Abstract
Peripheral nerve injury induces increased expression of thrombospondin-4 (TSP4) in spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia that contributes to neuropathic pain states through unknown mechanisms. Here, we test the hypothesis that TSP4 activates its receptor, the voltage-gated calcium channel Cavα2δ1 subunit (Cavα2δ1), on sensory afferent terminals in dorsal spinal cord to promote excitatory synaptogenesis and central sensitization that contribute to neuropathic pain states. We show that there is a direct molecular interaction between TSP4 and Cavα2δ1 in the spinal cord in vivo and that TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes lead to increased behavioral sensitivities to stimuli. In dorsal spinal cord, TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes lead to increased frequency of miniature and amplitude of evoked excitatory post-synaptic currents in second-order neurons as well as increased VGlut2- and PSD95-positive puncta, indicative of increased excitatory synapses. Blockade of TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes with Cavα2δ1 ligand gabapentin or genetic Cavα2δ1 knockdown blocks TSP4 induced nociception and its pathological correlates. Conversely, TSP4 antibodies or genetic ablation blocks nociception and changes in synaptic transmission in mice overexpressing Cavα2δ1. Importantly, TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes also lead to similar behavioral and pathological changes in a neuropathic pain model of peripheral nerve injury. Thus, a TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent pathway activated by TSP4 or peripheral nerve injury promotes exaggerated presynaptic excitatory input and evoked sensory neuron hyperexcitability and excitatory synaptogenesis, which together lead to central sensitization and pain state development.
Keywords: gene knockout, gene regulation, mouse genetics, neurobiology, neuroscience, pain, signaling
Introduction
Neuropathic pain due to peripheral nerve injury is associated with up-regulation of expression of thrombospondin-4 (TSP4)5 in spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia (DRG) that induces increased frequency of miniature excitatory post-synaptic currents (mEPSC) in dorsal spinal cord and neuropathic pain states (1, 2). Details about the mechanisms remain to be defined however. TSP4 belongs to a five-member thrombospondin superfamily of oligomeric, extracellular matrix glycoproteins (TSP1–5) that can be subdivided into groups A (TSP1/2) and B (TSP3/4/5) based on structure and functional domain similarities (3). TSP proteins are important in mediating cell-to-cell and cell-to-matrix interactions (3, 4). TSP4 is expressed in multiple sites, and its functions are not well defined (5) although there is evidence that TSP4 promotes neurite outgrowth (6).
Recently, TSPs have been shown to regulate early excitatory synaptogenesis in the brain by interacting with its receptor, the voltage-gated calcium channel α2δ1 subunit (Cavα2δ1) proteins (7, 8). The Cavα2δ subunit family of the voltage-gated calcium channels includes four Cavα2δ subunits (Cavα2δ1–4) encoded by different genes (9–11). Cavα2δ functions include trafficking and stabilizing voltage-gated calcium channel to the plasma membrane and pre-synaptic terminals (12–14), fine-tuning channel functions, and gating properties (13, 15, 16).
Importantly, Cavα2δ1 and Cavα2δ2 subunits are binding sites of gabapentinoids (17, 18), which have anti-neuropathic pain efficacy in patients (19–22) and animal models (23–26). Cavα2δ1, but not Cavα2δ2, is up-regulated in sensory neurons after peripheral nerve injury (27, 28), leading to increased Cavα2δ1 axonal transport to the central presynaptic terminals of sensory neurons in dorsal spinal cord (27, 29). Similar to injury-induced TSP4, injury-induced Cavα2δ1 also has been shown to increase mEPSC frequency in neurons of dorsal spinal cord, which may contribute to central sensitization and neuropathic pain states (24, 25, 27, 29–31, 33).
Collectively, these observations suggest the following intriguing hypothetical mechanistic model: 1) peripheral nerve injury up-regulates Cavα2δ1 in peripheral sensory neurons and its central terminals; 2) peripheral nerve injury also triggers increased synthesis and release of TSP4 in spinal cord and DRG; 3) increased TSP4 interacts directly with its receptor Cavα2δ1 on the central terminals of sensory neurons to increase excitatory synaptogenesis and synaptic neurotransmission; 4) increased excitatory transmission in dorsal spinal cord contributes to central sensitization and neuropathic pain development. This model leads to several predictions. First, there should be direct molecular interactions between TSP4 and Cavα2δ1 in the adult spinal cord in vivo. Second, if TSP4 and Cavα2δ1 are mechanistically linked, then manipulations of one protein should alter the development of pain states induced by manipulations of the other protein. Here, we tested critical aspects of this model and the underlying mechanisms.
Materials and Methods
Mouse Genetics
The Cavα2δ1 overexpressing transgenic (TG) mice were generated as described previously (34). TSP4 knock-out (KO) mice were from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME). The Cavα2δ1 TG/TSP4 KO double mutant mice and their control littermates were bred internally. The Cavα2δ1 conditional knock-out (CKO) mice were generated by floxing exon 6 of the Cavα2δ1 gene (MGI (Mouse Genomics Informatics) ID 88295) with loxP sites. Homozygous Cavα2δ1 CKO mice were crossed with the Advillin-Cre mice with Cre recombinase expression only in Advillin-positive sensory neurons (35) to generate heterozygous CKOAdv-Cre+/− mice, which were used to generate homozygous CKOAdv-Cre+/− mice for experiments. Mouse genotyping was performed by TransnetYX, Inc. (Cordova, TN). All the mice appeared normal with respect to grooming, social interactions, and feeding and showed no signs of abnormality or any obvious motor defects, tremor, seizure, or ataxia. Only adult male mice were used for the experiments. All animal care and experiments were performed according to protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care Committee of the University of California, Irvine.
Expression and Purification of Recombinant TSP4
Human embryonic kidney cell line 293-EBNA (Invitrogen) in DMEM/F-12 medium (Mediatech, Manassas, VA) was transfected with recombinant rat TSP4 with N-terminal His tag using the calcium phosphate transfection method, then transfected cells were selected with 0.5 μg/ml puromycin. Secreted TSP4 was confirmed by Western blots using anti-Tetra-His monoclonal antibodies (catalog #34670, negligible cross-reactivity with mammalian and other species cell lysates validated by Qiagen, Valencia, CA). The His-tagged proteins were purified using a nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid column based on the manufacturer's instructions (Invitrogen), concentrated and buffer-exchanged to PBS with Amicon Ultra-4 Centrifugal Filter Unit (50K molecular weight cutoff; Millipore, Billerica, MA), aliquoted, and stored at −80 °C until use.
Immunoprecipitation
The spinal cord tissues from adult male mice and adult male Harlan Sprague-Dawley rats were collected by hydraulic extrusion from animals deeply anesthetized with isoflurane and lysed in protein extraction buffer (50 mm Tris buffer, pH 8.0, 0.1% Triton X-100, 150 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, and protease inhibitors). The cell lysate was then incubated on ice for 15 min, centrifuged ×20,000 × g for 20 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was incubated with anti-TSP4 polyclonal antibody (guinea pig, 1:750, validated previously; Ref. 36) overnight at 4 °C. Protein A/G-agarose beads (Thermo, Waltham, MA) were then added, incubated for 2 h at 4°C, and washed with protein extraction buffer. The antibody-captured proteins were eluted in non-reducing condition with low pH elution buffer (Thermo, Waltham, MA) at room temperature, and the same volume of control supernatant or immunocomplex samples was analyzed by Western blots under non-reducing conditions.
Solid-phase Binding
Briefly, FLAG-Cavα2δ1cDNA was transiently transfected into the tsA-201 cell line stably expressing Cav2.2 and Cavβ3 (a gift from Dr. D. Lipscombe from Brown University (37) by Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen). The transfected cells were washed and extracted in protein extraction buffer (50 mm Tris, 150 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 0.1% Triton-X, pH 7.4) in 2–3 days. The cell lysate was incubated on ice for 15 min, then centrifuged ×13,000 × g at 4 °C for 20 min. The supernatant was rotating-incubated with anti-FLAG M2 agarose affinity resin (Sigma) for 2 h at 4 °C and washed with protein extraction buffer. FLAG-Cavα2δ1 was eluted in elution buffer (0.1 m glycine, pH 3.5) and stored at −20 °C until use.
The reagents for solid-phase binding were from Invitrogen. Recombinant TSP4 proteins (80 μg/ml) were immobilized onto a 96-well polystyrene plates (Thermo, Waltham, MA) overnight at 4 °C in coating buffer A. All further incubations were carried out at room temperature for 1 h, and proteins or antibodies were diluted in assay buffer containing bovine serum albumin (BSA). After washing and blocking, the plates were incubated with FLAG-Cavα2δ1, washed, then incubated with mouse monoclonal anti-FLAG antibodies (1:1000; catalog #F1804, validated against FLAG fusion proteins by Sigma) followed by horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies. The bound FLAG-Cavα2δ1 complexes were detected by measuring a color reaction at 450 nm after adding tetramethylbenzidine for 15 min followed by adding sulfuric acid to stop the reaction.
Surface Plasmon Resonance Binding (38)
All experiments were carried out using BIAcore 3000 and CM5 Sensor Chip (GE Healthcare) at 25 °C. Cavα2δ1antibody (mouse, catalog #D219, Sigma) was coupled to the dextran matrix of a CM5 sensor chip using Amine Coupling kit as described (39). The antibody specificity for Cavα2δ1 was confirmed with tissue samples from Cavα2δ1knock-out mice (Fig. 4C). Excess reactive esters were quenched by injection of 1.0 m ethanolamine-hydrochloride, pH 8.5. The binding assays were performed using HBS-P buffer (0.01 m HEPES, pH 7.4, 0.15 m NaCl, 0.005%, and surfactant P20) as running buffer. Purified TSP4 proteins and Cavα2δ1 protein extracts from tsA-201 cells stably expressing CaV2.2e (Δ24a, 31a), CaVβ3, and Cavα2δ1 as described (40) were diluted in HBS-P buffer (GE Healthcare). Cavα2δ1 protein extracts were injected at a flow rate of 10 μl/min over the immobilized Cavα2δ1 antibody flow cells followed by injection of purified TSP4 proteins at a flow rate of 20 μl/min. Nonspecific binding of TSP4 to the flow cell without immobilized Cavα2δ1 antibody was subtracted from all binding curves using BIAevaluation software (version 3.0, GE Healthcare) and plotted using Graphpad Prism (Graphpad Software, San Diego, CA).
