Abstract
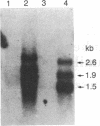
cDNA encoding human monocyte/neutrophil elastase inhibitor (EI), a M(r) approximately 42,000 protein with serpin-like functional properties, has been sequenced. The 1316-base-pair sequence was obtained from overlapping clones and amplified DNA from libraries of monocyte-like and neutrophil-like cells. Hybridization with EI cDNA identified three EI mRNA species of 1.5, 1.9, and 2.6 kilobases in U937 monocyte-like cells and no hybridizing mRNA in lymphoblastoid cells lacking detectable EI. The cDNA open reading frame encodes a 379-amino acid protein, of which 167 residues were confirmed by tryptic peptides. Although EI may function extracellularly as well as intracellularly, its deduced sequence lacks a typical cleavable N-terminal signal sequence. Sequence analysis established that EI is a member of the serpin superfamily. EI has greatest homology (50.1% identity of amino acids) with plasminogen activator inhibitor 2, also a monocyte protein, and ovalbumin and gene Y, which were previously grouped as an ancient branch of the serpin superfamily. The extent of EI identity with the functionally related serpin alpha 1 antitrypsin is only 30.1%. Sequence alignment indicates that the reactive center P1 residue is Cys-344, consistent with abrogation of elastase inhibitory activity by iodoacetamide and making EI a naturally occurring Cys-serpin. The cleavable bond, Cys-Met, suggests an oxidation-sensitive molecule capable of inhibiting more than one serine protease. Oxidation sensitivity would limit the place of action of EI to the immediate vicinity of carrier cells. The molecular structure will help clarify the likely role of EI in regulating protease action and preventing tissue damage by phagocytic cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antalis T. M., Clark M. A., Barnes T., Lehrbach P. R., Devine P. L., Schevzov G., Goss N. H., Stephens R. W., Tolstoshev P. Cloning and expression of a cDNA coding for a human monocyte-derived plasminogen activator inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):985–989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin D., Wohlwend A., Schleuning W. D., Kruithof E. K., Vassalli J. D. Facultative polypeptide translocation allows a single mRNA to encode the secreted and cytosolic forms of plasminogen activators inhibitor 2. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3287–3294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondin J., Rosenberg R., Janoff A. An inhibitor in human lung macrophages active against human neutrophil elastase. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 Sep;106(3):477–479. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.106.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock S. C., Wion K. L., Vehar G. A., Lawn R. M. Cloning and expression of the cDNA for human antithrombin III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8113–8125. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campanelli D., Melchior M., Fu Y., Nakata M., Shuman H., Nathan C., Gabay J. E. Cloning of cDNA for proteinase 3: a serine protease, antibiotic, and autoantigen from human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1709–1715. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Jeppsson J. O., Laurell C. B., Brennan S. O., Owen M. C., Vaughan L., Boswell D. R. Structure and variation of human alpha 1-antitrypsin. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):329–334. doi: 10.1038/298329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Pemberton P. A., Boswell D. R. The serpins: evolution and adaptation in a family of protease inhibitors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:527–535. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig R., Muraskowsky R., Kloepfer C., Mandel J. L. The ovalbumin gene family: complete sequence and structure of the Y gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 24;10(14):4363–4382. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.14.4363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Carrell R. W. Implications of the three-dimensional structure of alpha 1-antitrypsin for structure and function of serpins. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):8951–8966. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt L. T., Dayhoff M. O. A surprising new protein superfamily containing ovalbumin, antithrombin-III, and alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jul 31;95(2):864–871. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90867-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A., Blondin J. Inhibition of the elastase-like esterase in human leukocyte granules by human leukocyte cell sap. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Apr;136(4):1050–1053. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A. Elastase in tissue injury. Annu Rev Med. 1985;36:207–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.36.020185.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junger W., Hallström S., Redl H., Schlag G. Preliminary data on isolation of an elastase-like proteinase and its inhibitor from ovine neutrophil granulocytes. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 May;369 (Suppl):63–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao R. C., Wehner N. G., Skubitz K. M., Gray B. H., Hoidal J. R. Proteinase 3. A distinct human polymorphonuclear leukocyte proteinase that produces emphysema in hamsters. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):1963–1973. doi: 10.1172/JCI113816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loebermann H., Tokuoka R., Deisenhofer J., Huber R. Human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Crystal structure analysis of two crystal modifications, molecular model and preliminary analysis of the implications for function. