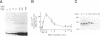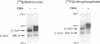Abstract
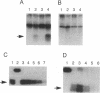
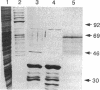
c-Jun and its oncogenic counterpart v-Jun are completely conserved within the region from Ser-63 to Ser-73; these serines are sites for phorbol ester-inducible c-Jun phosphorylation. Using a U937 human leukemic cell line stably expressing v-Jun, we have demonstrated that phorbol esters stimulate the in vivo phosphorylation of c-Jun but not v-Jun. We developed an in vitro protein kinase assay to characterize the c-Jun protein kinase and to examine the determinants underlying this differential phosphorylation. Fusion proteins between glutathione S-transferase and the N terminus of c-Jun, v-Jun, or several c-Jun mutants were used as substrates. A c-Jun kinase activity was affinity-purified 5000-fold by using glutathione S-transferase-c-Jun-glutathione-Sepharose beads and was found to phosphorylate the N terminus of c-Jun but not v-Jun or c-Jun containing a 27-amino acid N-terminal deletion found in v-Jun. These effects were also observed in vivo as phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate did not induce the phosphorylation of v-Jun or the c-Jun deletion mutant in U937 cell lines stably expressing these proteins. These findings indicate that the delta domain of c-Jun (amino acids 34-60), which is deleted in v-Jun, plays a critical role in regulating N-terminal c-Jun phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Luk D., Curran T. Transcriptional regulation by Fos and Jun in vitro: interaction among multiple activator and regulatory domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3624–3632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez E., Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Latour D. A., Seth A., Abate C., Curran T., Davis R. J. Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus primary sequence for substrate protein phosphorylation. Characterization of the phosphorylation of c-myc and c-jun proteins by an epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 669 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15277–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Park A., Tjian R. v-Src and EJ Ras alleviate repression of c-Jun by a cell-specific inhibitor. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):165–168. doi: 10.1038/352165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Tjian R. Control of c-Jun activity by interaction of a cell-specific inhibitor with regulatory domain delta: differences between v- and c-Jun. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binétruy B., Smeal T., Karin M. Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):122–127. doi: 10.1038/351122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Tjian R. Biochemical analysis of transcriptional activation by Jun: differential activity of c- and v-Jun. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Bohmann D., Tsuchie H., Tjian R., Vogt P. K. v-jun encodes a nuclear protein with enhancer binding properties of AP-1. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):705–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90408-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Monteclaro F. S., Mitsunobu F., Ball A. R., Jr, Chang C. H., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K. Efficient transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts by c-Jun requires structural modification in coding and noncoding sequences. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1677–1687. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T., Vogt P. K. The carboxy terminus of the viral Jun oncoprotein is required for complex formation with the cellular Fos protein. Oncogene. 1989 Feb;4(2):123–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin C. C., Kraft A. S. Protein kinase C-independent activation of c-jun and c-fos transcription by epidermal growth factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Mar 16;1134(2):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90036-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P., Ralph P. Human leukemic models of myelomonocytic development: a review of the HL-60 and U937 cell lines. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Apr;37(4):407–422. doi: 10.1002/jlb.37.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki Y., Bos T. J., Davis C., Starbuck M., Vogt P. K. Avian sarcoma virus 17 carries the jun oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2848–2852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Bos T. J., Vogt P. K., Bohmann D., Tjian R., Franza B. R., Jr Fos-associated protein p39 is the product of the jun proto-oncogene. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1010–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.3130660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütte J., Minna J. D., Birrer M. J. Deregulated expression of human c-jun transforms primary rat embryo cells in cooperation with an activated c-Ha-ras gene and transforms rat-1a cells as a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2257–2261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. L., Stone R. M., Datta R., Bernstein S. H., Kufe D. W. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of c-jun expression during monocytic differentiation of human myeloid leukemic cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3320–3323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo E., Preis L. H., Brown P. H., Birrer M. J. The role of jun and fos gene family members in 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate induced hemopoietic differentiation. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Oct;2(10):475–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- William F., Wagner F., Karin M., Kraft A. S. Multiple doses of diacylglycerol and calcium ionophore are necessary to activate AP-1 enhancer activity and induce markers of macrophage differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18166–18171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]