Abstract
Rce1p and Ste24p are integral membrane proteins involved in the proteolytic maturation of isoprenylated proteins. Extensive published evidence indicates that Rce1p requires the isoprenyl moiety as an important substrate determinant. By contrast, we report that Ste24p can cleave both isoprenylated and non-prenylated substrates in vitro, indicating that the isoprenyl moiety is not required for substrate recognition. Steady-state enzyme kinetics are significantly different for prenylated versus non-prenylated substrates, strongly suggestive of a role for substrate-membrane interaction in protease function. Mass spectroscopy analyses identify a cleavage preference at bonds where P1′ is aliphatic in both isoprenylated and non-prenylated substrates, although this is not necessarily predictive. The identified cleavage sites are not at a fixed distance position relative to the C terminus. In this study, the substrates cleaved by Ste24p are based on known isoprenylated proteins (i.e. K-Ras4b and the yeast a-factor mating pheromone) and non-prenylated biological peptides (Aβ and insulin chains) that are known substrates of the M16A family of soluble zinc-dependent metalloproteases. These results establish that the substrate profile of Ste24p is broader than anticipated, being more similar to that of the M16A protease family than that of the Rce1p CAAX protease with which it has been functionally associated.
Keywords: enzyme kinetics, membrane enzyme, metalloprotease, peptidase, protein isoprenylation
Introduction
The CAAX motif is a loosely defined tetrapeptide C-terminal sequence; C represents cysteine, A is typically aliphatic, and X can be one of several amino acids. Proteins bearing a CAAX motif (i.e. CAAX proteins) are abundant, estimated at 1–2% of eukaryotic proteins. They have roles in many biological processes, including cancer, development, aging, and parasitic growth, among others. Canonical CAAX proteins undergo an ordered series of post-translational modification: isoprenylation (farnesylation or geranylgeranylation) of cysteine (C), endoproteolysis by the Rce1p and/or Ste24p protease to remove the C-terminal tripeptide (AAX), and carboxyl methylation of the isoprenylated cysteine. These modifications are generally thought to modulate CAAX protein function and/or localization (1). Although these modifications are not known to occur within bacteria, prokaryotic orthologs of both CAAX proteases exist.
The necessity for two CAAX proteases with differing specificity is proposed to stem from the many possible permutations of the CAAX motif (2, 3). Rce1p and Ste24p are both ER2 membrane-localized proteases capable of cleaving isoprenylated CAAX proteins, yet they are neither structurally related nor functionally redundant (3–7). Rce1p cleaves the isoprenylated CAAX motifs of Ras and Ras-related GTPases (Rho, Rac, etc.) in various species (8–12). Both Rce1p and Ste24p can cleave the CAAX motif of the yeast a-factor precursor (CVIA). No naturally occurring Ste24p-specific CAAX motifs have been discovered. The few Ste24p-specific CAAX motifs reported thus far have been identified by mutating the natural CAAX motif of yeast a-factor. In addition to its reported role as a CAAX protease, Ste24p also cleaves the precursors of a-factor and human lamin A (prelamin A) at sites distal to the CAAX motif (13–15). The distal cleavage sites of these proteins lack sequence similarity and vary in distance from the isoprenylated cysteine (14 and 25 residues, respectively).
Orthologs of Rce1p and Ste24p are found across diverse species, including bacteria, and in all cases, the proteases are membrane proteins. The structure of Methanococcus maripauludis Rce1p (MmRce1p) reveals a hydrophobic substrate-binding pocket that is solvent-exposed and a novel aspartate-histidine dependent active site (16). The structure is consistent with mutational studies identifying these residues as critical for activity of Rce1p from various eukaryotic species (4, 5, 17). Despite the absence of identified isoprenylated proteins in prokaryotes, MmRce1p cleaves a farnesylated substrate in vitro (18, 19).
Structures of yeast and human Ste24p reveal this protease family to form a large fully enclosed chamber that contains a zinc-dependent active site (6, 7). The chambered active site is fully protected from its membrane surroundings, leaving open the question of how substrates gain access. A chambered active site, although unusual, exists in other metalloprotease families, notably the M16A family of soluble zinc-dependent metalloproteases (20, 21). The Ste24p chamber (∼14,000 Å3) has dimensions similar to those of the typical M16A protease chamber (∼16,000 Å3). Interestingly, both protease families possess extended β-strand secondary structure near the active site that, in the case of M16A proteases, is responsible for orienting substrates (Fig. 1) (20). The human M16A protease IDE cleaves numerous small peptides and has been implicated in the clearance of neurotoxic Aβ peptides and other amyloidogenic peptides (22–26). The yeast M16A protease Ste23p also cleaves amyloidogenic peptides (27). Coincidentally, the yeast M16A proteases Axl1p and Ste23p are both involved in a-factor production (28).
FIGURE 1.
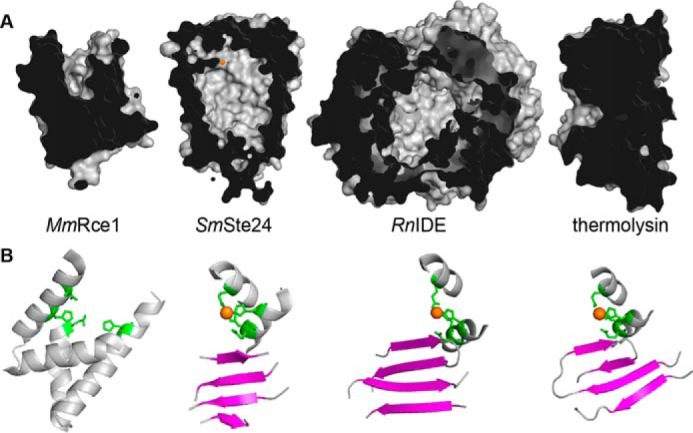
Structural views of MmRce1, SmSte24p, RnIDE, and BtThermolysin. A, cut-away views reveal the groove of MmRce1p, chambers of SmSte24p and RnIDE, and globular structure of BtThermolysin. The structures were created using PyMOL from Protein Data Bank files 4CAD, 4IL3, 2JG4, and 1LND. B, structure surrounding active sites of MmRce1, SmSte24p, RnIDE, and BtThermolysin. The active sites of the metalloproteases were oriented similarly to showcase the active site Zn2+ co-factor (orange), Zn2+-chelating residues (green), and nearby β-strand platform (magenta). The structures were created using PyMOL from Protein Data Bank files 4CAD (residues 138–179, 200–215, and 218–236), 4IL3 (223–227, 248–254, 274–280, 263–268, 295–305, and 386–394), 2JG4 (83–94, 106–115, 135–155, 185–193, and 253–261), and 1LND (37–47, 98–124, 140–148, and 163–170).
Ste24p is found in all domains of life. In humans, loss of Ste24p function is associated with defective deposition of nuclear lamin A and is associated with several diseases: Hutchinson-Gilford progeria, mandibuloacral dysplasia, and generalized lipodystrophy (29). In Drosophila, Ste24p is implicated in regulation of cytoskeletal remodeling associated with spermatid maturation and a germ cell migration event that is posited to involve production of a yet to be identified secreted, isoprenylated signaling molecule (30, 31). In yeast, where the precursor of the a-factor mating pheromone is the best described Ste24p substrate to date, other substrates are highly likely. Their existence is inferred from the observation that Ste24p is expressed at high levels (i.e. among the top 10% most abundant proteins in yeast) and in cells that do not produce a-factor (i.e. MATα and diploid cells) (32, 33).
In this study, we have taken cues from substrate competition experiments and the similarity in structures between Ste24p and M16A family enzymes to more deeply explore the substrate profile of Ste24p. We have determined that Ste24p cleaves non-prenylated peptides, including the Aβ peptide. By contrast, Rce1p does not cleave these substrates. Our findings firmly establish that Ste24p has a broader substrate specificity than previously recognized. These findings provide potential insight into the biological function of Ste24p and suggest that its major biological role may not be as a CAAX protease.
Experimental Procedures
Substrates, Competitors, and Other Reagents
Peptides and reagents were purchased from commercial sources: Aβ 1–40 (rPeptide, Bogart, GA); a-factor, human recombinant insulin, bovine insulin B-chain, and trans,trans-farnesyl bromide(Sigma-Aldrich); carboxymethylated porcine insulin A- and B-chains (Schwarz/Mann); 15-mers based on a-factor YIIKGVFWDPACVIA and YIIKGVFWDPAC(farnesyl)VIA (California Peptide, Napa, CA); Zymolyase 100T (Cape Cod Inc., East Falmouth, MA); Escherichia coli polar lipid (Avanti Polar Lipids, Alabaster, AL). The fluorescent, farnesylated 9-mer peptides ABZ-KSKTKC(farnesyl)VIKD and ABZ-KSKTKC(farnesyl)KDIM were purchased from Anaspec (San Jose, CA); KD was denoted as QL in previous publications (4, 34). The fluorescent, non-prenylated, peptides based on a-factor (ABZ-SEKKDNYIIKGVYNITRO; M16A reporter) and human Aβ (DAEFRHDSGYEVHHQKDABCYLLVFFAEEDANSDVGSNK) werepurchased from CHI Scientific (Maynard, MA); YNITRO was denoted as nitroY in previous publications (27, 35). Trans,trans-farnesyl bromide was prepared as 100 mm stock in DMSO. E. coli polar lipid was prepared at 50 mg/ml in H2O and stored under nitrogen gas. Fluorescent isoprenylated and non-prenylated peptides were prepared as 1 mm stocks in 4% DMSO. Isoprenylated and non-prenylated a-factor-based peptides were prepared as 1 mm stocks in methanol. Non-prenylated Aβ 1–40 and insulin-based peptides were prepared as 4 mg/ml stocks in 100% DMSO. Before use, Aβ 1–40 and insulin-based peptides were incubated for 20 min in a water bath sonicator and heated at 65 °C for 5 min.
