Abstract
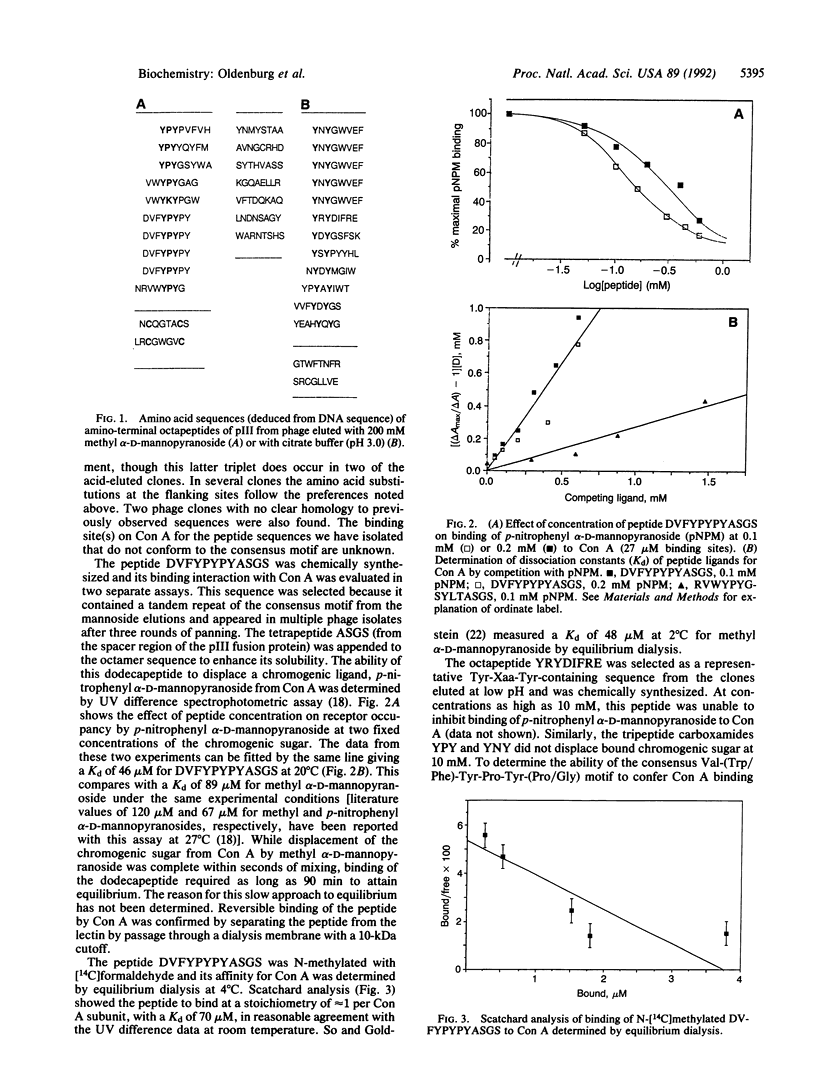
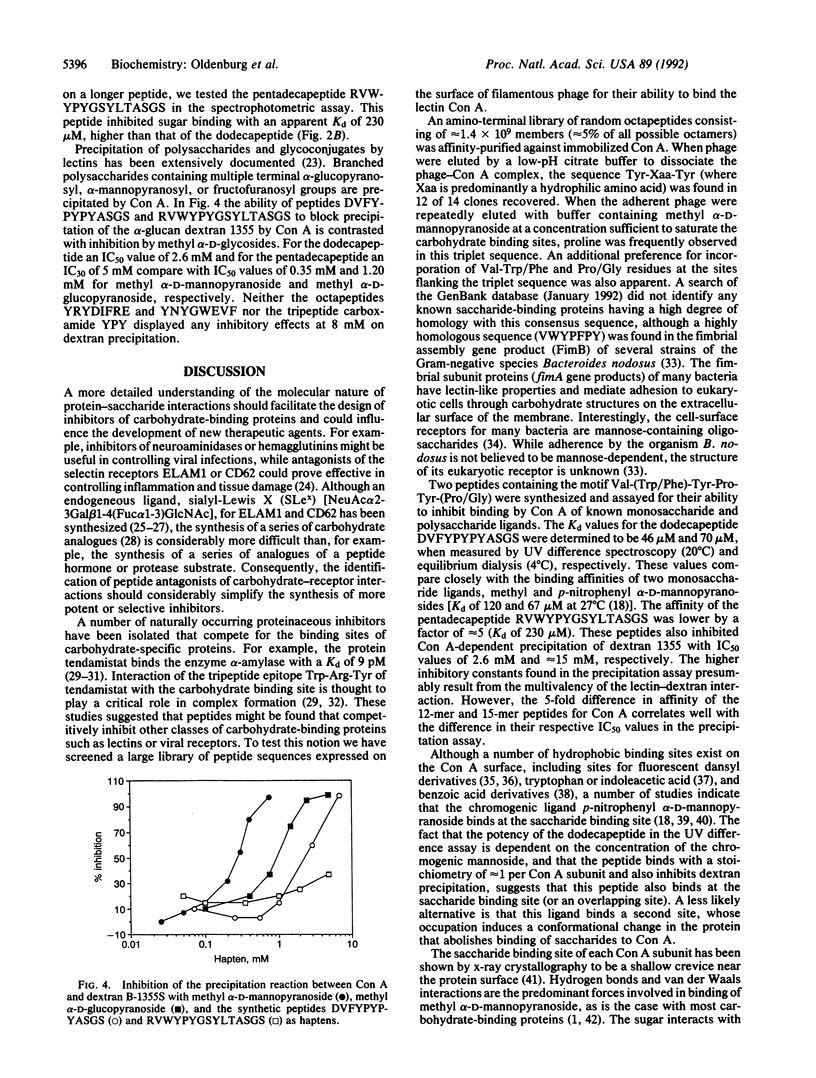
Peptide ligands for the carbohydrate-binding protein concanavalin A (Con A) have been identified by screening a large, diverse peptide library expressed on the surface of filamentous phage. A dodecapeptide containing the consensus sequence Tyr-Pro-Tyr was found to bind Con A with an affinity (dissociation constant, Kd) of 46 microM, comparable to that of a known carbohydrate ligand, methyl alpha-D-mannopyranoside (Kd of 89 microM). In addition the peptide inhibited precipitation of the alpha-glucan dextran 1355 by Con A. Given the complexity of oligosaccharide synthesis, the prospect of finding peptides that competitively inhibit carbohydrate-specific receptors may simplify the development of new therapeutic agents.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass S., Greene R., Wells J. A. Hormone phage: an enrichment method for variant proteins with altered binding properties. Proteins. 1990;8(4):309–314. doi: 10.1002/prot.340080405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessler W., Shafer J. A., Goldstein I. J. A spectrophotometric study of the carbohydrate binding site of concanavalina. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2819–2822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cwirla S. E., Peters E. A., Barrett R. W., Dower W. J. Peptides on phage: a vast library of peptides for identifying ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6378–6382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derewenda Z., Yariv J., Helliwell J. R., Kalb A. J., Dodson E. J., Papiz M. Z., Wan T., Campbell J. The structure of the saccharide-binding site of concanavalin A. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2189–2193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08341.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin J. J., Panganiban L. C., Devlin P. E. Random peptide libraries: a source of specific protein binding molecules. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):404–406. doi: 10.1126/science.2143033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Wang J. L. Binding and functional properties of concanavalin A and its derivatives. III. Interactions with indoleacetic acid and other hydrophobic ligands. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3016–3022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor S. P., Read J. L., Pirrung M. C., Stryer L., Lu A. T., Solas D. Light-directed, spatially addressable parallel chemical synthesis. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):767–773. doi: 10.1126/science.1990438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., Hayes C. E. The lectins: carbohydrate-binding proteins of plants and animals. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1978;35:127–340. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman K. D., Ainsworth C. F. Structure of the concanavalin A-methyl alpha-D-mannopyranoside complex at 6-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):1120–1128. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassing G. S., Goldstein I. J. Ultraviolet difference spectral studies on concanavalin A. Carbohydrate interaction. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Nov;16(3):549–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs M., Dalrymple B. P., Cox P. T., Livingstone S. P., Delaney S. F., Mattick J. S. Organization of the fimbrial gene region of Bacteroides nodosus: class I and class II strains. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):543–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann O., Vértesy L., Braunitzer G. The primary structure of alpha-amylase inhibitor Z-2685 from Streptomyces parvullus FH-1641. Sequence homology between inhibitor and alpha-amylase. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Dec;366(12):1161–1168. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Pinilla C., Blondelle S. E., Appel J. R., Dooley C. T., Cuervo J. H. Generation and use of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for basic research and drug discovery. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):84–86. doi: 10.1038/354084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet M. Factors affecting the molecular structure and the agglutinating ability of concanavalin A and other lectins. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 15;59(2):627–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyama A., Ishida H., Kiso M., Hasegawa A. Total synthesis of sialyl Lewis X. Carbohydr Res. 1991 Jan 15;209:c1–c4. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(91)80171-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline A. D., Braun W., Wüthrich K. Studies by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry of the solution conformation of the alpha-amylase inhibitor tendamistat. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 20;189(2):377–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90519-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. S., Salmon S. E., Hersh E. M., Hruby V. J., Kazmierski W. M., Knapp R. J. A new type of synthetic peptide library for identifying ligand-binding activity. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):82–84. doi: 10.1038/354082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C. Ecology, physiology, and genetics of fimbriae and pili. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:79–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmley S. F., Smith G. P. Antibody-selectable filamentous fd phage vectors: affinity purification of target genes. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):305–318. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90495-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pflugrath J. W., Wiegand G., Huber R., Vértesy L. Crystal structure determination, refinement and the molecular model of the alpha-amylase inhibitor Hoe-467A. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 20;189(2):383–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90520-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A. Atomic structures of periplasmic binding proteins and the high-affinity active transport systems in bacteria. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Jan 30;326(1236):341–352. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1990.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A. Carbohydrate-binding proteins: tertiary structures and protein-sugar interactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:287–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. H., Means G. E. Radioactive labeling of proteins in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):831–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. D., Goldstein I. J. Binding of hydrophobic ligands to plant lectins: titration with arylaminonaphthalenesulfonates. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 15;224(2):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90235-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. K., Smith G. P. Searching for peptide ligands with an epitope library. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):386–390. doi: 10.1126/science.1696028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins as cell recognition molecules. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):227–234. doi: 10.1126/science.2552581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So L. L., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. IV. Application of the quantitative precipitin method to polysaccharide-concanavalin A interaction. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1617–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Lasky L. A. Cell adhesion. Sticky sugars for selectins. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):196–197. doi: 10.1038/349196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoolman L. M. Adhesion molecules controlling lymphocyte migration. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):907–910. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90620-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D., James P., Rao N., Foxall C., Abbas S., Dasgupta F., Nashed M., Hasegawa A., Kiso M., Asa D. Structural requirements for the carbohydrate ligand of E-selectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10372–10376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vértesy L., Oeding V., Bender R., Zepf K., Nesemann G. Tendamistat (HOE 467), a tight-binding alpha-amylase inhibitor from Streptomyces tendae 4158. Isolation, biochemical properties. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 15;141(3):505–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Skehel J. J. The structure and function of the hemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:365–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Homer L. D., Shafer J. A., Goldstein I. J., Garegg P. J., Hultberg H., Iversen T., Johansson R. Characterization of the extended carbohydrate binding site of concanavalin A: specificity for interaction with the nonreducing termini of alpha-(1 leads to 2)-linked disaccharides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jul;209(2):555–564. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90313-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Shafer J. A., Goldstein I. J., Adamson T. Biphasic association of p-nitrophenyl 2-O-alpha-D-mannopyranosyl-alpha-D-mannopyranoside and concanavalin A as detected by stopped flow spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8538–8544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Shafer J. A., Goldstein I. J. Heterogeneity of concanavalin A as detected by its binding to p-nitrophenyl 2-O-alpha-D-mannopyranosyl-alpha-D-mannopyranoside. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8533–8537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang D. C., Gall W. E., Edelman G. M. Rotational correlation time of concanavalin A after interaction with a fluorescent probe. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):7018–7023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



