Abstract
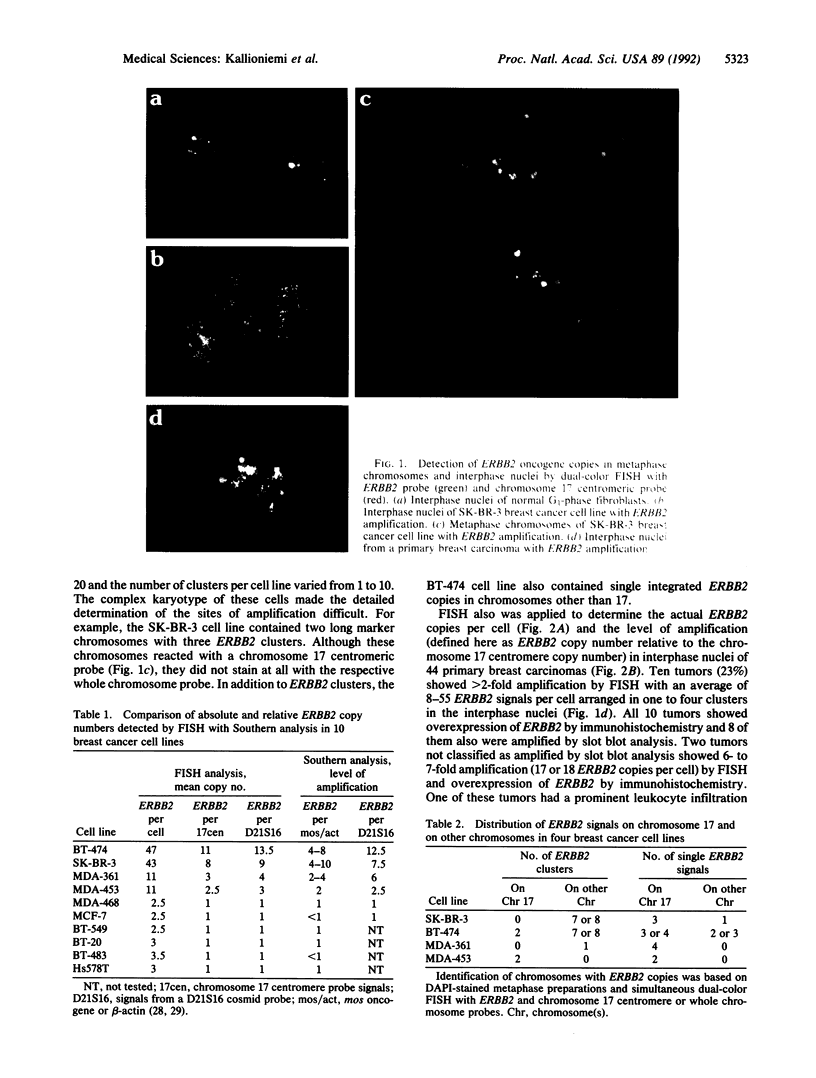
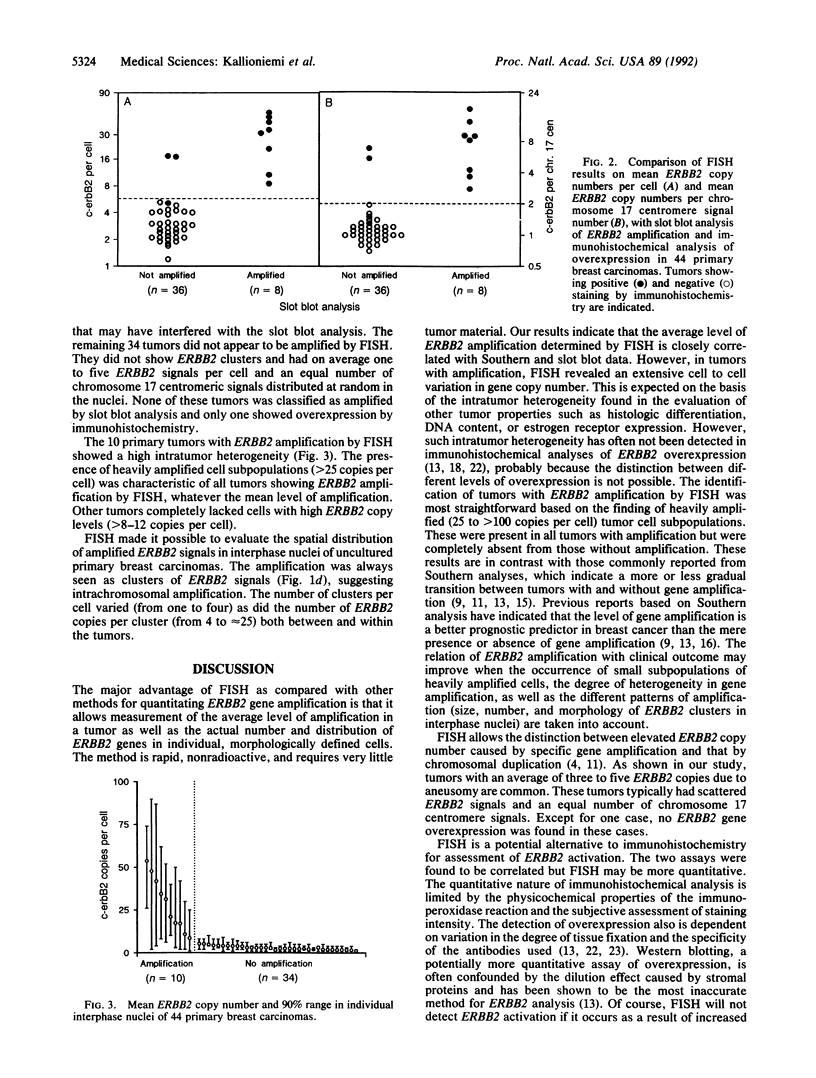
We illustrate the use of fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) for analysis of ERBB2 oncogene copy number, the level of amplification (here defined as the ratio of ERBB2 copy number to copy number of chromosome 17 centromeres), and the distribution of amplified genes in breast cancer cell lines and uncultured primary breast carcinomas. The relative ERBB2 copy number determined by FISH in 10 breast cancer cell lines correlated strongly with Southern blot results (r = 0.98) when probes for an identical reference locus were used in the two methods. Metaphase analysis of cell lines showed that amplified ERBB2 copies always occurred in intrachromosomal clusters but that the number and chromosomal location of these clusters varied among the cell lines. In interphase nuclei of primary tumors showing ERBB2 amplification (10/44), ERBB2 copies were seen as one to four clusters, also suggesting intrachromosomal localization. Regardless of the average level of amplification, all these tumors contained highly amplified cell subpopulations with at least 25, and sometimes more than 100, ERBB2 copies per cell. Tumors that did not show amplification by FISH (34/44) had an average of one to five ERBB2 copies scattered randomly in the nuclei and completely lacked cells with high copy levels. FISH results on primary tumors were concordant with slot blot results on amplification and with immunohistochemical detection of overexpression. Quantitative analysis of ERBB2 amplification by FISH may improve prognostic assessments based on the pattern of amplification and detection of heavily amplified tumor cell subpopulations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Schwab M. Oncogene amplification in tumor cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1986;47:235–281. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Band V., Zajchowski D., Stenman G., Morton C. C., Kulesa V., Connolly J., Sager R. A newly established metastatic breast tumor cell line with integrated amplified copies of ERBB2 and double minute chromosomes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1989 Sep;1(1):48–58. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870010109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Molecular themes in oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90636-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg A., Baldetorp B., Fernö M., Killander D., Olsson H., Sigurdsson H. ERBB2 amplification in breast cancer with a high rate of proliferation. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):137–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. M., McGuire W. L. Follow-up study of HER-2/neu amplification in primary breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Feb 1;51(3):944–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett I. P., Henry J. A., Angus B., Watchorn C. J., Wilkinson L., Hennessy C., Gullick W. J., Tuzi N. L., May F. E., Westley B. R. NCL-CB11, a new monoclonal antibody recognizing the internal domain of the c-erbB-2 oncogene protein effective for use on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue. J Pathol. 1990 May;161(1):15–25. doi: 10.1002/path.1711610105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Love S. B., Wright C., Barnes D. M., Gusterson B., Harris A. L., Altman D. G. c-erbB-2 protein overexpression in breast cancer is a risk factor in patients with involved and uninvolved lymph nodes. Br J Cancer. 