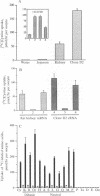
Abstract
The transport of amino acids across cell membranes is believed to be mediated by integral membrane proteins with distinct substrate specificities. Using expression cloning in Xenopus oocytes and assaying for the uptake of 14C-labeled cystine, we isolated a 2.3-kilobase cDNA (D2) from a rat kidney library. D2 is expressed specifically in kidney and intestine and induces the transport of both neutral and cationic amino acids. The deduced amino acid sequence predicts a 78-kDa protein with a single transmembrane domain, a structure not typical of the known membrane transport proteins, which generally have multiple membrane-spanning regions. The putative extracellular region is highly similar to the 4F2 heavy-chain cell surface antigen and to a family of alpha-glucosidases, which raises the possibility that D2 encodes a transport activator or regulatory subunit.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoshima H., Tomita K., Sugio S. Expression of amino acid transport systems in Xenopus oocytes injected with mRNA of rat small intestine and kidney. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Aug 15;265(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90372-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertran J., Werner A., Moore M. L., Stange G., Markovich D., Biber J., Testar X., Zorzano A., Palacin M., Murer H. Expression cloning of a cDNA from rabbit kidney cortex that induces a single transport system for cystine and dibasic and neutral amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5601–5605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertran J., Werner A., Stange G., Markovich D., Biber J., Testar X., Zorzano A., Palacin M., Murer H. Expression of Na(+)-independent amino acid transport in Xenopus laevis oocytes by injection of rabbit kidney cortex mRNA. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 1;281(Pt 3):717–723. doi: 10.1042/bj2810717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biber J., Stange G., Stieger B., Murer H. Transport of L-cystine by rat renal brush border membrane vesicles. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Mar;396(4):335–341. doi: 10.1007/BF01063939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B., Wright C. V., De Robertis E. M., Cho K. W. Organizer-specific homeobox genes in Xenopus laevis embryos. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):194–196. doi: 10.1126/science.1677215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buisson G., Duée E., Haser R., Payan F. Three dimensional structure of porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase at 2.9 A resolution. Role of calcium in structure and activity. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3909–3916. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02731.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campa M. J., Kilberg M. S. Characterization of neutral and cationic amino acid transport in Xenopus oocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Dec;141(3):645–652. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041410324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENT C. E., ROSE G. A. Aminoacid metabolism in cystinuria. Q J Med. 1951 Jul;20(79):205–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J. W., Hwang S. M., Segal S. Transport interactions of cystine and dibasic amino acids in isolated rat renal tubules. Metabolism. 1980 Jan;29(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guastella J., Nelson N., Nelson H., Czyzyk L., Keynan S., Miedel M. C., Davidson N., Lester H. A., Kanner B. I. Cloning and expression of a rat brain GABA transporter. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.1975955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Coady M. J., Ikeda T. S., Wright E. M. Expression cloning and cDNA sequencing of the Na+/glucose co-transporter. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):379–381. doi: 10.1038/330379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A. High resolution preparative gel electrophoresis of DNA fragments and plasmid DNA using a continuous elution apparatus. Anal Biochem. 1986 Dec;159(2):280–286. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Ikeda T., Coady M., Gundersen C. B., Wright E. M. Expression of size-selected mRNA encoding the intestinal Na/glucose cotransporter in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2634–2637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Mendlein J., Lee H. S., Wright E. M. Biosynthesis of the cloned intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporter. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 7;1064(2):360–364. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90323-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Fukusumi S., Ohshima T., Beppu T. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of two additional amylase genes of a strictly anaerobic thermophile, Dictyoglomus thermophilum, and their nucleotide sequences with extremely low guanine-plus-cytosine contents. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 15;176(2):243–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii T., Nakayama K., Sato H., Miura K., Yamada M., Yamada K., Sugita Y., Bannai S. Expression of the mouse macrophage cystine transporter in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Aug 15;289(1):71–75. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90443-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. A., Blackmer K., Racioppi J. V. A salivary gland-specific, maltase-like gene of the vector mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Gene. 1989 Jan 30;75(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. W., Closs E. I., Albritton L. M., Cunningham J. M. Transport of cationic amino acids by the mouse ecotropic retrovirus receptor. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):725–728. doi: 10.1038/352725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Structural features in eukaryotic mRNAs that modulate the initiation of translation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19867–19870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara P. D., Rea C. T., Segal S. Expression of rat jejunal cystine carrier in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):986–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mircheff A. K., Kippen I., Hirayama B., Wright E. M. Delineation of sodium-stimulated amino acid transport pathways in rabbit kidney brush border vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1982;64(1-2):113–122. doi: 10.1007/BF01870773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacholczyk T., Blakely R. D., Amara S. G. Expression cloning of a cocaine- and antidepressant-sensitive human noradrenaline transporter. Nature. 1991 Mar 28;350(6316):350–354. doi: 10.1038/350350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmacek M. S., Karpinski B. A., Gottesdiener K. M., Thompson C. B., Leiden J. M. Structure, expression and regulation of the murine 4F2 heavy chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1915–1931. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quackenbush E., Clabby M., Gottesdiener K. M., Barbosa J., Jones N. H., Strominger J. L., Speck S., Leiden J. M. Molecular cloning of complementary DNAs encoding the heavy chain of the human 4F2 cell-surface antigen: a type II membrane glycoprotein involved in normal and neoplastic cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6526–6530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. E., Durant J. L., Holland J. M. Intestinal absorption and renal extraction of cystine and cysteine in cystinuria. N Engl J Med. 1965 Dec 2;273(23):1239–1245. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196512022732303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal S., McNamara P. D., Pepe L. M. Transport interaction of cystine and dibasic amino acids in renal brush border vesicles. Science. 1977 Jul 8;197(4299):169–171. doi: 10.1126/science.877548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakarjian M. P., Carchman R. A. Alteration of human granulocyte functional responses by menadione. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Nov 15;283(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90604-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Leonard J. P., Gilbert M. M., Lester H. A., Davidson N. Rat brain expresses a heterogeneous family of calcium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3391–3395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Davidson N. Two gene families clustered in a small region of the Drosophila genome. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):101–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson B. Regional distant sequence homology between amylases, alpha-glucosidases and transglucanosylases. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 28;230(1-2):72–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80644-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takumi T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Cloning of a membrane protein that induces a slow voltage-gated potassium current. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1042–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.3194754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira S., Di Grandi S., Kühn L. C. Primary structure of the human 4F2 antigen heavy chain predicts a transmembrane protein with a cytoplasmic NH2 terminus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9574–9580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Winkle L. J., Campione A. L., Gorman J. M. Na+-independent transport of basic and zwitterionic amino acids in mouse blastocysts by a shared system and by processes which distinguish between these substrates. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3150–3163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Kavanaugh M. P., North R. A., Kabat D. Cell-surface receptor for ecotropic murine retroviruses is a basic amino-acid transporter. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):729–731. doi: 10.1038/352729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe K., Kitamura K., Iha H., Suzuki Y. Primary structure of the oligo-1,6-glucosidase of Bacillus cereus ATCC7064 deduced from the nucleotide sequence of the cloned gene. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Sep 24;192(3):609–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]