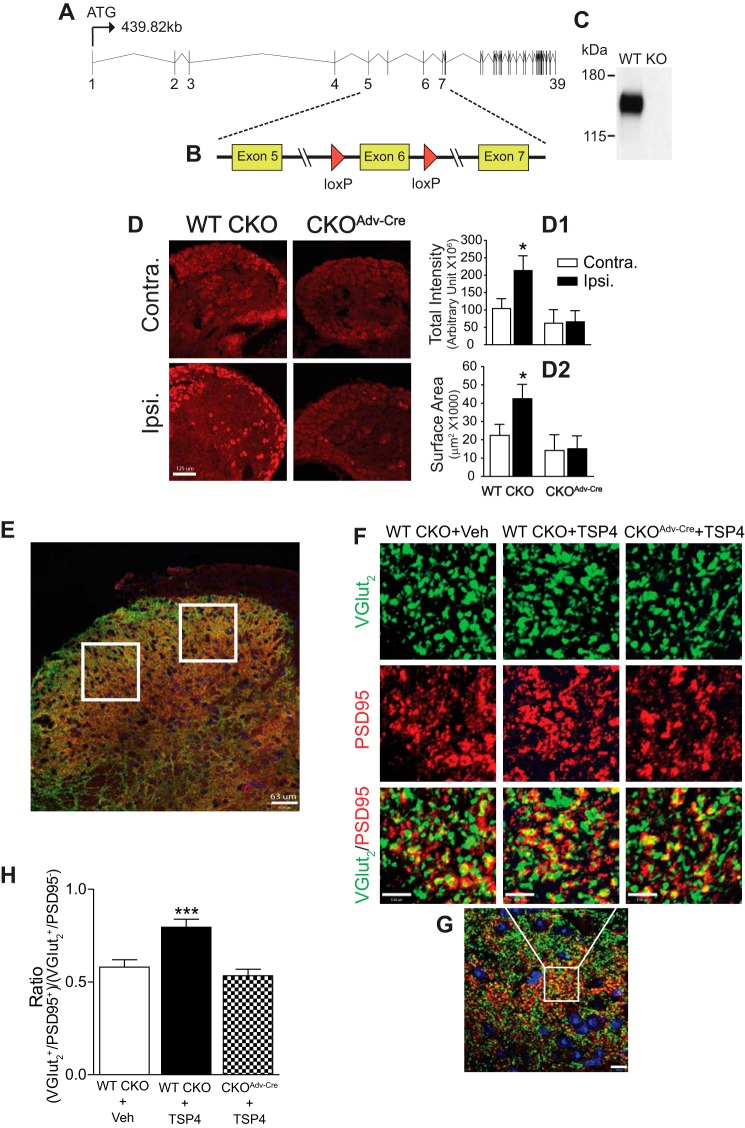
FIGURE 4.
Cavα2δ1 ablation from Advillin+ DRG neurons blocked TSP4-induced excitatory synaptogenesis. A, Cavα2δ1 gene structure. B, a strategy diagram of generating the Cavα2δ1 conditional knock-out mice. C, a representative Western blot (from n = 3) showing null Cavα2δ1 expression (KO) in brain lysates from homozygous Cavα2δ1 KO mice crossed with germ line Cre mice (FVB/N-Tg(ACTB-cre)2Mrt/J (The Jackson Laboratory). D, validation of Cavα2δ1 conditional knock-out from Advillin-Cre expressing DRG neurons in 2-week SNL WT CKO control or CKOAdv-Cre mice with Cavα2δ1 antibody immunofluorescent staining (red). Contra., non-injury; Ipsi., injury side. Summarized total intensity (D1) and surface area (D2) data are presented as the means ± S.E. from 12 sections, three mice in each group. *, p < 0.05 compared with non-injury (contra.) side in each group with paired Student's t test. Scale bar: 125 μm for all panels. E, a representative L4 dorsal spinal cord image showing random sampling (white squares) of fluorescent immunoreactivity from superficial dorsal horn for data analysis. Scale bar: 63 μm. F, representative images from co-immunostaining in thin sections of L4 dorsal spinal cord from WT CKO or CKOAdv-Cre mice 4-days post-i.t. saline (vehicle) or TSP4 (5 μg/5 μl/mouse) injection. VGlut2 (green), excitatory presynaptic marker; PSD95 (red), post-synaptic marker; yellow, colocalized immunoreactivity. Scale bar: 5 μm for all panels. Each of these images was enlarged to show detailed structure from a small area (similar to the white box in G) of a sampling image. G, a representative sampling image showing the area (in the white box) that was enlarged to show detailed structure above. Scale bar: 10 μm. H, summarized ratio of VGlut2+/PSD95+ over VGlut2+/PSD95− immunoreactive puncta. Data are the means ± S.E., 36 sections from 3 mice each. ***, p < 0.001 versus vehicle injected WT CKO mice by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test.
Spinal Nerve Ligation (SNL) (41)
Briefly, the left L4 spinal nerve of mice, which is equivalent to L5 spinal nerve in rats (42), was exposed in isoflurane-anesthetized animals and tightly ligated between the DRG and their conjunction to form the sciatic nerve with a silk suture. Sham procedures were done in the same way without spinal nerve ligation. Behavioral tests were performed at designated times before collection of tissue samples, which were either processed immediately for biochemical studies or kept at −80 °C until use.
Cavα2δ1 shRNA design and delivery via an adeno-associated viral vector (scAAV). A cDNA encoding the complete coding sequence of the mouse Cavα2δ1 subunit was obtained from Open Biosystems (IMAGE: 40061614), then cloned into a mammalian expression vector (pYFP-C1, Clontech). Candidate shRNAs were designed using publicly available web tools (Invitrogen Block-it and Genscript). These shRNAs were imbedded in a mir30 backbone using opposing BsmBI sites to insert complementary oligonucleotides encoding the shRNAs without altering the miR sequence (43, 44). The shRNAs were cloned into a human H1 promoter amplified from pLVUTH (Addgene clone 11650). We engineered a novel scAAV using the pLVUTH backbone and the δ-ITR sequences described by McCarty et al. (45). This vector uses a CMV enhanced human synapsin-1 promoter (46) to drive the expression of mCherry (provided by Dr. Roger Y. Tsien, UCSD) that was modified by adding the C-terminal ER export signal (FCYENE) from Kir2.1 (47). Four shRNAs were screened for target knockdown after expression in HEK-293 cells. Knockdown efficiency was measured using quantitative PCR with primers that encompassed the shRNA binding site (48). The shRNA with the highest knockdown efficacy (80%) relative to a scrambled control was AD1: AACTGGACAAGTGCCTTAGAT. CSRH1AD1 scAAV particles pseudotyped with serotype 8 were purified by the University of North Carolina Vector Core (titer 2 × 1012 virus molecules/ml).
Intrathecal Injection
Intrathecal injections between lumbar L5/6 regions for rats or L4/5 regions for mice were performed under light isoflurane anesthesia through a 30-gauge needle connected to a microinjector (Tritech Research, Inc., Los Angeles, CA). A total volume of 10 μl per rat or 5 μl per mouse was injected.
Behavioral Test
Testing was performed in a blinded fashion. Behavioral test values between left and right hind paws from the SNL groups were recorded separately and used for statistical analysis, and that from non-SNL groups were averaged and used for statistical analysis.
Tactile Allodynia
Hind paw sensitivities to von Frey filament stimulation were tested for tactile allodynia as described previously (2, 49, 50). After acclimatization in wire mesh-floored transparent enclosures, the animals were accessed for the 50% paw withdrawal thresholds (PWT) to von Frey filament (Stoelting Wood Dale) stimulation using the up-down method (51). Briefly, the plantar surface of the hind paw was contacted perpendicularly with the first filament (2.0 g for rats or 0.41 g for mice) until it was slightly bent. A positive response of paw lifting within 5 s led to the use of the next lighter filament, and a negative response led to the use of the next heavier filament until a total of six measurements had been made, starting from the one before any change in the behavioral response. A score of 15 g for rats or 3 g for mice was assigned if five consecutive negative responses had occurred or a score of 0.25 g for rats or 0.01 g for mice was assigned if four consecutive positive responses had occurred. The data were then used to determine the 50% response threshold described previously (25).
Thermal Hyperalgesia
Reduced hind paw withdrawal latency to thermal stimuli was measured using a Hargreaves (hot box) apparatus (University of California San Diego, CA) (52) as the indication of thermal hyperalgesia. After acclimatization for at least 30 min on a glass floor maintained at 30 ± 0.1 °C in transparent enclosures, the hind paw plantar surface of a free-moving animal was stimulated by radiant heat projecting from a high intensity light bulb through a small aperture below the glass surface. When the animal moved the paw away from the thermal stimulus, motion detectors on the apparatus turned off the heating light automatically. The paw withdrawal latency was recorded as the time between thermal stimulus application and hind paw withdrawal. 20 s were set as the cutoff time to prevent thermal injury or skin sensitization. Two readings per paw were averaged for statistical analysis.
Mechanical Hyperalgesia
After acclimatization for 1 week to human holding and touch, rats were tested for mechanical hyperalgesia (Randall-Selitto Test (53) using a Paw Pressure Analgesymeter (Ugo Basil North America)). Briefly, a rat hind paw was placed between a blunt pointer and a flat surface and subjected to an escalating force (16 g/s) until paw withdrawal by the animal. The recorded hind paw withdrawal inducing force was used as the paw pressure withdrawal thresholds.
Locomotor Function Tests
After acclimatization daily for 1 week to human handling and the open field test apparatus, mice were tested for locomotor function by a blinded observer using scores of 0–9 arranging from no ankle movement (0) to frequent or consistent coordinated plantar stepping, normal trunk stability, and tail up position (9) as described by Basso et al. (54).
Western Blots
Briefly, equal amounts of proteins were separated in 3–8% NuPAGE Tris acetate gels (Invitrogen) by electrophoresis, then transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes electrophoretically. After blocking nonspecific binding sites with 5% low fat milk (in PBS-T containing 137 mm NaCl, 2.7 mm KCl, 4.3 mm Na2HPO4 1.4 mm KH2PO4, 0.1% Tween 20, pH 7.4), the membranes were cut into sections containing different target proteins and incubated with primary antibodies against Cavα2δ1 (mouse, 1:1000, catalog #D219, Sigma), TSP4 (rabbit, 1:1000, custom made and validated against purified TSP4 proteins, Genscript, Piscataway, NJ), β-actin (mouse, 1:10,000, catalog #MAB8929, validated against various β-actin expressing cell lines, Novus Biologicals, LLC, Littleton, CO) overnight at 4 °C followed by horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (1:2000, Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA) for 1 h at room temperature. After a brief incubation with chemiluminescent reagents (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA), the band densities were quantified by either imaging quantification (Kodak Image Station 2000MM) or densitometry within the linear range of the film sensitivity curve. The Cavα2δ1 band detected by the mouse Cavα2δ1 antibodies reflected the Cavα2 protein only (≈150 kDa) as the Cavδ1 peptide separates from the Cavα2 protein under reducing conditions in Western blots (55). For quantification, band density ratios for the protein of interest over that of β-actin (≈42 kDa) were calculated within each sample first for normalization of total protein loading before cross-sample comparisons. Band density variations for the proteins of interest in the contralateral (non-injury) side were determined by comparing each band density with the mean of that from at least two different control samples in the same Western blot after taking the ratios to β-actin band densities.