1991 Mar;63(3):434–438. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi O. P., Holli K., Visakorpi T., Koivula T., Helin H. H., Isola J. J. Association of c-erbB-2 protein over-expression with high rate of cell proliferation, increased risk of visceral metastasis and poor long-term survival in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1991 Nov 11;49(5):650–655. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910490504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M. H., Popescu N. C., Amsbaugh S. C., King C. R. Overexpression of the EGF receptor-related proto-oncogene erbB-2 in human mammary tumor cell lines by different molecular mechanisms. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):605–610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre P., Stark G. R. A quantitative method for analyzing specific DNA sequences directly from whole cells. Anal Biochem. 1988 Oct;174(1):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. Mechanisms of tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1986 May;46(5):2203–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paik S., Hazan R., Fisher E. R., Sass R. E., Fisher B., Redmond C., Schlessinger J., Lippman M. E., King C. R. Pathologic findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project: prognostic significance of erbB-2 protein overexpression in primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1990 Jan;8(1):103–112. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1990.8.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson M. C., Dietrich K. D., Danyluk J., Paterson A. H., Lees A. W., Jamil N., Hanson J., Jenkins H., Krause B. E., McBlain W. A. Correlation between c-erbB-2 amplification and risk of recurrent disease in node-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 15;51(2):556–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Landegent J., Collins C., Fuscoe J., Segraves R., Lucas J., Gray J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome-specific libraries: detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9138–9142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saint-Ruf C., Gerbault-Seureau M., Viegas-Péquignot E., Zafrani B., Cassingena R., Dutrillaux B. Proto-oncogene amplification and homogeneously staining regions in human breast carcinomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1990 May;2(1):18–26. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870020105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):5989–5992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Amler L. C. Amplification of cellular oncogenes: a predictor of clinical outcome in human cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1990 Jan;1(3):181–193. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Godolphin W., Jones L. A., Holt J. A., Wong S. G., Keith D. E., Levin W. J., Stuart S. G., Udove J., Ullrich A. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):707–712. doi: 10.1126/science.2470152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Gorman P. A., Stark M. B., Groves R. P., Stark G. R. Distinctive chromosomal structures are formed very early in the amplification of CAD genes in Syrian hamster cells. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1219–1227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90417-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Debatisse M., Giulotto E., Wahl G. M. Recent progress in understanding mechanisms of mammalian DNA amplification. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90328-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandon A. K., Clark G. M., Chamness G. C., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. HER-2/neu oncogene protein and prognosis in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Aug;7(8):1120–1128. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.8.1120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkachuk D. C., Westbrook C. A., Andreeff M., Donlon T. A., Cleary M. L., Suryanarayan K., Homge M., Redner A., Gray J., Pinkel D. Detection of bcr-abl fusion in chronic myelogeneous leukemia by in situ hybridization. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):559–562. doi: 10.1126/science.2237408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask B. J., Hamlin J. L. Early dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification events in CHO cells usually occur on the same chromosome arm as the original locus. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1913–1925. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask B. J., Massa H., Kenwrick S., Gitschier J. Mapping of human chromosome Xq28 by two-color fluorescence in situ hybridization of DNA sequences to interphase cell nuclei. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):1–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda H., Hirohashi S., Shimosato Y., Hirota T., Tsugane S., Yamamoto H., Miyajima N., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T., Yokota J. Correlation between long-term survival in breast cancer patients and amplification of two putative oncogene-coamplification units: hst-1/int-2 and c-erbB-2/ear-1. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 1;49(11):3104–3108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanDevanter D. R., Piaskowski V. D., Casper J. T., Douglass E. C., Von Hoff D. D. Ability of circular extrachromosomal DNA molecules to carry amplified MYCN proto-oncogenes in human neuroblastomas in vivo. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Dec 5;82(23):1815–1821. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.23.1815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venter D. J., Tuzi N. L., Kumar S., Gullick W. J. Overexpression of the c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in human breast carcinomas: immunohistological assessment correlates with gene amplification. Lancet. 1987 Jul 11;2(8550):69–72. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92736-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M. The importance of circular DNA in mammalian gene amplification. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 15;49(6):1333–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M. J., Peterse J. L., Mooi W. J., Wisman P., Lomans J., Dalesio O., Nusse R. Neu-protein overexpression in breast cancer. Association with comedo-type ductal carcinoma in situ and limited prognostic value in stage II breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1988 Nov 10;319(19):1239–1245. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198811103191902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M., van de Bersselaar R., Devilee P., Cornelisse C., Peterse J., Nusse R. Amplification of the neu (c-erbB-2) oncogene in human mammmary tumors is relatively frequent and is often accompanied by amplification of the linked c-erbA oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):2019–2023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]