Abstract
Results from epidemiological studies suggest that there is an association between periodontitis and prediabetes, however, causality is not known. The results from our previous studies suggest that induction of periodontitis leads to hyperinsulinemia glucose intolerance and insulin resistance, all hallmarks of prediabetes. However, global effects of periodontitis on critical organs in terms of metabolic alterations are unknown.
We determined the metabolic effects of periodontitis on brain, liver, heart and plasma resulting from Porphyromonas gingivalis induced periodontitis in mice. Periodontitis was induced by oral application of the periodontal pathogen, Porphyromonas gingivalis for 22 weeks. Global untargeted biochemical profiles in samples from these organs/plasma were determined by liquid and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and compared between controls and animals with periodontitis.
Oral application of Porphyromonas gingivalis induced chronic periodontitis and hallmarks of prediabetes. The results of sample analyses indicated a number of changes in metabolic readouts, including changes in metabolites related to glucose and arginine metabolism, inflammation and redox homeostasis. Changes in biochemicals suggested subtle systemic effects related to periodontal disease, with increases in markers of inflammation and oxidative stress most prominent in the liver. Signs of changes in redox homeostasis were also seen in the brain and heart. Elevated bile acids in liver were suggestive of increased biosynthesis, which may reflect changes in liver function. Interestingly, signs of decreasing glucose availability were seen in the brain. In all three organs and plasma, there was a significant increase in the microbiome-derived bioactive metabolite 4-ethylphenylsulfate sulfate in animals with periodontitis.
The results of metabolic profiling suggest that periodontitis/bacterial products alter metabolomic signatures of brain, heart, liver, and plasma in the prediabetic state. These data provide scientific community valuable metabolic signatures that become the basis for understanding the impact of periodontitis on a systemic disease and potentially targets for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: Prediabetes, Global metabolomic analysis, Experimental periodontitis
Introduction
Epidemiological and clinical studies have identified a clinically important association between periodontitis (gum disease with associated loss of tooth supporting bone) and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) [1,2]. Results from epidemiological studies also suggest a close association between periodontitis and both prediabetes and metabolic syndrome [3]. However, a causal relationship between periodontitis and prediabetes has not been established.
A major limitation in determining causality is that experimental induction of destructive periodontal disease (periodontitis) is clearly not acceptable in humans. In previous studies, we have established animal models of induced periodontitis and studied the causality linking periodontitis to the development of glucose intolerance (GI), hyperinsulinemia (HI), and insulin resistance (IR), all hallmarks of prediabetes. Results from our previous studies demonstrate that animals with LPS/bacterial product-induced periodontitis develop prediabetes [4,5] and that bacterial products/LPS are an important initiator of HI, GI, and IR [5]. However, the global impact of periodontitis on metabolism in organs distant from the oral cavity has not been investigated.
Metabolomics is the systematic study of the unique biochemical fingerprint (metabolic signature) that results from specific cellular processes [6] and is one of the core disciplines of systems biology [7]. The metabolome is the collective signature of all metabolites in a biological cell, tissue, organ or organism, which are the intermediate and end products of cellular processes [8]. Thus, sample specific metabolomes from saliva, plasma, heart, liver etc. can be analyzed to determine disease effects locally and systemically [9–11]. Metabolomics is a powerful tool to identify alterations in specific metabolic pathways that result from disease with the potential to map early biochemical changes in pathophysiology, identify predictive biomarkers as well as identify targets that can be exploited for early prevention and/or treatment of the disease [12].
Only a limited number of studies have focused on identifying differences in metabolic profiles between periodontitis and control subjects. These studies focused on salivary biochemical [9,13,14] and reported various differences in metabolites in these fluids. These differences included dipeptide, amino acid, carbohydrate, lipid, and nucleotide metabolites consistent with the degradation of macromolecules including proteins, triacylglycerol, glycerolphospholipids, polysaccharides, and polynucleotides, which may reflect the outcome of host-bacterial interactions [13]. The differences in the biochemical profiles between healthy and periodontitis saliva samples in non-diabetic subjects also included increased levels of markers of cellular metabolic stress and increased purine catabolism and glutathione metabolism [9]. However, how periodontitis/periodontal pathogen impacts metabolism in organs distant from the oral cavity has not been investigated. In this study we determined the effects of oral application of Porphyromonas gingivalis (Pg) on metabolism in critical organs (brain, liver, heart), and plasma, using untargeted global metabolomic profiling of control animals and animals with oral Pg application. These data provide the first systematic comprehensive overview of metabolic changes that occur as a result of oral application of a periodontal pathogen and provide a valuable resource of candidate metabolites and metabolic pathways to the scientific community to undertake further studies. Future studies will lead to the potential for development of strategies to prevent periodontal pathogen induced metabolic disturbances such as development of prediabetes, dementia, atherosclerosis, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with which periodontitis has been associated.
Materials and Methods
Animals
This study was carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations outlined in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health. The protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of Illinois at Chicago (Protocol approval #12-152).
Twenty 6-week old male C57BL/6 mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, ME). Following one-week acclimatization, mice were maintained on regular chow (7912 Teklad LM-485) (Envigo RMS, Indianapolis, IN) and water ad libitum at a constant temperature (22 °C) with humidity of 45% to 55% in a 12-hour light/dark cycle.
Bacterial culture and preparation
Porphyromonas gingivalis (strain W83) was grown anaerobically (85% N2, 10% H2 and 5% CO2) in GasPak anaerobic containers (Becton Dickinson (BD), Franklin Lakes, NJ) using GasPak EZ pouches (BD) at 37 °C in sterile 3% Bacto Todd Hewitt Broth (BD) (pH 7.4) supplemented with 0.001% hemin and 0.0001% vitamin K1 (both from Sigma, St. Louis, MO). Bacteria were grown overnight and approximate cell density was determined by spectrophotometry at an optical density of 550 nm, based on a standard curve established by colony formation on bacterial plates. The density of the culture was adjusted to an O.D. of ~ 1.5 (2 × 109 cells/ml). Appropriate amounts of culture containing 1 × 109 cells were transferred to 10 microfuge tubes, vortexed briefly and centrifuged at 10,000 g for 2 minutes at 4 °C. The supernatants were discarded and the pellets were re-suspended in 4 °C PBS and repelleted by centrifugation. The supernatants were removed and bacteria re-suspended in 100 μl of 2% carboxymethyl cellulose in PBS and immediately placed on ice until used for oral application in mice.
Study design
Animals were divided into 2 groups (n=10 per group): 100 ul of Pg in carboxymethylcellulose was applied (2 applications of 50 ul) in the oral cavity every other day (Monday, Wednesday, and Friday) for 22 weeks (experimental group) and carboxymethylcellulose vehicle alone was applied in the oral cavity (control group). Mice that received oral applications of Pg were kept in a separate room (Biohazard Room) from control mice to avoid cross contamination. All animals were weighed once a week for the duration of the experiment. Mice were sacrificed during the 23rd week. A portion of liver, brain, and the entire heart and a sample of plasma from each animal were snap frozen in liquid nitrogen and shipped to Metabolon, Inc. (Durham, NC) for analyses of metabolic products. Maxillae were used to assess bone loss by microtomography as described below. Individuals performing examination of bone loss and metabolic analyses were blinded to the group to which individual animals were assigned.