Spinal Cord Slice Recording
α-Amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid(AMPA) receptor-mediated mEPSC and evoked excitatory post-synaptic currents (eEPSC) were recorded from lumbar spinal cord transverse slices (300 μm). Briefly, spinal cord slices were prepared and transferred to the recording chamber as described previously (30, 33). The patch electrode had a resistance of 5–7 megaohms when filled with pipette solution that contained 135 mm potassium gluconate, 5 mm KCl, 5 mm EGTA, 0.5 mm CaCl2, 10 mm HEPES, 2 mm MgATP, and 0.1 mm GTP, pH 7.2, with an osmolarity 300 mosmol/liter. Superficial dorsal horn neurons were visualized with an upright microscope (Eclipse FN1, Nikon, Japan) and near-infrared illumination based on the gelatinous (semi-transparent) appearance of lamina II (substantia gelatinosa). Although neurons in superficial dorsal horn (including lamina I, lamina II outer or IIo, and lamina II inner or IIi) are heterogeneous (56, 57), the boundaries of laminae I, IIo, and IIi are ambiguous in live spinal cord slices so it was difficult to classify lamina-specific neuron populations, a limitation of our sampling method. Thus, we pooled all recording data together for a general view of TSP4 effects in modulating synaptic transmission and regulation in superficial dorsal horn neurons. All recordings were performed at 32 ± 0.5 °C with MultiClamp 700B amplifiers (Axon Instruments, Molecular Devices, Union City, CA), Digidata 1440 analog-to-digital converters (Axon Instruments), and pClamp 10.2 software (Axon Instruments).
mEPSCs were recorded as described previously (2, 30, 33) in the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX, 1 μm), strychnine (1 μm), bicuculline (10 μm), and 2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (AP5, 50 μm) to block TTX-sensitive Na+, glycinergic, GABAergic, and N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) currents, respectively. Membrane potential was held at −60 mV so that N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated currents were blocked (58), which only represented <10% mEPSCs in dorsal horn neurons, and the remaining 90% mEPSCs could be blocked by AMPA receptor antagonist 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX) (59). Series resistance was monitored without compensation throughout the experiment (Multiclamp 700B). Cells were excluded from analysis if the series resistance changed by >20% during the whole-cell recording. Signals were analyzed using clampfit 10.3 (Molecular Devices) after the traces were low-pass-filtered at 2 kHz. Cumulative distribution of mEPSC frequency or amplitude of individual neurons from each experimental group was analyzed with Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.
eEPSCs were similarly recorded from superficial dorsal horn neurons of L4 lumbar spinal cord slices upon stimulating (0.1 ms, 0.05 Hz) the attached dorsal roots or dorsal root entry zone with 0–500-μA stimulus intensity. At least six eEPSC events were recorded at each stimulus intensity. QX314 (5 mm) was added in intrapipette solution to prevent sodium channel activation.
Immunohistochemistry (2, 28)
Lumbar spinal cord and DRG samples were fixed in 4%paraformaldehyde overnight, cryoprotected in 30% sucrose, mounted in Optimum Cutting Temperature (O.C.T., Sakura Finetek, Torrance, CA), and sectioned with a cryostat (CM1900, Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) into 10-μm slices. Slices of spinal cord samples were pretreated with heat-based antigen retrieval (10 nm sodium citrate, 0.05% Tween 20, pH 6.0, 5 min in a pressure cooker). Spinal cord and DRG slices were incubated with primary antibodies against Cavα2δ1 (rabbit polyclonal, custom made by Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, for spinal cord samples after antigen retrieval; or mouse monoclonal, Sigma, for DRG samples without antigen retrieval; both antibodies were validated with Cavα2δ1 knock-out mice shown in Fig. 4, A–D), VGlut2 (guinea pig, catalog #135404, validated previously (Refs. 28 and 60–62); Synaptic Systems, Germany), and PSD95 (rabbit, catalog #MA1-045, validated previously (Refs. 28, 63, and 64), Thermo Fisher Scientific) followed by secondary antibodies with Alexafluor 488 or 594 (Invitrogen) against IgG of corresponding species of the primary antibodies. Sample sections from control and experimental groups (sides) within the same set of experiments were stained at the same time. Samples were mounted with Vectashield containing DAPI for cell nuclei staining (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA). Two images were taken from each superficial dorsal horn section randomly using a Zeiss LSM780 confocal microscope (UC Irvine Optical Biology Core) in 0.3-μm Z-stacks, and three consecutive Z stacks with the best signal were merged and used for data analysis with Volocity 6.0 (PerkinElmer Life Sciences). Briefly, images from control and experimental groups within the same set of experiment were captured with the same setting. Volocity Find Object Using Percentage Intensity function was used to define background threshold, which was used for both contralateral and injury sides within each set of experiment. Fluorescent immunoreactivities above the background level were selected for analysis. From TSP4 or saline-injected mouse samples, VGlut2/PSD95 co-stained samples (n = 36 over 3 animals, 100 μm apart) were analyzed to determine the numbers of total VGlut2+ (green), PSD95+ (red), and VGlut2+/PSD95+ (yellow) puncta. Because the effect of intrathecal injection was bilateral, the ratio of VGlut2+/PSD95+ over VGlut2+/PSD95− puncta from both sides was used to compare the differences between the TSP4- and saline-treated groups. From 2-week SNL samples, VGlut2/Cavα2δ1 (n = 60 over 3 animals, 100 μm apart) co-stained samples were analyzed to determine the numbers of total Cavα2δ1 (red), VGlut2+ (green), and VGlut2+/Cavα2δ1+ (yellow) puncta. Data from the injury (ipsilateral) side were compared with that from the non-injury (contralateral) side.
Statistics
One-way or two-way ANOVA with post-tests were performed for multigroup comparisons, and unpaired Student's t tests were performed for pair-wise comparisons as indicated in figure legends. Significance was determined by a two-tailed p value < 0.05.
Results
TSP4 Interacts Directly with Cavα2δ1 in Rodent Spinal Cord in Vivo
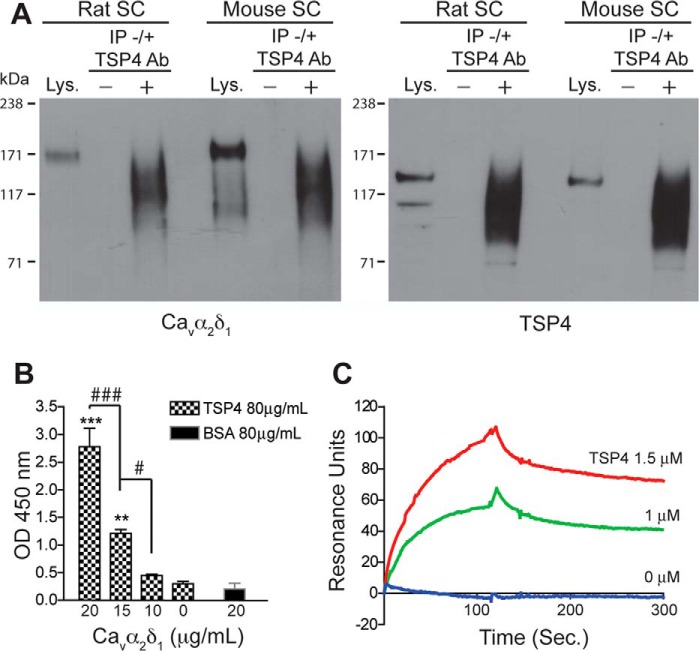
Data from in vitro immunoprecipitation and functional assays suggest that TSP4/Cavα2δ1 forms a complex in mediating abnormal excitatory synapse formation in rat cerebral cortex (8). However, a direct binding or functional interaction between these proteins in spinal cord has not been shown. If interactions of these proteins lead to abnormal synaptogenesis and neuropathic pain states post injury, there should be direct molecular interactions between astrocyte-secreted TSP4 and Cavα2δ1 in the adult spinal cord in vivo. To test this, we first examined if TSP4 and Cavα2δ1 proteins were detectable in immunoprecipitation (IP) complexes from rodent spinal cord samples. Our results confirmed previous findings in rat cerebral cortex (8) and showed that Cavα2δ1 was detectable in TSP4 immunoprecipitates from rat and mouse spinal cord (Fig. 1A), suggesting that these proteins may interact directly or indirectly in rodent spinal cord. The differences in the patterns of bands between the spinal cord lysates and IP samples are likely due to these factors. First, IP samples were more concentrated compared with the “Lys” control samples as we loaded an equal volume of each sample onto the same blot. Under non-reducing conditions, the IP complexes might contain more target proteins and other associated proteins. Second, it is possible, but needs to be confirmed, that TSP4 antibodies might have pulled down the extracellular Cavα2 domain (150 kDa) of the Cavα2δ1 subunit (175 kDa) without the Cavδ1 peptide (25 kDa).
FIGURE 1.
TSP4 and Cavα2δ1 interaction. Immunoprecipitation, solid-phase binding, and surface plasmon resonance binding were performed as described under “Materials and Methods” to detect TSP4/Cavα2δ1 interaction in rodent spinal cord and in vitro. A, typical Western blots showing Cavα2δ1 co-immunoprecipitation with TSP4 proteins (IP) by anti-TSP4 antibodies from rat or mouse spinal cord (SC) samples (from n ≥ 3 each). Lys, spinal cord lysate positive control. −, no anti-TSP4 IP antibody. +, with anti-TSP4 IP antibody. Approximate positions of prestained molecular weight markers are shown on the left of each gel. B, solid phase binding showing dose-dependent FLAG-Cavα2δ1 binding to immobilized TSP4. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 compared with no Cavα2δ1; #, p < 0.05; ###, p < 0.001 between adjacent doses by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. C, surface plasmon resonance binding sensogram of dose-dependent TSP4 binding to captured Cavα2δ1 (typical of three independent experiments).
To further assess whether TSP4 interacts with Cavα2δ1 directly, we examined interactions with solid phase binding and surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy assays. The solid phase binding assay confirmed that recombinant Cavα2δ1 proteins bind directly to immobilized TSP4 in a dose-dependent fashion (Fig. 1B). Conversely, surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy demonstrated dose-dependent binding of TSP4 to immobilized Cavα2δ1 on a BIAcore CM5 sensor chip with fast association and slow dissociation (Fig. 1C).
