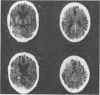
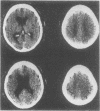
Abstract
To identity those patients with hydrocephalus as a basis for their presenile dementia it is suggested that such patients be screened non-invasively by CT scan. If there is ventricular dilatation and small cortical sulci, intracranial pressure should be monitored for 48 hours to detect `B' waves. Patients with significant `B' waves (10 mmHg) for at least two hours in the day might benefit from a shunt.
Full text
PDF
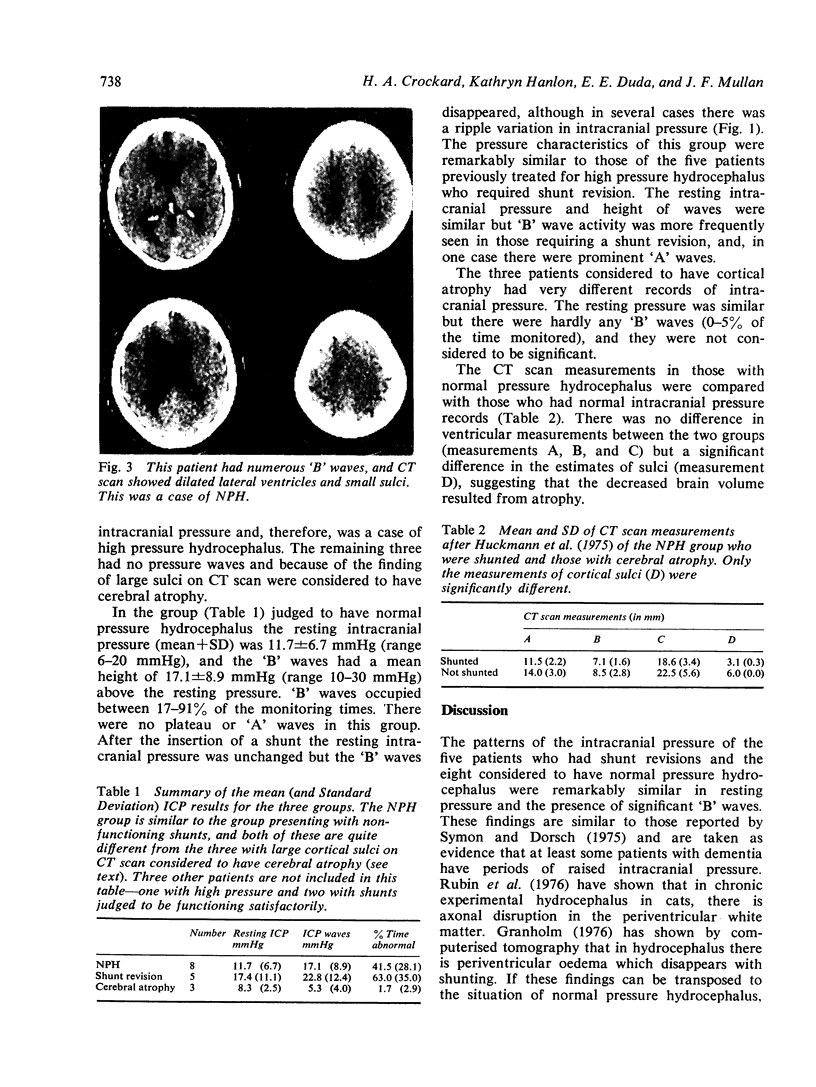


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS R. D., FISHER C. M., HAKIM S., OJEMANN R. G., SWEET W. H. SYMPTOMATIC OCCULT HYDROCEPHALUS WITH "NORMAL" CEREBROSPINAL-FLUID PRESSURE.A TREATABLE SYNDROME. N Engl J Med. 1965 Jul 15;273:117–126. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196507152730301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister C. M. A report of eight patients with low pressure hydrocephalus treated by C.S.F. diversion with disappointing results. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1972;27(1):11–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01402168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chawla J. C., Hulme A., Cooper R. Intracranial pressure in patients with dementia and communicating hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg. 1974 Mar;40(3):376–380. doi: 10.3171/jns.1974.40.3.0376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coblentz J. M., Mattis S., Zingesser L. H., Kasoff S. S., Wiśniewski H. M., Katzman R. Presenile dementia. Clinical aspects and evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics. Arch Neurol. 1973 Nov;29(5):299–308. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490290039003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hounsfield G. N. Computerized transverse axial scanning (tomography). 1. Description of system. Br J Radiol. 1973 Dec;46(552):1016–1022. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-46-552-1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckman M. S., Fox J., Topel J. The validity of criteria for the evaluation of cerebral atrophy by computed tomography. Radiology. 1975 Jul;116(1):85–92. doi: 10.1148/116.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman R., Hussey F. A simple constant-infusion manometric test for measurement of CSF absorption. I. Rationale and method. Neurology. 1970 Jun;20(6):534–544. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.6.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnum A., Kornstad S. Long-term prognosis of patients with central cerebral ventricular enlargement. A fourth follow-up study of 100 patients with a 3rd ventricle measuring 12 mm or more in width. Acta Neurol Scand. 1974;50(4):409–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. C., Hochwald G. M., Tiell M., Mizutani H., Ghatak N. Hydrocephalus: I. Histological and ultrastructural changes in the pre-shunted cortical mantle. Surg Neurol. 1976 Feb;5(2):109–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. H. Adult hydrocephalus. Evaluation of shunt therapy in 80 patients. J Neurosurg. 1972 Oct;37(4):423–428. doi: 10.3171/jns.1972.37.4.0423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S. C., Langfitt T. W. Normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Predicting the results of cerebrospinal fluid shunting. J Neurosurg. 1974 Oct;41(4):463–470. doi: 10.3171/jns.1974.41.4.0463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symon L., Dorsch N. W. Use of long-term intracranial pressure measurement to assess hydrocephalic patients prior to shunt surgery. J Neurosurg. 1975 Mar;42(3):258–273. doi: 10.3171/jns.1975.42.3.0258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]