Plasmids and Yeast Strains
Plasmid-transformed versions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain SM3614 (MATa trp1 leu2 ura3 his4 can1 rce1::TRP1 ste24::LEU2) were created using published methods (2). Previously described plasmids used were pRS316 (CEN URA3) (36), pSM1282 (2μ URA3 PPGK-HIS-HA-ScSTE24) (2), pWS804 (pT7-HIS-RnIDEM42-L1019) (27), pWS335 (2μ URA3 PPGK-HIS-HA-HsRce1Δ22), and pWS479 (2μ URA3 PPGK-ScRCE1-HA) (4). pWS1275 (2μ URA3 PPGK-HA-HsSTE24) was created by PCR-directed, plasmid-based recombination (37). The PCR fragment containing HA-HsSTE24 was derived from pSM1468 (CEN URA3 HsSTE24) using appropriately designed PCR primers (2); the recipient vector pWS767 (2μ URA3 PPGK-HIS-HA-TbSTE24) was digested using EcoRI and MluI before use (5).
Proteases
Rat IDE was expressed in BL21 DE3 E. coli from plasmid pWS804 and was purified as described previously (38). Saccharomyces mikatae Ste24p (SmSte24p) was purified as described previously (6). Membranes used as a source of protease activities were prepared from yeast strains expressing Rce1p or Ste24p according to our previously reported methods (4, 5, 39). The yeast strains were derived by transforming SM3614 with the desired overexpression plasmid: vector (pRS316), ScSte24p (pSM1282), HsRce1 (pWS335), ScRce1p (pWS479), or pWS1275 (HsSTE24). Isolated membranes were stored at −80 °C as 1 mg/ml total protein stocks in Lysis Buffer (50 mm Tris, pH 7.5, 0.2 m sorbitol, 1 mm EDTA, 0.2% NaN3) containing protease inhibitors (1 μg/ml each chymostatin, leupeptin, pepstatin, and aprotinin; 1 μm PMSF).
In Vitro Fluorescence-based Proteolysis Assay
A fluorescence-based assay was used to monitor protease-dependent cleavage of internally quenched fluorogenic peptide substrates (4, 40, 41). In general, the assay involved mixing 50 μl of substrate with 50 μl of yeast membrane suspension or purified protease, where each individual component was prepared at twice the intended final concentration. The individual components were assembled in a 96-well microtiter plate (Corning 3631), and fluorescence was measured at regular intervals over a 60-min time course at 30 °C using a Bio-Tek Synergy fluorometer equipped with a 320/420-nm excitation/emission filter set. For the Aβ 1–28 peptide, a 320/485-nm filter set was used. Samples were typically analyzed in duplicate.
Unless otherwise noted, the substrate components were prepared by dilution of stocks to 40 μm with HM buffer (100 mm HEPES, pH 7.5, 10 mm MgCl2). The enzyme components were prepared by diluting membrane stocks to 0.2 mg/ml (total protein concentration determined by the Bradford protein assay) with HM-BSA buffer (100 mm HEPES, pH 7.5, 10 mm MgCl2, 1 mg/ml BSA), purified rat IDE to 0.08 mg/ml (measured using A280 nm and a calculated extinction coefficient of 113,570 m−1 cm−1) with HM-BSA buffer, and purified SmSte24p (measured using A280 nm and a calculated extinction coefficient of 58,790 m−1 cm−1) to 0.08 mg/ml in HM buffer. Studies involving purified SmSte24p included added E. coli polar lipid (125 or 500 μg/ml) as a buffer component, except for mass spectroscopy studies (see below). For competition assays, substrate and competitor were premixed at appropriate molar ratios in the microtiter plate before the addition of enzyme. For Km determinations, a range of substrate concentration was used (0–200 μm).
Activity and Kinetic Analyses
For all fluorescence-based assays, data were graphed using Microsoft Excel. Initial linear slopes (relative fluorescence units/min) were determined using a time window that was manually optimized for each condition (usually minutes 1–10).
To obtain percent activity, values were calculated relative to an appropriate control (i.e. solvent-, DMSO-, or methanol-treated). When DTT and iodoacetamide were used in reactions, insulin or DMSO was preincubated for 15 min at room temperature with a 3-fold molar excess of DTT followed by quenching for 15 min with a 2-fold molar excess of iodoacetamide relative to DTT. The data for each experimental condition were generally collected in replicate, often across two or more independent experiments. See the figure legends for details.
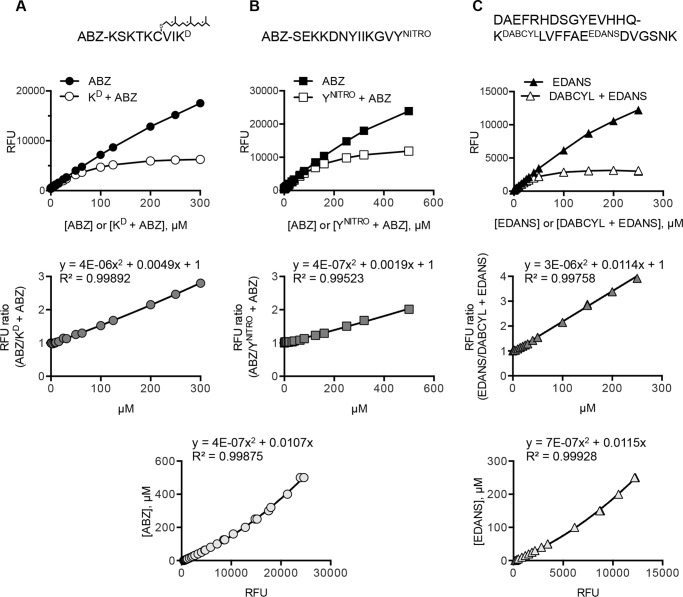
To obtain reaction rates and other kinetic parameters, rate values (relative fluorescence units/min) were converted to product amounts per minute (μmol/min) by referencing two standard curves (27, 35, 42). First, the amount of fluorescence observed was corrected for intermolecular quenching using standard curves for fluorophore alone and a 1:1 mixture of fluorophore and quencher pair (Fig. 2). This was necessary at high substrate concentration but not generally needed for comparative activity assays at lower concentrations. Second, the corrected amount of fluorescent product was converted to a mole amount of product using a fluorophore-only standard curve. Kinetic parameters (i.e. Km and Vmax) were extracted from a curve fit by non-linear regression methods (Prism version 6.0, GraphPad Software Inc.).
FIGURE 2.
Correlation between fluorescence and peptide concentration. Peptides used in kinetic studies are indicated at the top of each column of corresponding calibration curves. Top row of graphs, effect of intermolecular quenching on fluorescence. Fluorescence output (relative fluorescence units (RFU)) was independently measured for free ABZ (A and B) and EDANS (C) and a 1:1 molar mixture of KD and ABZ (A), YNITRO and ABZ (B), and DABCYL and EDANS (C) in HM buffer. Middle row of graphs, the ratio between unquenched and (intermolecular) quenched fluorescence was graphed as a function of concentration. The data were fit to a polynomial equation, which was used to calculate a correction factor at any particular substrate concentration. The correction factor was multiplied by the raw fluorescence data to obtain a normalized fluorescence value. Bottom row of graphs, relationship between fluorescence of ABZ (A and B used the same graph) and EDANS (C) versus concentration of fluorophore. The data were fit to a polynomial equation that was used to convert normalized fluorescence values to micromolar values.
Mass Spectroscopy
Generally, cleavage products were prepared by incubating peptides with or without purified SmSte24p in Buffer MS (40 mm HEPES, pH 7.5, 250 mm NaCl, 1.3% glycerol, 0.01% C12E7) for 12 h at room temperature, stopping reactions with EDTA (12 mm), and then analyzing products by LC-MS. Specifically, M16A reporter ABZ-SEKKDNYIIKGVYNITRO (25 μm), K-Ras4b reporter ABZ-KSKTKC(farnesyl)VIKD (25 μm), and carboxymethylated insulin B-chain (68 μm) were incubated with 18, 20, and 50 μg/ml purified SmSTE24p, respectively. For the fluorescent peptides, these reaction conditions yielded 45–85% sample cleavage as judged by comparing the fluorescence of SmSte24p-treated samples with that of trypsin-treated samples prepared in parallel; the extent of insulin B-chain cleavage was not determined. Products were analyzed by LC-MS using appropriate acetonitrile/trifluoroacetic acid gradients and a Kromasil C-18 column (Keystone Scientific/Thermo Scientific) with mass spectra being acquired using a mass spectrometer with electrospray ionization source (i.e. Waters Micromass Q-Tof Micro or Bruker Esquire 3000 Plus ion trap). Peptide masses within the spectra were identified manually with the aid of FindPept (ExPASy Bioinformatics Research Portal).
SDS-PAGE Analysis of Peptide Degradation
Reactions were assembled in HM buffer to contain purified SmSte24p (0.05 mg/ml) or purified rat IDE (0.05 mg/ml), E. coli lipid (0.6 mg/ml), and a peptide substrate. The peptide substrates evaluated were as follows: human insulin (54 μm), porcine insulin B-chain (70 μm), and human Aβ 1–40 (60 μm). Reactions were incubated for 12 h at 30 °C and quenched with EDTA (12 mm), and samples were analyzed by 18% SDS-PAGE and staining with Coomassie R250.