Measurement of alveolar bone loss by microtomography
To assess alveolar bone loss, image acquisition was performed at the Integrated Small Animal Imaging Research Resource (iSAIRR) at the University of Chicago, Chicago, IL. Maxillae were scanned on a Trifoil GMI Triumph (Northridge, CA) with the following parameters: voltage: 60 k; V current: 140 uA; field of view: 28.16 mm; projections: 1024; pixel size: 54 mm. AMIRA software (FEI, Hillsboro, OR) was used for image analysis. Maxillae were rendered in 3D and cross sections cut through the distal root of 1st molars were visualized and linear measurements were taken in millimeters from the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ) to the alveolar bone crest to assess bone loss.
Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (ipGTT)
ipGTTs were performed at baseline and at 22 weeks post-initiation of Pg application. Briefly, following a 14 hr fast and collection of blood samples to determine glucose and insulin levels, 50% dextrose (2 g/kg body weight) was administered intraperitoneally and glucose levels in tail blood were determined after 15, 30, 60, 90 and 120 min using a glucometer.
Metabolomic profiling
Metabolomic and statistical analyses were conducted at Metabolon, Inc. (Durham, NC) as described previously [15]. Briefly, tissue samples from control and periodontitis groups (n=9 animals per group) were homogenized, subjected to methanol extraction and then split into aliquots for analyses by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (UHPLC/MS) in the positive (two methods, one optimized for hydrophilic, the other hydrophobic compounds), negative or polar ion mode. Metabolites were identified by automated comparison of ion features to a reference library of chemical standards followed by visual inspection for quality control. For quality assurance/control, a pooled matrix (or for plasma, an internal matrix) as well as several internal standards were assessed to determine instrument variability, with relative standard deviation; at 4% (plasma) or 2% (brain, liver, and heart).
Statistical analysis
For statistical analyses and data display, any missing values were assumed to be below the limits of detection; these values were imputed with the compound minimum (minimum value imputation). Welch’s two-sample t-test was used to identify biochemical that differed significantly between groups. Mann-Whitney test was used to assess differences in ipGTT, glucose, insulin and HOMA-IR for control and periodontitis groups. P< 0.05 was considered as a significant difference between periodontitis and control samples with a trend value of 0.05<p<0.1 as approaching significance.
Results
Oral application of P. gingivalis induced periodontitis, glucose intolerance, hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance
Repeated oral application of Pg induced significant alveolar bone loss compared to control animals (Figure 1). The results from ipGTT at week 22 revealed impaired glucose tolerance in Pg-treated mice, with hyperglycemia persisting for up to 120 min post-glucose load in mice with periodontitis as evidenced by p values at each time point (Table 1). Hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance were also observed, however, fasting glucose levels were within the normal range (Table 2). Thus, oral application of Pg resulted in the development of prediabetes.
Figure 1.
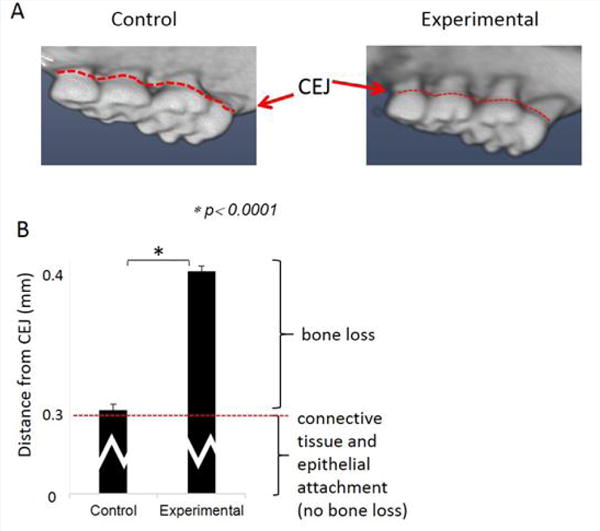
Oral application of Pg induces alveolar bone loss.
A) Image from micro-tomography. B) Alveolar bone loss. The bracket on the right bottom indicates the mean distance where epithelia and connective tissue attach thus not considered as bone loss. The bracket on the top indicates the mean bone loss. (mean±SD). Periodontitis: oral application of Pg, Control: vehicle alone.
Table 1.
Glucose tolerance test results at week 22 in control and periodontitis mice (n=10 animals per group). Data presented are mean±S.D. Mann-Whitney test.
| Time (min.) | Control (mg/dL) | Experimental (mg/dL) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 171.4±34.6 | 142.5±27.8 | 0.049 |
| 15 | 408.7±73.1 | 499.7±80.6 | 0.023 |
| 30 | 436.6±92.84 | 529.3±67.9 | 0.037 |
| 60 | 360.5±105.6 | 510.1±109.4 | 0.019 |
| 90 | 269.4±83.3 | 524.7±88.2 | 0.0002 |
| 120 | 174±24.4 | 441.3±103.1 | 3.41E-05 |
Table 2.
Fasting glucose, insulin levels and HOMA-IR at week 22 (n=10 animals per group). Data presented are mean±S.D. Mann-Whitney test.
| Control | Experimental | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 182±39.5 | 150.2±24.9 | 0.08 |
| Insulin (μg/L) | 0.4±0.2 | 0.8±0.3 | 0.03 |
| HOMA-IR | 3.9±2.5 | 8.1±1.7 | 0.03 |
Global metabolomic analyses identified a number of biochemicals which were significantly altered by oral application of Pg
Following data acquisition and curation, a total of 552 biochemicals were identified in plasma, 442 in brain, 576 in liver, and 580 in heart. Following log transformation and imputation of missing values, if any, with the minimum observed value for each compound, Welch’s two-sample t-test was used to identify biochemicals that differed significantly between groups. In plasma, the levels of 24 biochemicals were significantly different between groups (p< 0.05); 4 metabolites were increased and 20 decreased. In brain, there were 29 biochemicals with significant alterations between groups; 6 were increased and 23 were decreased. Liver had 43 biochemicals with significant alterations: 40 were increased and 3 were decreased. In heart, 23 biochemicals were significant altered between groups of which 20 were increased and 3 were decreased (Table 3).
Table 3.
Summary of biochemical alterations induced by Pg application (experimental group) from a total of 552 named biochemicals identified in plasma, 442 in brain, 576 in liver and 580 in heart. Red arrow indicates the number of biochemicals increased. Green arrow indicates the number of biochemicals decreased. Experimental: oral application of Pg, Control: vehicle alone.
| Biochemical Alterations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Welch’s Two-Sample t-Test | Experimental Control | |||
| Plasma | Brain | Liver | Heart | |
| Total biochemicals p≤0.05 | 24 | 29 | 43 | 23 |
|
Biochemicals (↑↓) |
4/20 | 6/23 | 40/3 | 20/3 |
| Total biochemicals 0.05<p<0.10 | 25 | 24 | 42 | 24 |
|
Biochemicals (↑↓) |
8/17 | 10/14 | 38/4 | 19/5 |
In addition, there were a similar number of biochemicals which achieved a trend value (0.05<p<0.10) toward significance in these analyses (Table 3).
Oral application of Pg induced changes in glucose metabolism in the brain
Glucose is utilized to support a variety of physiological processes, including energy generation, fatty acid synthesis, protein glycosylation, and nucleotide biogenesis. Glucose is the obligatory energy substrate of the adult brain. In the brain, decreases in glucose (p=0.093), glucose 6-phosphate (p=0.0299), and fructose-6-phosphate (p=0.0338) suggest changes in glucose metabolism or glucose availability in animals with periodontitis. Pentose phosphate metabolites (6-phosphogluconate and sedoheptulose-7-phosphate) (p=0.0159 and p=0.0611 respectively), the hexosamineglucosamine-6-phosphate (p=0.0152), and the glycolytic end-product pyruvate (p=0.0802), were also decreased, which would be consistent with decreasing glucose availability in animals with periodontitis. Collectively, these data suggest that glucose utilization is relatively reduced in the brain of animals with periodontitis compared to controls (Figure 2 and Table 4).