Interdependent Interactions between TSP4 and Cavα2δ1 Proteins Contribute to Pain States and Dorsal Horn Neuron Sensitization
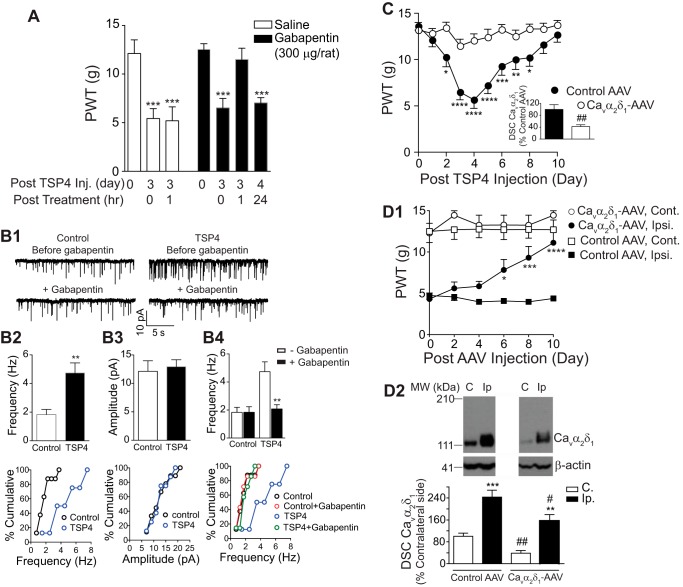
If TSP4 induces neuropathic pain by interacting with Cavα2δ1, then blocking this interaction pharmacologically should abrogate TSP4-induced pain. It is known that gabapentin specifically binds to Cavα2δ1 (17, 18) and blocks neuropathic pain states induced by nerve injury-induced Cavα2δ1 (23–25). Thus, we tested whether gabapentin treatment could reverse TSP4-induced pain states. As reported previously (2), TSP4 intrathecal (i.t.) injection (45 μg/rat) induced tactile allodynia as evidenced by reduced PWT to von Frey filament (mechanical) stimulation 3 days post-TSP4 injection (open bars, Fig. 2A). One hour after gabapentin injection (300 μg/rat, i.t.), PWT increased to near the control levels. The effect of gabapentin was reversible because PWT were again reduced to the pretreatment level 24 h post-gabapentin treatment (filled bars, Fig. 2A). Gabapentin treatment had a similar effect on TSP4-induced thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical hyperalgesia (data not shown).
FIGURE 2.
Blocking or depleting Cavα2δ1 reverses pain states and exaggerated presynaptic excitatory input induced by elevated TSP4 or SNL. A, Gabapentin (i.t. injected 3 days post-TSP4 injection) reversed tactile allodynia induced by TSP4 (45 μg/rat, i.t.) in 1 h. Data are the means ± S.E. from n = 6 (saline) to 8 (gabapentin (GBP)) rats. ***, p < 0.001 versus pre-TSP4 by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. B1, mEPSCs from rat L5 superficial dorsal horn neurons 3 days after the same TSP4 injection. Top, mEPSC frequency, but not amplitude, was increased in TSP4 injected rats versus control rats injected with an equal molar dose of His-tag peptides. Bottom, gabapentin (50 μm) blocked the TSP4 effects. B2–B4, top, summarized data. Date are the means ± S.E., n ≥ 7 neurons from 4 rats in each group. **, p < 0.01 compared with control (B2) or pre-treatment (B4) level by Student's t test. B2–B4 bottom, cumulative distribution of mEPSC frequency (B2 bottom) and amplitude (B3 bottom) in neurons from control and TSP4 injected rats (p < 0.01 for comparison of mEPSC frequency; p > 0.05 for comparison of mEPSC amplitude; Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). B4 bottom, application of gabapentin (50 μm) significantly reduced the mEPSCs frequency in neurons from TSP4-injected rats to a level similar to that in control neurons (p < 0.001 for comparison of mEPSC frequency before and during gabapentin treatment in TSP4 injected group; Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). C, preemptive knockdown of Cavα2δ1 in rat dorsal spinal cord (DSC, inset) with bolus intrathecal injection (L5/6 region) of anti-Cavα2δ1 small hairpin RNA (Cavα2δ1-AAV), but not control (Control-AAV), AAV vectors (106 units in 2 μl) 10 days before TSP4 injection (45 μg/10 μl/rat, i.t. at day 0) blocked TSP4-induced allodynia. Data are the means ± S.E. from seven rats each. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001 versus pre-TSP4 by repeated measures two-way ANOVA analysis with Bonferroni post-tests; ##, p < 0.01 versus the control AAV group by Student's t test (inset). D1, similar intrathecal injection of Cavα2δ1, but not control, AAV into L5/6 regions of 2-week SNL rats led to a gradual reversal of established allodynia in the hind paws of the injury (Ipsi.) side without affecting the behavioral sensitivity in that of the non-injury (Cont.) side. Data are the means ± S.E. from six rats each. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001 compared with the pretreatment level by repeated measures two-way ANOVA analysis with Bonferroni post-tests. D2, dorsal spinal cord Cavα2δ1 levels were down-regulated significantly from both sides of rats similarly injected with Cavα2δ1-AAV 10 days ago compared with that in rats injected with the control AAV. Top, representative images from the same Western blot showing Cavα2δ1 levels in both sides of dorsal spinal cord samples. β-Actin bands were used for normalization of total protein loading (see “Materials and Methods”). Approximate positions of prestained molecular weight (MW) markers are shown on the left. Bottom, summarized Western blot data. Data are the means ± S.E. from six rats each. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 compared with non-injury side. #, p < 0.05; ##, p < 0.01 compared with the same side in control-AAV treated rats by Student's t test. C, contralateral (non-injury) side. Ip, ipsilateral (injury) side.
We previously reported that TSP4-induced pain states correlated with increased mEPSC frequency, but not amplitude, in superficial dorsal horn neurons (2). If TSP4 mediates this effect via ongoing interaction with Cavα2δ1, then blocking Cavα2δ1 with gabapentin should reduce mEPSC frequency. Consistent with our previous study (2), recordings from superficial dorsal horn neurons 3 days after TSP4 injection revealed a significant >100% increase in average mEPSC frequency without significant changes in its amplitude (Fig. 2, B1, B2, and B3). After treatment with gabapentin (50 μm), elevated mEPSC frequency was dramatically decreased to the control level, but its basal level in the control group was not affected significantly (Fig. 2, B1 and B4). These changes were confirmed by Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests using cumulative distribution of mEPSC frequency or amplitude of individual neurons from each experimental group (bottom panels of Fig. 2, B2–B4). This gabapentin concentration is close to that in patient cerebrospinal fluid after chronic gabapentin treatments. It has been reported that oral 900 mg/day gabapentin treatment for 3 months can reach peak plasmid concentration ∼10 mg/liter (58 μm) 3 h after the last dose (65), and cerebrospinal fluid gabapentin concentration range was ∼20–35% that in the plasma after multiple dosing (65, 66). Collectively, these results support the idea that TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes mediate both TSP4-induced pain states and the putative pathological underpinning (increased mEPSC frequency).
To further test whether blocking TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes by biochemical knocking down Cavα2δ1 could prevent TSP4-induced pain states, we investigated if TSP4-induced behavioral hypersensitivity could be prevented by pre-emptive knockdown of Cavα2δ1 with intrathecal treatment of anti-Cavα2δ1 small hairpin RNA in AAV vectors (Cavα2δ1-AAV). We previously showed that bolus intrathecal TSP4 injection induced tactile allodynia as evidenced by progressive reduction in PWT to a tactile stimulus (2). This effect was confirmed in the present study in rats that were pretreated with intrathecal control AAV (106 units in 2 μl) 10 days before bolus TSP4 injection (45 μg/rat, i.t.) (Fig. 2C). In contrast, rats pretreated with Cavα2δ1-AAV (106 units in 2 μl), which diminished dorsal spinal cord Cavα2δ1 levels (Fig. 2C, inset), did not exhibit the progressive decreases in PWT that reflect tactile allodynia (Fig. 2C). These results support the conclusion that TSP4-induced allodynia does depend on Cavα2δ1.
To further test this idea in the clinically relevant neuropathic model of SNL, we investigated whether knock down of Cavα2δ1 by intrathecal Cavα2δ1-AAV could reverse SNL-induced behavioral hypersensitivity as our previous studies have implicated either Cavα2δ1 or TSP4 in neuropathic pain states (2, 24, 25, 28, 29). Bolus i.t Cavα2δ1-AAV, but not the control vector, treatments (106 units in 2 μl) caused a time-dependent reversal of 2-week SNL-induced tactile allodynia without affecting the behavioral sensitivity in the contralateral (non-injury) side. The anti-allodynic effects of Cavα2δ1-AAV peaked ∼10 days after the i.t. injection (Fig. 2D1) and lasted for >2 weeks (data not shown). Western blot analysis of spinal cord samples from control and Cavα2δ1-AAV-treated rats at the peak allodynia reversal time point (10 days post-Cavα2δ1-AAV treatment) confirmed Cavα2δ1 knockdown on both sides of dorsal spinal cord. Cavα2δ1 levels on the injury side were not significantly different from levels in the non-injury side of control vector-treated rats (Fig. 2D2). The fact that Cavα2δ1 knockdown prevented allodynia development (Fig. 2C) and reversed established allodynia (Fig. 2D1) indicates that TSP-induced behavioral hypersensitivity requires ongoing interactions between TSP4 and Cavα2δ1 at the spinal cord level.