Results
Rce1p and Ste24p Differ in Their Requirements for an Isoprenylated Substrate
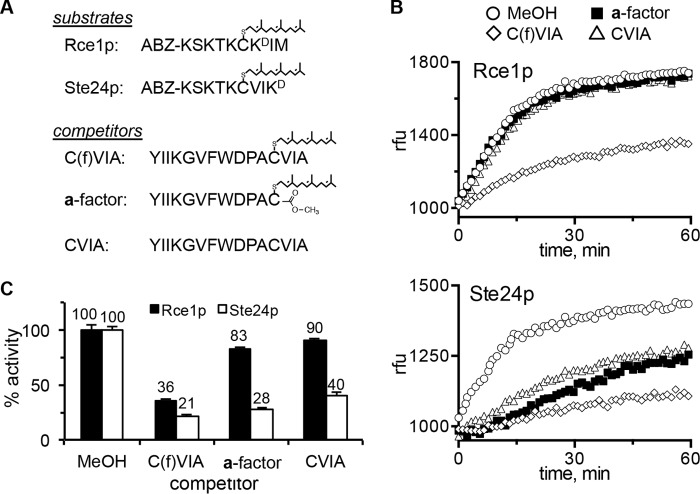
An expected unifying feature of the Rce1p and Ste24p CAAX proteases is that both recognize the isoprenylated CAAX sequence as a specific recognition determinant. In fact, the lack of an isoprenyl group was the reason given for the “misalignment” of the non-prenylated CSIM tetrapeptide in the co-crystal structure of human Ste24p (i.e. predicted cleavage at P1′–P2′ rather than P1–P1′) (7). To initially test this “standard model” of substrate recognition for yeast Rce1p and Ste24p, we performed competition assays involving isoprenylated reporter substrates in combination with isoprenylated and non-prenylated peptides (Fig. 3A). The reporters were internally quenched fluorogenic nonapeptides based on the farnesylated C terminus of K-Ras4b (i.e. K-Ras4b reporter), whereas the competitors were based on the a-factor sequence (34). ER membranes enriched from yeast were used as the source of activity; both proteases are ER-associated membrane proteins (8). The yeast strains used for membrane isolation were designed to overexpress either Rce1p or Ste24p in the absence of the other CAAX protease.
FIGURE 3.
Ste24p-mediated cleavage of a farnesylated substrate is competed by non-prenylated peptides. A, sequences of farnesylated and non-prenylated peptides used in this experiment. Optimal Rce1p and Ste24p activities require differential placement of the quenching group (34). B, time course activity profiles of Rce1p (top) and Ste24p (bottom) measured in relative fluorescence units (rfu) in the presence of methanol or competitor (2-fold molar excess); the farnesylated substrates are as described in A. Initial linear velocities were used to calculate percentage of activity relative to the methanol condition. C, the indicated enzyme activities were calculated for activity against the appropriate farnesylated substrate in the absence or presence of competing peptides. Bars, average of values from duplicate samples within this single experiment; error bars, range. Similar results were observed in five independent iterations of the experiment having subtle variations in the experimental setup (e.g. different molar ratios of substrate/competitor; different membrane preparations of protease activity, etc.). The yeast membranes used as the source of protease activity were derived from SM3614 transformed with either pWS479 (RCE1) or pSM1282 (STE24).
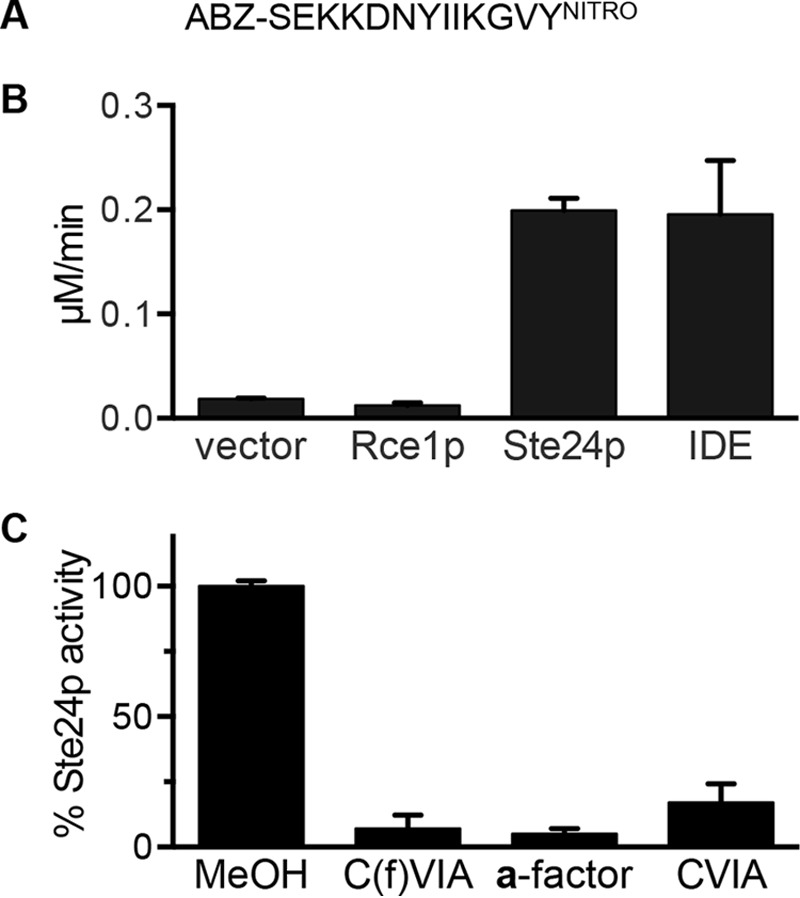
The standard model predicts that cleavage of the K-Ras4b reporter by Rce1p and Ste24p would be diminished by the presence of competing isoprenylated CAAX peptides. Indeed, we observed this to be the case for both proteases. Cleavage of the K-Ras4b reporter was significantly reduced when a competing non-fluorescent farnesylated substrate (C(f)VIA) was present in a 2-fold molar excess (Fig. 3, B and C). The standard model also predicts that cleavage of the K-Ras4b reporter by Rce1p and Ste24p would be relatively unaffected by competing peptides lacking either the CAAX motif or isoprenoid moiety. Indeed, for Rce1p, such peptides had only a minor impact on cleavage of the K-Ras4b reporter. Significant activity was still observed in the presence of mature a-factor (an isoprenylated and carboxylmethylated peptide lacking a CAAX motif) and a non-prenylated peptide matching the preprocessed form of the a-factor sequence that contains a CAAX motif (CVIA). These results indicate that optimal substrate recognition by Rce1p relies on both the isoprenoid and AAX features of substrates. For Ste24p, however, we unexpectedly observed that all three peptides had a significant negative impact on cleavage of the K-Ras4b reporter. The effective competition by these peptides suggests that a farnesylated CAAX sequence is a minimal recognition determinant for Rce1p but not Ste24p.
Ste24p Cleaves a Peptide Modeled on the M16A Protease Cleavage Site in the a-Factor Precursor
We interpreted the findings of our competition experiments to indicate that non-prenylated peptides can influence the activity of Ste24p. Due to experimental design, however, we could not establish whether non-prenylated peptides were actually being cleaved or binding non-productively. We did note, however, that Quigley et al. (7) reported, but did not discuss, cleavage of a non-prenylated peptide based on the lamin A precursor. To probe this issue further, we sought to directly investigate whether Ste24p could cleave non-prenylated substrates.
Our choice of non-prenylated substrates to evaluate was directed by shared structural and functional similarities between membrane-bound Ste24p and soluble M16A proteases. Both are zinc-dependent metalloproteases with active sites sequestered in a large chamber. Both proteases have a β-sheet domain near the site of peptide hydrolysis that properly positions substrates for cleavage (6, 7, 20); this structural feature is not observed in Rce1p family members (Fig. 1) (16). Moreover, yeast Ste24p and M16A proteases (Ste23p and Axl1p) cleave the a-factor precursor at different sites that are each distal from the CAAX motif, indicating that they can cleave non-prenylated regions of the same peptide, albeit at different locations (27, 28, 32). M16A proteases cleave a variety of small peptides, potentially up to ∼80 amino acids in length (20, 21, 43). The maximum substrate size is limited by the volume of the M16A protease chamber (∼16,000 Å3). The Ste24p chamber has a similar sized chamber (∼14,000 Å3) (6).
For studies of yeast M16A proteases, we previously developed a reporter peptide (M16A reporter) that contains the site within the a-factor that is normally cleaved by Axl1p and Ste23p (Fig. 4A) (27, 28). The mammalian M16A protease IDE also cleaves this reporter (Fig. 4B) (27, 35). Yeast Ste24p readily cleaved the M16A reporter, whereas Rce1p could not. As observed with the farnesylated K-Ras4b reporter, cleavage of the M16A reporter was significantly reduced under mixed substrate conditions involving both prenylated and non-prenylated peptides based on a-factor (Fig. 4C).
FIGURE 4.
Ste24p-mediated cleavage of an M16A protease substrate. A, sequence of M16A reporter. B, the indicated enzyme activities were assayed for activity against a non-prenylated M16A protease substrate. Bars, average values of multiple replicates (n = 7) from two independent experiments; error bars, S.D. All enzyme components (i.e. membranes enriched for Rce1p or Ste24p; recombinant IDE) were used at 0.25 mg/ml final concentration. C, activity of Ste24p against the M16A reporter in the absence or presence of competing peptides as described for Fig. 3. The membranes used as the source of Rce1p and Ste24p protease activities were derived as described for Fig. 3. Purified rat IDE was isolated as described previously (38). Bars, average values of multiple replicates (n = 5) from two independent experiments; error bars, S.D.