Figure 2.
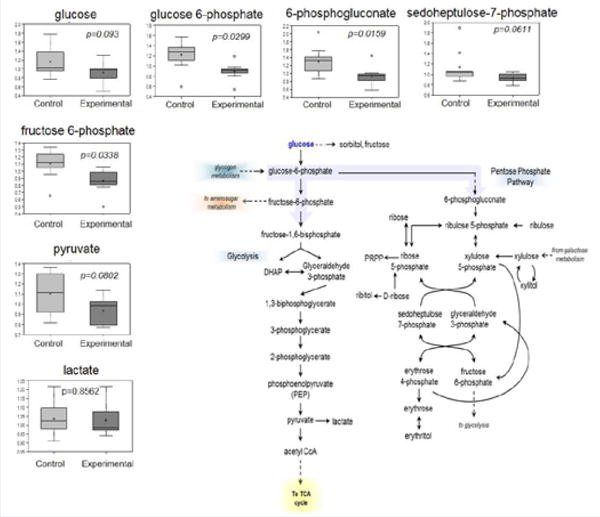
Glucose metabolism in brain of control and experimental animals.
Glucose levels tend to be low in the brain of mice with periodontitis. Glucose utilization is significantly lower in these animals compared to controls. Data presented are mean±S.D. Welch’s two-sample t-test. N=9 animals per group. Experimental: oral application of Pg, Control: vehicle alone.
Table 4.
Metabolic differences in the brain of experimental vs control animals. Fold change is expressed as Experimental/Control. N=9 animals per group.
| Super Pathway | Sub Pathway | Biochemical Name | Fold changes | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino Acid | Creatine Metabolism | creatinine | 0.91 | 0.0004 |
| Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | N-acetylarginine | 0.87 | 0.0018 | |
| Polyamine Metabolism | spermine | 0.17 | 0.0032 | |
| spermidine | 0.34 | 0.0059 | ||
| Lysine Metabolism | N2-acetyllysine/N6-acetyllysine | 0.89 | 0.009 | |
| Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism | O-methyltyrosine | 0.82 | 0.0152 | |
| Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | citrulline | 0.84 | 0.0264 | |
| urea | 0.8 | 0.0275 | ||
| Glutamate Metabolism | S-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate | 0.77 | 0.0399 | |
| glutamate, gamma-methyl ester | 0.88 | 0.0498 | ||
| Carbohydrate | Aminosugar Metabolism | glucosamine-6-phosphate | 0.84 | 0.0152 |
| Pentose Phosphate Pathway | 6-phosphogluconate | 0.72 | 0.0159 | |
| Glycolysis, Gluconeogenesis, and Pyruvate Metabolism | 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) | 1.18 | 0.0173 | |
| glucose 6-phosphate | 0.74 | 0.0299 | ||
| fructose-6-phosphate | 0.79 | 0.0338 | ||
| Cofactors and Vitamins | Riboflavin Metabolism | flavin mononucleotide (FMN) | 0.71 | 0.0101 |
| Pantothenate and CoA Metabolism | pantothenate | 0.87 | 0.0299 | |
| Hemoglobin and Porphyrin Metabolism | heme | 0.62 | 0.0433 | |
| Lipid | Sterol | campesterol | 0.85 | 0.0243 |
| Sphingolipid Metabolism | sphingomyelin (d18:1/21:0, d17:1/22:0, d16:1/23:0)* | 1.11 | 0.0272 | |
| Phospholipid Metabolism | 1,2-distearoyl-GPC (18:0/18:0) | 1.07 | 0.0276 | |
| Lysolipid | 2-stearoyl-GPE (18:0)* | 1.41 | 0.0315 | |
| Nucleotide | Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism | methylphosphate | 0.86 | 0.0261 |
| Peptide | Dipeptide | glycylvaline | 1.31 | 0.0055 |
| Gamma-glutamyl Amino Acid | gamma-glutamyl-epsilon-lysine | 0.62 | 0.0455 | |
| Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | gluconate | 0.73 | 0.0271 |
| stachydrine | 0.69 | 0.0379 | ||
| ergothioneine | 0.63 | 0.0407 |
Oral application of Pg induced changes in other biochemicals in the brain
Between group analyses also revealed changes in redox homeostasis in brain: for example, decrease in anserine (a dipeptide metabolite of histidine with anti-oxidant function) (p=0.0649) (Table 4).
The benzoate metabolite 4-ethylphenylsulfate (4-EPS), which is derived from liver modifications of a microbiome-derived tyrosine metabolite 4-ethylphenol, was marginally increased in the brains of animals with Pg application (p=0.0574) compared to control animals.
Analysis also revealed a decrease in several arginine-derived biochemicals such as citrulline in the brain (p=0.0264) in animals with periodontitis compared to control animals. In addition, ornithine (p=0.078) and acetylated derivatives of arginine and ornithine, N-acetylarginine and N-delta-acetylornithine (p=0.00118, p=0.075 respectively), creatinine (p=0.004), and the polyamines, spermine (p=0.032) and spermidine (p=0.0059), were also decreased in animals with periodontitis compared to control animals (Table 4). While arginine was not decreased in the dataset, decreases in related metabolites could suggest limiting availability. We also observed elevated levels of 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) (p=0.0093), a naturally occurring monosaccharide, in the brains of animals with periodontitis compared with controls.
Finally, lysolipid is significantly increased in the brain of animals with Pg application (p=0.0315).
Changes in biomarkers of oxidative stress in the liver were evident in animals with periodontitis
A number of changes in biomarkers of oxidative stress were observed in the liver of mice with periodontitis compared to controls (Table 5). Methionine sulfoxide and S-methylcysteine, products of methionine and cysteine oxidation respectively, were elevated in the liver of animals with periodontitis (p=0.06 and p=0.0268 respectively), consistent with an increasingly oxidizing environment. Further, increases in the diols 9,10-DiHOME and 12,13-DiHOME (p=0.0452 and p=0.045 respectively), derived from the opening of epoxides derived from linoleate, the diol 19,20-DiHDPA (p=0.0821), derived from the hydrolysis of the epoxide formed from docosahexaenoate or DHA, and 14/17-HDoHE (p=0.2637), an oxidation product of DHA were observed in the liver of animals with periodontitis. 9/13-HODE (p=0.0149), derived from the oxidation of the PUFA linoleate, was also elevated. 9/13-HODE is a biomarker of oxidative stress but also can be produced by lipoxygenases which produce proinflammatory eicosanoids. Glutathione levels, either reduced (GSH, p=0.6202) or oxidized (GSSG, p=0.2061) were not significantly changed, but anserine (p=0.0236) and carnosine (p=0.0461), both dipeptide metabolites of histidine with antioxidant function, were elevated in the liver of animals with periodontitis, which suggests increased synthesis to meet an anti-oxidant demand.
Table 5.
