Abstract
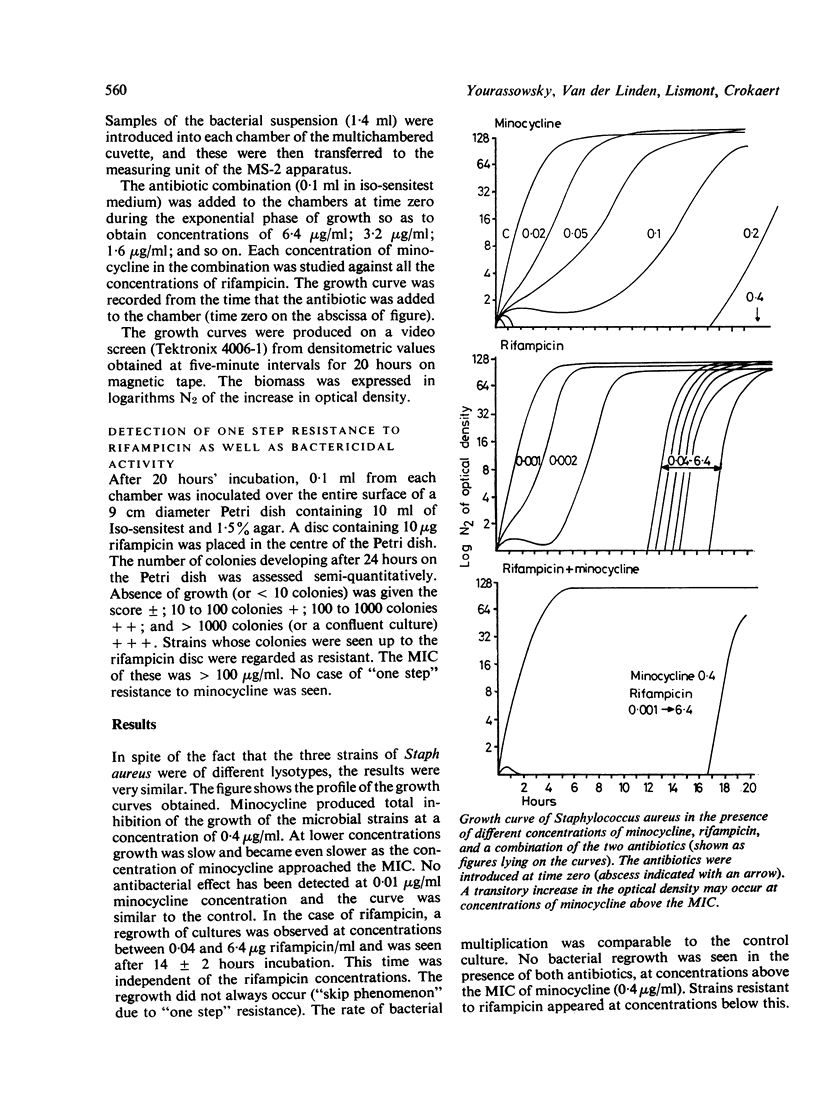
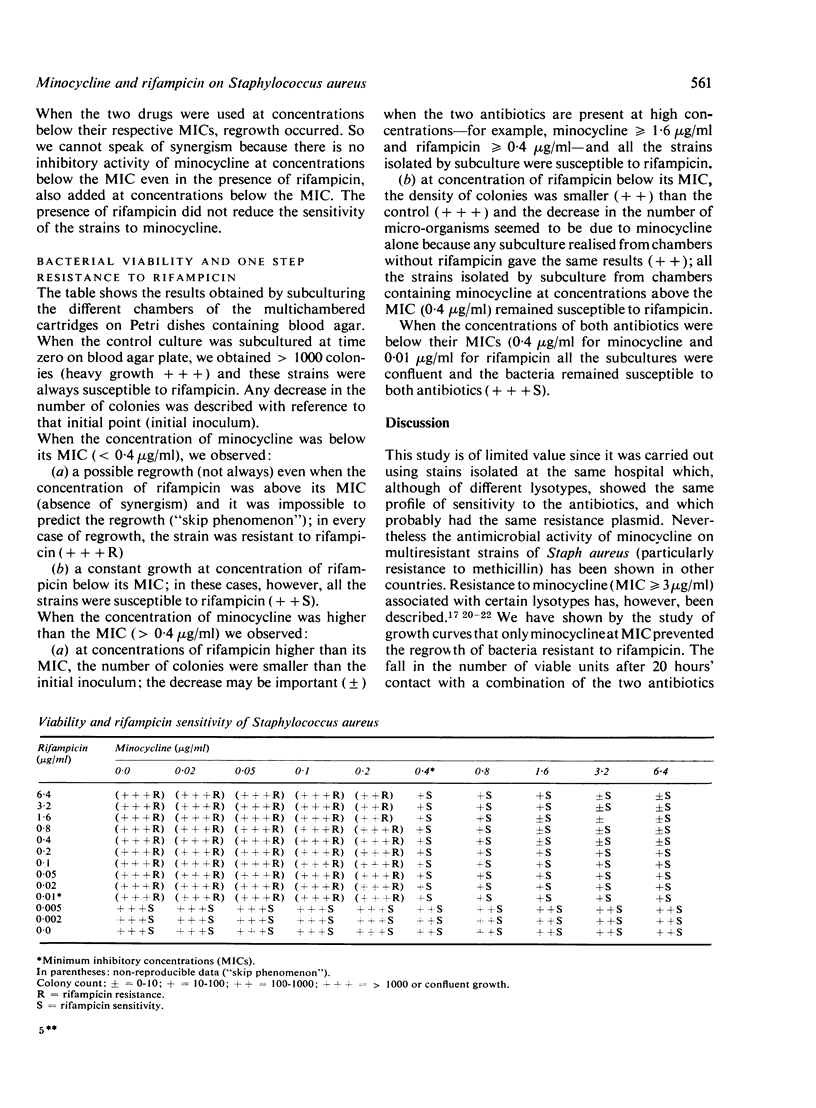
Methicillin- and gentamicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus may remain sensitive to minocycline and to rifampicin. A study of growth curves has shown that at inhibitory concentrations (0·4 μg/ml), minocycline prevents the development of mutants resistant to rifampicin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. C. Minocycline. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Oct;85(4):482–487. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-4-482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas E., Turck M. Laboratory and clinical evaluation of rifampicin. Am J Med Sci. 1968 Oct;256(4):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banic S., Stropnik Z. Synergistic effects of oleandomycin and rifamycin SV in experimental staphylococcal septicaemia in rabbits. Infection. 1974;2(3):160–161. doi: 10.1007/BF01642237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Brown R. B., Shanks C., Gamble C., Weinstein L. Relation between lipophilicity and pharmacological behavior of minocycline, doxycycline, tetracycline, and oxytetracycline in dogs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Dec;8(6):713–720. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.6.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bint A. J., George R. H., Healing D. E., Wise R., Davies M. An outbreak of infection caused by a gentamicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Feb;30(2):165–167. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogden R. N., Speight T. M., Avery G. S. Minocycline: A review of its antibacterial and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1975;9(4):251–291. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197509040-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell W., Wilks M., Drasar F. A. The action of trimethoprim and rifampicin in combination against Gram-negative rods resistant to gentamicin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Sep;3(5):459–462. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.5.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., Andrew J. Rifampicin plus nalidixic acid: a rational combination for the treatment of urinary infection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Nov;4(6):533–538. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.6.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. J. Antagonistic interaction of rifampicin and trimethoprim. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Jul;4(4):315–327. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.4.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Interaction between rifampicin and trimethoprim. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Jan;5(1):113–115. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.1.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kensit J. G., Shanson D. C. Gentamicin resistance in methicillin-sensitive and resistant Staphyococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Sep;2(3):311–312. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerry D. W., Hamilton-Miller J. M., Brumfitt W. Trimethoprim and rifampicin: in vitro activities separately and in combination. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1975 Dec;1(4):417–427. doi: 10.1093/jac/1.4.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M., Brandt D., Wood H. Bacteriologic studies of rifampin, a new semisynthetic antibiotic. J Infect Dis. 1969 Feb;119(2):132–137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.2.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo M. C., Mandell G. L. Treatment of experimental staphylococcal infection with rifampin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Sep;2(3):195–200. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.3.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Interaction of intraleukocytic bacteria and antibiotics. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1673–1679. doi: 10.1172/JCI107348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L., Vest T. K. Killing of intraleukocytic Staphylococcus aureus by rifampin: in-vitro and in-vivo studies. J Infect Dis. 1972 May;125(5):486–490. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.5.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minuth J. N., Holmes T. M., Musher D. M. Activity of tetracycline, doxycycline, and minocycline against methicillin-susceptible and -resistant staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Oct;6(4):411–414. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.4.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peard M. C., Fleck D. G., Garrod L. P., Waterworth P. M. Combined rifampicin and erythromycin for bacterial endocarditis. Br Med J. 1970 Nov 14;4(5732):410–411. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5732.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phair J. P., Carleton J. Susceptibility of Staphylococci to Minocycline In Vitro: Identification of Group III Bacteriophage Types by Characteristic Inhibition of Growth. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):669–671. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.669-671.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phair J. P., Hartman R. E., Carleton J. Evaluation of the efficacy of minocycline therapy for staphylococcal soft-tissue infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):551–553. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porthouse A., Brown D. F., Smith R. G., Rogers T. Gentamicin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1976 Jan 3;1(7949):20–21. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92912-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. M., Reeve E. C. Analysis of the resistance mediated by several R-factors to tetracycline and minocycline. Genet Res. 1972 Oct;20(2):239–252. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300013744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S., Francois W., Ruby C. L. Minocycline resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: effect on phage susceptibility. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):600–613. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon K. P., Phillips I. Letter: Gentamicin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1976 Sep 11;2(7985):580–581. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91835-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanson D. C., Kensit J. C., Duke R. Outbreak of hospital infection with a strain of Staphylococcus aureus resistant to gentamicin and methicillin. Lancet. 1976 Dec 18;2(7999):1347–1348. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91986-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speller D. C., Raghunath D., Stephens M., Viant A. C., Reeves D. S., Wilkinson P. J., Broughall J. M., Holt H. A. Epidemic infection by a gentamicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in three hospitals. Lancet. 1976 Feb 28;1(7957):464–466. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Kleber I. In vitro additive effect of polymxin B and rifampin against Serratia marcesen. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jun;7(6):874–876. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.6.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon C. U., Lin M. Y., Sheagren J. N. In vitro activity of rifampin alone and in combination with nafcillin and Vancomycin against pathogenic strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):759–761. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urena M. T., Barasoain I., Espinosa M., Garcia E., Portoles A. Evaluation of different antibiotic actions combined with rifampicin. In vitro synergism against Pseudomonas and Proteus. Chemotherapy. 1975;21(2):82–89. doi: 10.1159/000221850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel L., Nathan C., Sweeney H. M., Kabins S. A., Cohen S. Infections due to gentamicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain in a nursery for neonatal infants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):466–472. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