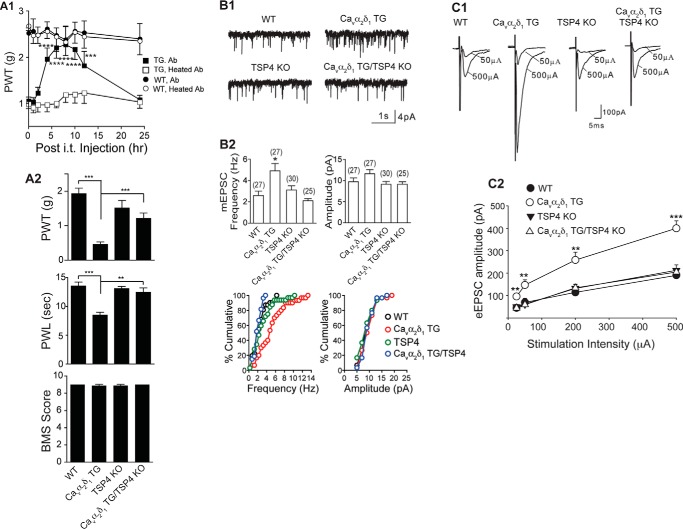
Next, we examined if blocking TSP4 could diminish pain states and putative pathological underpinning due to elevation of Cavα2δ1. We previously showed that TG mice with neuronal Cavα2δ1 overexpression have increased mEPSC frequency and pain states similar to mice with SNL injury (30, 33, 34, 59, 67). We first tested whether blocking TSP4-dependent processes with TSP4 antibodies would reverse Cavα2δ1 overexpression-induced allodynia. Consistent with previous findings (34), TG mice with neuronal Cavα2δ1 overexpression have greatly reduced PWT to mechanical stimuli (the behavioral reflection of allodynia). After treatment with the TSP4 antibody (10 μg/mouse, i.t., chicken polyclonal, validated previously; Ref. 68), PWT gradually increased to near the control level by 8 h post-treatment and then returned to the pretreatment level by 24 h (Fig. 3A1). Antibody treatment did not affect baseline thresholds in age- and sex-matched wild type (WT) mice. Heat-denatured antibody was without effect (Fig. 3A1). Similar treatment with this antibody also prevented the development and reversed established neuropathic pain states in the more clinically relevant SNL model (2).
FIGURE 3.
Depleting or blocking TSP4 reverses Cavα2δ1-induced pain states and dorsal horn neuron sensitization. A1, TSP4 antibody (Ab, chicken, 10 μg/5 μl/mouse, i.t.), but not heated TSP4 antibody, reversed allodynia induced by neuronal Cavα2δ1 overexpression in the Cavα2δ1-TG mice without affecting baseline sensitivity in WT mice. Data are the means ± S.E. from n = 5 (WT) or 6 (TG). ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001 versus pretreatment level by repeated measures two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. A2, TSP4 ablation did not affect baseline sensitivity but reversed tactile allodynia (top) and thermal hyperalgesia (middle) in the Cavα2δ1 TG mice. Locomotor functions were not affected in these genetically modified mice as analyzed with the Basso Mouse Scale for locomotion (BMS), bottom). Data are the means ± S.E. from n = 8–10 each group. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 by Student's t test. B1, mEPSCs from L4 superficial dorsal horn neurons of the same mouse groups. Cavα2δ1-induced increase of mEPSC frequency in the Cavα2δ1 TG mice was blocked by TSP4 ablation. B2 top, summarized data. Data are the means ± S.E. from the number of neurons shown in parentheses that were obtained from ≥ 5 mice in each group. *, p < 0.05 versus WT by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. B2 bottom, cumulative distribution of mEPSC frequency and amplitude in each group (p < 0.01 for frequency comparisons between the Cavα2δ1 TG group and each of the other three groups; Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). C1, TSP4 ablation also blocked Cavα2δ1-induced increase of eEPSC amplitude in response to dorsal root entry zone stimulation without affecting baseline eEPSCs significantly. C2, summarized data, means ± S.E. from n ≥ 7 for each stimulus intensity (≥5 mice). **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 versus WT by repeated measures two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests.
As an alternative approach, we tested if genetic ablation of TSP4 from the Cavα2δ1 TG mice would eliminate behavioral hypersensitivities previously reported in Cavα2δ1 TG mice (30, 33, 34, 59). To test this, we crossed Cavα2δ1 TG mice that develop hypersensitivity to stimuli with TSP4 knock-out mice to generate Cavα2δ1 TG/TSP4 KO mice with elevated neuronal Cavα2δ1 and TSP4 ablation. Similar to our previous findings (34), Cavα2δ1 overexpression in the TG mice resulted in behavioral hypersensitivities to mechanical (allodynia; Fig. 3A2, top) and thermal (thermal hyperalgesia; Fig. 3A2, middle) stimuli. Assessment of pain sensitivity in Cavα2δ1 TG/TSP4 KO mice revealed no increased sensitivity to either of these stimuli. Behavioral thresholds in mice with TSP4 knock-out alone (TSP4 KO) were comparable with that in WT control mice (Fig. 3A2, top and middle). The locomotor function test scores of Basso Mouse Scale (BMS) in mice with these genetic modifications were similar to that in the control mice (Fig. 3A2, bottom). Thus, TSP4 basal level is not critical in maintaining basal sensory/motor functions, and differences in behavioral sensitivities to stimuli among these mouse groups are not due to changes in motor functions. Together, these findings support that TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes are also required for pain state processing induced by elevated Cavα2δ1.
We also assessed whether the increase in mEPSC frequency reported previously in Cavα2δ1 TG mice (30, 33, 59) could be normalized by deleting TSP4 from the Cavα2δ1 TG/TSP4 KO mice. Similar to our previous findings (30, 33, 59), recordings from superficial dorsal horn neurons of Cavα2δ1 TG mice revealed significantly elevated frequency, but not amplitude, of mEPSC compared with that from control WT mice (Fig. 3B). As another control, recordings from superficial dorsal horn neurons of TSP4 KO mice revealed mEPSC frequency/amplitude comparable with that seen in WT neurons (Fig. 3B). However, recordings from superficial dorsal horn neurons of Cavα2δ1 TG/TSP4 KO mice revealed that mEPSC frequency and amplitude were within the range of that in control mice (Fig. 3B). These findings were confirmed by Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests using cumulative distribution of mEPSC frequency or amplitude of individual neurons from each experimental group (bottom panels of Fig. 3B2). Collectively, these findings support that although basal level TSP4 is not required for maintaining a normal level of mEPSC, TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes are required for Cavα2δ1-induced increase of mEPSC frequency, an indication of enhanced presynaptic excitatory input.
We hypothesized that increased TSP4/Cavα2δ1 interactions in the spinal cord of the TG mice could lead to hyperexcitability of dorsal horn neurons to peripheral stimulation. To test this, we examined the amplitude of eEPSCs in L4 superficial dorsal horn neurons from the Cavα2δ1 TG mice in response to escalating intensities of stimulation to dorsal root entry zone. Compared with that from WT littermates, eEPSC amplitudes were increased at all levels of stimulus intensity tested (Fig. 3C), indicating hyperresponsiveness of the dorsal horn neurons to afferent activation as a result of Cavα2δ1 overexpression. Similar recordings in Cavα2δ1 TG/TSP4 KO mice revealed that eEPSC frequency was within the range of WT mice, as was also the case with TSP4 KO alone (Fig. 3C). These findings suggest that although basal level TSP4 is not required for maintaining normal dorsal horn neuron excitatory tone, TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes are required for Cavα2δ1-mediated dorsal horn neuron sensitization.
Interdependent Interactions between TSP4 and Cavα2δ1 Proteins Promote Aberrant Excitatory Synaptogenesis in Animal Models with Pain States
Previous studies have shown that Cavα2δ1 proteins in sensory neurons are transported to central afferent terminals in the spinal dorsal horn under normal and post-injury conditions (27, 29). Other studies have shown that TSP interactions with Cavα2δ1 promote excitatory synaptogenesis in vitro (8) and increased excitatory synapses are associated with neuropathic pain states (28, 69). Together, these findings raise the possibility that injury-induced TSP4 in spinal cord might interact with Cavα2δ1 at the pre-synaptic terminals of sensory afferents to promote aberrant excitatory synaptogenesis, which in turn would contribute to enhanced transmission along pain pathways.
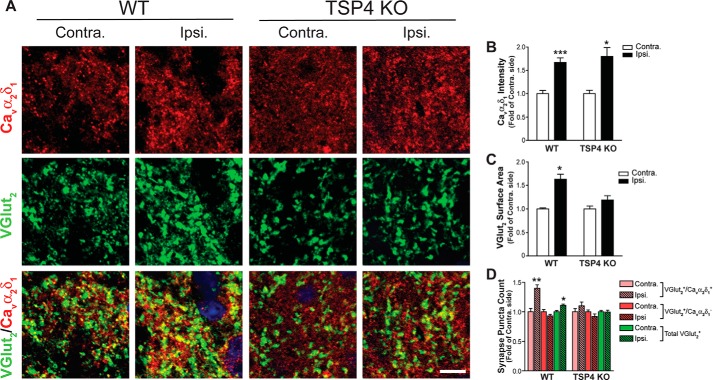
To test this hypothesis, we took the first step in determining whether there was evidence for aberrant excitatory synaptogenesis with TSP4-induced pain states; when so, we tried to determine if genetic ablation of Cavα2δ1 could block TSP4-induced synaptogenesis. We generated Cavα2δ1 conditional knock-out (WT CKO) mice in which exon 6 of the Cavα2δ1 gene was floxed with loxP sites (Fig. 4, A and B). Crossing these mice with Cre-recombinase expressing mice resulted in deletion of Cavα2δ1 from Cre-expressing cells (Fig. 4C). The WT CKO mice were crossed with Advillin-Cre mice with Cre recombinase expression only in Advillin-positive sensory neurons that cover ∼94% of all DRG neurons (35). Cre-driven Cavα2δ1 deletion from DRG neurons in homozygous CKOAdv-Cre+/− mice was confirmed by immunostaining data showing that 2-week SNL could induce DRG Cavα2δ1 up-regulation indicated as increased Cavα2δ1 antibody immunoreactivity in DRG neurons of control mice (WT CKO), as we have reported previously (25), but failed to do so in homozygous CKOAdv-Cre+/− mice (Fig. 4D). We then immunostained sections of L4 lumbar spinal cord from TSP4 (5 μg/mouse, i.t.)-injected mice 4 days after the injection (peak pain states in control mice) with markers for excitatory synapses (VGlut2 and post-synaptic density marker PSD95). Measurements of total number of synaptic puncta immunoreactive to both synaptic marker antibodies in spinal cord superficial dorsal horn (Fig. 4E) revealed substantial increases in excitatory synapses in TSP4 injected control WT CKO mice compared with vehicle-injected WT CKO mice. These TSP4-induced changes were not seen with Cavα2δ1 ablation in the CKOAdv-Cre+/− mice (Fig. 4, F–H). Thus, TSP4-induced aberrant excitatory synaptogenesis in dorsal spinal cord requires TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes.