Metabolic differences in liver of experimental vs control animals. Fold change is expressed as Experimental/Control. N=9 animals per group.
| Super Pathway | Sub Pathway | Biochemical Name | Fold Change | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino Acid | Histidine Metabolism | N-acetyl-1-methylhistidine* | 1.51 | 0.0047 |
| 1-methylhistidine | 1.46 | 0.0054 | ||
| Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism | O-methyltyrosine | 1.29 | 0.0056 | |
| Leucine, Isoleucine and Valine Metabolism | N-acetylleucine | 1.6 | 0.0092 | |
| isovalerylglycine | 1.35 | 0.0395 | ||
| Methionine, Cysteine, SAM and Taurine Metabolism | S-methylcysteine | 1.28 | 0.0268 | |
| Lysine Metabolism | N6,N6,N6-trimethyllysine | 1.24 | 0.0337 | |
| Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | proline | 1.13 | 0.0351 | |
| Tryptophan Metabolism | kynurenate | 1.72 | 0.0354 | |
| Glutamate Metabolism | N-methyl-4-aminobutyric acid | 0.71 | 0.0162 | |
| Carbohydrate | Glycolysis, Gluconeogenesis, and Pyruvate Metabolism | 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) | 1.3 | 0.0082 |
| glycerate | 1.15 | 0.0322 | ||
| Cofactors and Vitamins | Hemoglobin and Porphyrin Metabolism | heme | 1.63 | 0.0226 |
| Energy | TCA Cycle | tricarballylate | 1.68 | 0.0441 |
| Lipid | Phospholipid Metabolism | cytidine-5′-diphosphoethanolamine | 1.46 | 0.0029 |
| Sphingolipid Metabolism | sphingomyelin (d18:2/16:0, d18:1/16:1) | 1.13 | 0.0229 | |
| Primary Bile Acid Metabolism | glycocholate | 3 | 0.0263 | |
| Fatty Acid Metabolism(Acyl Glycine) | valerylglycine | 1.81 | 0.0421 | |
| Fatty Acid, Monohydroxy | 13-HODE + 9-HODE | 1.52 | 0.0149 | |
| 3-hydroxyoctanoate | 1.32 | 0.0425 | ||
| Fatty Acid, Dihydroxy | 12,13-DiHOME | 1.37 | 0.045 | |
| 9,10-DiHOME | 1.48 | 0.0452 | ||
| Secondary Bile Acid Metabolism | taurodeoxycholate | 2.17 | 0.0065 | |
| deoxycholate | 1.81 | 0.0137 | ||
| ursodeoxycholate | 1.56 | 0.031 | ||
| 6-beta-hydroxylithocholate | 1.79 | 0.0368 | ||
| Monoacylglycerol | 2-docosahexaenoylglycerol (22:6) | 1.64 | 0.011 | |
| 1-docosahexaenoylglycerol (22:6) | 1.46 | 0.0305 | ||
| 2-linoleoylglycerol (18:2) | 1.51 | 0.0412 | ||
| Lysolipid | 1-stearoyl-GPS (18:0)* | 1.57 | 0.0269 | |
| 1-stearoyl-GPE (18:0) | 1.14 | 0.0303 | ||
| 1-palmitoyl-GPE (16:0) | 1.13 | 0.0304 | ||
| 2-stearoyl-GPE (18:0)* | 1.43 | 0.0497 | ||
| Nucleotide | Purine Metabolism, Guanine containing | guanosine | 0.8 | 0.0373 |
| Peptide | Dipeptide | tryptophylglycine | 1.86 | 0.0033 |
| phenylalanylglycine | 1.37 | 0.0362 | ||
| phenylalanylalanine | 1.31 | 0.0357 | ||
| Dipeptide Derivative | anserine | 1.19 | 0.0236 | |
| carnosine | 1.22 | 0.0461 | ||
| Xenobiotics | Chemical | sulfate | 1.19 | 0.005 |
| Benzoate Metabolism | 4-ethylphenylsulfate | 3.62 | 0.0113 | |
| Food Component/Plant | 4-ethylphenol glucuronide | 3.06 | 0.0232 | |
| ergothioneine | 0.67 | 0.0296 |
Signs of increasing inflammation are observed in the liver
Several markers are useful in detecting subtle changes in inflammation. For example, changes in tryptophan metabolites can reflect an inflammatory state. Proinflammatory cytokines such as TNFα and INFɣ can activate conversion of tryptophan to kynurenine [16–18] which is catalyzed by indole amine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). Kynurenate was significantly increased (p=0.0354) (Table 5) and tryptophan and anthranilate were marginally increased (p=0.0842 and 0.067 respectively) in the liver of animals with periodontitis. This may reflect increasing tryptophan availability or may reflect changes in indole amine 2,3-IDO expression or activity which has been shown to be induced in pathological conditions such as altered function of T-cells at the level of antigen processing/presentation and during the early stage of primary biliary cirrhosis [19,20].
Levels of biochemicals related to bile acid metabolism were also altered in the liver of animals with periodontitis; although cholesterol was not significantly changed, increases in 7-hydroxycholesterol (p=0.0519) suggest increased bile acid synthesis. Consistently, primary (e.g. glycocholate, p=0.0263 and taurochenodeoxycholate, p=0.0542) and secondary (e.g. deoxycholate, p=0.0137 and urosodeoxycholate, p=0.031) bile acids were also increased in animals with periodontitis. Increased bile acid production has been associated with liver disease such as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [21] and cholesterol gallstone formation [22].
Alterations in redox homeostasis were observed in the heart
Signs of changes in redox homeostasis were observed in the heart. For example, a significant increase in cysteine (oxidized form of cysteine) (p=0.0423) (Table 6) and a marginally significant increase in cysteine-glutathione disulfide (p=0.0771) were observed. Because of the ability of thiols to undergo redox reactions, cysteine has antioxidant properties. Thus, increases in these biochemicals suggest, that the heart may be under oxidative stress in animals with periodontitis. Given the importance of oxidative metabolism to the heart, these changes may be early biomarkers of compromised cardiovascular function which is characteristic of diabetes.
Table 6.
Metabolic changes in the heart of experimental vs control animals. Fold change is expressed as Experimental/Control. N=9 animals/group.
| Super Pathway | Sub Pathway | Biochemical Name | Fold changes | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino Acid | Methionine, Cysteine, SAM and Taurine Metabolism | taurocyamine | 1.31 | 0.0174 |
| cystine | 1.39 | 0.0423 | ||
| Leucine, Isoleucine and Valine Metabolism | leucine | 1.13 | 0.0342 | |
| Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | N-delta-acetylornithine | 0.87 | 0.0373 | |
| Alanine and Aspartate Metabolism | N-acetylalanine | 1.16 | 0.0235 | |
| Carbohydrate | Glycolysis, Gluconeogenesis, and Pyruvate Metabolism | 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) | 1.26 | 0.0089 |
| pyruvate | 1.38 | 0.0496 | ||
| Advanced Glycation End-product | N6-carboxymethyllysine | 1.16 | 0.0292 | |
| Pentose Metabolism | ribonate | 1.27 | 0.0365 | |
| Cofactors and Vitamins | Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Metabolism | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced (NADH) | 2.03 | 0.0228 |
| Lipid | Monoacylglycerol | 2-oleoylglycerol (18:1) | 1.67 | 0.0132 |
| 2-palmitoleoylglycerol (16:1) | 2.35 | 0.0392 | ||
| 1-oleoylglycerol (18:1) | 1.98 | 0.0405 | ||
| Phospholipid Metabolism | 1-palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl-GPC (16:0/18:2) | 0.84 | 0.0303 | |
| 1-palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl-GPE (16:0/18:2) | 0.85 | 0.0431 | ||
| Fatty Acid, Keto | 1-dihomo-linoleoylglycerol (20:2) | 2.13 | 0.0414 | |
| Long Chain Fatty Acid | 10-nonadecenoate (19:1n9) | 1.45 | 0.0355 | |
| Sphingolipid Metabolism | sphingomyelin (d18:2/16:0, d18:1/16:1) | 1.16 | 0.0375 | |
| glycosyl-N-palmitoyl-sphingosine | 1.28 | 0.0441 | ||
| Fatty Acid, Dicarboxylate | undecanedioate | 1.24 | 0.0448 | |
| Diacylglycerol | 1-palmitoleoyl-3-oleoyl-glycerol (16:1/18:1) | 1.73 | 0.0465 | |
| Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | 4-ethylphenol glucuronide | 2.22 | 0.0146 |
| Benzoate Metabolism | 4-ethylphenylsulfate | 3.43 | 0.0149 |
Pyruvate levels in the heart were significantly elevated (p=0.0496). The heart typically relies on beta-oxidation for the majority of its energy, which shifts towards increased glycolytic metabolism seen during ischemic events [23,24]. Activated immune cells are highly glycolytic [25,26] and infiltration of immune cells into the heart could contribute to changes in observed energy metabolism. The observed significant increase in reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NADH, (p=0.0228) could reflect increased glycolytic metabolism. 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) levels are elevated (p=0.0089) in the heart also indicating an increased reliance on glycolysis, and an increase in the pentose metabolism product ribonate (p=0.0365), a ribose-derived product also is consistent with this concept.
