Abstract
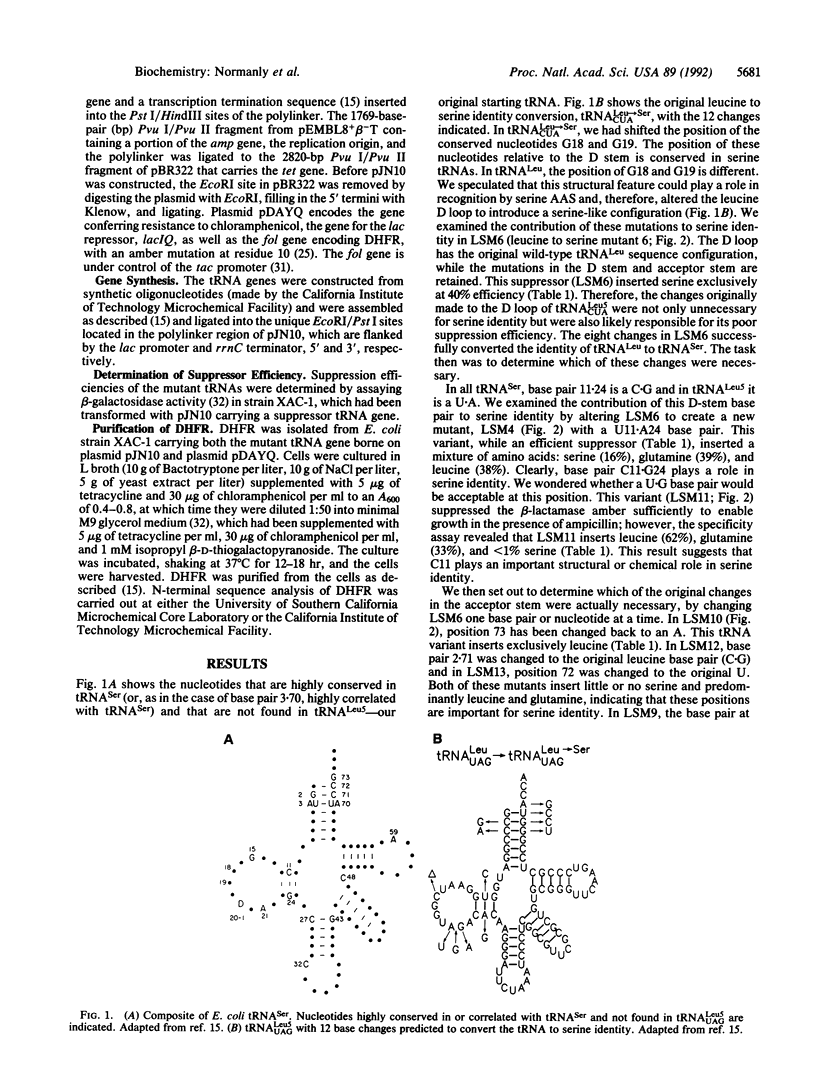
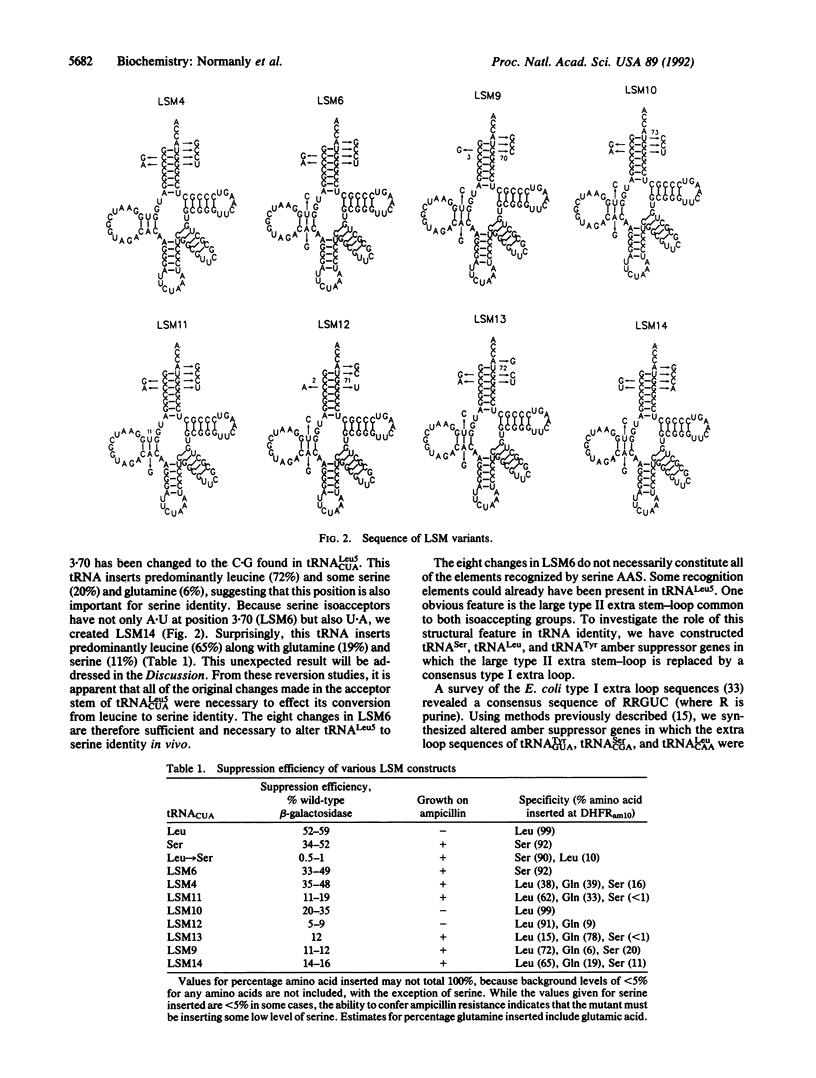
Each aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase must functionally distinguish its cognate tRNAs from all others. We have determined the minimum number of changes required to transform a leucine amber suppressor tRNA to serine identity. Eight changes are required. These are located in the acceptor stem and in the D stem.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann E., Brosius J., Ptashne M. Vectors bearing a hybrid trp-lac promoter useful for regulated expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Hooper M. L., Smith J. D. Amino acid acceptor stem of E. coli suppressor tRNA tyr is a site of synthetase recognition. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 29;244(139):261–264. doi: 10.1038/newbio244261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattapadhyay R., Pelka H., Schulman L. H. Initiation of in vivo protein synthesis with non-methionine amino acids. Biochemistry. 1990 May 8;29(18):4263–4268. doi: 10.1021/bi00470a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusack S., Berthet-Colominas C., Härtlein M., Nassar N., Leberman R. A second class of synthetase structure revealed by X-ray analysis of Escherichia coli seryl-tRNA synthetase at 2.5 A. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):249–255. doi: 10.1038/347249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dock-Bregeon A. C., Garcia A., Giegé R., Moras D. The contacts of yeast tRNA(Ser) with seryl-tRNA synthetase studied by footprinting experiments. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Mar 10;188(2):283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards H., Trézéguet V., Schimmel P. An Escherichia coli tyrosine transfer RNA is a leucine-specific transfer RNA in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1153–1156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysen A., Celis J. E. Mischarging single and double mutants of Escherichia coli sup3 tyrosine transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar;83(3):333–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giegé R., Florentz C., Garcia A., Grosjean H., Perret V., Puglisi J., Théobald-Dietrich A., Ebel J. P. Exploring the aminoacylation function of transfer RNA by macromolecular engineering approaches. Involvement of conformational features in the charging process of yeast tRNA(Asp). Biochimie. 1990 Jun-Jul;72(6-7):453–461. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90069-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himeno H., Hasegawa T., Ueda T., Watanabe K., Shimizu M. Conversion of aminoacylation specificity from tRNA(Tyr) to tRNA(Ser) in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6815–6819. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper M. L., Russell R. L., Smith J. D. Mischarging in mutant tyrosine transfer RNAs. FEBS Lett. 1972 Apr 15;22(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou Y. M., Schimmel P. A simple structural feature is a major determinant of the identity of a transfer RNA. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):140–145. doi: 10.1038/333140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inokuchi H., Celis J. E., Smith J. D. Letter: Mutant tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acids of Escherichia coli: construction by recombination of a double mutant A1G82 chargeable with glutamine. