Abstract
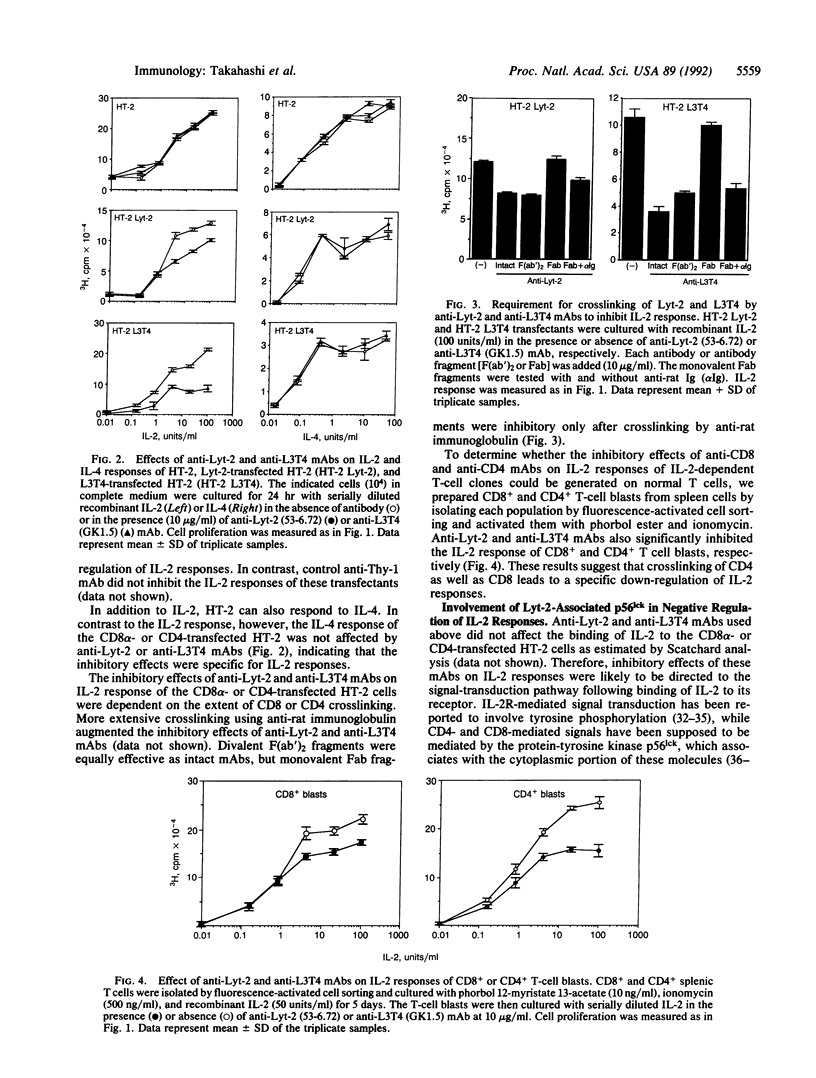
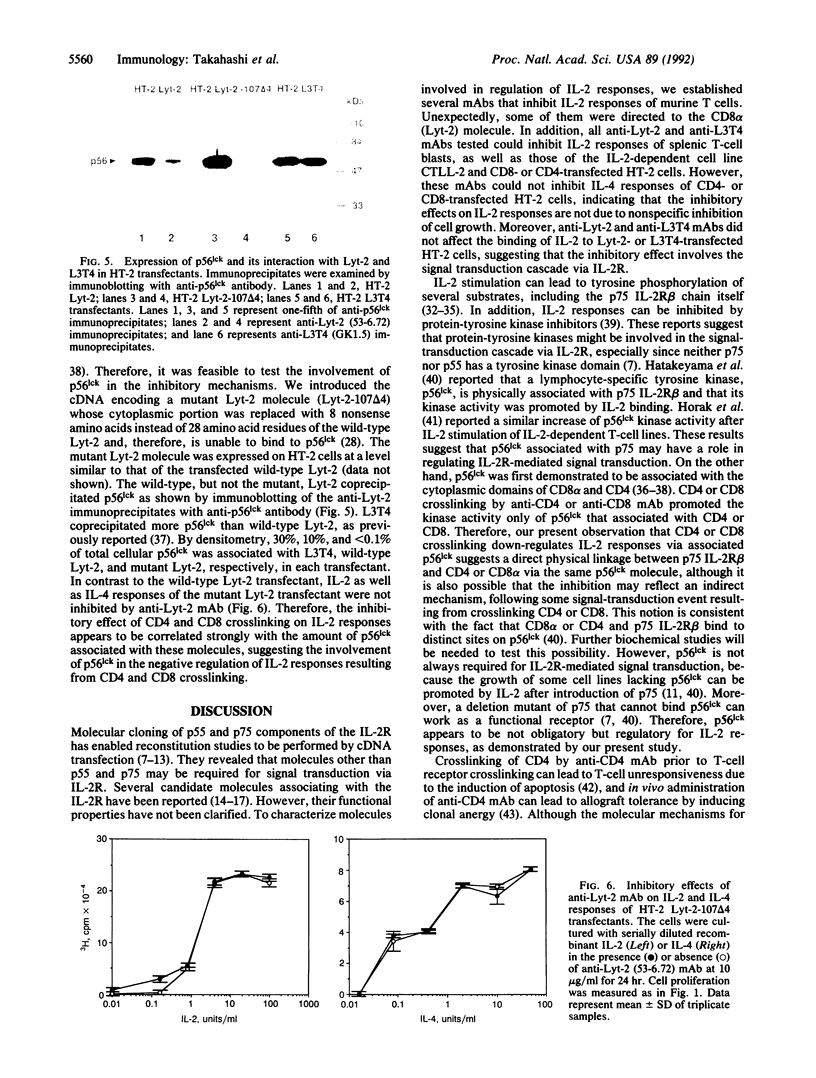
To characterize the T-cell surface molecules involved in regulation of T-cell interleukin 2 (IL-2) responses, we established several monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that inhibit IL-2 responses of freshly isolated CD8+ T cells and the IL-2-dependent cell line CTLL-2. Here we show that two inhibitory mAbs are directed against Lyt-2 (CD8 alpha). In fact, all anti-Lyt-2 mAbs tested were able to inhibit the IL-2 response of the Lyt-2- and L3T4-deficient cell line HT-2 after transfection with a Lyt-2 cDNA clone. Similarly, anti-L3T4 mAbs inhibited the IL-2 response of CD4-transfected HT-2 cells. These inhibitory effects of anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 mAbs occur on normal T lymphocytes, since they also were observed with CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell blasts, and are specific for IL-2 responses, since IL-4 responses of CD4- and CD8-transfected HT-2 cells were not affected by the anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 mAbs. The inhibitory effects of anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 mAbs could not be explained by interference with IL-2 binding and depended on CD4 and CD8 crosslinking, because F(ab')2 or Fab plus crosslinking second antibody, but not Fab alone, were effective. A mutant Lyt-2 molecule lacking the cytoplasmic region that mediates p56lck binding could not mediate the inhibitory effect upon crosslinking. These results suggest that CD4 and CD8 mediate negative regulation of T-cell IL-2 responses via cytoplasmically associated p56lck.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alters S. E., Shizuru J. A., Ackerman J., Grossman D., Seydel K. B., Fathman C. G. Anti-CD4 mediates clonal anergy during transplantation tolerance induction. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):491–494. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asao H., Takeshita T., Nakamura M., Nagata K., Sugamura K. Interleukin 2 (IL-2)-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of IL-2 receptor p75. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):637–644. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballhausen W. G., Reske-Kunz A. B., Tourvieille B., Ohashi P. S., Parnes J. R., Mak T. W. Acquisition of an additional antigen specificity after mouse CD4 gene transfer into a T helper hybridoma. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1493–1498. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber E. K., Dasgupta J. D., Schlossman S. F., Trevillyan J. M., Rudd C. E. The CD4 and CD8 antigens are coupled to a protein-tyrosine kinase (p56lck) that phosphorylates the CD3 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3277–3281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Haemopoietic receptors and helical cytokines. Immunol Today. 1990 Oct;11(10):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90139-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., Neckers L. M., Rosolen A. Putative gamma-subunit of the IL-2 receptor is detected in low, intermediate, and high affinity IL-2 receptor-bearing cells. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi T., Hatakeyama M., Minamoto S., Kono T., Mori H., Taniguchi T. Human interleukin 2 (IL 2) receptor beta chain allows transduction of IL 2-induced proliferation signal(s) in a murine cell line. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2375–2378. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris D. K., Willette-Brown J., Ortaldo J. R., Farrar W. L. IL-2 regulation of tyrosine kinase activity is mediated through the p70-75 beta-subunit of the IL-2 receptor. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):870–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. R., Scearce R. M., Hoffman J. A., Peffer N. J., Hammes S. R., Hosking J. B., Schmandt R., Kuziel W. A., Haynes B. F., Mills G. B. A tyrosine kinase physically associates with the beta-subunit of the human IL-2 receptor. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1253–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Kono T., Kobayashi N., Kawahara A., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M., Taniguchi T. Interaction of the IL-2 receptor with the src-family kinase p56lck: identification of novel intermolecular association. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1523–1528. doi: 10.1126/science.2047859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Mori H., Doi T., Taniguchi T. A restricted cytoplasmic region of IL-2 receptor beta chain is essential for growth signal transduction but not for ligand binding and internalization. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90607-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Tsudo M., Minamoto S., Kono T., Doi T., Miyata T., Miyasaka M., Taniguchi T. Interleukin-2 receptor beta chain gene: generation of three receptor forms by cloned human alpha and beta chain cDNA's. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):551–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2785715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I. D., Gress R. E., Lucas P. J., Horak E. M., Waldmann T. A., Bolen J. B. T-lymphocyte interleukin 2-dependent tyrosine protein kinase signal transduction involves the activation of p56lck. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1996–2000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Melchers F. Establishment of mouse cell lines which constitutively secrete large quantities of interleukin 2, 3, 4 or 5, using modified cDNA expression vectors. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):97–104. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo O., Foo M., Sachs D. H., Samelson L. E., Bluestone J. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody specific for a murine T3 polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman D. R. The structure of the CD4 and CD8 genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:561–584. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal J. W., Corthésy P., Tougne C., Lees R., MacDonald H. R., Nabholz M. High and low affinity IL 2 receptors: analysis by IL 2 dissociation rate and reactivity with monoclonal anti-receptor antibody PC61. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3988–3994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merida I., Gaulton G. N. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation associated with activation of the interleukin 2 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5690–5694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M., Isakov N., Altman A. T cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C requires tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1584–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.2138816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Takahashi K., Fukazawa T., Koyanagi M., Yokoyama A., Kato H., Yagita H., Okumura K. Relative contribution of CD2 and LFA-1 to murine T and natural killer cell functions. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3628–3634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Takahashi K., Koyanagi M., Yagita H., Okumura K. Activation of a natural killer clone upon target cell binding via CD2. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Mar;21(3):831–834. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell M. K., Haughn L. J., Maroun C. R., Julius M. H. Death of mature T cells by separate ligation of CD4 and the T-cell receptor for antigen. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):286–289. doi: 10.1038/347286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta T., Yagita H., Azuma T., Sato K., Okumura K. Bispecific F (ab')2 monomer prepared with anti-CD3 and anti-tumor monoclonal antibodies is most potent in induction of cytolysis of human T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Aug;19(8):1437–1441. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto Y., Minamoto S., Shimizu K., Mogami H., Taniguchi T. Interleukin 2 receptor beta chain expressed in an oligodendroglioma line binds interleukin 2 and delivers growth signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6584–6588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Anderson P., Morimoto C., Streuli M., Schlossman S. F. Molecular interactions, T-cell subsets and a role of the CD4/CD8:p56lck complex in human T-cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1989 Oct;111:225–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragovi H., Malek T. R. Evidence for additional subunits associated to the mouse interleukin 2 receptor p55/p75 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon M., Gnarra J. R., Leonard W. J. A 100-kilodalton protein is associated with the murine interleukin 2 receptor: biochemical evidence that p100 is distinct from the alpha and beta chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4869–4873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon M., Klausner R. D., Cullen B. R., Chizzonite R., Leonard W. J. Novel interleukin-2 receptor subunit detected by cross-linking under high-affinity conditions. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):859–863. doi: 10.1126/science.3095922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin-2: inception, impact, and implications. Science. 1988 May 27;240(4856):1169–1176. doi: 10.1126/science.3131876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Yssel H., Paliard X., Kastelein R., Figdor C., de Vries J. E. IL-4 inhibits IL-2-mediated induction of human lymphokine-activated killer cells, but not the generation of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in mixed leukocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):29–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Nakamura T., Koyanagi M., Kato K., Hashimoto Y., Yagita H., Okumura K. A murine very late activation antigen-like extracellular matrix receptor involved in CD2- and lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1-independent killer-target cell interaction. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4371–4379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita T., Asao H., Suzuki J., Sugamura K. An associated molecule, p64, with high-affinity interleukin 2 receptor. Int Immunol. 1990;2(5):477–480. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.5.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Tsudo M., Karasuyama H., Toyama N., Hatakeyama M., Taniguchi T., Miyasaka M. Signal transduction through the human IL-2 receptor beta-chain expressed in IL-6-dependent mouse B cell hybridoma. Int Immunol. 1991 Jan;3(1):105–108. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teshigawara K., Wang H. M., Kato K., Smith K. A. Interleukin 2 high-affinity receptor expression requires two distinct binding proteins. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):223–238. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Karasuyama H., Kitamura F., Nagasaka Y., Tanaka T., Miyasaka M. Reconstitution of a functional IL-2 receptor by the beta-chain cDNA. A newly acquired receptor transduces negative signal. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4039–4043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Karasuyama H., Kitamura F., Tanaka T., Kubo S., Yamamura Y., Tamatani T., Hatakeyama M., Taniguchi T., Miyasaka M. The IL-2 receptor beta-chain (p70). Ligand binding ability of the cDNA-encoding membrane and secreted forms. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):599–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Kozak R. W., Goldman C. K., Waldmann T. A. Contribution of a p75 interleukin 2 binding peptide to a high-affinity interleukin 2 receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4215–4218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Kozak R. W., Goldman C. K., Waldmann T. A. Demonstration of a non-Tac peptide that binds interleukin 2: a potential participant in a multichain interleukin 2 receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9694–9698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Kappler J., Dialynas D. P., Fitch F. W. Evidence implicating L3T4 in class II MHC antigen reactivity; monoclonal antibody GK1.5 (anti-L3T4a) blocks class II MHC antigen-specific proliferation, release of lymphokines, and binding by cloned murine helper T lymphocyte lines. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2178–2183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagita H., Nakamura T., Karasuyama H., Okumura K. Monoclonal antibodies specific for murine CD2 reveal its presence on B as well as T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):645–649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagita H., Nakata M., Azuma A., Nitta T., Takeshita T., Sugamura K., Okumura K. Activation of peripheral blood T cells via the p75 interleukin 2 receptor. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1445–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao L., Nakauchi H., Honjo T., Kawakami T. The cytoplasmic domain of the CD8 alpha-chain is required for its interaction with p56lck. Immunol Lett. 1990 Jul;24(4):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90011-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]