If TSP4-induced aberrant excitatory synaptogenesis in dorsal spinal cord contributes to pain processing, one would expect to see that the absence of TSP4-induced excitatory synaptogenesis in the CKOAdv-Cre+/− mice correlates with the absence of TSP4-induced pain states. We tested this by examining behavioral sensitivity of control and CKOAdv-Cre+/− mice after TSP4 injections (5 μg/mouse, i.t.). Similar to previous findings in rats (2), TSP4 injection into control WT CKO mice led to tactile allodynia (Fig. 5, A and B) and thermal hyperalgesia (Fig. 5C), which peaked ∼4 days after TSP4 injections that correlated temporally with a significant increase of excitatory synapses in dorsal spinal cord of these mice (Fig. 4, F–H). In contrast, similar TSP4 injections into CKOAdv-Cre+/− mice failed to induce similar behavioral hypersensitivities (Fig. 5, A–C). This supports that TSP4-induced aberrant excitatory synaptogenesis through TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes plays a role in transmitting nociceptive signals.
FIGURE 5.
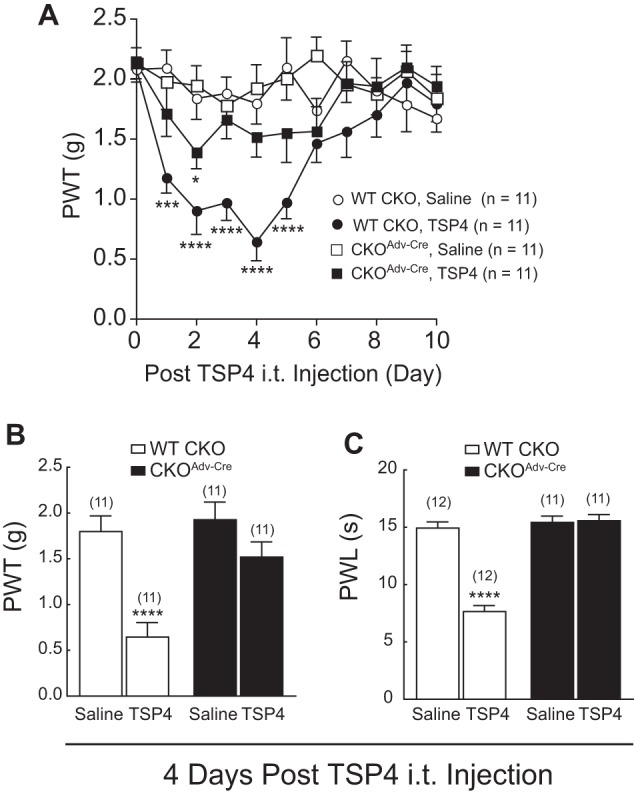
Cavα2δ1 ablation from DRG neurons blocked TSP4-induced pain states. Hind paw sensitivities to mechanical and thermal stimuli were measured in control WT CKO or CKOAdv-Cre mice post-bolus TSP4 (5 μg/5 μl/mouse, i.t.) injection as described under “Materials and Methods.” A, time course of TSP4-induced tactile allodynia in WT CKO mice that was diminished in CKOAdv-Cre mice with Cavα2δ1 ablation from Advillin+ DRG neurons. Data are the means ± S.E. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001 versus pretreatment level by repeated measures two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. Peak allodynia (B) and thermal hyperalgesia (C) seen in WT CKO mice were blocked in CKOAdv-Cre mice. Data are the means ± S.E. from (n) indicated. ****, p < 0.0001 versus saline group by Student's t test.
We next tested whether TSP4-induced synaptogenesis also plays a role in neuropathic pain development in the more clinically relevant SNL model. Our previous study has shown that SNL-induced allodynia is diminished in SNL TSP4 KO mice (2), suggesting a role of TSP4 in mediating neuropathic pain. Immunostaining for Cavα2δ1 revealed increases in Cavα2δ1 puncta in the superficial dorsal horn of the injury side in both WT and TSP4 KO mice 2 weeks post-SNL (Fig. 6, A and B), which correlated with severe allodynia in SNL WT, but not TSP4 KO, mice (2). Thus, elevated presynaptic Cavα2δ1 expression is not regulated by TSP4. Nerve injury also increased VGlut2 puncta that mainly co-localized with Cavα2δ1 puncta in the WT mice (Fig. 6, A, C, and D), supporting that injury-induced Cavα2δ1 up-regulation at the presynaptic terminals of injured afferents is associated with increased numbers of excitatory synapses in dorsal spinal card. Importantly, these changes were not seen in TSP4 KO mice with SNL (Fig. 6, A, C, and D). These data support that SNL does induce aberrant excitatory synaptogenesis that also requires TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes.
FIGURE 6.
TSP4 ablation blocked SNL-induced excitatory synaptogenesis. Co-immunostaining of Cavα2δ1 with synaptic markers was performed in thin sections of dorsal spinal cord samples from two-week SNL WT or TSP4 KO mice when behavioral hypersensitivity occurred in the injury (Ipsi.) side of SNL WT mice but not TSP4 KO mice (2). A, representative images showing Cavα2δ1 (red) and VGlut2 (green) immunoreactivity and their colocalization (yellow) in superficial dorsal horn. Scale bar = 5 μm for all image panels. Summarized data of total Cavα2δ1 immunoreactivity intensity (B), VGlut2 immunoreactivity surface area (C), and VGlut2+ puncta with (yellow) or without (green) co-localization with Cavα2δ1 immunoreactivity (D) are presented as the means ± S.E. collected from 60 images over three mice in each group. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 compared with non-injury (contra.) side by paired Student's t test.
Discussion
Peripheral nerve injury induces up-regulation of TSP4 and Cavα2δ1 in DRG/spinal cord that contributes to neuropathic pain states through mechanisms that were previously undefined (2, 24, 25, 27, 29, 31). Here, we provided a large body of evidence to support that TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes are required in promoting central sensitization and pain states.
Our data confirm that there is a direct interaction between TSP4 and Cavα2δ1 in rodent spinal cord and in vitro. In addition, blocking or down-regulating Cavα2δ1 can block TSP4-induced pain states and increased mEPSC frequency in spinal cord neurons. Conversely, blocking or genetically deleting TSP4 can block Cavα2δ1 overexpression-induced behavioral hypersensitivity, increased mEPSC frequency, and exaggerated eEPSC in spinal cord neurons. Furthermore, elevated TSP4 induces an increase of spinal excitatory synapses that correlates with heightened pain states, both of which can be normalized by Cavα2δ1 ablation from sensory neurons. Equally, TSP4 ablation blocks injury-induced excitatory synaptogenesis associated with elevated Cavα2δ1 without affecting nerve injury-induced Cavα2δ1 up-regulation in the dorsal horn. Together, these findings support that elevated TSP4 in dorsal spinal cord can induce central sensitization by promoting exaggerated presynaptic excitatory input, excitatory synaptogenesis, and evoked excitability of dorsal horn neurons through activation of TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes.
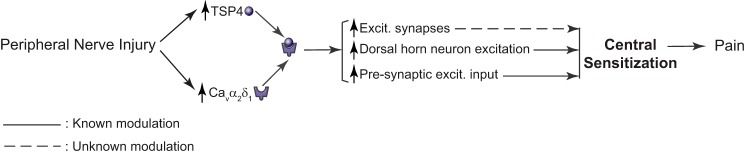
In combination with previous findings from peripheral nerve injury models, our data reveal the importance of TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes in mediating central sensitization and chronic pain states post injury. Although TSP4 is up-regulated within days after peripheral nerve injury in both DRG and dorsal spinal cord (1, 2), there is a significant delay in peak Cavα2δ1 up-regulation in the dorsal horn (weeks) (29), primarily due to time required for initial translocation of elevated Cavα2δ1 from DRG to pre-synaptic central terminals of sensory afferents in the dorsal horn (27, 29). The subsequent interaction of elevated TSP4 with excess pre-synaptic Cavα2δ1 in the dorsal horn then promotes aberrant excitatory synaptogenesis and dorsal horn neuron sensitization to maintain chronic pain states (Fig. 7). Although dorsal horn neurons are heterogeneous and play distinct roles in transmitting modality-specific information (56, 57), our sampling method would not allow us to perform a sensory neuron-type-specific dissection of these changes. Further studies, for example, using Cre-directed ablation of genes of interest from subpopulations of sensory neurons is necessary to provide more deep mechanistic insights about the TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes in mediating modality-specific nociception.
FIGURE 7.
Proposed mechanisms of the TSP4/Cavα2δ1 pathway in central sensitization and neuropathic pain.
Interestingly, although TSP4-induced dorsal horn neuron sensitization and behavioral hypersensitivity is a slow process that requires 4 days to reach the peak effects, gabapentin at a clinically relevant concentration can block these effects within 1 h. Even through we cannot rule out the possibility that a mechanism independent of its binging to Cavα2δ1 mediates the actions of gabapentin in reversing TSP4-induced dorsal spinal cord neuron sensitization and behavioral hyperalgesia, our data support that keeping the TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes in an active state is probably critical for the maintenance of TSP4-induced central sensitization and behavioral hypersensitivity. The fast anti-hyperalgesia actions of gabapentin may derive from interfering with the TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes that are likely key elements of pain genesis even after long term pathological changes, such as aberrant excitatory presynaptic input and synaptogenesis, are established post-TSP4 injection or peripheral nerve injury. This may explain why gabapentinoids exhibit inhibitory effects on sensitized spinal neurons (33, 70, 71) and neuropathic pain states in animal models (24, 25, 72–74) and patients (19–21, 75–82) but do not affect baseline sensory neuron excitability and sensory thresholds in control animals (33, 70, 71, 73, 83) and healthy volunteers (84, 85), who should not have increased expression of Cavα2δ1 and/or TSP4 in the sensory pathway. This may also explain why gabapentin is only effective in some, but not all, neuropathic pain patients with various etiologies (32) as it is less likely that all pain-inducing conditions are associated with increased expression of Cavα2δ1 and/or TSP4.
In summary, even though some details remained elusive, our findings provide a large body of multidimensional evidence to support that activation of the TSP4/Cavα2δ1-dependent processes is required for TSP4-induced central sensitization that leads to pain state development. Blocking this pathway may be a novel strategy for development of target-specific analgesics for chronic pain management.
Author Contributions
J. P. designed, performed, and analyzed experiments of in vitro binding, immunoprecipitation, protein expression, and purification. Y. P. Y. designed, performed, and analyzed experiments of confocal imaging and synaptogenesis. C.-Y. Z. designed, performed, and analyzed experiments of electrophysiology. K.-W. L., E. C., D.-S. K., B. V., X. Z., and N. G. designed, performed, and analyzed experiments of transgenic animal models and behavioral pharmacology. I. V. and E. P.-R. designed and constructed the shRNA-AAV vectors for the behavioral pharmacology experiments. K. S. and O. S. designed, performed, and analyzed experiments of motor functions. D. W. and G. F. designed, generated, and analyzed the conditional knockout mice. C. E. and B. B. provided the TSP4 KO mice and contributed to conception of the study. F. Z. designed and constructed the TSP4 expression vectors, assisted in protein purification, and contributed to conception of the study. Z. D. L. conceived and coordinated the study. Z. D. L., J. P., Y. P. Y., C.-Y. Z., and E. P.-R. contributed to preparation of the figures and writing the paper. Z. D. L., J. P., Y. P. Y., C.-Y. Z., O. S., C. E., and B. B. contributed to editing of the paper. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Diane Lipscombe for the tsA-201 cell lines, Dr. Fan Wang for the Advillin-Cre mice, and Drs. Anatoly Kiyatkin, Ping Deng, Zao Xu, and Joshua Lee for assistance in some initial experiments.
