Abstract
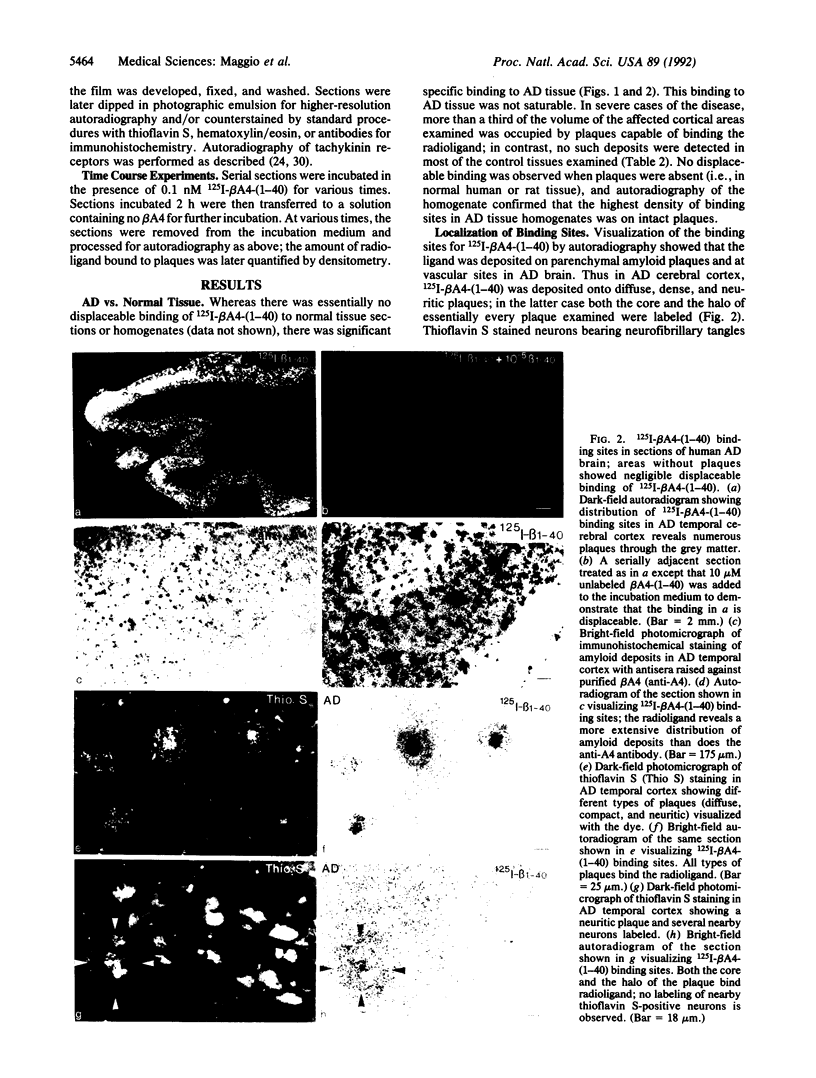
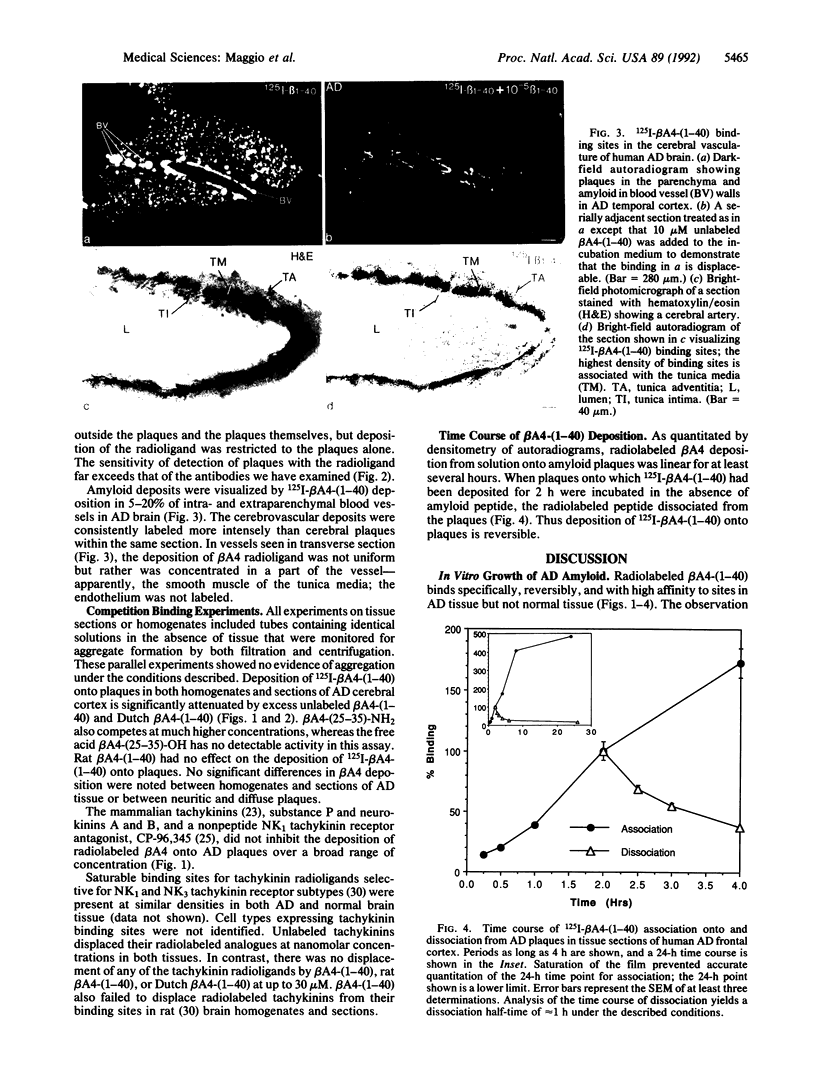
The salient pathological feature of Alzheimer disease (AD) is the presence of a high density of amyloid plaques in the brain tissue of victims. The plaques are predominantly composed of human beta-amyloid peptide (beta A4), a 40-mer whose neurotoxicity is related to its aggregation. Radioiodinated human beta A4 is rapidly deposited in vitro from a dilute (less than 10 pM) solution onto neuritic and diffuse plaques and cerebrovascular amyloid in AD brain tissue, whereas no deposition is detectable in tissue without performed plaques. This growth of plaques by deposition of radiolabeled beta A4 to plaques is reversible, with a dissociation half-time of approximately 1 h. The fraction of grey matter occupied by plaques that bind radiolabeled beta A4 in vitro is dramatically larger in AD cortex (23 +/- 11%) than in age-matched normal controls (less than 2%). In contrast to the human peptide, rat/mouse beta A4 (differing at three positions from human beta A4) does not affect the deposition of radiolabeled human beta A4. beta A4 has no detectable interaction with tachykinin receptors in rat or human brain. The use of radioiodinated beta A4 provides an in vitro system for the quantitative evaluation of agents or conditions that may inhibit or enhance the growth or dissolution of AD plaques. This reagent also provides an extremely sensitive method for visualizing various types of amyloid deposits and a means for characterizing and locating sites of amyloid peptide binding to cells and tissues.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrow C. J., Zagorski M. G. Solution structures of beta peptide and its constituent fragments: relation to amyloid deposition. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):179–182. doi: 10.1126/science.1853202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño E. M., Ghiso J., Prelli F., Gorevic P. D., Migheli A., Frangione B. In vitro formation of amyloid fibrils from two synthetic peptides of different lengths homologous to Alzheimer's disease beta-protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):782–789. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flood J. F., Morley J. E., Roberts E. Amnestic effects in mice of four synthetic peptides homologous to amyloid beta protein from patients with Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3363–3366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halverson K., Fraser P. E., Kirschner D. A., Lansbury P. T., Jr Molecular determinants of amyloid deposition in Alzheimer's disease: conformational studies of synthetic beta-protein fragments. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2639–2644. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilbich C., Kisters-Woike B., Reed J., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Aggregation and secondary structure of synthetic amyloid beta A4 peptides of Alzheimer's disease. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):149–163. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90881-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman R., Saitoh T. Advances in Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J. 1991 Mar 1;5(3):278–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner D. A., Inouye H., Duffy L. K., Sinclair A., Lind M., Selkoe D. J. Synthetic peptide homologous to beta protein from Alzheimer disease forms amyloid-like fibrils in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6953–6957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh J. Y., Yang L. L., Cotman C. W. Beta-amyloid protein increases the vulnerability of cultured cortical neurons to excitotoxic damage. Brain Res. 1990 Nov 19;533(2):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91355-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowall N. W., Beal M. F., Busciglio J., Duffy L. K., Yankner B. A. An in vivo model for the neurodegenerative effects of beta amyloid and protection by substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7247–7251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggio J. E. Tachykinins. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:13–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh P. W., Gates T., Mantyh C. R., Maggio J. E. Autoradiographic localization and characterization of tachykinin receptor binding sites in the rat brain and peripheral tissues. J Neurosci. 1989 Jan;9(1):258–279. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-01-00258.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh P. W., Johnson D. J., Boehmer C. G., Catton M. D., Vinters H. V., Maggio J. E., Too H. P., Vigna S. R. Substance P receptor binding sites are expressed by glia in vivo after neuronal injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5193–5197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hill B., Beyreuther K. Molecular biology of Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:287–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike C. J., Walencewicz A. J., Glabe C. G., Cotman C. W. Aggregation-related toxicity of synthetic beta-amyloid protein in hippocampal cultures. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug 14;207(4):367–368. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike C. J., Walencewicz A. J., Glabe C. G., Cotman C. W. In vitro aging of beta-amyloid protein causes peptide aggregation and neurotoxicity. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 1;563(1-2):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91553-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quon D., Wang Y., Catalano R., Scardina J. M., Murakami K., Cordell B. Formation of beta-amyloid protein deposits in brains of transgenic mice. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):239–241. doi: 10.1038/352239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Ramakrishna N., Wolfe G., Wisniewski H. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the cerebrovascular and the neuritic plaque amyloid peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4190–4194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J. Deciphering Alzheimer's disease: the amyloid precursor protein yields new clues. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1058–1060. doi: 10.1126/science.2111582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J. The molecular pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider R. M., Constantine J. W., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Longo K. P., Lebel W. S., Woody H. A., Drozda S. E., Desai M. C., Vinick F. J., Spencer R. W. A potent nonpeptide antagonist of the substance P (NK1) receptor. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):435–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1703323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Too H. P., Hanley M. R. Solubilization and characterization of substance P-binding sites from chick brain membranes. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):545–551. doi: 10.1042/bj2520545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitson J. S., Selkoe D. J., Cotman C. W. Amyloid beta protein enhances the survival of hippocampal neurons in vitro. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1488–1490. doi: 10.1126/science.2928783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Dawes L. R., Fisher S., Villa-Komaroff L., Oster-Granite M. L., Neve R. L. Neurotoxicity of a fragment of the amyloid precursor associated with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):417–420. doi: 10.1126/science.2474201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Duffy L. K., Kirschner D. A. Neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta protein: reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):279–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2218531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]