Abstract
A 3-kilobase-pair gene for rat brain prostaglandin D synthase [(5Z,13E)-(15S)-9 alpha,11 alpha-epidoxy-15-hydroxyprosta-5,13- dienoate D-isomerase, EC 5.3.99.2], which belongs to the lipocalin family, was isolated from a rat genomic DNA library by plaque hybridization with the cDNA for the enzyme. The gene contains seven exons, and all the splice donor and acceptor sites conform to the GT/AG rule. Transcription initiates at a guanine residue 39 base pairs upstream of the translation initiation codon, as determined by primer-extension analysis of rat brain mRNA. The 5'-flanking region of the gene lacks typical transcriptional regulatory sequences, such as TATA and CAAT boxes, but contains several sets of inverted repeats, direct repeats, and sequences resembling the transcriptional factor Sp1-binding site. The gene structure of prostaglandin D synthase is remarkably analogous to those of other lipocalins, such as beta-lactoglobulin, alpha 2-urinary globulin, placental protein 14, and alpha 1-microglobulin, in terms of number and sizes of exons and phase of splicing of introns. Furthermore, in a multiple alignment of the deduced amino acid sequences, positions of exon/intron junction of the prostaglandin D synthase gene are highly conserved and located around the positions of those of the genes for other lipocalins despite a weak homology.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali S., Clark A. J. Characterization of the gene encoding ovine beta-lactoglobulin. Similarity to the genes for retinol binding protein and other secretory proteins. J Mol Biol. 1988 Feb 5;199(3):415–426. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90614-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Ghazal P., Bingham R. W., Barrett D., Bishop J. O. Sequence structures of a mouse major urinary protein gene and pseudogene compared. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3159–3165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04059.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colantuoni V., Romano V., Bensi G., Santoro C., Costanzo F., Raugei G., Cortese R. Cloning and sequencing of a full length cDNA coding for human retinol-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7769–7776. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R., Eckley D. M., Papaconstantinou J. Nucleotide sequence of the mouse alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene 1. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 25;26(17):5244–5250. doi: 10.1021/bi00391a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan S. W., Newcomer M. E., Jones T. A. Crystallographic refinement of human serum retinol binding protein at 2A resolution. Proteins. 1990;8(1):44–61. doi: 10.1002/prot.340080108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dear T. N., Campbell K., Rabbitts T. H. Molecular cloning of putative odorant-binding and odorant-metabolizing proteins. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10376–10382. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Pizza M. G., Metspalu A., Cortese R. Structure and expression of the genes coding for human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2289–2296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02503.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D. T., McLean J. W., Wion K. L., Trent J. M., Drabkin H. A., Lawn R. M. Human apolipoprotein D gene: gene sequence, chromosome localization, and homology to the alpha 2u-globulin superfamily. DNA. 1987 Jun;6(3):199–204. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower D. R., North A. C., Attwood T. K. Mouse oncogene protein 24p3 is a member of the lipocalin protein family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 15;180(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh Y., Urade Y., Fujimoto N., Hayaishi O. Content and formation of prostaglandins and distribution of prostaglandin-related enzyme activities in the rat ocular system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 25;921(2):302–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayaishi O. Molecular mechanisms of sleep-wake regulation: roles of prostaglandins D2 and E2. FASEB J. 1991 Aug;5(11):2575–2581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Schneider M., Epp O., Mayr I., Messerschmidt A., Pflugrath J., Kayser H. Crystallization, crystal structure analysis and preliminary molecular model of the bilin binding protein from the insect Pieris brassicae. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):423–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiyoshi Y., Endo H., Yamamoto M. Length polymorphism in the 3' noncoding region of rat hepatic alpha 2u-globulin mRNAs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 9;910(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Narumiya S., Hayaishi O. Prostaglandin D2: a biochemical perspective. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1989 Sep;37(4):219–234. doi: 10.1016/0952-3278(89)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumeyer J. F., Polazzi J. O., Kotick M. P. The mRNA for a proteinase inhibitor related to the HI-30 domain of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor also encodes alpha-1-microglobulin (protein HC). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):7839–7850. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen J. N., Caceres I., Eliopoulos E. E., Zagalsky P. F., Findlay J. B. Complete sequence and model for the A2 subunit of the carotenoid pigment complex, crustacyanin. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 23;197(2):407–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent B. C., Nilsson M. H., Båvik C. O., Jones T. A., Sundelin J., Peterson P. A. Characterization of the rat retinol-binding protein gene and its comparison to the three-dimensional structure of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11476–11480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent B. C., Nilsson M. H., Båvik C. O., Jones T. A., Sundelin J., Peterson P. A. Characterization of the rat retinol-binding protein gene and its comparison to the three-dimensional structure of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11476–11480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt C. M., Board P. G. Structure and characterisation of a duplicated human alpha 1 acid glycoprotein gene. Gene. 1988 Jun 15;66(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
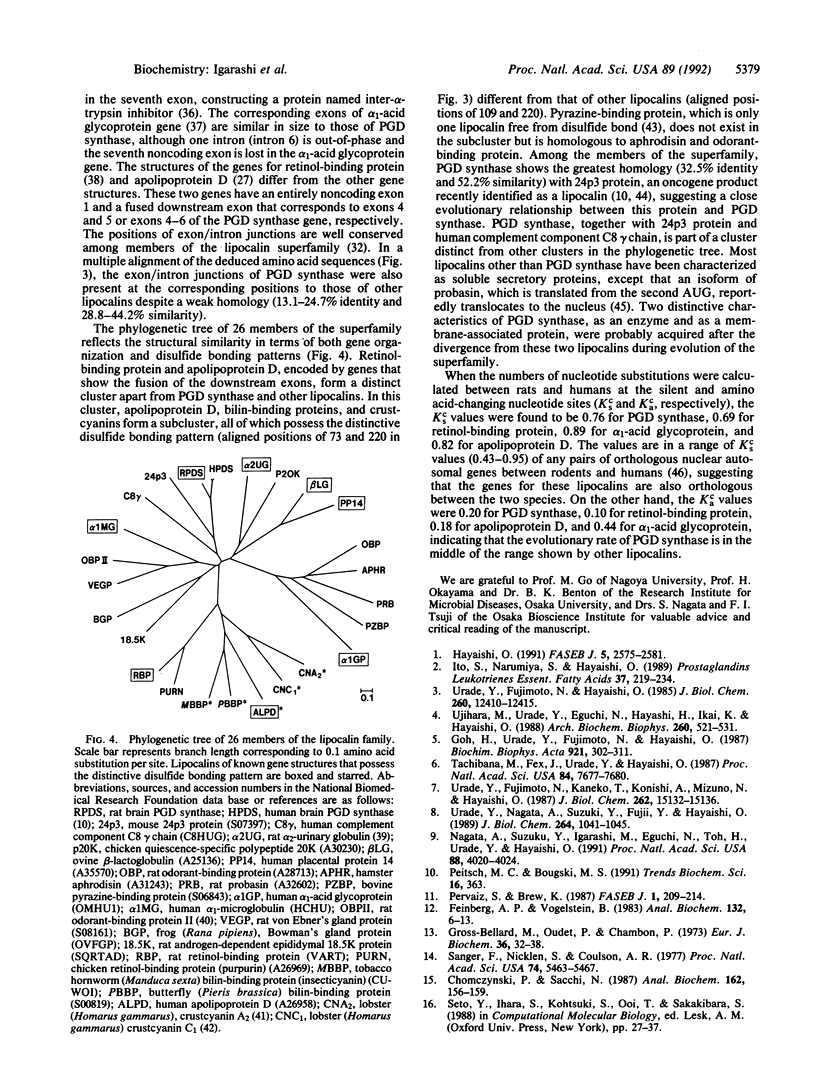
- Nagata A., Suzuki Y., Igarashi M., Eguchi N., Toh H., Urade Y., Hayaishi O. Human brain prostaglandin D synthase has been evolutionarily differentiated from lipophilic-ligand carrier proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4020–4024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Nakashima H., Kanehisa M., Ooi T. Detection of weak sequence homology of proteins for tertiary structure prediction. Protein Seq Data Anal. 1987;1(2):107–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North A. C. Three-dimensional arrangement of conserved amino acid residues in a superfamily of specific ligand-binding proteins. Int J Biol Macromol. 1989 Feb;11(1):56–58. doi: 10.1016/0141-8130(89)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peitsch M. C., Boguski M. S. The first lipocalin with enzymatic activity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Oct;16(10):363–363. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90149-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pervaiz S., Brew K. Homology and structure-function correlations between alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and serum retinol-binding protein and its relatives. FASEB J. 1987 Sep;1(3):209–214. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.3.3622999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence A. M., Sheppard P. C., Davie J. R., Matuo Y., Nishi N., McKeehan W. L., Dodd J. G., Matusik R. J. Regulation of a bifunctional mRNA results in synthesis of secreted and nuclear probasin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7843–7847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spreyer P., Schaal H., Kuhn G., Rothe T., Unterbeck A., Olek K., Müller H. W. Regeneration-associated high level expression of apolipoprotein D mRNA in endoneurial fibroblasts of peripheral nerve. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2479–2484. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M., Fex J., Urade Y., Hayaishi O. Brain-type prostaglandin D synthetase occurs in the rat cochlea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7677–7680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirindelli R., Keen J. N., Cavaggioni A., Eliopoulos E. E., Findlay J. B. Complete amino acid sequence of pyrazine-binding protein from cow nasal mucosa. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 20;185(3):569–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ujihara M., Urade Y., Eguchi N., Hayashi H., Ikai K., Hayaishi O. Prostaglandin D2 formation and characterization of its synthetases in various tissues of adult rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Feb 1;260(2):521–531. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90477-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urade Y., Fujimoto N., Hayaishi O. Purification and characterization of rat brain prostaglandin D synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12410–12415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urade Y., Fujimoto N., Kaneko T., Konishi A., Mizuno N., Hayaishi O. Postnatal changes in the localization of prostaglandin D synthetase from neurons to oligodendrocytes in the rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15132–15136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urade Y., Nagata A., Suzuki Y., Fujii Y., Hayaishi O. Primary structure of rat brain prostaglandin D synthetase deduced from cDNA sequence. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1041–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaisse C., Atger M., Potier B., Milgrom E. Human placental protein 14 gene: sequence and characterization of a short duplication. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Jul-Aug;9(6):401–413. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetr H., Gebhard W. Structure of the human alpha 1-microglobulin-bikunin gene. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990 Dec;371(12):1185–1196. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1990.371.2.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagalsky P. F., Eliopoulos E. E., Findlay J. B. The architecture of invertebrate carotenoproteins. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1990;97(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(90)90171-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]