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 15;177(3):531–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRae B., Nakajima K., Travis J., Powers J. C. Studies on reactivity of human leukocyte elastase, cathepsin G, and porcine pancreatic elastase toward peptides including sequences related to the reactive site of alpha 1-protease inhibitor (alpha 1-antitrypsin). Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 19;19(17):3973–3978. doi: 10.1021/bi00558a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McReynolds L., O'Malley B. W., Nisbet A. D., Fothergill J. E., Givol D., Fields S., Robertson M., Brownlee G. G. Sequence of chicken ovalbumin mRNA. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):723–728. doi: 10.1038/273723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moremen K. W. Isolation of a rat liver Golgi mannosidase II clone by mixed oligonucleotide-primed amplification of cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5276–5280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Gagnon J., Walsh K. A. Ovalbumin: a secreted protein without a transient hydrophobic leader sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):94–98. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkos C. A., Dinauer M. C., Walker L. E., Allen R. A., Jesaitis A. J., Orkin S. H. Primary structure and unique expression of the 22-kilodalton light chain of human neutrophil cytochrome b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potempa J., Dubin A., Watorek W., Travis J. An elastase inhibitor from equine leukocyte cytosol belongs to the serpin superfamily. Further characterization and amino acid sequence of the reactive center. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7364–7369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E. A fast-acting elastase inhibitor in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2142–2155. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Lewandrowski K. Two proteinase inhibitors associated with peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3251–3257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Nixon J. C., Rose R. M. Elastase inhibitor. Characterization of the human elastase inhibitor molecule associated with monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):1071–1086. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H. F., Corrette S. E., Tenen D. G., Ackerman S. J. Rapid cDNA library screening using the polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques. 1991 Jan;10(1):53–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvesen G., Farley D., Shuman J., Przybyla A., Reilly C., Travis J. Molecular cloning of human cathepsin G: structural similarity to mast cell and cytotoxic T lymphocyte proteinases. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2289–2293. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samia J. A., Alexander S. J., Horton K. W., Auron P. E., Byers M. G., Shows T. B., Webb A. C. Chromosomal organization and localization of the human urokinase inhibitor gene: perfect structural conservation with ovalbumin. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90461-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleuning W. D., Medcalf R. L., Hession C., Rothenbühler R., Shaw A., Kruithof E. K. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 2: regulation of gene transcription during phorbol ester-mediated differentiation of U-937 human histiocytic lymphoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4564–4567. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemüller U., Arnhold M., Fritz H., Wiedenmann K., Machleidt W., Heinzel R., Appelhans H., Gassen H. G., Lottspeich F. The acid-stable proteinase inhibitor of human mucous secretions (HUSI-I, antileukoprotease). Complete amino acid sequence as revealed by protein and cDNA sequencing and structural homology to whey proteins and Red Sea turtle proteinase inhibitor. FEBS Lett. 1986 Apr 7;199(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Nukiwa T., Basset P., Crystal R. G. Myelomonocytic cell lineage expression of the neutrophil elastase gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2543–2547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi K. H., Swank R. T. Inhibitors of elastase and cathepsin G in Chédiak-Higashi (beige) neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7431–7436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. M., Nauseef W. M., Iyer S. S., Peterson M. W., Stone P. J., Clark R. A. A cytosolic inhibitor of human neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Dec;50(6):568–579. doi: 10.1002/jlb.50.6.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Ohlsson K. Isolation, properties, and complete amino acid sequence of human secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor, a potent inhibitor of leukocyte elastase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6692–6696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb A. C., Collins K. L., Snyder S. E., Alexander S. J., Rosenwasser L. J., Eddy R. L., Shows T. B., Auron P. E. Human monocyte Arg-Serpin cDNA. Sequence, chromosomal assignment, and homology to plasminogen activator-inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):77–94. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedow O., Schröder J. M., Gregory H., Young J. A., Christophers E. Elafin: an elastase-specific inhibitor of human skin. Purification, characterization, and complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14791–14795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye R. D., Ahern S. M., Le Beau M. M., Lebo R. V., Sadler J. E. Structure of the gene for human plasminogen activator inhibitor-2. The nearest mammalian homologue of chicken ovalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5495–5502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye R. D., Wun T. C., Sadler J. E. Mammalian protein secretion without signal peptide removal. Biosynthesis of plasminogen activator inhibitor-2 in U-937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4869–4875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]