Abstract
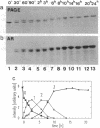
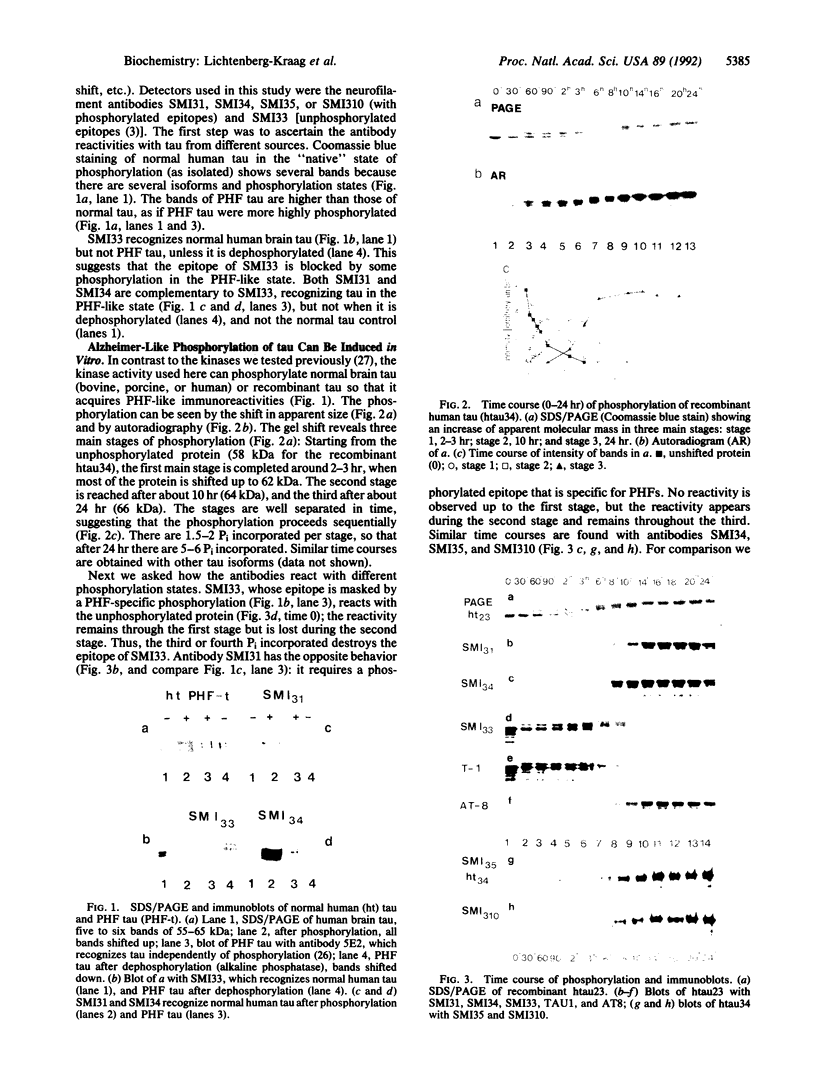
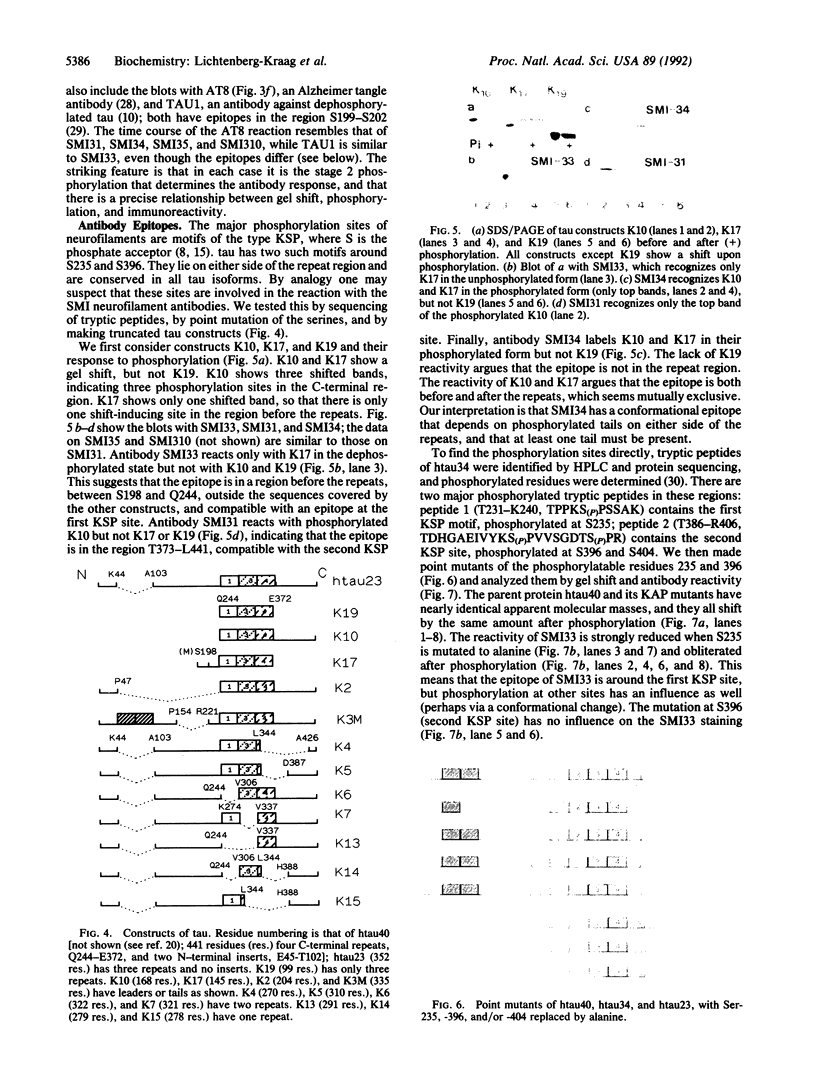
We have studied the phosphorylation of tau protein from Alzheimer paired helical filaments, of tau from normal human brain, and of recombinant tau isoforms. As a tool we used monoclonal antibodies against neurofilament protein [Sternberger, N., Sternberger, L. & Ulrich, J. (1985) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 4274-4276] that crossreact with tau in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. This allowed us to deduce the state of phosphorylation in normal and pathological tau, as well as antibody epitopes. The epitope of antibody SMI33 is at the first Lys-Ser-Pro sequence motif (residues 234-236) and requires an unphosphorylated Ser-235. Antibody SMI31 binds between Ser-396 (in the second Lys-Ser-Pro motif) and Ser-404, both of which must be phosphorylated. SMI34 has a conformational epitope that depends on the interaction between regions on either side of the microtubule-binding region; it also requires phosphorylation. The phosphorylatable serines detected by the SMI antibodies are part of Ser-Pro motifs and can be phosphorylated by a protein kinase activity that can be used to induce a paired helical filament-like state in human brain tau in vitro. The phosphates are incorporated in several stages that can be identified by antibody reactivity and gel shift. This suggests a role for the phosphorylation sites in Alzheimer disease, as well as the involvement of a Ser-Pro-directed protein kinase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bancher C., Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Fried V. A., Smith H. T., Wisniewski H. M. Abnormal phosphorylation of tau precedes ubiquitination in neurofibrillary pathology of Alzheimer disease. Brain Res. 1991 Jan 18;539(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90681-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Cole R. D. Phosphorylation of tau proteins to a state like that in Alzheimer's brain is catalyzed by a calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase and modulated by phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17577–17583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biernat J., Mandelkow E. M., Schröter C., Lichtenberg-Kraag B., Steiner B., Berling B., Meyer H., Mercken M., Vandermeeren A., Goedert M. The switch of tau protein to an Alzheimer-like state includes the phosphorylation of two serine-proline motifs upstream of the microtubule binding region. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1593–1597. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05204.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder L. I., Frankfurter A., Rebhun L. I. The distribution of tau in the mammalian central nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1371–1378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard B. J., Ingram V. M. Age-related neurofilament phosphorylation in normal human brains. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 May-Jun;10(3):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90059-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman M. P., Anderton B. H. Phosphate-dependent monoclonal antibodies to neurofilaments and Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles recognize a synthetic phosphopeptide. J Neurochem. 