The Shape of Ste24p Progress Curves Depends on Substrate
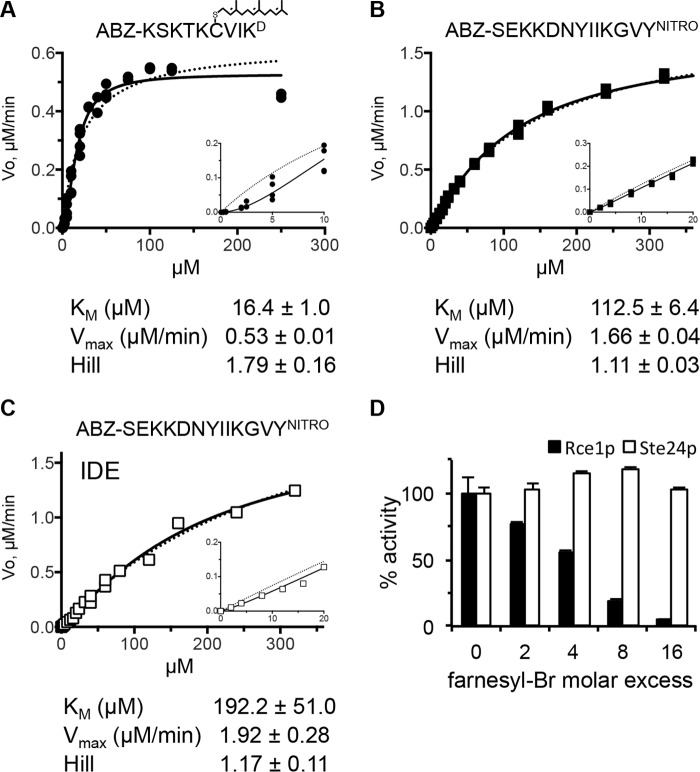
To assess the relative cleavage efficiency of both isoprenylated and non-prenylated peptides by Ste24p, we determined kinetic parameters (Fig. 5, A–C). This analysis revealed that the Km of yeast Ste24p for the farnesylated K-Ras4b reporter (16.4 μm) was similar to our previously published values (34); the slightly higher Km value reported here is the consequence of normalizing for intermolecular quenching, which was not done in prior studies. The data fit well (R2 = 0.98) to an allosteric sigmoidal model, with a Hill coefficient of 1.8, suggestive of positive cooperativity. By contrast, the Km of yeast Ste24p for the non-prenylated M16A reporter was much higher (i.e. 112.5 μm), the Vmax was substantially higher (1.66 μm/min versus 0.53 μm/min), and the data fit to standard Michaelis-Menten kinetics. Taken together, the data suggest that Ste24p recruits the prenylated peptide better than the non-prenylated peptide but can efficiently cleave the non-prenylated peptide once acquired. Curiously, both Ste24p and rat IDE have a high Km for the non-prenylated M16A reporter under the same reaction conditions.
FIGURE 5.
Enzyme kinetics. A and B, yeast membranes containing Ste24p were assayed for activity against the indicated farnesylated (A) or non-prenylated peptide (B) over a range of concentrations. C, activity of purified rat IDE against the non-prenylated peptide described for B. Solid lines, curve fitting using an allosteric-sigmoidal model. Dashed lines, data fit to a Michaelis-Menten model. Insets are magnified parts of the curve at the lowest concentrations evaluated. Each graph is representative of multiple independent experiments: A, n = 5; B, n = 2; C, n = 1 (also see Ref. 35). The kinetic parameters associated with each panel were derived using Prism version 6 for the representative data set; S.E. values shown represent error with respect to curve fitting. D, activity of membrane-associated Rce1p and Ste24p in the presence of increasing amounts of trans,trans-farnesyl bromide. The farnesylated substrates are as described in the legend to Fig. 3A. The graph is representative of two independent experiments; error bars represent the range from duplicate samples within a single experiment.
We next considered a possible underlying reason for the non-Michaelis-Menten kinetics observed for Ste24p with the farnesylated K-Ras4b reporter. Such behavior is often associated with positive cooperativity, which can result from several scenarios. Subunit cooperativity (i.e. multimerization) is a common reason. However, purified recombinant yeast and human Ste24p are both monomeric in solution, and there is no evidence of functionally relevant oligomerization in crystals used to determine their structures (6, 7). Kinetic cooperativity due to enzyme hysteresis (i.e. a slow, substrate-induced isomerization of the enzyme) is also possible, but this would be accompanied by a lag in enzyme activation time, which was not readily observed in Ste24p progress curves. Multiple substrate binding sites can also lead to sigmoidal kinetics, so it is possible that Ste24p has separate peptide and isoprenoid binding sites that act cooperatively. This seems unlikely, given that Ste24p activity was largely unaffected by the presence of excess farnesyl (Fig. 5D). By comparison, Rce1p activity was significantly reduced. Curves resembling, but not indicative of, cooperative kinetics are also observed when substrates bind both specific and nonspecific sites (44). Because lipidation can increase a protein or peptide's membrane binding affinity, the lipid bilayer surrounding Ste24p in membranes could be acting as an abundant, low affinity binding site for the substrate. To test this possibility, we measured the activity of membrane-enriched Ste24p after mixing with increasing amounts of membrane devoid of both Rce1p and Ste24p (rce1Δ ste24Δ). We observed increasing sequestration of the farnesylated substrate into an inactive pool (Fig. 6). By contrast, no sequestration was observed for the non-prenylated substrate.
FIGURE 6.
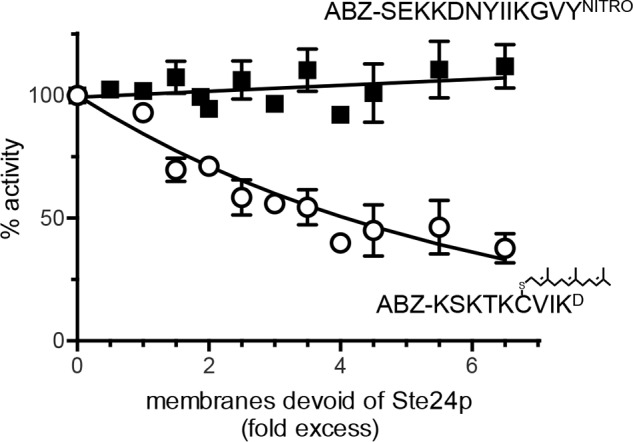
Impact of membrane concentration on Ste24p activity. Yeast membranes containing Ste24p were assayed for activity against a farnesylated (open circle) or non-prenylated peptide (closed square) in the presence of increasing amounts of yeast membranes devoid of Ste24p activity. The source of Ste24p activity was derived as previously described for Fig. 3. The membranes devoid of Ste24p activity were derived from SM3614 transformed with pRS316 (CEN URA3). The data points plotted represent the average value from several independent experiments (n = 5, farnesylated; n = 4, non-prenylated); error bars, S.D. Curve fitting was either linear (non-prenylated) or exponential (farnesylated).
Ste24p Cleaves a Peptide Modeled on Aβ
M16A proteases are perhaps best known for their ability to cleave small peptides that adopt β-strand secondary structure when positioned in the M16A active site. Biomedically relevant substrates include the Aβ peptides and insulin chains. We thus challenged Ste24p and Rce1p to cleave an internally quenched fluorogenic peptide based on Aβ that includes a cleavage site recognized by IDE (Phe-Phe) (45). This reporter is cleaved by rat, worm, and human IDE (35). Both yeast and human Ste24p cleaved the reporter, whereas yeast and human Rce1p did not (Fig. 7). As observed for the M16A reporter, a hyperbolic kinetic curve was observed with the Aβ reporter. The Km for Ste24p (Km = 52.3 μm) was ∼3 times lower than the reported value for rat IDE against this same peptide (i.e. Km = 142.3 μm), albeit under different buffering conditions (35). Nonetheless, these results indicate that Ste24p cleaves the Aβ reporter somewhere among the six peptide bonds that exist between the fluorophore and quencher (i.e. FRET pair).
FIGURE 7.
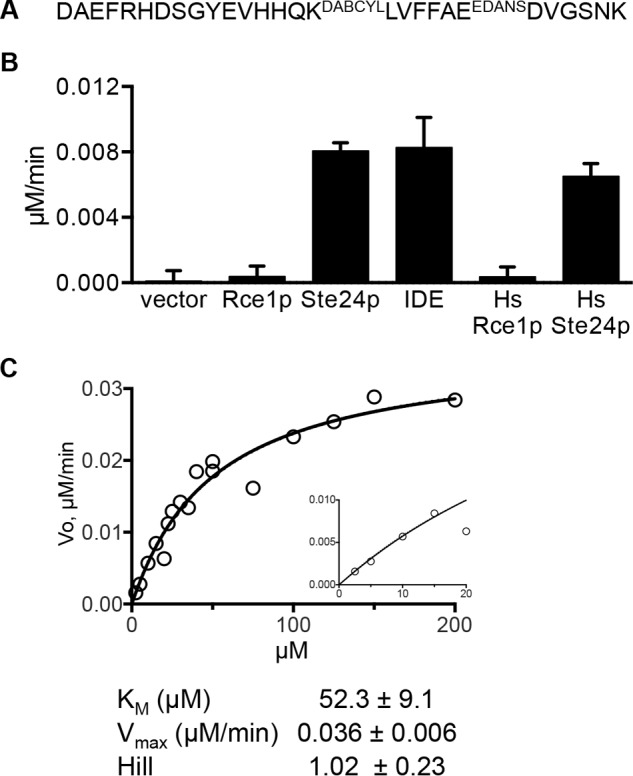
Ste24p cleaves an Aβ 1–28-based peptide. A, sequence of Aβ 1–28-based substrate. B, the indicated enzyme activities were observed using the Aβ 1–28 substrate. The graph is representative of two independent experiments. Bars, average values of multiple replicates (n = 5); error bars, S.D. The sources of enzyme activities were derived as described previously for Fig. 4. Membranes containing human Rce1p or Ste24p were derived from SM3614 transformed with either pWS335 (HsRCE1) or pWS1275 (HsSTE24). C, the kinetic curve was determined as described for Fig. 5 using the Aβ 1–28 substrate and membranes containing ScSte24p. Curve fitting to the data using an allosteric-sigmoidal model and a Michaelis-Menten model gave nearly identical results. The kinetic parameters were derived using Prism version 6; S.E. values shown represent error with respect to curve fitting.