This work was supported, in part, through access to the confocal facility of the Optical Biology Shared Resource of the Cancer Center, Support Grant CA-62203, at the University of California Irvine and by National Institutes of Health Grants NS069524 (to E. P.-R.), NS40135, DE014545, and NS064341 (to Z. D. L.), and DE021847 (to O. S. and Z. D. L).The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
- TSP4
- thrombospondin-4
- DRG
- dorsal root ganglia
- mEPSC
- miniature excitatory post-synaptic current(s)
- eEPSC
- evoked excitatory post-synaptic current(s)
- TG
- transgenic
- CKO
- conditional knock-out
- SNL
- spinal nerve ligation
- AAV
- adeno-associated virus
- scAAV
- self-complementary recombinant AAV
- PWT
- paw withdrawal thresholds
- ANOVA
- analysis of variance
- IP
- immunoprecipitation
- i.t.
- intrathecal.
References
- 1. Pan B., Yu H., Park J., Yu Y. P., Luo Z. D., and Hogan Q. H. (2015) Painful nerve injury up-regulates thrombospondin-4 expression in dorsal root ganglia. J. Neurosci. Res. 93, 443–453 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Kim D. S., Li K. W., Boroujerdi A., Peter Yu Y., Zhou C. Y., Deng P., Park J., Zhang X., Lee J., Corpe M., Sharp K., Steward O., Eroglu C., Barres B., Zaucke F., Xu Z. C., and Luo Z. D. (2012) Thrombospondin-4 contributes to spinal sensitization and neuropathic pain states. J. Neurosci. 32, 8977–8987 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Adams J. C. (2001) Thrombospondins: multifunctional regulators of cell interactions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 17, 25–51 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Bornstein P. (2001) Thrombospondins as matricellular modulators of cell function. J. Clin. Invest. 107, 929–934 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Adams J. C., and Lawler J. (2004) The thrombospondins. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 36, 961–968 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Arber S., and Caroni P. (1995) Thrombospondin-4, an extracellular matrix protein expressed in the developing and adult nervous system promotes neurite outgrowth. J. Cell Biol. 131, 1083–1094 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Xu J., Xiao N., and Xia J. (2010) Thrombospondin 1 accelerates synaptogenesis in hippocampal neurons through neuroligin 1. Nat. Neurosci. 13, 22–24 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Eroglu C., Allen N. J., Susman M. W., O'Rourke N. A., Park C. Y., Ozkan E., Chakraborty C., Mulinyawe S. B., Annis D. S., Huberman A. D., Green E. M., Lawler J., Dolmetsch R., Garcia K. C., Smith S. J., Luo Z. D., Rosenthal A., Mosher D. F., and Barres B. A. (2009) Gabapentin receptor α2δ1 is a neuronal thrombospondin receptor responsible for excitatory CNS synaptogenesis. Cell 139, 380–392 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Qin N., Yagel S., Momplaisir M. L., Codd E. E., and D'Andrea M. R. (2002) Molecular cloning and characterization of the human voltage-gated calcium channel α2δ-4 subunit. Mol. Pharmacol. 62, 485–496 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Klugbauer N., Lacinová L., Marais E., Hobom M., and Hofmann F. (1999) Molecular diversity of the calcium channel α2δ subunit. J. Neurosci. 19, 684–691 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Ellis S. B., Williams M. E., Ways N. R., Brenner R., Sharp A. H., Leung A. T., Campbell K. P., McKenna E., Koch W. J., and Hui A. (1988) Sequence and expression of mRNAs encoding the α1 and α2 subunits of a DHP-sensitive calcium channel. Science 241, 1661–1664 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Bernstein G. M., and Jones O. T. (2007) Kinetics of internalization and degradation of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels: role of the α2/δ subunit. Cell Calcium 41, 27–40 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Davies A., Hendrich J., Van Minh A. T., Wratten J., Douglas L., and Dolphin A. C. (2007) Functional biology of the α2δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 28, 220–228 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Hoppa M. B., Lana B., Margas W., Dolphin A. C., and Ryan T. A. (2012) α2δ expression sets presynaptic calcium channel abundance and release probability. Nature 486, 122–125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Davies A., Kadurin I., Alvarez-Laviada A., Douglas L., Nieto-Rostro M., Bauer C. S., Pratt W. S., and Dolphin A. C. (2010) The α2δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels form GPI-anchored proteins, a posttranslational modification essential for function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 1654–1659 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Klugbauer N., Marais E., and Hofmann F. (2003) Calcium channel α2δ subunits: differential expression, function, and drug binding. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 35, 639–647 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Gee N. S., Brown J. P., Dissanayake V. U., Offord J., Thurlow R., and Woodruff G. N. (1996) The novel anticonvulsant drug, gabapentin (Neurontin), binds to the α2δ subunit of a calcium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 5768–5776 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Marais E., Klugbauer N., and Hofmann F. (2001) Calcium channel α2δ subunits-structure and gabapentin binding. Mol. Pharmacol. 59, 1243–1248 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Backonja M., and Glanzman R. L. (2003) Gabapentin dosing for neuropathic pain: evidence from randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Clin. Ther. 25, 81–104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Dworkin R. H., and Kirkpatrick P. (2005) Pregabalin. Pregabalin. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 4, 455–456 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Guay D. R. (2005) Pregabalin in neuropathic pain: a more “pharmaceutically elegant” gabapentin? Am. J. Geriatr. Pharmacother. 3, 274–287 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Zareba G. (2005) Pregabalin: a new agent for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Drugs Today 41, 509–516 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Hwang J. H., and Yaksh T. L. (1997) Effect of subarachnoid gabapentin on tactile-evoked allodynia in a surgically induced neuropathic pain model in the rat. Reg. Anesth. 22, 249–256 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Luo Z. D., Calcutt N. A., Higuera E. S., Valder C. R., Song Y. H., Svensson C. I., and Myers R. R. (2002) Injury type-specific calcium channel α2δ1 subunit up-regulation in rat neuropathic pain models correlates with antiallodynic effects of gabapentin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 303, 1199–1205 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Luo Z. D., Chaplan S. R., Higuera E. S., Sorkin L. S., Stauderman K. A., Williams M. E., and Yaksh T. L. (2001) Up-regulation of dorsal root ganglion α2δ calcium channel subunit and its correlation with allodynia in spinal nerve-injured rats. J. Neurosci. 21, 1868–1875 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Field M. J., Cox P. J., Stott E., Melrose H., Offord J., Su T. Z., Bramwell S., Corradini L., England S., Winks J., Kinloch R. A., Hendrich J., Dolphin A. C., Webb T., and Williams D. (2006) Identification of the α2δ1 subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels as a molecular target for pain mediating the analgesic actions of pregabalin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 17537–17542 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Bauer C. S., Nieto-Rostro M., Rahman W., Tran-Van-Minh A., Ferron L., Douglas L., Kadurin I., Sri Ranjan Y., Fernandez-Alacid L., Millar N. S., Dickenson A. H., Lujan R., and Dolphin A. C. (2009) The increased trafficking of the calcium channel subunit α2δ1 to presynaptic terminals in neuropathic pain is inhibited by the α2δ ligand pregabalin. J. Neurosci. 29, 4076–4088 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Li K. W., Yu Y. P., Zhou C., Kim D. S., Lin B., Sharp K., Steward O., and Luo Z. D. (2014) Calcium channel α2δ1 proteins mediate trigeminal neuropathic pain states associated with aberrant excitatory synaptogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 7025–7037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Li C. Y., Song Y. H., Higuera E. S., and Luo Z. D. (2004) Spinal dorsal horn calcium channel α2δ1 subunit up-regulation contributes to peripheral nerve injury-induced tactile allodynia. J. Neurosci. 24, 8494–8499 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Zhou C., and Luo Z. D. (2015) Nerve injury-induced calcium channel α2δ1 protein dysregulation leads to increased pre-synaptic excitatory input into deep dorsal horn neurons and neuropathic allodynia. Eur. J. Pain 19, 1267–1276 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Newton R. A., Bingham S., Case P. C., Sanger G. J., and Lawson S. N. (2001) Dorsal root ganglion neurons show increased expression of the calcium channel α2δ1 subunit following partial sciatic nerve injury. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 95, 1–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Gordh T. E., Stubhaug A., Jensen T. S., Arnèr S., Biber B., Boivie J., Mannheimer C., Kalliomäki J., and Kalso E. (2008) Gabapentin in traumatic nerve injury pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over, multi-center study. Pain 138, 255–266 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Zhou C., and Luo Z. D. (2014) Electrophysiological characterization of spinal neuron sensitization by elevated calcium channel α2δ1 subunit protein. Eur. J. Pain 18, 649–658 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Li C. Y., Zhang X. L., Matthews E. A., Li K. W., Kurwa A., Boroujerdi A., Gross J., Gold M. S., Dickenson A. H., Feng G., and Luo Z. D. (2006) Calcium channel α2δ1 subunit mediates spinal hyperexcitability in pain modulation. Pain 125, 20–34 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Hasegawa H., Abbott S., Han B. X., Qi Y., and Wang F. (2007) Analyzing somatosensory axon projections with the sensory neuron-specific Advillin gene. J. Neurosci. 27, 14404–14414 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Södersten F., Ekman S., Schmitz M., Paulsson M., and Zaucke F. (2006) Thrombospondin-4 and cartilage oligomeric matrix protein form heterooligomers in equine tendon. Connect Tissue Res 47, 85–91 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Pan J. Q., and Lipscombe D. (2000) Alternative splicing in the cytoplasmic II-III loop of the N-type Ca channel α 1B subunit: functional differences are β subunit-specific. J. Neurosci. 20, 4769–4775 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Jönsson U., Fägerstam L., Ivarsson B., Johnsson B., Karlsson R., Lundh K., Löfås S., Persson B., Roos H., and Rönnberg I. (1991) Real-time biospecific interaction analysis using surface plasmon resonance and a sensor chip technology. BioTechniques 11, 620–627 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Johnsson B., Löfås S., and Lindquist G. (1991) Immobilization of proteins to a carboxymethyldextran-modified gold surface for biospecific interaction analysis in surface plasmon resonance sensors. Anal. Biochem. 198, 268–277 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Lin Y., McDonough S. I., and Lipscombe D. (2004) Alternative splicing in the voltage-sensing region of N-type CaV2.2 channels modulates channel kinetics. J. Neurophysiol. 