In addition, the advanced glycation end-product (AGE) pathway product, N6-carboxymethyllysine was significantly increased (p=0.0292) in the heart.
Xanthurenate, a degradative product of kynurenine, is marginally increased in the heart of animals with periodontitis (p=0.052), which could also reflect a subtle change in inflammation.
Changes in the benzoate metabolite 4-ethylphenylsulfate (4-EPS) in animals administered Pg may reflect changes in the microbiome
4-EPS and 4-ethylphenol glucuronide, derived from liver modifications of a microbiome-derived tyrosine metabolite 4-ethylphenol, were increased in all matrices in animals with periodontitis compared to control animals (Figure 3). 4-EPS is a bioactive metabolite linked to autism-like behavioral changes in mouse models [27], but little is known regarding the biological functions of this metabolite. Further studies to determine if this metabolite is derived from changes in the oral, intestinal, or both microbiomes would be of value.
Figure 3.
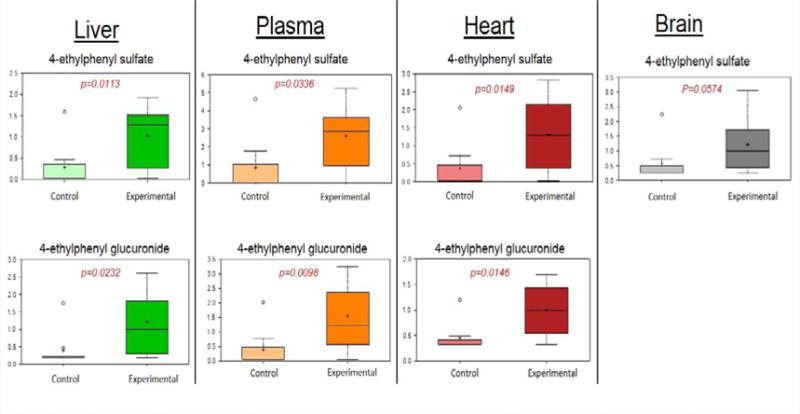
Levels of 4-EPS and 4-EPG in organs and plasma of experimental vs. control animals.
Data presented are mean±S.D. Welch’s two sample t-tests. N=9 animals per group. Experimental: oral application of Pg, control vehicle alone.
Plasma
Decreased levels of the polyamine-related metabolites 5-methylthioadenosine (MTA) (p=0.0063), and citrulline (p=0.036), a urea cycle/arginine metabolite, were observed in animals with periodontitis compared with controls. In addition, multiple lysolipid metabolites were significantly reduced in animals with periodontitis compared with controls (Table 7). Lysolipids are soluble in lipid bilayers and are capable of altering particular membrane functions [28]. For example, it has been shown that serum lysolipids can be readily incorporated into erythrocyte cell membranes and alter glucose transport [28].
Table 7.
Metabolic differences in plasma of experimental vs control animals. Fold change is expressed as Experimental/Control. N=9 animals per group
| Super Pathway | Sub Pathway | Biochemical Name | Fold changes | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino Acid | Polyamine Metabolism | 5-methylthioadenosine (MTA) | 0.78 | 0.0063 |
| Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism | o-cresol sulfate | 0.58 | 0.0197 | |
| Methionine, Cysteine, SAM and Taurine Metabolism | methionine sulfone | 0.66 | 0.0288 | |
| Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | citrulline | 0.86 | 0.0364 | |
| Glutamate Metabolism | S-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate | 0.8 | 0.0391 | |
| Carbohydrate | Glycolysis, Gluconeogenesis, and Pyruvate Metabolism | 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) | 1.22 | 0.0059 |
| Advanced Glycation End-product | N6-carboxymethyllysine | 0.65 | 0.0107 | |
| Cofactors and Vitamins | Thiamine Metabolism | thiamin monophosphate | 1.32 | 0.0042 |
| Lipid | Lysolipid | 1-linoleoyl-GPE (18:2) | 0.64 | 0.001 |
| 1-palmitoyl-GPE (16:0) | 0.85 | 0.0076 | ||
| 1-arachidonoyl-GPE (20:4) | 0.69 | 0.0089 | ||
| 1-palmitoyl-GPI (16:0) | 0.65 | 0.0114 | ||
| 1-stearoyl-GPI (18:0) | 0.7 | 0.015 | ||
| 1-oleoyl-GPE (18:1) | 0.75 | 0.0179 | ||
| 1-linoleoyl-GPI (18:2) | 0.66 | 0.0228 | ||
| 2-palmitoleoyl-GPC (16:1) | 0.8 | 0.0345 | ||
| 1-stearoyl-GPE (18:0) | 0.8 | 0.044 | ||
| Lysoplasmalogen | 1-(1-enyl-palmitoyl)-GPE (P-16:0) | 0.81 | 0.0238 | |
| 1-(1-enyl-stearoyl)-GPE (P-18:0) | 0.76 | 0.0061 | ||
| 1-(1-enyl-oleoyl)-GPE (P-18:1) | 0.63 | 0.01 | ||
| Sterol | campesterol | 0.75 | 0.0415 | |
| Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | 4-ethylphenol glucuronide | 3.95 | 0.0098 |
| indoleacrylate | 0.39 | 0.0246 | ||
| Benzoate Metabolism | 4-ethylphenylsulfate | 3.06 | 0.0336 |
In addition, a significant reduction in lysoplasmalogen occurred in animals with periodontitis (Table 7). Plasmalogens act as antioxidants to protect cells against reactive oxygen species produced during oxidative stress [29]. The decrease in plasmalogen content may reflect its function as a scavenger [30].
Discussion
Although the results from epidemiological and clinical studies demonstrate a close association between periodontitis and metabolic disorders such as metabolic syndrome and T2DM [3], the underlying metabolic alterations induced by periodontitis/periodontal pathogens have not been elucidated. In the current study, we used the oral application of a periodontal pathogen, Pg, to induce chronic periodontitis (alveolar bone loss) and investigated changes in metabolism in critical organs distant from the oral cavity. All matrices (brain, liver, heart, plasma) that we examined exhibited altered biochemicals in response to oral application of Pg compared with control. This strongly suggests that repeated oral application of Pg alters metabolism in distinct patterns in organs distant from the oral cavity. This is the first time that such global change in vital organs has been reported. The results have important implications for the documented association between periodontal pathogen/bacterial products and a number of systemic diseases and conditions including the development of periodontitis and prediabetes.