Ste24p Cleaves Biological Peptides
Our investigations involving FRET reporters indicated that Ste24p can cleave non-prenylated peptides. Because these modified peptides may have altered substrate properties, we investigated whether Ste24p could cleave unadulterated substrates of IDE. Through competition assays, we observed that whole insulin minimally reduced the activities of both Ste24p and Rce1p against their farnesylated K-Ras4b reporters. As expected, insulin had a much larger impact on IDE cleavage of the M16A reporter (Fig. 8A). We next evaluated the competitive nature of individual insulin chains to address the possibility that the size and/or constrained conformation of insulin might prevent its interaction with Ste24p. We observed that both insulin A- and B-chains reduced Ste24p activity to a similar extent (Fig. 8B); minimal effects on activity were observed for Rce1p in the presence of insulin chains in parallel studies.3 With increasing amounts of competing insulin B-chain in Ste24p reactions, we observed a concomitant increase in Km and no change in Vmax (Table 1), indicative of competitive inhibition. A mixture of unlinked insulin A- and B-chains also competed for Ste24p activity; the mixture was prepared by DTT/iodoacetamide treatment of whole insulin. These results suggest that, by comparison with insulin chains, the size and/or conformation of whole insulin might indeed influence its availability as a competitor. Unfortunately, these two possibilities are not separable by our experimental approach. Nonetheless, they demonstrate a critical difference between Ste24p and IDE. Ste24p is unlikely to bind and therefore cleave whole insulin, whereas IDE has this ability.
FIGURE 8.
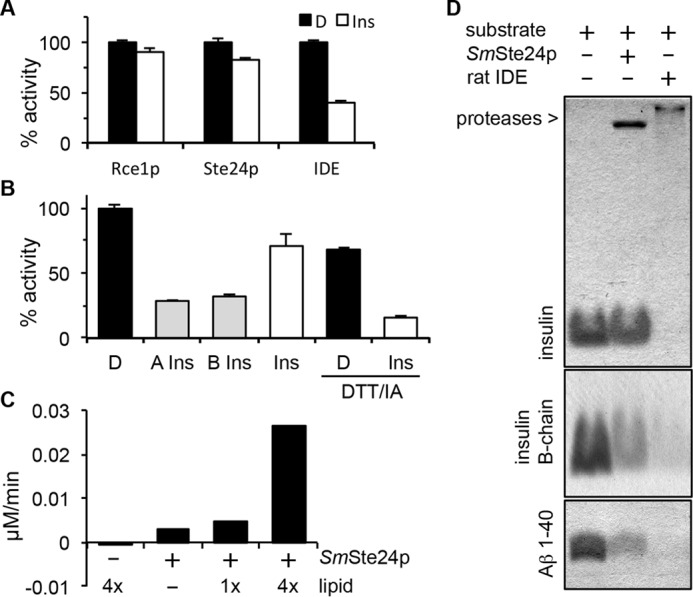
Evaluation of Ste24p activity against biological peptides. A, competition assays were performed using the indicated protease and appropriate FRET substrate in the absence or presence of insulin. See Fig. 3A for Rce1p and Ste24p substrates and Fig. 4A for the IDE substrate. Substrates were used at 10 μm, and competing peptide was used at 40 μm. D, DMSO; Ins, whole insulin. B, competition assays were performed as described for A using Ste24p membranes and the indicated insulin species. DTT/IA, pretreatment of the competitor with a 3-fold molar excess of DTT, followed by a 6-fold molar excess of iodoacetamide (IA). This serves to dissociate insulin A- and B-chains and block reformation of disulfide bonds. D, DMSO; A Ins, carboxymethylated insulin A-chain; B Ins, carboxymethylated insulin B-chain; Ins, whole insulin. The graphs for A and B are representative of multiple independent experiments (three in each case). The specific graphs represent the averaged value of replicates (n = 2) from a single experiment where the DMSO-treated control was set to 100% activity; error bars represent the range. C, purified SmSte24p (0.8 μm) was incubated with the Aβ 1–28 FRET reporter (50 μm) in the absence and presence of E. coli lipid. 1x, 125 μg/ml total E. coli lipid. rfu, relative fluorescence units. The graph is representative of five independent tests of lipid effects on this enzyme/substrate combination. D, SDS-PAGE analysis of products derived from incubation of purified SmSte24p or rat IDE with indicated substrates in the presence of E. coli lipid. The gels are representative of five independent experiments. The concentrations of enzymes, substrates, and lipids used are described under “Experimental Procedures.”
TABLE 1.
Kinetics of Ste24p cleavage of K-Ras4b reporter in the presence of increasing concentrations of insulin B-chain
All reaction conditions were the same as described in the legend to Fig. 5A. Data shown represent one of two biological replicates. Similar values and trends for Km and Vmax parameters were observed in both experiments. S.E. values shown represent error with respect to curve fitting using Prism version 6.
| Insulin B-chain |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 μm | 10 μm | 20 μm | 33 μm | |
| Km (μm) | 23.2 ± 0.8 | 29.7 ± 1.2 | 37.5 ± 2.8 | 37.5 ± 2.3 |
| Vmax (μm/min) | 0.56 ± 0.01 | 0.52 ± 0.02 | 0.56 ± 0.03 | 0.46 ± 0.02 |
| Hill coefficient | 2.04 ± 0.13 | 2.49 ± 0.20 | 2.16 ± 0.21 | 2.38 ± 0.23 |
For a more direct assessment of the ability of Ste24p to cleave IDE substrates, we used purified components and a gel-based assay to examine products formed after in vitro cleavage reactions. Initial experiments using purified SmSte24p revealed little if any cleavage of whole insulin, insulin chains, or Aβ 1–40. We then took advantage of an observation that adding lipid to the enzyme significantly improved in vitro cleavage of the Aβ FRET reporter (Fig. 8C); the reason for this effect is unknown and could stem from stabilizing a more active form of purified SmSte24p, which was detergent-solubilized, or shifting the state of the substrate to a more readily cleaved conformer. Repeating the gel-based assay under conditions of added lipid revealed reduced levels of both Aβ 1–40 and insulin B-chain in the presence of protease (Fig. 8D). Consistent with in vitro competition experiments, we observed little if any reduction in the level of whole insulin under conditions of added lipid, whereas whole insulin was cleaved by IDE. Together, these findings indicate that non-prenylated peptides exhibiting strong competitive behavior are indeed cleaved by Ste24p.
Mass Spectroscopic Analysis of Ste24p Cleavage Sites
The cleavage sites recognized by Ste24p have been identified in various ways. For example, the distal cleavage site in a-factor was identified by N-terminal sequencing of an immunopurified a-factor intermediate (46). The CAAX cleavage sites of a-factor and prelamin A were both revealed by mass spectroscopy using purified components and model synthetic peptides (7, 13). For both, cleavage occurred between the farnesylated cysteine and the A1 position of the CAAX motif, although the prelamin A peptide was predominantly cleaved between A1 and A2.
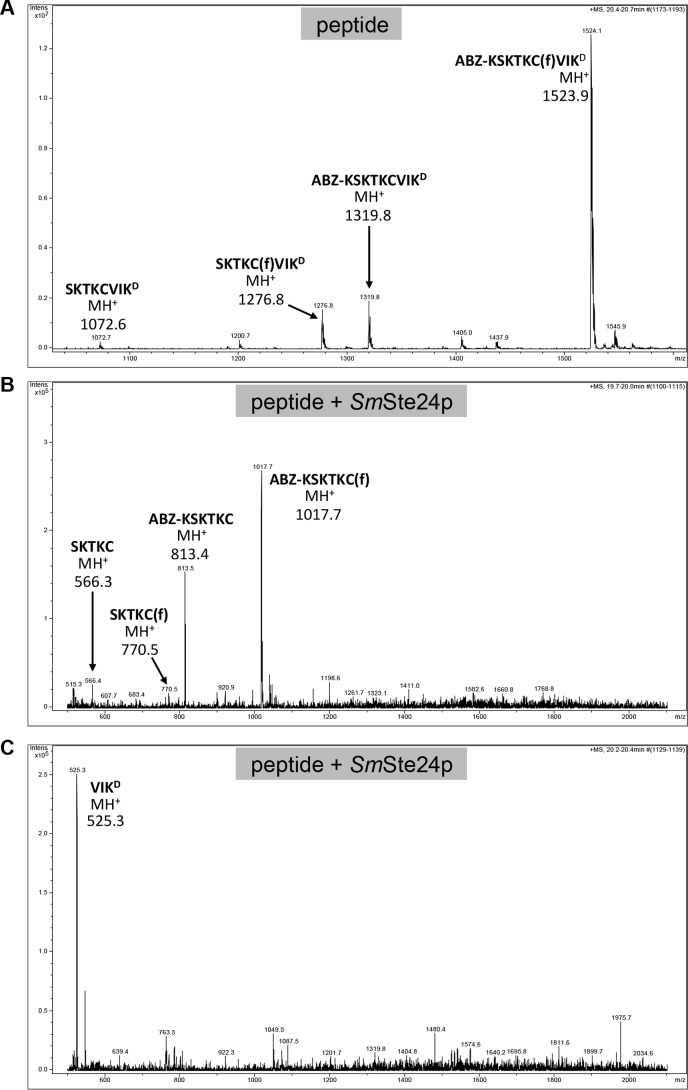
Despite its utility for monitoring protease activity, the readout of FRET-based methods does not include the precise sequence location(s) of cleavage, because cleavage occurring anywhere between the FRET pair will yield a positive signal. Moreover, cleavage outside the FRET pair can occur and not yield a signal. To precisely determine the Ste24p cleavage sites in three of the substrates investigated in this study, we used mass spectroscopy to analyze the proteolytic products generated by purified SmSte24p. The products derived from the K-Ras4b reporter were as predicted for CAAX proteolysis: cleavage between farnesylated cysteine and the A1 position of the CAAX motif (Figs. 9D and 10). We next examined the products derived from the non-prenylated M16A reporter. This peptide was cleaved at a single site, between Gly and Val, near the C terminus of the substrate (Fig. 9). The analysis also revealed a minor impurity in the sample that was derived from inefficient peptide synthesis. The minor peptide lacks an Asn near the middle of the sequence. Nonetheless, this peptide was also cleaved at the same Gly-Val bond. Finally, analysis of products generated from insulin B-chain revealed two major cleavage sites near the middle of the peptide. Cleavage occurred between Tyr-16 and Leu-17 or between Leu-17 and Val-18 (Figs. 9D and 11).
FIGURE 9.