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 5;85(1):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISELEV L. L., FROLOVA L. Iu. "KONTAKTNYE UCHASTKI" TRANSPORTNYKH RNK PRI SPETSIFICHESKOM VZAIMODE ISTVI I S AMINOATSIL-RNK-SINTETAZAMI. Biokhimiia. 1964 Nov-Dec;29:1177–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleina L. G., Masson J. M., Normanly J., Abelson J., Miller J. H. Construction of Escherichia coli amber suppressor tRNA genes. II. Synthesis of additional tRNA genes and improvement of suppressor efficiency. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):705–717. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80257-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Foss K. Changing the acceptor identity of a transfer RNA by altering nucleotides in a "variable pocket". Science. 1988 Sep 30;241(4874):1804–1807. doi: 10.1126/science.2459773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Foss K. Changing the identity of a tRNA by introducing a G-U wobble pair near the 3' acceptor end. Science. 1988 May 6;240(4853):793–796. doi: 10.1126/science.2452483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Foss K., Jenkins R. A., Schneider J. Nucleotides that determine Escherichia coli tRNA(Arg) and tRNA(Lys) acceptor identities revealed by analyses of mutant opal and amber suppressor tRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9260–9264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Foss K. Nucleotides that contribute to the identity of Escherichia coli tRNA(Phe). J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):697–709. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90551-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normanly J., Abelson J. tRNA identity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:1029–1049. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.005121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normanly J., Kleina L. G., Masson J. M., Abelson J., Miller J. H. Construction of Escherichia coli amber suppressor tRNA genes. III. Determination of tRNA specificity. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):719–726. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80258-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normanly J., Masson J. M., Kleina L. G., Abelson J., Miller J. H. Construction of two Escherichia coli amber suppressor genes: tRNAPheCUA and tRNACysCUA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6548–6552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normanly J., Ogden R. C., Horvath S. J., Abelson J. Changing the identity of a transfer RNA. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):213–219. doi: 10.1038/321213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallanck L., Schulman L. H. Anticodon-dependent aminoacylation of a noncognate tRNA with isoleucine, valine, and phenylalanine in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery L. A., Yarus M. Systematic alterations in the anticodon arm make tRNA(Glu)-Suoc a more efficient suppressor. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1499–1506. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. J., Söll D. Discrimination between glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase and seryl-tRNA synthetase involves nucleotides in the acceptor helix of tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6627–6631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rould M. A., Perona J. J., Steitz T. A. Structural basis of anticodon loop recognition by glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):213–218. doi: 10.1038/352213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rould M. A., Perona J. J., Söll D., Steitz T. A. Structure of E. coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Gln) and ATP at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1135–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.2479982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. R., DiRenzo A. B., Behlen L. S., Uhlenbeck O. C. Nucleotides in yeast tRNAPhe required for the specific recognition by its cognate synthetase. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1363–1366. doi: 10.1126/science.2646717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. R., DiRenzo A. B., Behlen L. S., Uhlenbeck O. C. Role of the tertiary nucleotides in the interaction of yeast phenylalanine tRNA with its cognate synthetase. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 13;29(10):2523–2532. doi: 10.1021/bi00462a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D., Leberman R., Eckstein F. Interaction of Escherichia coli tRNA(Ser) with its cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase as determined by footprinting with phosphorothioate-containing tRNA transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6132–6136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H., Goddard J. P. Loss of methionine acceptor activity resulting from a base change in the anticodon of Escherichia coli formylmethionine transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1341–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H., Pelka H. Anticodon switching changes the identity of methionine and valine transfer RNAs. Science. 1988 Nov 4;242(4879):765–768. doi: 10.1126/science.3055296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H. Recognition of tRNAs by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;41:23–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimura Y., Aono H., Ozeki H., Sarabhai A., Lamfrom H., Abelson J. Mutant tyrosine tRNA of altered amino acid specificity. FEBS Lett. 1972 Apr 15;22(1):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., Celis J. E. Mutant tyrosine transfer RNA that can be charged with glutamine. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 16;243(124):66–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Hartmann T., Weber J., Blank J., Zeidler R. Compilation of tRNA sequences and sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17 (Suppl):r1–172. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.suppl.r1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M., Folk W. R., Berg P., Soll L. A single mutational modification of a tryptophan-specific transfer RNA permits aminoacylation by glutamine and translation of the codon UAG. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):245–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



