Abstract
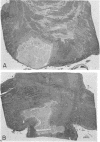
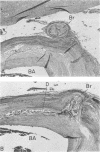
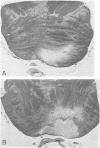
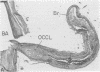
In a case in which the patient became totally paralysed except for blinking and vertical eye movements, microscopic serial sections of the pons showed bilateral infarcts which were due to occlusion of two small basilar branch arteries, one on each side. One basilar branch was occluded by an atheroma lying at its junction with the basilar artery and the other by an intramural dissection within the wall of the basilar artery. This case provides the clinico-pathological correlation for two further basilar branch infarcts. An unusual finding was that one of the branch arteries supplied the basis pontis and medulla bilaterally.
Full text
PDF
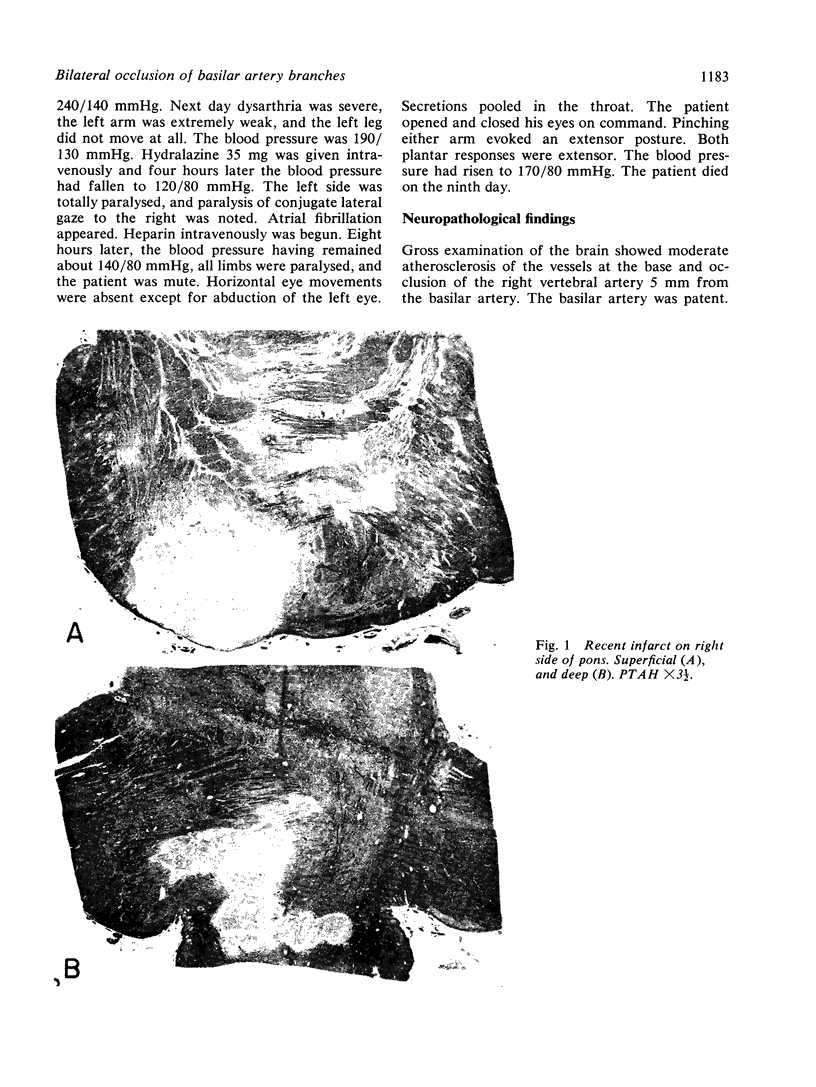
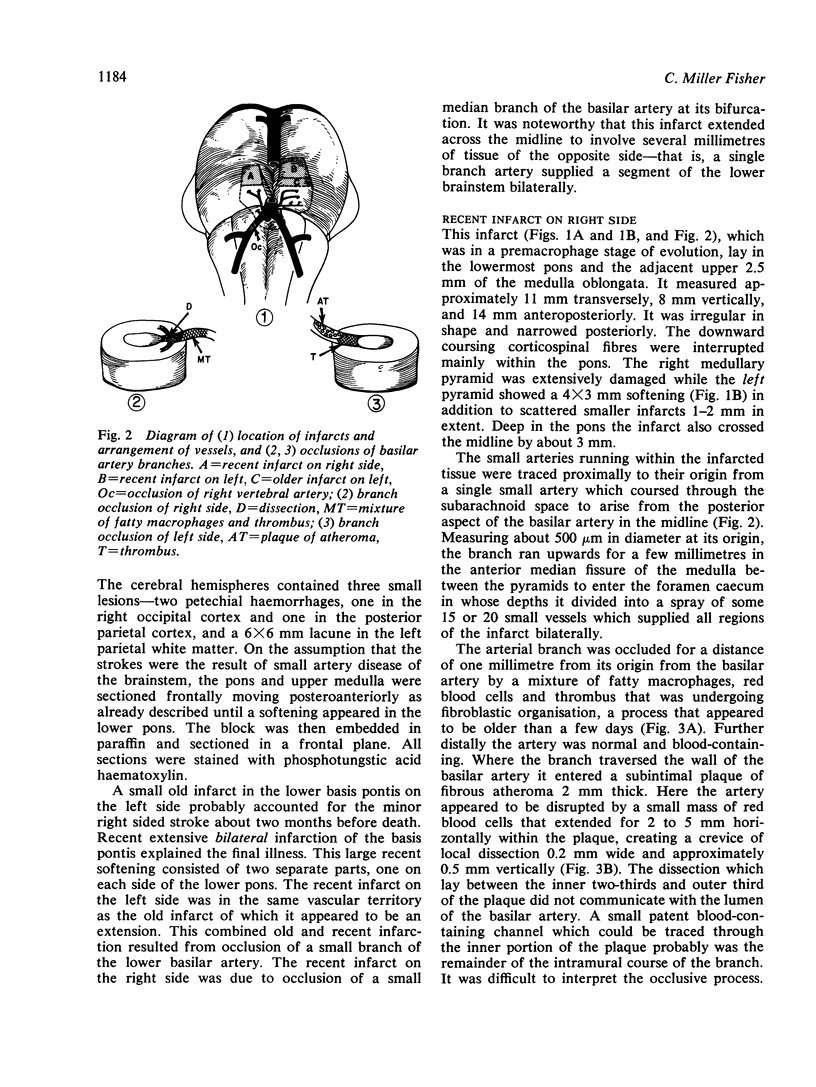
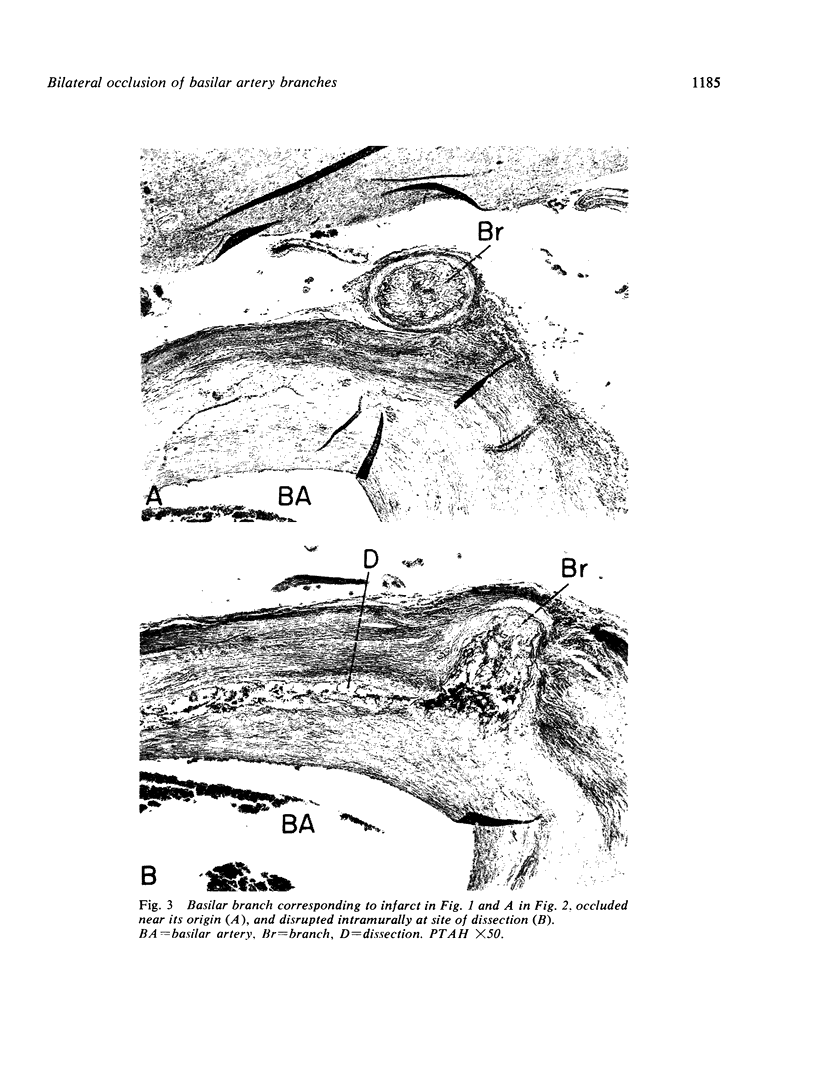
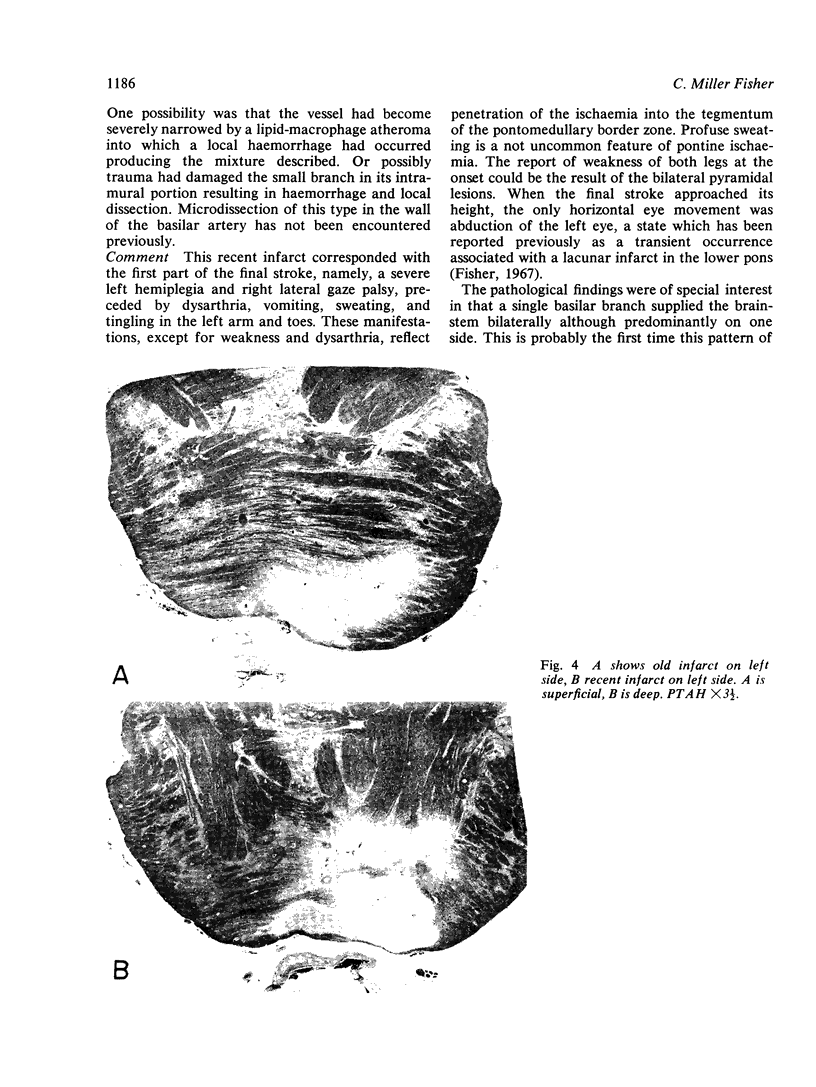