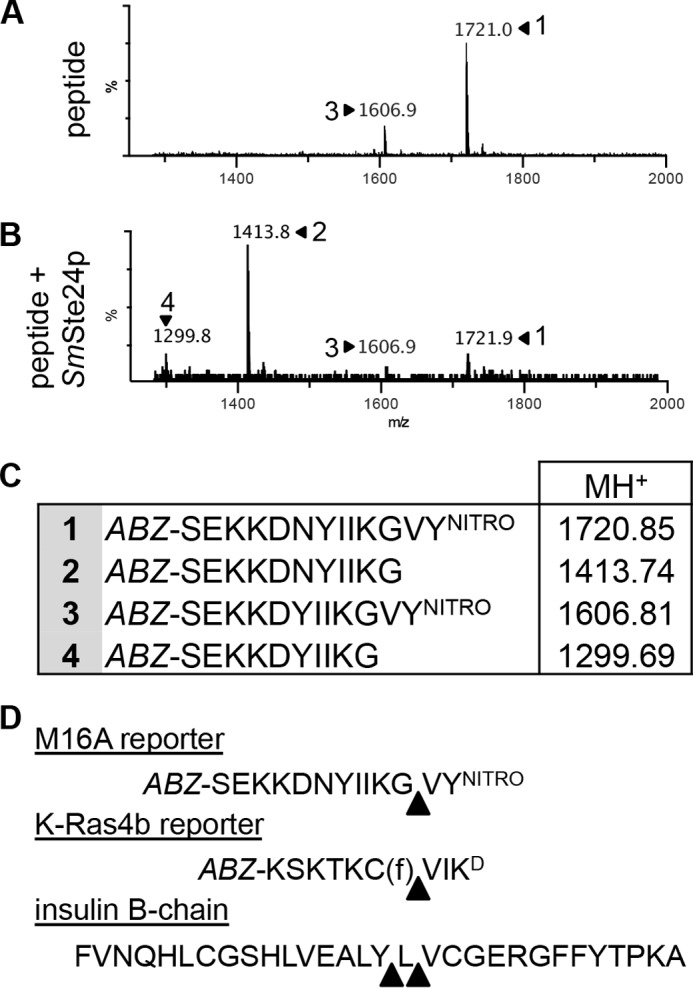
Mass spectroscopic analysis of Ste24p cleavage products. A and B, mass spectra of the M16A reporter in the absence (A) and presence of purified SmSte24p (B). C, the peaks identified in A and B correspond to the indicated species. Peptide 3 is a minor contaminating peptide that lacks the Asn residue present in peptide 1. D, analysis of mass spectra (see Figs. 10 and 11) reveals cleavage sites in the indicated reporter substrates. Triangles, major cleavage sites that were identified.
FIGURE 10.
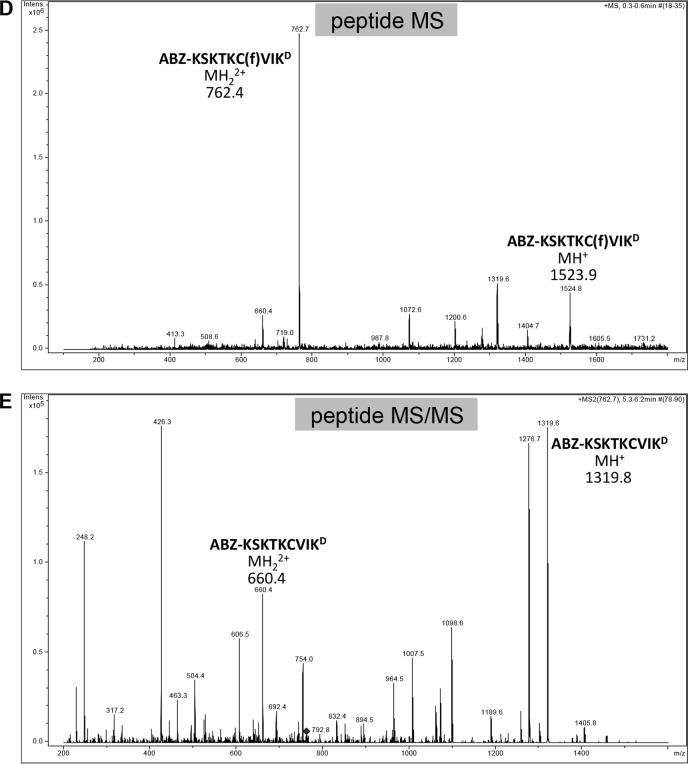
Mass spectra of products derived from the K-Ras4b reporter treated with purified SmSte24p. A–C, samples of K-Ras4b reporter incubated in the absence (A) and presence of purified SmSte24p (B and C) were analyzed by LC-MS using a Bruker Esquire 3000 Plus mass spectrometer. The sequences and theoretical masses that correspond to identified peaks are shown centered or adjacent to appropriate peaks. One of the prenylated species in A lacking ABZ and N-terminal Lys (SKTKC(f)VIKD) is probably a minor impurity from peptide synthesis. Spectra for B and C were derived from different LC fractions corresponding to 19.7–20 min and 20.2–20.4 min, respectively. D and E, the non-prenylated species detected in A was not present in mass spectra provided by the peptide manufacturer; they are probably a by-product of ionization (67). In support of this, we observed that MS/MS analysis of the double ion form of the uncleaved farnesylated peptide (m/z 762.4) resulted in the loss of farnesylated peptide ions (MH+, m/z 1523.9; MH22+, m/z 762.4 m/z) (D) and the appearance of non-prenylated peptide ions (MH+, m/z 1319.8; MH22+, m/z 660.4) (E).
FIGURE 11.
Mass spectra of products derived from insulin B-chain treated with purified SmSte24p. Spectra of carboxymethylated insulin B-chain in the absence (A) and presence of SmSte24p (B) were analyzed by LC-MS using a Bruker Esquire 3000 Plus mass spectrometer. The amino acid ranges of insulin B-chain and corresponding theoretical monoisotopic masses are shown centered or adjacent to appropriate peaks. Spectra for A and B were derived from different LC fractions corresponding to 20.5–20.6 min and 17.8–18.0 min, respectively. Peaks for products corresponding to amino acids 1–17 were observed in other LC fractions but are not shown. For the few instances where the theoretical mass did not exactly match the major peak detected, magnification of the peak region to increase resolution revealed the theoretical mass as part of an isotopic set. As examples, magnification of spectra centered on m/z 823.9 and m/z 945.4 (B) revealed monoisotopic peaks nearly identical to theoretical masses of m/z 823.4 (C) and m/z 944.5 (D), respectively.
Discussion
The major finding of this study is the ability of Ste24p to cleave several non-prenylated oligopeptides in vitro. In terms of specificity, we determined that Ste24p cleaves both the non-prenylated M16A reporter and farnesylated K-Ras4b reporter at a bond containing Val at the P1′ position (i.e. X-Val). In these instances, the bond resides near the C terminus (Fig. 9D). This specificity may in part explain the ability of Ste24p to cleave the CVIA CAAX motif of the yeast a-factor precursor and a-factor CAAX mutants where Val has been substituted by other aliphatic residues (Ile and Leu) but generally not other types of amino acids (3, 47, 48). Curiously, the Gly-Val bond within the M16A reporter is cleaved in vivo in the context of a-factor processing; the protease responsible is not believed to be Ste24p, although this conclusion should be revisited in light of our current findings (49). By comparison, insulin B-chain has two major in vitro cleavage sites where P1′ is also an aliphatic amino acid (Leu or Val), but the bond is considerably farther from the C terminus. The Aβ FRET reporter has aliphatic residues (i.e. Ala, Leu, and Val) in the region between the FRET pair (LVFFAE) where Ste24p must be cleaving in order to yield a fluorescence signal. The known biological cleavage sites of Ste24p, in prelamin A (RSY-LLG) and a-factor (TAT-AAP), also bear aliphatic residues at the P1′ position (46, 50). In vitro, purified Ste24p cleaves synthetic peptides based on the prelamin A C terminus at multiple sites bearing a P1′ aliphatic residue (Gly, Ile, Leu, and to a lesser degree Met) (7). By contrast, Ste24p poorly cleaves after the farnesylated cysteine of the FRET peptide that we typically use to monitor Rce1p activity (Fig. 3A) (34). This substrate has dinitrophenyl-lysine instead of Val at the P1′ position (i.e. A1 position of the CAAX motif). Moreover, Ste24p cannot cleave the prelamin A distal site when the P1′ position is mutated to Arg (RSY-RLG) (15). From these limited data, it appears that Ste24p prefers to cleave peptide bonds where P1′ is an aliphatic residue (i.e. Ala, Leu, and Val), as long as other, yet to be identified, constraints are satisfied. We expect that this in vitro specificity will be preserved in vivo.
The anticipation of additional constraints for Ste24p is needed to explain why cleavage does not occur at all bonds containing a P1′ aliphatic. Additional constraints are observed for thermolysin, which cleaves substrates containing aliphatic or hydrophobic P1′ residues (Ala, Leu, Val, Ile, Met, or Phe) unless P1 is an acidic residue (Asp or Glu) (51). Likewise, the bacterial Ste24p homolog, HtpX, cleaves a variety of non-prenylated substrates in vitro, including β-casein, SecY, and itself (self-cleavage), but it does not appear to cleave indiscriminately. The precise cleavage site preferences of HtpX have not been defined (52). Determining the specificity of promiscuous proteases can be difficult. For example, the site preferences of M16A proteases remain relatively undefined despite over 100 known cleavage sites (MEROPS peptidase database). Future investigations of Ste24p substrate interactions are likely to reveal the additional constraints on cleavage sites, which we predict will depend on conformational malleability around the cleaved bond. Ultimately, we predict that Ste24p will be found to cleave many substrates, as has been commonly observed for M16A proteases and thermolysin.
