It was an error in the structure of dopamine o-quinone published in the commentary on Evaluation of models of Parkinson's disease since the benzene ring contained an extra double bound between the carbonyls. The actual structure of dopamine o-quinone is the correct structure.
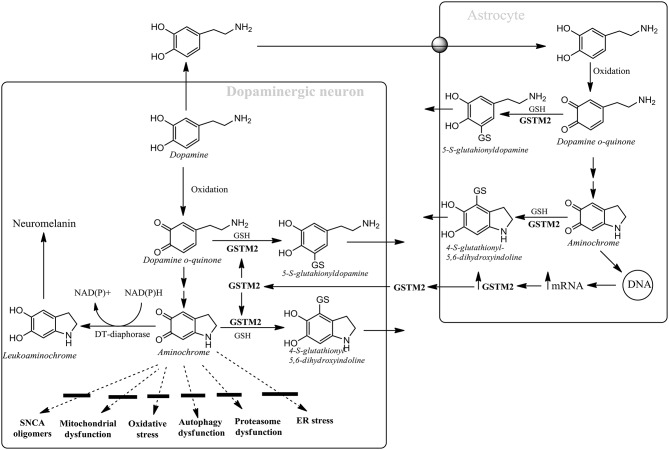
Figure 1.
Astrocytes protect dopaminergic neurons against aminochrome neurotoxicity. Astrocytes secrete GSTM2 which is internalized by dopaminergic neurons in order to increase their protection against aminochrome. Dopamine oxidation to neuromelanin is a harmless pathway due to the presence of DT-diaphorase and GSTM2 that prevent aminochrome-dependent neurotoxicity by inhibiting the formation of alpha-synuclein (SNCA) neurotoxic oligomers, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, autophagy, and proteasome dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Author contributions
All authors listed, have made substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
Funding
Supported by University of Chile (ENL014/14).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.