92, 2820–2830 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Kim S. H., and Chung J. M. (1992) An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain 50, 355–363 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Rigaud M., Gemes G., Barabas M. E., Chernoff D. I., Abram S. E., Stucky C. L., and Hogan Q. H. (2008) Species and strain differences in rodent sciatic nerve anatomy: implications for studies of neuropathic pain. Pain 136, 188–201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Chang K., Elledge S. J., and Hannon G. J. (2006) Lessons from nature: microRNA-based shRNA libraries. Nat. Methods 3, 707–714 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Chung K. H., Hart C. C., Al-Bassam S., Avery A., Taylor J., Patel P. D., Vojtek A. B., and Turner D. L. (2006) Polycistronic RNA polymerase II expression vectors for RNA interference based on BIC/miR-155. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, e53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. McCarty D. M., Monahan P. E., and Samulski R. J. (2001) Self-complementary recombinant adeno-associated virus (scAAV) vectors promote efficient transduction independently of DNA synthesis. Gene Ther. 8, 1248–1254 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Hioki H., Kameda H., Nakamura H., Okunomiya T., Ohira K., Nakamura K., Kuroda M., Furuta T., and Kaneko T. (2007) Efficient gene transduction of neurons by lentivirus with enhanced neuron-specific promoters. Gene Ther. 14, 872–882 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Ma D., Zerangue N., Lin Y. F., Collins A., Yu M., Jan Y. N., and Jan L. Y. (2001) Role of ER export signals in controlling surface potassium channel numbers. Science 291, 316–319 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Shepard A. R., Jacobson N., and Clark A. F. (2005) Importance of quantitative PCR primer location for short interfering RNA efficacy determination. Anal. Biochem. 344, 287–288 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Boroujerdi A., Zeng J., Sharp K., Kim D., Steward O., and Luo Z. D. (2011) Calcium channel α2δ1 protein up-regulation in dorsal spinal cord mediates spinal cord injury-induced neuropathic pain states. Pain 152, 649–655 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Kim D. S., Figueroa K. W., Li K. W., Boroujerdi A., Yolo T., and Luo Z. D. (2009) Profiling of dynamically changed gene expression in dorsal root ganglia post peripheral nerve injury and a critical role of injury-induced glial fibrillary acidic protein in maintenance of pain behaviors [corrected]. Pain 143, 114–122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Dixon W. J. (1980) Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 20, 441–462 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Hargreaves K., Dubner R., Brown F., Flores C., and Joris J. (1988) A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32, 77–88 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Randall L. O., and Selitto J. J. (1957) A method for measurement of analgesic activity on inflamed tissue. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 111, 409–419 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Basso D. M., Fisher L. C., Anderson A. J., Jakeman L. B., McTigue D. M., and Popovich P. G. (2006) Basso mouse scale for locomotion detects differences in recovery after spinal cord injury in five common mouse strains. J. Neurotrauma 23, 635–659 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Jay S. D., Sharp A. H., Kahl S. D., Vedvick T. S., Harpold M. M., and Campbell K. P. (1991) Structural characterization of the dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel α2-subunit and the associated delta peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 3287–3293 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Graham B. A., Brichta A. M., and Callister R. J. (2007) Moving from an averaged to specific view of spinal cord pain processing circuits. J. Neurophysiol. 98, 1057–1063 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Braz J., Solorzano C., Wang X., and Basbaum A. I. (2014) Transmitting pain and itch messages: a contemporary view of the spinal cord circuits that generate gate control. Neuron 82, 522–536 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Shimoyama M., Shimoyama N., and Hori Y. (2000) Gabapentin affects glutamatergic excitatory neurotransmission in the rat dorsal horn. Pain 85, 405–414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Nguyen D., Deng P., Matthews E. A., Kim D. S., Feng G., Dickenson A. H., Xu Z. C., and Luo Z. D. (2009) Enhanced pre-synaptic glutamate release in deep-dorsal horn contributes to calcium channel α2δ1 protein-mediated spinal sensitization and behavioral hypersensitivity. Mol. Pain 5, 6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Michalski D., Härtig W., Krügel K., Edwards R. H., Böddener M., Böhme L., Pannicke T., Reichenbach A., and Grosche A. (2013) Region-specific expression of vesicular glutamate and GABA transporters under various ischaemic conditions in mouse forebrain and retina. Neuroscience 231, 328–344 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Perederiy J. V., Luikart B. W., Washburn E. K., Schnell E., and Westbrook G. L. (2013) Neural injury alters proliferation and integration of adult-generated neurons in the dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 33, 4754–4767 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Faralli A., Dagna F., Albera A., Bekku Y., Oohashi T., Albera R., Rossi F., and Carulli D. (2015) Modifications of perineuronal nets and remodelling of excitatory and inhibitory afferents during vestibular compensation in the adult mouse. Brain Struct Funct. 10.1007/s00429-015-1095-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Underhill S. M., Wheeler D. S., and Amara S. G. (2015) Differential regulation of two isoforms of the glial glutamate transporter EAAT2 by DLG1 and CaMKII. J. Neurosci. 35, 5260–5270 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Nikitczuk J. S., Patil S. B., Matikainen-Ankney B. A., Scarpa J., Shapiro M. L., Benson D. L., and Huntley G. W. (2014) N-cadherin regulates molecular organization of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic circuits in adult hippocampus in vivo. Hippocampus 24, 943–962 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Ben-Menachem E., Söderfelt B., Hamberger A., Hedner T., and Persson L. I. (1995) Seizure frequency and CSF parameters in a double-blind placebo controlled trial of gabapentin in patients with intractable complex partial seizures. Epilepsy Res. 21, 231–236 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Rose M. A., and Kam P. C. A. (2002) Gabapentin: pharmacology and its use in pain management. Anaesthesia 57, 451–462 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Chang E. Y., Chen X., Sandhu A., Li C. Y., and Luo Z. D. (2013) Spinal 5-HT3 receptors facilitate behavioural hypersensitivity induced by elevated calcium channel α2δ1 protein. Eur. J. Pain 17, 505–513 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Dunkle E. T., Zaucke F., and Clegg D. O. (2007) Thrombospondin-4 and matrix three-dimensionality in axon outgrowth and adhesion in the developing retina. Exp. Eye Res. 84, 707–717 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Park J., Trinh V. N., Sears-Kraxberger I., Li K. W., Steward O., and Luo Z. D. (2016) Synaptic ultrastructure changes in trigeminocervical complex posttrigeminal nerve injury. J. Comp. Neurol. 524, 309–322 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Stanfa L. C., Singh L., Williams R. G., and Dickenson A. H. (1997) Gabapentin, ineffective in normal rats, markedly reduces C-fibre evoked responses after inflammation. Neuroreport 8, 587–590 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Patel M. K., Gonzalez M. I., Bramwell S., Pinnock R. D., and Lee K. (2000) Gabapentin inhibits excitatory synaptic transmission in the hyperalgesic spinal cord. Br. J. Pharmacol. 130, 1731–1734 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Xiao W., Boroujerdi A., Bennett G. J., and Luo Z. D. (2007) Chemotherapy-evoked painful peripheral neuropathy: Analgesic effects of gabapentin and effects on expression of the α2δ type-1 calcium channel subunit. Neuroscience 144, 714–720 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Hunter J. C., Gogas K. R., Hedley L. R., Jacobson L. O., Kassotakis L., Thompson J., and Fontana D. J. (1997) The effect of novel anti-epileptic drugs in rat experimental models of acute and chronic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 324, 153–160 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Abdi S., Lee D. H., and Chung J. M. (1998) The anti-allodynic effects of amitriptyline, gabapentin, and lidocaine in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Anesth. Analg. 87, 1360–1366 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. To T. P., Lim T. C., Hill S. T., Frauman A. G., Cooper N., Kirsa S. W., and Brown D. J. (2002) Gabapentin for neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 40, 282–285 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Stacey B. R., Dworkin R. H., Murphy K., Sharma U., Emir B., and Griesing T. (2008) Pregabalin in the treatment of refractory neuropathic pain: results of a 15-month open-label trial. Pain Med. 9, 1202–1208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Levendoglu F., Ogün C. O., Ozerbil O, Ogün T. C., Ugurlu H. (2004) Gabapentin is a first line drug for the treatment of neuropathic pain in spinal cord injury. Spine 29, 743–751 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Backonja M., Beydoun A., Edwards K. R., Schwartz S. L., Fonseca V., Hes M., LaMoreaux L., and Garofalo E. (1998) Gabapentin for the symptomatic treatment of painful neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial (see comments). JAMA 280, 1831–1836 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Ahn S. H., Park H. W., Lee B. S., Moon H. W., Jang S. H., Sakong J., and Bae J. H. (2003) Gabapentin effect on neuropathic pain compared among patients with spinal cord injury and different durations of symptoms. Spine 28, 341–346 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Dworkin R. H., O'Connor A. B., Backonja M., Farrar J. T., Finnerup N. B., Jensen T. S., Kalso E. A., Loeser J. D., Miaskowski C., Nurmikko T. J., Portenoy R. K., Rice A. S., Stacey B. R., Treede R. D., Turk D. C., and Wallace M. S. (2007) Pharmacologic management of neuropathic pain: evidence-based recommendations. Pain 132, 237–251 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Rosenberg J. M., Harrell C., Ristic H., Werner R. A., and de Rosayro A. M. (1997) The effect of gabapentin on neuropathic pain. Clin. J. Pain 13, 251–255 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Rosner H., Rubin L., and Kestenbaum A. (1996) Gabapentin adjunctive therapy in neuropathic pain states. Clin. J. Pain 12, 56–58 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Field M. J., Oles R. J., Lewis A. S., McCleary S., Hughes J., and Singh L. (1997) Gabapentin (neurontin) and S-(+)-3-isobutylgaba represent a novel class of selective antihyperalgesic agents. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 121, 1513–1522 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Werner M. U., Perkins F. M., Holte K., Pedersen J. L., and Kehlet H. (2001) Effects of gabapentin in acute inflammatory pain in humans. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 26, 322–328 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Gustorff B., Hoechtl K., Sycha T., Felouzis E., Lehr S., and Kress H. G. (2004) The effects of remifentanil and gabapentin on hyperalgesia in a new extended inflammatory skin pain model in healthy volunteers. Anesth. Analg. 98, 401–407 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]