The fact that Ste24p is not isoprenoid-dependent is clearly unusual for a protein canonically referred to as a CAAX-specific protease. By comparison, our evidence and data published elsewhere indicate that Rce1p is isoprenoid-dependent (9, 40). Our findings further suggest that Ste24p has more biochemical similarity to M16A proteases than to Rce1p. Whereas our initial experiments involving non-prenylated peptides were largely directed by the similarity of Ste24p and M16A protease structures (i.e. possession of voluminous internal cavities containing the active sites), we have now established that there are several non-prenylated substrates, including biological peptides, that can be cleaved by both proteases in vitro. M16A proteases use their β-sheet domain to properly position substrates for cleavage (i.e. a β-strand addition mechanism), so it is tempting to speculate that Ste24p uses its β-sheet domain in similar fashion (20, 53). Consistent with this model is the observation that certain HIV inhibitors that inhibit Ste24p are known to be β-strand mimetics (e.g. ritonavir) (54, 55). Although Ste24p and M16A proteases can cleave common substrates in vitro (e.g. insulin B-chain, M16A reporter, and a-factor precursor), these proteases cleave at different bond positions, indicating that the precise cleavage sites differ between the protease families (20). Additionally, the ability of insulin A- and B-chains to act as competitive substrates for Ste24 cleavage, whereas whole insulin cannot compete, hints that size and/or structural constraints differ between Ste24p and M16A proteases.
A critically unresolved issue regarding Ste24p relates to its biological function. Ste24p is referred to as a CAAX protease and more specifically as a type I CAAX protease in functional databases. However, evidence to date suggests that Rce1p is the more biologically relevant CAAX protease. For example, multiple CAAX proteins are recognized by Rce1p, whereas the only proteins recognized by Ste24p are precursors to a-factor and lamin A, and neither necessarily uses Ste24p exclusively for CAAX proteolysis (8–12, 56). In additional support of Rce1p as the major CAAX protease, rce1−/− mice accumulate cleavable and methylatable substrates, whereas ZmpSte24−/− mice do not (57). Although Ste24p has the capacity to cleave certain CAAX proteins, we contend that its major biological functions lie elsewhere.
One intriguing potential role suggested by our observations is that Ste24p is generally involved in cleaving oligopeptides that have a high local concentration near or on the membrane in which Ste24p resides. These peptides would arise from normal protein turnover events that generate oligopeptides of varying length, hydrophobic character, and secondary structure predilection (e.g. farnesylated stubs of CAAX proteins; palmitoylated fragments, amyloidogenic peptides, etc.). Ste24p could be working in concert with M16A proteases in this manner. Ste24p would have primary responsibility for those that partition onto membranes, and M16A proteases would primarily cleave cytosolic oligopeptides. Our oligopeptidase model is fully compatible with observations about Ste24p and its interactions with hydrophobic a-factor, which is small enough to be captured within the Ste24p chamber, facilitating cleavage at multiple sites. For the larger prelamin A, we propose that Rce1p is mainly responsible for CAAX cleavage and that the oligopeptidase activity of Ste24p has been co-opted for cleavage at the prelamin A distal site during protein maturation, much as NF-κB and certain transcription factors use the proteasome for partial proteolysis and conversion to active forms (58–60).
Our model is also compatible with observations that Ste24p is involved in membrane protein quality control (61–63). It was recently reported that Ste24p is important for the clearance of a non-prenylated reporter protein that is stuck mid-translocation into the ER during signal recognition particle-independent protein translocation (63). Although the exact role of Ste24p in this process remains unclear, it could be acting directly on the stuck polypeptide or as an oligopeptidase on peptide products derived by the action of other proteases more intimately involved in the extraction and clearance of the stuck polypeptide. Regardless, it is likely that Ste24p is one of several components that partner to efficiently clear the stuck polypeptide. Consistent with this model are strong genetic interactions between STE24 and CDC48 (an AAA ATPase involved in ER-associated degradation), Cdc48p interactors (i.e. UBX2), and proteasome components (i.e. UBC7) (64–66).
Finally, we should also make clear that our model is not meant to suggest direct cleavage of insulin chains and Aβ 1–40 by Ste24p in vivo despite their cleavage in vitro. We do not expect these peptides to be primary substrates due to their differential localization relative to ER-localized Ste24p (insulin and Aβ are primarily extracellular). Identification of additional interacting substrates will certainly provide more clarity to the biological role of this enigmatic protease.
Author Contributions
E. R. H. conceived and executed the majority of experiments, analyzed data, and drafted the original manuscript; B. T. A. provided purified SmSte24p; M. C. W. provided intellectual guidance on the project and helped to revise the manuscript; and W. K. S. secured funding for the project, generally supervised the project, and edited the final copy of the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript and approved the final submitted version.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Dennis Phillips (Proteomics and Mass Spectrometry Core Facility, University of Georgia) for mass spectrometry analysis and Dr. Brandon Goblirsch (University of Virginia), Dr. Zachary Wood (University of Georgia), Ben Boward (University of Georgia), and members of the Schmidt laboratory (University of Georgia) for reagents and critical discussions that were instrumental to this study.
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant GM108612 (to M. C. W.) and University of Georgia institutional funds (to W. K. S.). The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
E. R. Hildebrandt and W. K. Schmidt, unpublished observations.
- ER
- endoplasmic reticulum
- ABZ
- aminobenzoic acid
- EDANS
- 5-((2-aminoethyl)amino)naphthalene-1-sulfonic acid
- EEDANS
- EDANS-l-glutamate
- IDE
- insulin-degrading enzyme or insulysin
- KD
- ϵ-dinitrophenyl-lysine
- DABCYL
- 4-[4-(dimethylamino)-phenylazo)benzoic acid
- KDABCYL
- ϵ-DABCYL-l-lysine
- YNITRO
- 3-nitro-l-tyrosine.
References
- 1. Silvius J. R. (2002) Mechanisms of Ras protein targeting in mammalian cells. J. Membr. Biol. 190, 83–92 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Tam A., Nouvet F. J., Fujimura-Kamada K., Slunt H., Sisodia S. S., and Michaelis S. (1998) Dual roles for Ste24p in yeast a-factor maturation: NH2-terminal proteolysis and COOH-terminal CAAX processing. J. Cell Biol. 142, 635–649 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Trueblood C. E., Boyartchuk V. L., Picologlou E. A., Rozema D., Poulter C. D., and Rine J. (2000) The CaaX proteases, Afc1p and Rce1p, have overlapping but distinct substrate specificities. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 4381–4392 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Plummer L. J., Hildebrandt E. R., Porter S. B., Rogers V. A., McCracken J., and Schmidt W. K. (2006) Mutational analysis of the Ras converting enzyme reveals a requirement for glutamate and histidine residues. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 4596–4605 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Mokry D. Z., Manandhar S. P., Chicola K. A., Santangelo G. M., and Schmidt W. K. (2009) Heterologous expression studies of Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveal two distinct trypanosomatid CaaX protease activities and identify their potential targets. Eukaryot. Cell 8, 1891–1900 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Pryor E. E. Jr., Horanyi P. S., Clark K. M., Fedoriw N., Connelly S. M., Koszelak-Rosenblum M., Zhu G., Malkowski M. G., Wiener M. C., and Dumont M. E. (2013) Structure of the integral membrane protein CAAX protease Ste24p. Science 339, 1600–1604 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Quigley A., Dong Y. Y., Pike A. C., Dong L., Shrestha L., Berridge G., Stansfeld P. J., Sansom M. S., Edwards A. M., Bountra C., von Delft F., Bullock A. N., Burgess-Brown N. A., and Carpenter E. P. (2013) The structural basis of ZMPSTE24-dependent laminopathies. Science 339, 1604–1607 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Schmidt W. K., Tam A., Fujimura-Kamada K., and Michaelis S. (1998) Endoplasmic reticulum membrane localization of Rce1p and Ste24p, yeast proteases involved in carboxyl-terminal CAAX protein processing and amino-terminal a-factor cleavage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95, 11175–11180 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Otto J. C., Kim E., Young S. G., and Casey P. J. (1999) Cloning and characterization of a mammalian prenyl protein-specific protease. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 8379–8382 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Bergo M. O., Ambroziak P., Gregory C., George A., Otto J. C., Kim E., Nagase H., Casey P. J., Balmain A., and Young S. G. (2002) Absence of the CAAX endoprotease Rce1: effects on cell growth and transformation. Mol. Cell Biol. 22, 171–181 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Roberts P. J., Mitin N., Keller P. J., Chenette E. J., Madigan J. P., Currin R. O., Cox A. D., Wilson O., Kirschmeier P., and Der C. J. (2008) Rho family GTPase modification and dependence on CAAX motif-signaled posttranslational modification. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 25150–25163 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Hanker A. B., Mitin N., Wilder R. S., Henske E. P., Tamanoi F., Cox A. D., and Der C. J. (2010) Differential requirement of CAAX-mediated posttranslational processing for Rheb localization and signaling. Oncogene 29, 380–391 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Tam A., Schmidt W. K., and Michaelis S. (2001) The multispanning membrane protein Ste24p catalyzes CAAX proteolysis and NH2-terminal processing of the yeast a-factor precursor. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 46798–46806 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Corrigan D. P., Kuszczak D., Rusinol A. E., Thewke D. P., Hrycyna C. A., Michaelis S., and Sinensky M. S. (2005) Prelamin A endoproteolytic processing in vitro by recombinant Zmpste24. Biochem. J. 387, 129–138 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Barrowman J., Hamblet C., Kane M. S., and Michaelis S. (2012) Requirements for efficient proteolytic cleavage of prelamin A by ZMPSTE24. PLoS One 7, e32120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Manolaridis I., Kulkarni K., Dodd R. B., Ogasawara S., Zhang Z., Bineva G., O'Reilly N., Hanrahan S. J., Thompson A. J., Cronin N., Iwata S., and Barford D. (2013) Mechanism of farnesylated CAAX protein processing by the intramembrane protease Rce1. Nature 504, 301–305 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Hildebrandt E. R., Davis D. M., Deaton J., Krishnankutty R. K., Lilla E., and Schmidt W. K. (2013) Topology of the yeast Ras converting enzyme as inferred from cysteine accessibility studies. Biochemistry 52, 6601–6614 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Erez E., Fass D., and Bibi E. (2009) How intramembrane proteases bury hydrolytic reactions in the membrane. Nature 459, 371–378 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Wolfe M. (2009) Intramembrane-cleaving proteases. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 13969–13973 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Shen Y., Joachimiak A., Rosner M. R., and Tang W. J. (2006) Structures of human insulin-degrading enzyme reveal a new substrate recognition mechanism. Nature 443, 870–874 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Im H., Manolopoulou M., Malito E., Shen Y., Zhao J., Neant-Fery M., Sun C. Y., Meredith S. C., Sisodia S. S., Leissring M. A., and Tang W. J. (2007) Structure of substrate-free human insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) and biophysical analysis of ATP-induced conformational switch of IDE. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 25453–25463 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Kurochkin I. V. (1998) Amyloidogenic determinant as a substrate recognition motif of insulin-degrading enzyme. FEBS Lett. 427, 153–156 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Kurochkin I. V. (2001) Insulin-degrading enzyme: embarking on amyloid destruction. Trends Biochem. Sci. 26, 421–425 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Selkoe D. J. (2001) Clearing the brain's amyloid cobwebs. Neuron 32, 177–180 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Farris W., Mansourian S., Chang Y., Lindsley L., Eckman E. A., Frosch M. P., Eckman C. B., Tanzi R. E., Selkoe D. J., and Guenette S. (2003) Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid β-protein, and the β-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 4162–4167 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Leissring M. A., Farris W., Chang A. Y., Walsh D. M., Wu X., Sun X., Frosch M. P., and Selkoe D. J. (2003) Enhanced proteolysis of β-amyloid in APP transgenic mice prevents plaque formation, secondary pathology, and premature death. Neuron 40, 1087–1093 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Alper B. J., Rowse J. W., and Schmidt W. K. (2009) Yeast Ste23p shares functional similarities with mammalian insulin-degrading enzymes. Yeast 26, 595–610 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Adames N., Blundell K., Ashby M. N., and Boone C. (1995) Role of yeast insulin-degrading enzyme homologs in propheromone processing and bud site selection. Science 270, 464–467 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Barrowman J., Wiley P. A., Hudon-Miller S. E., Hrycyna C. A., and Michaelis S. (2012) Human ZMPSTE24 disease mutations: residual proteolytic activity correlates with disease severity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 21, 4084–4093 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Ricardo S., and Lehmann R. (2009) An ABC transporter controls export of a Drosophila germ cell attractant. Science 323, 943–946 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Adolphsen K., Amell A., Havko N., Kevorkian S., Mears K., Neher H., Schwarz D., and Schulze S. R. (2012) Type-I prenyl protease function is required in the male germline of Drosophila melanogaster. G3 2, 629–642 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Fujimura-Kamada K., Nouvet F. J., and Michaelis S. (1997) A novel membrane-associated metalloprotease, Ste24p, is required for the first step of NH2-terminal processing of the yeast a-factor precursor. J. Cell Biol. 136, 271–285 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Ghaemmaghami S., Huh W. K., Bower K., Howson R. W., Belle A., Dephoure N., O'Shea E. K., and Weissman J. S. (2003) Global analysis of protein expression in yeast. Nature 425, 737–741 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Porter S. B., Hildebrandt E. R., Breevoort S. R., Mokry D. Z., Dore T. M., and Schmidt W. K. (2007) Inhibition of the CaaX proteases Rce1p and Ste24p by peptidyl (acyloxy)methyl ketones. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1773, 853–862 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Kukday S. S., Manandhar S. P., Ludley M. C., Burriss M. E., Alper B. J., and Schmidt W. K. (2012) Cell-permeable, small-molecule activators of the insulin-degrading enzyme. J. Biomol. Screen 17, 1348–1361 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Sikorski R. S., and Hieter P. (1989) A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 122, 19–27 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Oldenburg K. R., Vo K. T., Michaelis S., and Paddon C. (1997) Recombination-mediated PCR-directed plasmid construction in vivo in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 451–452 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Alper B. J., and Schmidt W. K. (2009) A capillary electrophoresis method for evaluation of Aβ proteolysis in vitro. J. Neurosci. Methods 178, 40–45 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Schmidt W. K., Tam A., and Michaelis S. (2000) Reconstitution of the Ste24p-dependent N-terminal proteolytic step in yeast a-factor biogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 6227–6233 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Hollander I., Frommer E., and Mallon R. (2000) Human ras-converting enzyme (hRCE1) endoproteolytic activity on K-ras-derived peptides. Anal. Biochem. 286, 129–137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Manandhar S. P., Hildebrandt E. R., and Schmidt W. K. (2007) Small-molecule inhibitors of the Rce1p CaaX protease. J. Biomol. Screen. 12, 983–993 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Lazure C., Gauthier D., Jean F., Boudreault A., Seidah N. G., Bennett H. P., and Hendy G. N. (1998) In vitro cleavage of internally quenched fluorogenic human proparathyroid hormone and proparathyroid-related peptide substrates by furin. Generation of a potent inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 8572–8580 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Guo Q., Manolopoulou M., Bian Y., Schilling A. B., and Tang W. J. (2010) Molecular basis for the recognition and cleavages of IGF-II, TGF-α, and amylin by human insulin-degrading enzyme. J. Mol. Biol. 395, 430–443 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. McLure J. A., Miners J. O., and Birkett D. J. (2000) Nonspecific binding of drugs to human liver microsomes. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 49, 453–461 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Mukherjee A., Song E., Kihiko-Ehmann M., Goodman J. P. Jr., Pyrek J. S., Estus S., and Hersh L. B. (2000) Insulysin hydrolyzes amyloid β peptides to products that are neither neurotoxic nor deposit on amyloid plaques. J. Neurosci. 20, 8745–8749 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Chen P., Sapperstein S. K., Choi J. D., and Michaelis S. (1997) Biogenesis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating pheromone a-factor. J. Cell Biol. 136, 251–269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Boyartchuk V. L., and Rine J. (1998) Roles of prenyl protein proteases in maturation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae a-factor. Genetics 150, 95–101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Krishnankutty R. K., Kukday S. S., Castleberry A. J., Breevoort S. R., and Schmidt W. K. (2009) Proteolytic processing of certain CaaX motifs can occur in the absence of the Rce1p and Ste24p CaaX proteases. Yeast 26, 451–463 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Chen P., Choi J. D., Wang R., Cotter R. J., and Michaelis S. (1997) A novel a-factor-related peptide of Saccharomyces cerevisiae that exits the cell by a Ste6p-independent mechanism. Mol. Biol. Cell 8, 1273–1291 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Weber K., Plessmann U., and Traub P. (1989) Maturation of nuclear lamin A involves a specific carboxy-terminal trimming, which removes the polyisoprenylation site from the precursor; implications for the structure of the nuclear lamina. FEBS Lett. 257, 411–414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Keil B. (1992) Specificity of Proteolysis, p. 155, Springer-Verlag, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 52. Sakoh M., Ito K., and Akiyama Y. (2005) Proteolytic activity of HtpX, a membrane-bound and stress-controlled protease from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 33305–33310 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Remaut H., and Waksman G. (2006) Protein-protein interaction through β-strand addition. Trends Biochem. Sci. 31, 436–444 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Loughlin W. A., Tyndall J. D., Glenn M. P., and Fairlie D. P. (2004) β-Strand mimetics. Chem. Rev. 104, 6085–6117 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Loughlin W. A., Tyndall J. D., Glenn M. P., Hill T. A., and Fairlie D. P. (2010) Update 1 of: β-strand mimetics. Chem. Rev. 110, PR32–PR69 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Boyartchuk V. L., Ashby M. N., and Rine J. (1997) Modulation of Ras and a-factor function by carboxyl-terminal proteolysis. Science 275, 1796–1800 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Leung G. K., Schmidt W. K., Bergo M. O., Gavino B., Wong D. H., Tam A., Ashby M. N., Michaelis S., and Young S. G. (2001) Biochemical studies of Zmpste24-deficient mice. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 29051–29058 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Hoppe T., Matuschewski K., Rape M., Schlenker S., Ulrich H. D., and Jentsch S. (2000) Activation of a membrane-bound transcription factor by regulated ubiquitin/proteasome-dependent processing. Cell 102, 577–586 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Rape M., and Jentsch S. (2002) Taking a bite: proteasomal protein processing. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, E113–E116 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Skaug B., Jiang X., and Chen Z. J. (2009) The role of ubiquitin in NF-κB regulatory pathways. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 78, 769–796 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Tipper D. J., and Harley C. A. (2002) Yeast genes controlling responses to topogenic signals in a model transmembrane protein. Mol. Biol. Cell 13, 1158–1174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Akiyama Y. (2009) Quality control of cytoplasmic membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. J. Biochem. 146, 449–454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Ast T., Michaelis S., and Schuldiner M. (2016) The protease Ste24 clears clogged translocons. Cell 164, 103–114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Costanzo M., Baryshnikova A., Bellay J., Kim Y., Spear E. D., Sevier C. S., Ding H., Koh J. L., Toufighi K., Mostafavi S., Prinz J., St Onge R. P., VanderSluis B., Makhnevych T., Vizeacoumar F. J., et al. (2010) The genetic landscape of a cell. Science 327, 425–431 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Hoppins S., Collins S. R., Cassidy-Stone A., Hummel E., Devay R. M., Lackner L. L., Westermann B., Schuldiner M., Weissman J. S., and Nunnari J. (2011) A mitochondrial-focused genetic interaction map reveals a scaffold-like complex required for inner membrane organization in mitochondria. J. Cell Biol. 195, 323–340 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Schuldiner M., Collins S. R., Thompson N. J., Denic V., Bhamidipati A., Punna T., Ihmels J., Andrews B., Boone C., Greenblatt J. F., Weissman J. S., and Krogan N. J. (2005) Exploration of the function and organization of the yeast early secretory pathway through an epistatic miniarray profile. Cell 123, 507–519 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Anderegg R. J., Betz R., Carr S. A., Crabb J. W., and Duntze W. (1988) Structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating hormone a-factor: identification of S-farnesyl cysteine as a structural component. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 18236–18240 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]