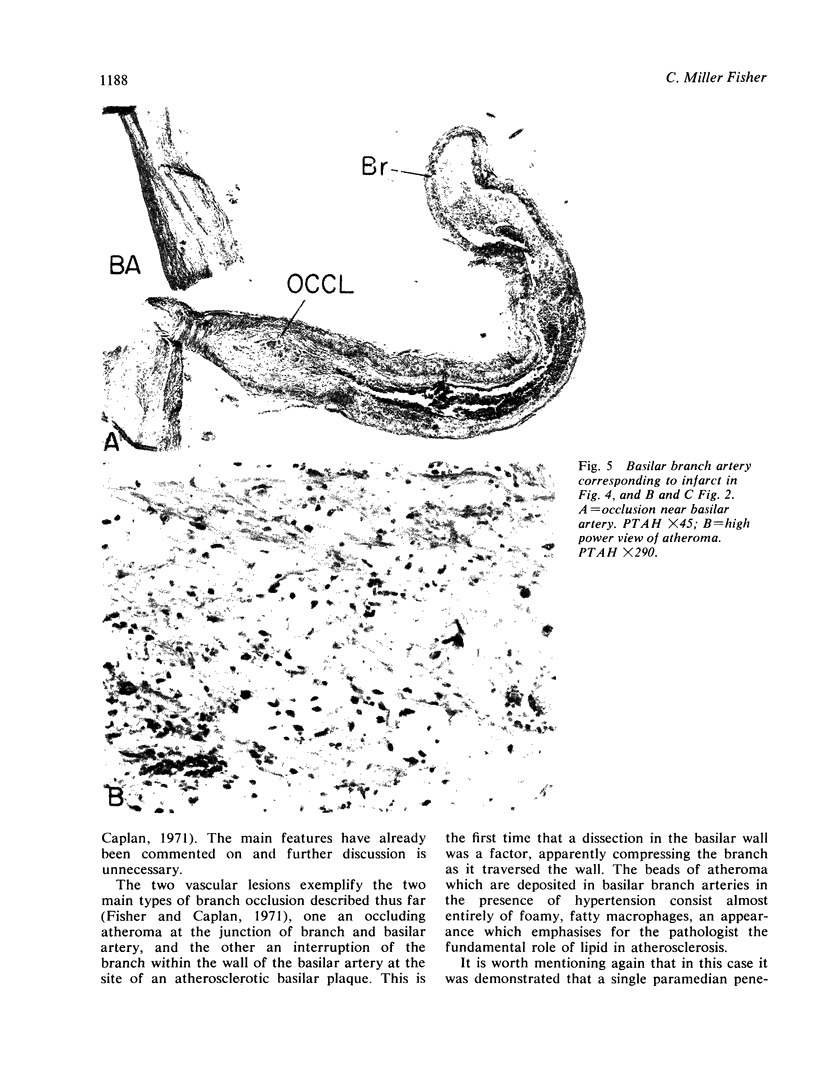

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fisher C. M., Caplan L. R. Basilar artery branch occlusion: a cause of pontine infarction. Neurology. 1971 Sep;21(9):900–905. doi: 10.1212/wnl.21.9.900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]