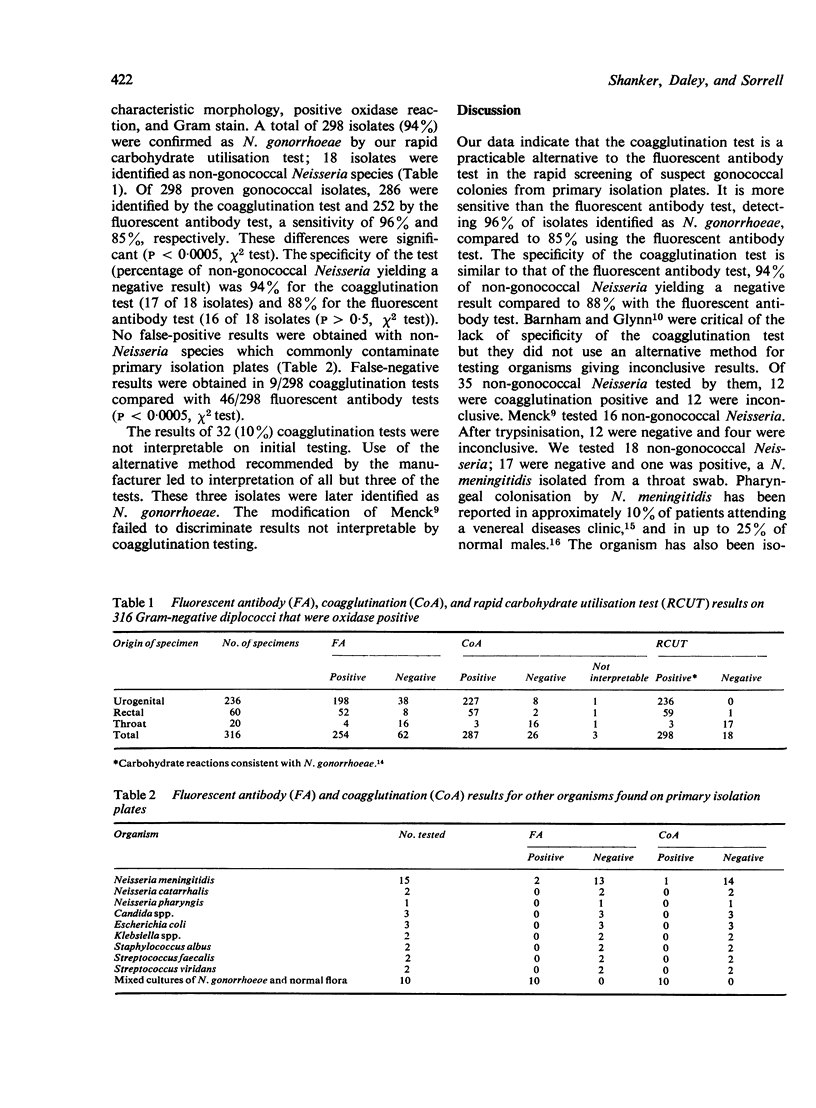
Abstract
The Phadebact(R) Gonococcus Test, a slide coagglutination test, was compared with the Difco fluorescent antibody test for the identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolated from 18- to 24-hour primary plates. A total of 316 morphologically characteristic, oxidase-positive, Gram-negative diplococci were tested. Altogether 298 isolates were identified definitively as N. gonorrhoeae by a rapid carbohydrate utilisation test; 287 of the 298 isolates of N. gonorrhoeae were identified by the coagglutination test, a sensitivity of 96%. The sensitivity of the fluorescent antibody test was 85% (254 of 298 isolates). False-positive results due to cross-reactions with non-gonococcal Neisseria were uncommon (1 of 18 non-gonococcal isolates in the coagglutination test, a specificity of 94%; 2 of 18 in the fluorescent antibody test, a specificity of 88%). None of the 14 other contaminant organisms seen frequently on primary isolation media gave positive reactions. Interpretation of the coagglutination test proved to be difficult initially. Thirty-two (10%) coagglutination tests had to be repeated; 3 of the 32 (1% of the total isolates tested) remained uninterpretable.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvilommi H. Grouping of beta-haemolytic streptococci by using coagglutination, precipitation or bacitracin sensitivity. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Apr;84(2):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnham M., Glynn A. A. Identification of clinical isolates of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by a coagglutination test. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Feb;31(2):189–193. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Kahlmeter G., Jonsson S., Kronvall G. New method for the serological grouping of Streptococci with specific antibodies adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):881–885. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.881-885.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson D., Kronvall G. Slide agglutination method for the serological identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with anti-gonococcal antibodies adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):368–374. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.368-374.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards E. A., Larson G. L. New method of grouping beta-hemolytic streptococci directly on sheep blood agar plates by coagglutination of specifically sensitized protein A-containing staphylococci. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):972–976. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.972-976.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Givan K. F., Thomas B. W., Johnston A. G. Isolation of Neisseria meningitidis from the urethra, cervix, and anal canal: further observations. Br J Vener Dis. 1977 Apr;53(2):109–112. doi: 10.1136/sti.53.2.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield S., Sheehe P. R., Feldman H. A. Meningococcal carriage in a population of "normal" families. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jan;123(1):67–73. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn G., Nyberg I. Identification of streptococcal groups A,B,C, and G by slide co-agglutination of antibody-sensitized protein A-containing staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):99–101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.99-101.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Turner E. M. Rapid fermentation confirmation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):550–552. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.550-552.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A rapid slide-agglutination method for typing pneumococci by means of specific antibody adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):187–190. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Efstratiou A., Parker M. T. Letter: Agglutination grouping of Streptococci. Lancet. 1976 Sep 25;2(7987):692–693. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92510-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menck H. Identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in cultures from tonsillo-pharyngeal specimens by means of a slide co-agglutination test (Phadebact Gonococcus Test). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Jun;84(3):139–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. A., Millikin P., Griffin P. S., Sexton R. A., Yousuf M. Neisseria meningitidis urethritis. A case report. JAMA. 1979 Oct 12;242(15):1656–1657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. C., Cooper R. M., Miller B. R. Pharyngeal colonisation by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis in black and white patients attending a venereal disease clinic. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Feb;55(1):14–19. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willmott F. E. Meningococcal salpingitis. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Jun;52(3):182–183. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.3.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. Cultural diagnosis of gonorrhoea with modified New York City (MNYC) medium. Br J Vener Dis. 1978 Feb;54(1):36–40. doi: 10.1136/sti.54.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H., Paterson I. C., McDonald D. R. Rapid carbohydrate utilization test for the identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Jun;52(3):172–175. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.3.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