1990 May;54(5):1548–1555. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Location and sequence characterization of the major phosphorylation sites of the high molecular mass neurofilament proteins M and H. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 14;221(2):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80964-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Sisodia S. S., Price D. L. Neurofibrillary tangles and beta-amyloid deposits in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1991 Oct;1(3):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(91)90067-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Jakes R., Rutherford D., Crowther R. A. Multiple isoforms of human microtubule-associated protein tau: sequences and localization in neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Wischik C. M., Crowther R. A., Walker J. E., Klug A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding a core protein of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease: identification as the microtubule-associated protein tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4051–4055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. G., Davies P. A preparation of Alzheimer paired helical filaments that displays distinct tau proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5827–5831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Tung Y. C., Quinlan M., Wisniewski H. M., Binder L. I. Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagestedt T., Lichtenberg B., Wille H., Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E. Tau protein becomes long and stiff upon phosphorylation: correlation between paracrystalline structure and degree of phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1643–1651. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmler A., Drechsel D., Kirschner M. W., Martin D. W., Jr Tau consists of a set of proteins with repeated C-terminal microtubule-binding domains and variable N-terminal domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1381–1388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro K., Omori A., Sato K., Tomizawa K., Imahori K., Uchida T. A serine/threonine proline kinase activity is included in the tau protein kinase fraction forming a paired helical filament epitope. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jul 22;128(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90259-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Orecchio L. D., Binder L., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M., Lee G. Epitopes that span the tau molecule are shared with paired helical filaments. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S. Tau protein and Alzheimer's disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;2(1):101–104. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ksiezak-Reding H., Davies P., Yen S. H. Alz 50, a monoclonal antibody to Alzheimer's disease antigen, cross-reacts with tau proteins from bovine and normal human brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):7943–7947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ksiezak-Reding H., Dickson D. W., Davies P., Yen S. H. Recognition of tau epitopes by anti-neurofilament antibodies that bind to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3410–3414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Cowan N., Kirschner M. The primary structure and heterogeneity of tau protein from mouse brain. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):285–288. doi: 10.1126/science.3122323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Balin B. J., Otvos L., Jr, Trojanowski J. Q. A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal Tau. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.1899488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Otvos L., Jr, Schmidt M. L., Trojanowski J. Q. Alzheimer disease tangles share immunological similarities with multiphosphorylation repeats in the two large neurofilament proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7384–7388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercken M., Vandermeeren M., Lübke U., Six J., Boons J., Vanmechelen E., Van de Voorde A., Gheuens J. Affinity purification of human tau proteins and the construction of a sensitive sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for human tau detection. J Neurochem. 1992 Feb;58(2):548–553. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H. E., Hoffmann-Posorske E., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Determination and location of phosphoserine in proteins and peptides by conversion to S-ethylcysteine. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:169–185. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01016-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukina N., Kosik K. S., Selkoe D. J. Recognition of Alzheimer paired helical filaments by monoclonal neurofilament antibodies is due to crossreaction with tau protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3415–3419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder H. M., Ingram V. M. Two novel kinases phosphorylate tau and the KSP site of heavy neurofilament subunits in high stoichiometric ratios. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3325–3343. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03325.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner B., Mandelkow E. M., Biernat J., Gustke N., Meyer H. E., Schmidt B., Mieskes G., Söling H. D., Drechsel D., Kirschner M. W. Phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein tau: identification of the site for Ca2(+)-calmodulin dependent kinase and relationship with tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer tangles. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3539–3544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Sternberger N. H. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated forms of neurofilaments in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6126–6130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger N. H., Sternberger L. A., Ulrich J. Aberrant neurofilament phosphorylation in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4274–4276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Mirra S. S., Pollock N. J., Binder L. I. Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer disease share antigenic determinants with the axonal microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4040–4043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Sternberger N. H., Rubinstein L. J., Herman M. M., Binder L. I., Sternberger L. A. Abnormal processing of multiple proteins in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8045–8049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]