patch electrodes. All experiments were performed at room temperature (20–25 °C).
Electrophysiological recordings of light-evoked responses were performed on retinal slices. Dark-adapted (3 h) rats were deeply anaesthetized and retinal slices were prepared under dim red illumination. Slices were transferred to a recording chamber and superfused constantly with oxygenated bicarbonate-buffered Ringer’s at 30–32 °C. The pipette solution consisted of (in mM): CsCH3SO3 120, TEA-Cl 10, Hepes 10, CaCl2 0.1, EGTA 1, phosphocreatine 12, ATP-Mg 3, GTP-Na 0.5; adjusted to pH 7.2 with CsOH. Whole cell light-evoked glycine receptor-mediated IPSCs of GCs were recorded with an EPC 10 amplifier. The cell was held at 0 mV. Bicuculline (10 μM) and TTX (0.5 μM) were added to the perfusion solution to block GABAA receptor and voltage-gated sodium channels, respectively. Light stimuli were generated using an LED (λ = 525 nm). Full-field illumination was delivered from the LED, which was controlled by Pulse software (HEKA Elektronik) and delivered to the retina through the microscope condenser. Photon fluxes on the surface of the superfusion chamber were measured with a linear/log optometer (S350, UDT Instruments, San Diego, CA, USA). Light stimuli of 0.5 μW/cm2 were provided for 3 s at 60 s intervals.
GCs were distinguished from displaced ACs in the ganglion cell layer (GCL) according to soma diameters and physiological criteria68,70,71,72. ON type GCs (ON-GCs) and OFF-GCs were further identified according to well-established morphological and physiological criteria30,68,70,73. Morphologically, ON- and OFF-GCs, revealed by Lucifer yellow, were characterized by their dendrites terminating in proximal and distal parts of the inner plexiform layer, respectively30,68,70. Physiologically, 500-ms negative current injection in the current-clamp mode led to rebound burst firing in the OFF-GCs, but not in the ON-GCs68,70,73. Figure S2 shows an OFF-GC intracellularly stained by Lucifer yellow (A) and its response to a 500-ms negative current injection (B).
Calcium imaging
Changes in intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) were assessed using the membrane permeable indicator fura-2 AM (Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan). Fura-2 AM was dissolved in 20% Pluronic F-127 (w/v, DMSO) and added to a chamber that contained Ringer’s, with a final fura-2 AM concentration of 2 μM. Isolated GCs were incubated in the dye solution for 30 min at room temperature and then perfused with dye-free Ringer’s for at least 15 min. Digital fluorescence images were acquired with an inverted microscope (IX-70, Olympus) furnished with a digital CCD camera (ORCA-ER; Hamamatsu Photonics, Shizuoka, Japan). A high-speed continuously scanning monochromatic light source (Polychrome V; Till Photonics, Gräfeling, Germany) was used for the excitations at wavelengths of 340 nm and 380 nm. Fluorescence intensities at both wavelengths (F340 and F380) were measured every 3–10 s, and images were obtained using PC-based software (C-imaging systems; Hamamatsu Photonic). The ratio between the two images was proportional to [Ca2+]i of the cell under study. Prior to an experiment, a background level of fluorescence (attributable to autofluorescence and camera noise) was measured and subtracted from all the obtained data.
Chemicals
D-AP5, PPADS, suramin, Evans blue, NF157, NF546, MRS2500, MRS2365, ARL67156, GPAnt-2a and ryanodine were purchased from Tocris Bioscience (Ellisville, MO, USA). All other chemicals were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Adenosine, U73122, ryanodine, Bis-IV, PMA and Gö6976 were initially dissolved in DMSO for stock and then diluted in solutions to final working concentrations. The final DMSO concentration was less than 0.1%, with no effects on glycine-induced currents of GCs. All other drug solutions were prepared in ion-free water, stored at −20 °C and freshly diluted to the working concentrations using normal solutions.