Of particular interest were the changes in the metabolic profile in the brain in response to oral application of Pg. Major changes include reduced glucose utilization which is indicated by decreased glucose-6-phosphate, fructose-6-phosphate and pyruvate levels. Decreased levels of 6-phosphogluconate suggest decreased pentose phosphate shunt activity which in turn leads to reduced NADPH which plays a role in preventing oxidative stress. Thus, when Pg is orally applied, host defense against oxidative stress may be compromised in the brain. Interestingly, decreased glucose availability was observed in the brains but not in plasma, heart or liver.
Polyamine metabolism was also significantly altered in the brain. Polyamines are ubiquitous molecules, highly regulated molecules that play critical roles in mammalian physiology including cell growth [31], cell division, differentiation, regulation of cell permeability and stability of cell membrane [32]. In addition, polyamines inhibit lipid peroxidation and prevent apoptosis [33]. Interestingly, they also modulate synaptic transmission in the central nervous system [34] and brain cells are extremely sensitive to reductions in polyamine levels [35]. Recently, polyamines were shown to protect memory impairment in an autophagy-dependent manner [36]. Thus, reduced polyamine levels in the brain may contribute to subtle changes in memory or cognition in animals with oral application of Pg in association with prediabetes.
The main energy source in the brain is glucose. However, during hypoglycemia, lactate from glycogen metabolism is used as a backup to ensure neuronal function [37]. We observed no significant difference in fasting glucose levels in plasma between control and periodontitis groups. However, biochemicals involved in the glycolysis pathway and amino (hexose) sugar metabolisms were significantly decreased, suggesting decreased glucose availability in the brain in animals with oral application of Pg.
Creatine, synthesized in the liver and kidney, is transported through the blood and taken up by tissues with high energy demands, such as the brain and skeletal muscle. In these tissues, they are converted to the high energy compound phosphocreatine and can be converted to creatinine [38]. Creatinine is degraded at a constant rate in the brain and secreted into the circulation [39]. We observed that creatinine was significantly reduced in the brain of animals with oral application of Pg but the implication of this finding is not known.
It is known that the plasma level of 1,5-AG decreases during hyperglycemia and therefore can be used to determine glycemic control [40]. The level of 1,5-AG in blood is inversely related to the concentration of glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin levels in humans [41]. In the brain, 1,5-AG levels are elevated significantly compared with control animals. This may reflect low availability of glucose in the brain which is consistent with the observed decreased in glycolysis and amino (hexose) sugar metabolism in animals with oral application of Pg.
Sphingolipid metabolism increased in all matrices except plasma. Sphingolipids are essential membrane lipids that are enriched in lipid rafts and play an essential role in cell signaling [42] and also serve a structural role in myelinated neurons. Changes in sphingolipids can be indicative of alterations in these two processes and/or may also reflect changes in fatty acid biosynthesis or oxidation. It has been shown that animals injected with LPS exhibited increased levels of sphingomyelin and ceramide synthesis in the liver [43]. Thus increased levels of sphingomyelin may be due to Pg LPS. Increased sphingomyelin accumulation in the hippocampus has been reported in rats fed high-fat high-sugar chow with water with high-fructose content for 3 months [44]. Interestingly, our animals were fed a regular chow and yet exhibited increased sphingomyelin levels compared with controls.
In addition to the brain, significant alterations in response to oral application of Pg were noted in other organs. For example, increases in glycocholate, deoxycholate and ursodeoxycholate in the liver of animals with periodontitis suggest increased bile acid production. It has been reported that increased bile acid production is associated with liver disease such as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [21] and cholesterol gallstone formation [22].
In the liver, increased biomarkers of oxidative stress such as methionine sulfoxide and S-methylcysteine, are increased in animals with oral application of Pg. This suggests that Pg or its products may disturb the physiological redox state resulting in production of peroxides and free radicals that damage cell components such as proteins, lipids, and DNA.
In contrast to the brain, the primary energy source for the heart is lipid oxidation (beta-oxidation). During ischemic damage or hypertrophy, however, energy utilization shifts towards glycolysis. Thus, elevated pyruvate levels may signify subtle metabolic changes associated with cardiac muscle damage [45,46].
Among the biochemicals which are significantly altered in animals with oral application of Pg compared with controls, 4-EPS and 1,5-AG increased in all matrices. Increased levels of 4-EPS in animals reflect changes in liver-modified microbiome-derived products [27]. Whether 4-EPS is a derivative of Pg or intestinal bacteria due to a systemic disturbance resulting from oral application of Pg is not clear. The function of the bioactive metabolite 4-EPS is not known but has been linked to behavioral changes in mouse models [27] and thus is of interest in regards to cognition. 4-EPS is also found to be associated with percent lean mass in humans but periodontal status of these subjects were unknown [47].
Recently, the effect of oral administration of Pg on the gut microbiome has been reported [48,49]. Interestingly, repeated oral application of Pg resulted in changes in the composition of gut microbiota, but minimal amount of alveolar bone loss following 5 weeks of application [49]. A single application of Pg altered gut microbiota, increased serum endotoxin levels, and changed expression levels of proteins involved in intestinal permeability [48]. These results suggest that changes in the microbiota and/or intestinal permeability in response to periodontopathic bacteria may have metabolic consequences. Using a similar animal model and a similar time course as used in our current study, we previously noted no significant increase in plasma cytokine levels in animals that were administered LPS in the gingival sulci for 18 weeks, but there were significant differences in serum LPS levels [5]. In addition, these animals developed significant glucose intolerance and alveolar bone loss. Thus, it is still not clear if oral application of Pg influenced metabolic profiles via an alteration in gut microbiota or via the periodontal pocket to the systemic circulation.
There are an ample number of studies using experimental periodontitis animal models in which repeated oral application of Pg has been used to determine the effects of a periodontal pathogen in inducing periodontitis and/or direct effects on distant organs. However, methodologies have differed widely in terms of the duration of Pg application [49–56]. In most of these studies animals did not develop significant alveolar bone loss. In addition, the number of Pg present in the gingival sulci/periodontal pocket was unknown. As Pg may be present at low levels in healthy subgingival plaque/biofilms, applying Pg to the oral cavity for short durations may not results in chronic periodontitis. Results from our previous studies indicate that application of LPS into the gingival sulci/periodontal pockets (without spilling out from the pockets) results in glucose intolerance and significant amount of alveolar bone loss [5]. Thus, monitoring glucose intolerance is one way to determine underlying systemic effects that relate to the development of periodontitis. In our current study, we applied Pg 3 times per week for 22 weeks based on the significant amount of alveolar bone loss (Figure 1) and the development of glucose intolerance (Table 1). In addition, all animals gained weight and consumed a normal amount of food (supplementary information) suggesting that they are apparently healthy.
In plasma, a decrease in 5-MTA in (p=0.0063) in animals with periodontitis compared with controls suggests declining polyamine production. This could relate to decreasing arginine availability. 1,5-AG (p=0.0059) is inversely-associated with glucose levels in biological fluids such as saliva and serum [41,57], thus, an increase in 1,5-AG levels could suggest subtle decreases in glucose availability. Trends toward decreases in lysolipids could reflect changes in signaling or demand for fatty acids to support beta-oxidation.
The purpose of the current study was to determine the effect of oral application of Pg on the metabolism in organs distant from the oral cavity using a global untargeted metabolic profiling in an experimental periodontitis model. The results provide a valuable resource of candidate metabolites and metabolic pathways to the scientific community to undertake further studies to unravel the consequences of oral application of periodontal pathogen(s) to a variety of systemic diseases and conditions, including prediabetes. Due to the large number of biochemicals that are altered upon oral application of Pg, it is beyond the scope of the current study to describe the possible involvement and effects of all the changes that occurred. However, certain pathways are clearly evident. These include glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathways, amino (hexose) sugar and polyamine metabolism in the brain and in the liver, primary and secondary bile acid metabolism, fatty acid, tryptophan, and methionine metabolism. Cysteine metabolism and glycolysis pathways appear to be altered in the heart. In addition, alterations in polyamine, arginine, lysolipid and lysoplasmalogen pathways are evident in the plasma of animals with oral application of Pg compared with controls.
