Abstract
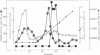
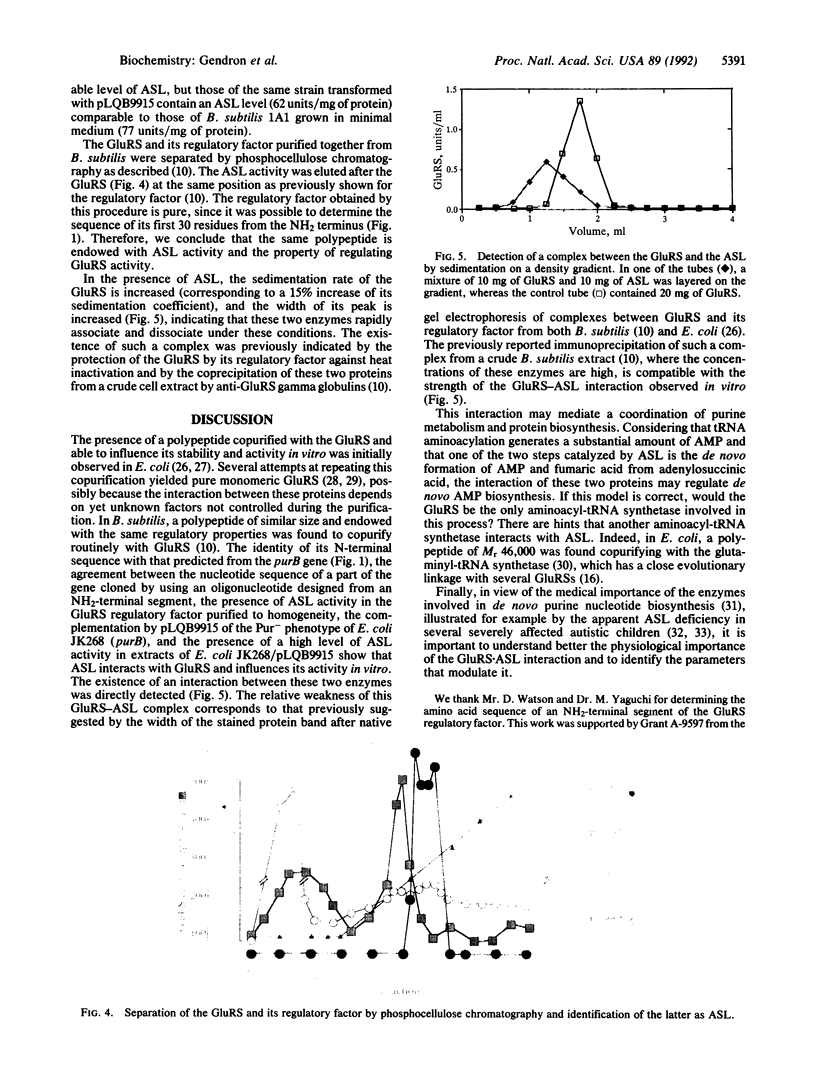
In Bacillus subtilis, the glutamyl-tRNA synthetase [L-glutamate:tRNA(Glu) ligase (AMP-forming), EC 6.1.1.17] is copurified with a polypeptide of M(r) 46,000 that influences its affinity for its substrates and increases its thermostability. The gene encoding this regulatory factor was cloned with the aid of a 41-mer oligonucleotide probe corresponding to the amino acid sequence of an NH2-terminal segment of this factor. The nucleotide sequence of this gene and the physical map of the 1475-base-pair fragment on which it was cloned are identical to those of purB, which encodes the adenylosuccinate lyase (adenylosuccinate AMP-lyase, EC 4.3.2.2), an enzyme involved in the de novo synthesis of purines. This gene complements the purB mutation of Escherichia coli JK268, and its presence on a multicopy plasmid behind the trc promoter in the purB- strain gives an adenylosuccinate lyase level comparable to that in wild-type B. subtilis. A complex between the adenylosuccinate lyase and the glutamyl-tRNA synthetase was detected by centrifugation on a density gradient. The interaction between these enzymes may play a role in the coordination of purine metabolism and protein biosynthesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aimi J., Badylak J., Williams J., Chen Z. D., Zalkin H., Dixon J. E. Cloning of a cDNA encoding adenylosuccinate lyase by functional complementation in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9011–9014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akins R. A., Lambowitz A. M. A protein required for splicing group I introns in Neurospora mitochondria is mitochondrial tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase or a derivative thereof. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann E., Ochs B., Abel K. J. Tightly regulated tac promoter vectors useful for the expression of unfused and fused proteins in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Sep 30;69(2):301–315. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barshop B. A., Alberts A. S., Gruber H. E. Kinetic studies of mutant human adenylosuccinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 9;999(1):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breton R., Watson D., Yaguchi M., Lapointe J. Glutamyl-tRNA synthetases of Bacillus subtilis 168T and of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Cloning and sequencing of the gltX genes and comparison with other aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18248–18255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow K. C., Wong J. T. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the structural gene coding for Bacillus subtilis tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):537–543. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90518-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS J. B., NIVEN C. F., Jr Nutrition of the heterofermentative Lactobacilli that cause greening of cured meat products. J Bacteriol. 1951 Nov;62(5):599–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.5.599-603.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebbole D. J., Zalkin H. Cloning and characterization of a 12-gene cluster from Bacillus subtilis encoding nine enzymes for de novo purine nucleotide synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8274–8287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriani G., Delarue M., Poch O., Gangloff J., Moras D. Partition of tRNA synthetases into two classes based on mutually exclusive sets of sequence motifs. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):203–206. doi: 10.1038/347203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadar R., Slonim A., Kuhn J. Role of D-tryptophan oxidase in D-tryptophan utilization by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1096–1104. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1096-1104.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert C. J., Labouesse M., Dujardin G., Slonimski P. P. The NAM2 proteins from S. cerevisiae and S. douglasii are mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetases, and are involved in mRNA splicing. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):473–483. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02835.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoben P., Söll D. Glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase of Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1985;113:55–59. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)13011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeken J., Van den Berghe G. An infantile autistic syndrome characterised by the presence of succinylpurines in body fluids. Lancet. 1984 Nov 10;2(8411):1058–1061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern D., Potier S., Boulanger Y., Lapointe J. The monomeric glutamyl-tRNA synthetase of Escherichia coli. Purification and relation between its structural and catalytic properties. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):518–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kittle J. D., Jr, Mohr G., Gianelos J. A., Wang H., Lambowitz A. M. The Neurospora mitochondrial tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase is sufficient for group I intron splicing in vitro and uses the carboxy-terminal tRNA-binding domain along with other regions. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1009–1021. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe J., Levasseur S., Kern D. Glutamyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1985;113:42–49. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)13009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe J., Söll D. Glutamyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase of Escherichia coli. 3. Influence of the 46K protein on the affinity of the 56K glutamyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase for its substrates. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):4982–4985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe J., Söll D. Glutamyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase of Escherichia coli. I. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):4966–4974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N. Markedly unbiased codon usage in Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1985;40(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers D. M., Ginsburg A. Monomeric structure of glutamyl-tRNA synthetase in Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Dec;191(2):673–679. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90406-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proulx M., Duplain L., Lacoste L., Yaguchi M., Lapointe J. The monomeric glutamyl-tRNA synthetase from Bacillus subtilis 168 and its regulatory factor. Their purification, characterization, and the study of their interaction. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):753–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney S. D., Schimmel P. An aminoacyl tRNA synthetase binds to a specific DNA sequence and regulates its gene transcription. Nature. 1981 Jun 25;291(5817):632–635. doi: 10.1038/291632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putzer H., Brakhage A. A., Grunberg-Manago M. Independent genes for two threonyl-tRNA synthetases in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4593–4602. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4593-4602.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields D. C., Sharp P. M. Synonymous codon usage in Bacillus subtilis reflects both translational selection and mutational biases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):8023–8040. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.8023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M., Graffe M., Dondon J., Grunberg-Manago M. tRNA-like structures and gene regulation at the translational level: a case of molecular mimicry in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2417–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward D. O. Adenylosuccinate AMP-lyase (Neurospora crassa). Methods Enzymol. 1978;51:202–207. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)51028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]