Statistical analysis
The data are presented as means ± SEM. Student’s t test (paired data) and one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by post hoc Tukey’s tests (multiple comparisons) were used to identify significant differences. In all cases, P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Zhang, P.-P. et al. Signaling mechanism for modulation by ATP of glycine receptors on rat retinal ganglion cells. Sci. Rep. 6, 28938; doi: 10.1038/srep28938 (2016).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China: 31171055, 31571075, 31421091, 81430007 and 31571072; the National Program of Basic Research sponsored by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China: 2011CB504602, 2015AA020512 and 2013CB835100.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author Contributions Y.-M.Z. and X.-L.Y. conceived and designed the study and experiments. P.-P.Z. and G.Z. performed the experiments. P.-P.Z., G.Z., W.Z., S.-J.W. and Y.-M.Z. analyzed and interpreted the data. Y.-M.Z., X.-L.Y. and P.-P.Z. wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
References
- North R. A. Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol. Rev. 82, 1013–1067 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowski E. R., Boucher R. C. & Harden T. K. Mechanisms of release of nucleotides and integration of their action as P2X- and P2Y-receptor activating molecules. Mol. Pharmacol. 64, 785–795 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm S. Selective inhibition of M-type potassium channels in rat sympathetic neurons by uridine nucleotide preferring receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 124, 1261–1269 (1998). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippov A. K., Webb T. E., Barnard E. A. & Brown D. A. Dual coupling of heterologously-expressed rat P2Y(6) nucleotide receptors to N-type Ca2+ and M-type K+ currents in rat sympathetic neurones. Br. J. Pharmacol. 126, 1009–1017 (1999). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bringmann A. et al. Activation of P2Y receptors stimulates potassium and cation currents in acutely isolated human Müller (glial) cells. Glia. 37, 139–152 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirkner K. et al. Interaction between P2Y and NMDA receptors in layer V pyramidal neurons of the rat prefrontal cortex. Neuropharmacol. 42, 476–488 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe M., Endoh T. & Suzuki T. Extracellular ATP-induced calcium channel inhibition mediated by P1/P2Y purinoceptors in hamster submandibular ganglion neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol. 138, 1535–1543 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthardt J. et al. P2Y1 receptor activation inhibits NMDA receptor-channels in layer V pyramidal neurons of the rat prefrontal and parietal cortex. Neurochem. Int. 42, 161–172 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerevich Z. et al. Inhibition of N-type voltage-activated calcium channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons by P2Y receptors is a possible mechanism of ADP-induced analgesia. J. Neurosci. 24, 797–807 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. L., Zhang M., Laties A. M. & Mitchell C. H. Stimulation of P2X(7) receptors elevates Ca2+ and kills retinal ganglion cells. IOVS. 46, 2183–2191 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trendelenburg A. U. & Bultmann R. P2 receptor-mediated inhibition of dopamine release in rat neostriatum. Neurosci. 96, 249–252 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues R. J., Almeida T., Richardson P. J., Oliveira C. R. & Cunha R. A. Dual presynaptic control by ATP of glutamate release via facilitatory P2X(1), P2X(2/3), and P2X(3) and inhibitory P2Y(1), P2Y(2), and/or P2Y(4) receptors in the rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 25, 6286–6295 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich A., Kittel A., Csoelle C., Vizi E. S. & Sperlagh B. Modulation of neurotransmitter release by P2X and P2Y receptors in the rat spinal cord. Neuropharmacol. 54, 375–386 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann H. Biochemistry, localization and functional roles of ecto-nucleotidases in the nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 49, 589–618 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. A. Glial cell inhibition of neurons by release of ATP. J. Neurosci. 23, 1659–1666 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. A. Glial modulation of synaptic transmission in the retina. Glia. 47, 268–274 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Kaneda M., Li H. B., Rockland K. S. & Hashikawa T. Neuron-specific distribution of P2X7 purinergic receptors in the monkey retina. J. Comp. Neurol. 459, 267–277 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries J. E., Wheeler-Schilling T. H., Guenther E. & Kohler K. Expression of P2Y1, P2Y2, P2Y4, and P2Y6 receptor subtypes in the rat retina. IOVS. 45, 3410–7 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puthussery T. & Fletcher E. L. P2X(2) receptors on ganglion and antacrine cells in cone pathways of the rat retina. J. Comp. Neurol. 496, 595–609 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigematsu Y., Shimoda Y. & Kaneda M. Distribution of immunoreactivity for P2X3, P2X5, and P2X6-purinoceptors in mouse retina. J. Mol. Histol. 38, 369–371 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. M., Puthussery T. & Fletcher E. L. Localization and possible function of P2Y(4) receptors in the rodent retina. Neurosci. 