Periodontal disease is associated with a complex subgingival biofilm including Pg and other bacteria. The implications of bacterial interactions in the etiology of periodontitis were described [58]. The current study is limited by the use of Pg alone rather than a combination of several periodontal pathogens such as T. denticola, T. forsythia, F. nucleatum, and P. Intermedia to mimic a polymicrobial infection [59]. Studies using polymicrobial infections mimicking the complexity of the biofilm may shed light further into the influence of periodontal disease on systemic conditions.
In summary, oral application of Pg induces periodontitis, prediabetes, and alterations in various metabolic pathways in organs distant from the oral cavity. Further studies are needed to validate and expand on our findings and explore the relationship of periodontal pathogens to the large number of systemic diseases and conditions, such as dementia, atherosclerosis, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with which periodontitis has been shown to be associated in humans [60–62].
As a path forward, we hope scientists will investigate various metabolites and metabolic pathways which are altered by periodontal pathogens/bacterial products by examining gene expression as well as post-transcriptional modifications of enzymes, and other proteins involved in these pathways. In addition, more quantitative analysis of biochemicals involved in these metabolic pathways and off shoot pathways using targeted metabolic analyses may greatly help understand the mechanisms that are involved in altered metabolism. Identification of bacterial composition and bacterial products in the gut, periodontal sites, and in different organs may be helpful in understanding the full systemic impact of periodontal pathogens/products. Lastly, identification of mechanisms by which periodontal pathogens/products induce changes in metabolism and how these changes affect the development of prediabetes/T2DM may contribute to the prevention of the global diabetes epidemic and its severe complications.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH R01 DE021405 (KW).
Abbreviations
- Pg
Porphyromonas gingivalis
- HI
hyperinsulinemia
- GI
glucose intolerance
- IR
insulin resistance
- T2DM
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- CEJ
cemento-enamel junction
- HOMA
Homeostatic model assessment
- ipGTT
intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test
- 4-EPS
4-ethylphenylsulfate
References
- 1.Genco RJ, Grossi SG, Ho A, Nishimura F, Murayama Y. A proposed model linking inflammation to obesity, diabetes, and periodontal infections. J Periodontol. 2005;76(11 Suppl):2075–2084. doi: 10.1902/jop.2005.76.11-S.2075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Saito T, Shimazaki Y. Metabolic disorders related to obesity and periodontal disease. Periodontol 2000. 2007;43:254–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2006.00186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Watanabe K, Cho YD. Periodontal disease and metabolic syndrome: a qualitative critical review of their association. Arch Oral Biol. 2014;59:855–870. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2014.05.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Watanabe K, Petro BJ, Shlimon AE, Unterman TG. Effect of periodontitis on insulin resistance and the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Periodontol. 2008;76:1208–1216. doi: 10.1902/jop.2008.070605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ilievski V, Cho Y, Katwala P, Rodriguez H, Tulowiecka M, et al. TLR4 expression by liver resident cells mediates the development of glucose intolerance and insulin resistance in experimental periodontitis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0136502. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Daviss B. Growing pains for metabolomics. The Scientist. 2005;19:25–28. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dunn WB, Broadhurst D, Begley P, Zelena E, Francis-McIntyre S, et al. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat Protoc. 2011;6:1060–1083. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2011.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jordan KW, Nordenstam J, Lauwers GY, Rothenberger DA, Alavi K, et al. Metabolomic characterization of human rectal adenocarcinoma with intact tissue magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Dis Colon Rectum. 2009;52:520–525. doi: 10.1007/DCR.0b013e31819c9a2c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Barnes VM, Kennedy AD, Panagakos F, Devizio W, Trivedi HM, et al. Global metabolomic analysis of human saliva and plasma from healthy and diabetic subjects, with and without periodontal disease. PLoS One. 2014;9:e105181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Marney LC, Kolwicz SC, Jr, Tian R, Synovec RE. Sample preparation methodology for mouse heart metabolomics using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Talanta. 2013;108:123–130. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2013.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cheema AK, Pathak R, Zandkarimi F, Kaur P, Alkhalil L, et al. Liver metabolomics reveals increased oxidative stress and fibrogenic potential in gfrp transgenic mice in response to ionizing radiation. J Proteome Res. 2014;13:3065–3074. doi: 10.1021/pr500278t. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mamas M, Dunn WB, Neyses L, Goodacre R. The role of metabolites and metabolomics in clinically applicable biomarkers of disease. Arch Toxicol. 2011;85:5–17. doi: 10.1007/s00204-010-0609-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Barnes VM, Ciancio SG, Shibly O, Xu T, Devizio W, et al. Metabolomics reveals elevated macromolecular degradation in periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 2011;90:1293–1297. doi: 10.1177/0022034511416240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Aimetti M, Cacciatore S, Graziano A, Tenori L. Metabonomic analysis of saliva reveals generalized chronic periodontitis signature. Metabolomics. 2012;8:465–474. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shin SY, Fauman EB, Petersen AK, Krumsiek J, Santos R, et al. An atlas of genetic influences on human blood metabolites. Nat Genet. 2014;46:543–550. doi: 10.1038/ng.2982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ito H, Hoshi M, Ohtaki H, Taguchi A, Ando K, et al. Ability of IDO to attenuate liver injury in alpha-galactosylceramide-induced hepatitis model. J Immunol. 2010;185:4554–4560. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0904173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ohtaki H, Ito H, Ando K, Ishikawa T, Hoshi M, et al. Kynurenine production mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase aggravates liver injury in HBV-specific CTL-induced fulminant hepatitis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1842:1464–1471. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cesario A, Rocca B, Rutella S. The interplay between indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 in chronic inflammation and cancer. Curr Med Chem. 2011;18:2263–2271. doi: 10.2174/092986711795656063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Larrea E, Riezu-Boj JI, Gil-Guerrero L, Casares N, Aldabe R, et al. Upregulation of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in hepatitis C virus infection. J Virol. 2007;81:3662–3666. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02248-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Oertelt-Prigione S, Mao TK, Selmi C, Tsuneyama K, Ansari AA, et al. Impaired indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase production contributes to the development of autoimmunity in primary biliary cirrhosis. Autoimmunity. 2008;41:92–99. doi: 10.1080/08916930701619730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tanaka N, Matsubara T, Krausz KW, Patterson AD, Gonzalez FJ. Disruption of phospholipid and bile acid homeostasis in mice with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2012;56:118–129. doi: 10.1002/hep.25630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Honda A, Yoshida T, Tanaka N, Matsuzaki Y, He B, et al. Increased bile acid concentration in liver tissue with cholesterol gallstone disease. J Gastroenterol. 1995;30:61–66. doi: 10.1007/BF01211376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lopaschuk GD. Alterations in fatty acid oxidation during reperfusion of the heart after myocardial ischemia. Am J Cardiol. 1997;80:11A–16A. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(97)00453-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jaswal JS, Keung W, Wang W, Ussher JR, Lopaschuk GD. Targeting fatty acid and carbohydrate oxidation – a novel therapeutic intervention in the ischemic and failing heart. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813:1333–1350. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Michalek RD, Rathmell JC. The metabolic life and times of a T-cell. Immunol Rev. 2011;236:190–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2010.00911.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Macintyre AN, Rathmell JC. Activated lymphocytes as a metabolic model for carcinogenesis. Cancer Metab. 2013;1:5. doi: 10.1186/2049-3002-1-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hsiao EY, McBride SW, Hsien S, Sharon G, Hyde ER, et al. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell. 2013;155:1451–1463. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Naderi S, Carruthers A, Melchior DL. Modulation of red blood cell sugar transport by lyso-lipid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989;985:173–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90363-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Reiss D, Beyer K, Engelmann B. Delayed oxidative degradation of polyunsaturated diacyl phospholipids in the presence of plasmalogen phospholipids in vitro. Biochem J. 1997;323:807–814. doi: 10.1042/bj3230807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dudda A, Spiteller G, Kobelt F. Lipid oxidation products in ischemic porcine heart tissue. Chem Phys Lipids. 1996;82:39–51. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(96)02557-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pegg AE. Mammalian polyamine metabolism and function. IUBMB Life. 2009;61:880–894. doi: 10.1002/iub.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schuber F. Influence of polyamines on membrane functions. Biochem J. 1989;260:1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj2600001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Thomas T, Thomas TJ. Polyamines in cell growth and cell death: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001;58:244–258. doi: 10.1007/PL00000852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Halonen T, Sivenius J, Miettinen R, Halmekytö M, Kauppinen R, et al. Elevated seizure threshold and impaired spatial learning in transgenic mice with putrescine overproduction in the brain. Eur J Neurosci. 1993;5:1233–1239. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Slotkin TA, Bartolome J, Persons D, Whitmore WL. Polyamines in brain and heart of the neonatal rat: effects of inhibitors of ornithine decarboxylase and spermidine synthase. Life Sci. 1984;35:1125–1131. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gupta VK, Scheunemann L, Eisenberg T, Mertel S, Bhukel A, et al. Restoring polyamines protects from age – induced memory impairment in an autophagy-dependent manner. Nat Neurosci. 2013;16:1453–1460. doi: 10.1038/nn.3512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Falkowska A, Gutowska I, Goschorska M, Nowacki P, Chlubek D, et al. Energy metabolism of the brain, including the cooperation between astrocytes and neurons, especially in the context of glycogen metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16:25959–25981. doi: 10.3390/ijms161125939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Howard AD, Moore J, Jr, Welch PG, Gouge SF. Analysis of the quantitative relationship between anemia and chronic renal failure. Am J Med Sci. 1989;297:309–313. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198905000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Stöckler S, Holzbach U, Hanefeld F, Marquardt I, Helms G, et al. Creatine deficiency in the brain: a new, treatable inborn error of metabolism. Pediatr Res. 1994;36:409–413. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199409000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dungan KM. 1,5-anhydroglucitol (GlycoMark) as a marker of short-term glycemic control and glycemic excursions. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2008;8:9–19. doi: 10.1586/14737159.8.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mook-Kanamori DO, Selim MM, Takiddin AH, Al-Homsi H, Al-Mahmoud KA, et al. 1,5-anhydroglucitol in saliva is a noninvasive marker of short-term glycemic control. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:E479–E483. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Simons K, Toomre D. Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000;1:31–39. doi: 10.1038/35036052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Memon RA, Holleran WM, Moser AH, Seki T, Uchida Y, et al. Endotoxin and cytokines increase hepatic sphingolipid biosynthesis and produce lipoproteins enriched in ceramides and sphingomyelin. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998;18:1257–1265. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.18.8.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Stranahan AM, Cutler RG, Button C, Telljohann R, Mattson MP. Diet-induced elevations in serum cholesterol are associated with alterations in hippocampal lipid metabolism and increased oxidative stress. J Neurochem. 2011;118:611–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Das DK, Engelman RM, Rousou JA, Breyer RH. Aerobic vs anaerobic metabolism during ischemia in heart muscle. Ann Chir Gynaecol. 1987;76:68–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kolwicz SC, Jr, Tian R. Glucose metabolism and cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;90:194–201. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lustgarten MS, Price LL, Phillips EM, Kirn D, Mills J, et al. Serum predictors of percent lean mass in young adults. J Strength Cond Res. 2013 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e31829eef24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Nakajima M, Arimatsu K, Kato T, Matsuda Y, Minagawa T, et al. Oral administration of P. gingivalis induces dysbiosis of gut microbiota and impaired barrier function leading to dissemination of enterobacteria to the liver. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0134234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Arimatsu K, Yamada H, Miyazawa H, Minagawa T, Nakajima M, et al. Oral pathobiont induces systemic inflammation and metabolic changes associated with alteration of gut microbiota. Sci Rep. 2014;4:4828. doi: 10.1038/srep04828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lalla E, Lamster IB, Hoffman MA, Bucciarelli L, Jerud AP, et al. Oral infection with a periodontal pathogen accelerates early atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-null mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23:1405–1411. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000082462.26258.FE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Baker PJ, DuFour L, Dixon M, Roopenian DC. Adhesion molecule deficiencies increase Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced alveolar bone loss in mice. Infect Immun. 2000;68:3103–3107. doi: 10.1128/iai.68.6.3103-3107.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kuula H, Salo T, Pirilä E, Tuomainen AM, Jauhiainen M, et al. Local and systemic responses in matrix metalloproteinase 8-deficient mice during Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced periodontitis. Infect Immun. 2009;77:850–859. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00873-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Polak D, Wilensky A, Shapira L, Halabi A, Goldstein D, et al. Mouse model of experimental periodontitis induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis/Fusobacterium nucleatum infection: bone loss and host response. J Clin Periodontol. 2009;36:406–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2009.01393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sasaki H, Okamatsu Y, Kawai T, Kent R, Taubman M, et al. The interleukin-10 knockout mouse is highly susceptible to Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced alveolar bone loss. J Periodontal Res. 2004;39:432–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2004.00760.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Burns E, Bachrach G, Shapira L, Nussbaum G. Cutting edge: TLR2 is required for the innate response to Porphyromonas gingivalis: activation leads to bacterial persistence and TLR2 deficiency attenuates induced alveolar bone resorption. J Immunol. 2006;177:8296–8300. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.12.8296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wilensky A, Gabet Y, Yumoto H, Houri-Haddad Y, Shapira L. Three-dimensional quantification of alveolar bone loss in Porphyromonas gingivalis-infected mice using micro-computed tomography. J Periodontol. 2005;76:1282–1286. doi: 10.1902/jop.2005.76.8.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Buse JB, Freeman JL, Edelman SV, Jovanovic L, McGill JB. Serum 1,5-anhydroglucitol (GlycoMark): a short-term glycemic marker. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2003;5:355–363. doi: 10.1089/152091503765691839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kuramitsu HK, He X, Lux R, Anderson MH, Shi W. Interspecies interactions within oral microbial communities. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007;71:653–670. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00024-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Rivera MF, Lee JY, Aneja M, Goswami V, Liu L, et al. Polymicrobial infection with major periodontal pathogens induced periodontal disease and aortic atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemicApoE(null) mice. PLoS One. 2013;8:e57178. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Noble JM, Borrell LN, Papapanou PN, Elkind MS, Scarmeas N, et al. Periodontitis is associated with cognitive impairment among older adults: analysis of NHANES-III. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009;80:1206–1211. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2009.174029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Söder PO, Söder B, Nowak J, Jogestrand T. Early carotid atherosclerosis in subjects with periodontal diseases. Stroke. 2005;36:1195–1200. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000165916.90593.cb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yoneda M, Naka S, Nakano K, Wada K, Endo H, et al. Involvement of a periodontal pathogen, Porphyromonas gingivalis on the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012;12:16. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-12-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