155, 1262–74 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. M. & Fletcher E. L. Subsets of retinal neurons and glia express P2Y1 receptors. Neurosci. 160, 555–66 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurm A., Erdmann I., Bringmann A., Reichenbach A. & Pannicke T. Expression and function of P2Y receptors on Müller cells of the postnatal rat retina. Glia. 57, 1680–1690 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang P. P., Yang X. L. & Zhong Y. M. Cellular localization of P2Y(6) receptor in rat retina. Neurosci. 220, 62–69 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilip R. et al. Distribution and development of P2Y(1)-purinoceptors in the mouse retina. J. Mol. Histol. 44, 639–644 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. & Cunningham J. Modulation by endogenous ATP of the light-evoked, release of ACh from retinal cholinergic neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol. 113, 1085–1087 (1994). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos P. F., Caramelo O. L., Carvalho A. P. & Duarte C. B. Characterization of ATP release from cultures enriched in cholinergic amacrine-like neurons. J. Neurobiol 41, 340–348 (1999). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famiglietti E. V., Kaneko A. & Tachibana M. Neuronal architecture of on and off pathways to ganglion-cells in carp retina. Science 198, 1267–1269 (1977). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R., Famiglietti E. V. & Kolb H. Intracellular staining reveals different levels of stratification for on- and off-center ganglion cells in cat retina. J. Neurophysiol 41, 472–483 (1978). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang J. J., Gao F. & Wu S. M. Light-evoked excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs to ON and OFF alpha ganglion cells in the mouse retina. J. Neurosci. 23, 6063–6073 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova E., Muller U. & Wässle H. Characterization of the glycinergic input to bipolar cells of the mouse retina. Eur. J. Neurosci. 23, 350–364 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. J. & Rieke F. Network variability limits stimulus-evoked spike timing precision in retinal ganglion cells. Neuron. 52, 511–524 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roska B., Molnar A. & Werblin F. S. Parallel processing in retinal ganglion cells: How integration of space-time patterns of excitation and inhibition form the spiking output. J. Neurophysiol. 95, 3810–3822 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar S., Heinze L., Haverkamp S., Ivanova E. & Waessle H. Glycine receptors of A-type ganglion cells of the mouse retina. Vis. Neurosci. 24, 471–487 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manookin M. B., Beaudoin D. L., Ernst Z. R., Flagel L. J. & Demb J. B. Disinhibition combines with excitation to extend the operating range of the OFF visual pathway in daylight. J. Neurosci. 28, 4136–50 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wyk M., Wässle H. & Taylor W. R. Receptive field properties of ON- and OFF-ganglion cells in the mouse retina. Vis. Neurosci. 26, 297–308 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggers E. D. & Lukasiewicz P. D. Interneuron circuits tune inhibition in retinal bipolar cells. J. Neurophysiol. 103, 25–37 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin F. S. Six different roles for crossover inhibition in the retina: Correcting the nonlinearities of synaptic transmission. Vis. Neurosci. 27, 1–8 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buldyrev I. & Taylor W. R. Inhibitory mechanisms that generate centre and surround properties in ON and OFF brisk-sustained ganglion cells in the rabbit retina. J. Physiol. 591, 303–325 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. J. & Rieke F. Signals and noise in an inhibitory interneuron diverge to control activity in nearby retinal ganglion cells. Nature Neurosci. 11, 318–326 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda M., Ishii T. & Hosoya T. Pathway-dependent modulation by P2-purinoceptors in the mouse retina. Eur. J. Neurosci. 28, 128–36 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Wässle H. & Voigt T. Pharmacological modulation of the rod pathway in the cat retina. J. Neurophysiol. 59, 1657–1672 (1988). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockhaus J., Dressel D., Herold S. & Deitmer J. W. Purinergic modulation of synaptic input to Purkinje neurons in rat cerebellar brain slices. Eur. J. Neurosci. 19, 2221–2230 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V. & Burnstock G. Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol. Rev. 50, 413–492 (1998). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abbracchio M. P. et al. International Union of Pharmacology LVIII: update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 58, 281–341 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malomouzh A. I., Nikolsky E. E. & Vyskocil F. Purine P2Y receptors in ATP-mediated regulation of non-quantal acetylcholine release from motor nerve endings of rat diaphragm. Neurosci. Res. 71, 219–25 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnin L., Hwang S. J., Ward S. M., Sanders K. M. & Mutafova-Yambolieva V. N. Adenosine 5-diphosphate-ribose is a neural regulator in primate and murine large intestine along with beta-NAD(+). J. Physio. 590, 1921–41 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaki H., Tsukimoto M., Harada H., Moriyama Y. & Kojima S. Autocrine regulation of macrophage activation via exocytosis of ATP and activation of P2Y11 receptor. PLos One 8, e59778 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meis S. et al. NF546 [4,4_-(Carbonylbis (imino-3,1-phenylene-carbonylimino-3, 1- (4-methyl- phenylene)-carbonylimino)) bis (1,3-xylene-_, diphosphonic Acid) Tetrasodium Salt] is a non-nucleotide P2Y11 agonist and stimulates release of interleukin-8 from human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J. Pharmaco. Exp. Therap. 332, 238–247 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvares T. S., Revill A. L., Huxtable A. G., Lorenz C. D. & Funk G. D. P2Y1 receptor-mediated potentiation of inspiratory motor output in neonatal rat in vitro. J Physiol. 592, 3089–3111 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai H., Munekata E. & Higashijima T. G-protein antagonists - a novel hydrophobic peptide competes with receptor for g-protein binding. J.Biol. Chem. 267, 16237–16243 (1992). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. G., Hanaoka K., Kumada M. & Takuwa Y. Molecular-cloning and functional-analysis of a novel P2 nucleotide receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 26152–26158 (1995). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shpakov A. O. & Pertseva M. N. Molecular mechanisms for the effect of mastoparan on G proteins in tissues of vertebrates and invertebrates. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 141, 302–306 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Communi D., Motte S., Boeynaems J. M. & Pirotton S. Pharmacological characterization of the human P2Y4 receptor. Eur. J. Pharmaco. 317, 383–389 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robaye B., Boeynaems J. M. & Communi D. Slow desensitization of the human P2Y(6) receptor. Eur. J. Pharmaco. 329, 231–236 (1997). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erb L. et al. An RGD sequence in the P2Y(2) receptor interacts with alpha(V)beta(3) integrins and is required for G(0)-mediated signal transduction. J. Cell. Biol. 153, 491–501 (2001). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W. S. & Zawalich K. C. Regulation of insulin secretion by phospholipase C. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 271, E409–E416 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnet F. P. Sigma-1 receptor as regulator of neuronal intracellular Ca2+: clinical and therapeutic relevance. Biol. Cell. 97, 873–883 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Patton C. W. & Nuccitelli R. A practical guide to the preparation of Ca2+ buffers. Met. Cell. Biol. 40, 3–29 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C. et al. Orexin-A differentially modulates AMPA-preferring responses of ganglion cells and amacrine cells in rat retina. Neuropharmacol. 93, 80–93 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck E., Zimanyi I., Abramson J. J. & Pessah I. N. Ryanodine stabilizes multiple conformational states of the skeletal-muscle calcium release channel. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 23560–23567 (1992). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducibella T. & Fissore R. The roles of Ca2+, downstream protein kinases, and oscillatory signaling in regulating fertilization and the activation of development. Dev. biol. 315, 257–79 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson T. S. et al. P2Y2 nucleotide receptor-mediated responses in brain cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 41, 356–66 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter M. W. & Hicks J. L. ATP causes release of intracellular Ca2+ via the phospholipase C-beta/IP3 pathway in astrocytes from the dorsal spinal-cord. J. Neurosci. 15, 2961–2971 (1995). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashioka S. et al. G. Purinergic responses of calcium-dependent signaling pathways in cultured adult human astrocytes. Bmc Neurosci. 15 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao W. J., Zhang M., Miao Y., Yang X. L. & Wang Z. Melatonin potentiates glycine currents through a PLC/PKC signalling pathway in rat retinal ganglion cells. J. Physio. 588, 2605–2619 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jo Y. H. et al. Cross-talk between P2X4 and gamma-aminobutyric acid, type A receptors determines synaptic efficacy at a central synapse. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 19993–20004 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. J., Liu L. L., Jiang S. X., Zhong Y. M. & Yang X. L. Activation of the sigma receptor 1 suppresses nmda responses in rat retinal ganglion cells. Neurosci. 177, 12–22 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Yu Y. C., Zhao J. W. & Yang X. L. Inwardly rectifying potassium channels in rat retinal ganglion cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 20, 956–964 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H. Evidence for an amacrine cell system in the ganglion-cell layer of the rat retina. Neurosci. 6, 931–944 (1981). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. & Yang X. L. Hyperpolarization-activated cation current is involved in modulation of the excitability of rat retinal ganglion cells by dopamine. Neurosci. 150, 299–308 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Weng S. J., Yang X. L. & Zhong Y. M. Orexin-a potentiates l-type calcium/barium currents in rat retinal ganglion cells. Neurosci. 305, 225–237 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis D. J. & Detwiler P. B. Different mechanisms generate maintained activity in ON and OFF retinal ganglion cells. J. Neurosci. 27, 5994–6005 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.