Abstract
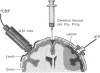
Increased intracranial pressure was induced in anaesthetized dogs by application of liquid nitrogen to the dura mater. Intracranial pressure and cerebral blood flow were measured, together with arterial blood pressure and arterial and cerebral venous blood gases.
Carbon dioxide was administered intermittently to test the responsiveness of the cerebral circulation, and hyperbaric oxygen was delivered at intervals in a walk-in hyperbaric chamber, pressurized to two atmospheres absolute.
Hyperbaric oxygen caused a 30% reduction of intracranial pressure and a 19% reduction of cerebral blood flow in the absence of changes in arterial PCO2 or blood pressure, but only as long as administration of carbon dioxide caused an increase in both intracranial pressure and cerebral blood flow. When carbon dioxide failed to influence intracranial pressure or cerebral blood flow then hyperbaric oxygen had no effect. This unresponsive state was reached at high levels of intracranial pressure.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTELS H., HARMS H. Sauerstoffdissoziationskurven des Blutes von Säugetieren (Mensch, Kaninchen, Meerschweinchen, Hund, Katze, Schwein, Rind und Schaf. Pflugers Arch. 1959;268(4):334–365. doi: 10.1007/BF00380734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLASEN R. A., BROWN D. V. L., LEAVITT S., HASS G. M. The production by liquid nitrogen of acute closed lesions. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1953 May;96(5):605–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coe J. E., Hayes T. M. Treatment of experimental brain injury by hyperbaric oxygenation. Preliminary report. Am Surg. 1966 Jul;32(7):493–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASS H. I., HARPER A. M. The measurement of the partition coefficient of krypton between brain cortex and blood by a double isotope method. Phys Med Biol. 1962 Dec;7:335–339. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/7/3/306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARPER A. M., GLASS H. I., GLOVER M. M. Measurement of blood flow in the cerebral cortex of dogs, by the clearance of krypton-85. Scott Med J. 1961 Jan;6:12–17. doi: 10.1177/003693306100600103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoedt-Rasmussen K., Skinhoj E., Paulson O., Ewald J., Bjerrum J. K., Fahrenkrug A., Lassen N. A. Regional cerebral blood flow in acute apoplexy. The "luxury perfusion syndrome" of brain tissue. Arch Neurol. 1967 Sep;17(3):271–281. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470270049007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollin S. A., Espinosa O. E., Sukoff M. H., Jacobson J. H., 2nd The effect of hyperbaric oxygenation on cerebrospinal fluid oxygen. J Neurosurg. 1968 Sep;29(3):229–235. doi: 10.3171/jns.1968.29.3.0229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON I., HARPER A. M., MCDOWALL D. G. THE EFFECTS OF OXYGEN UNDER PRESSURE ON CEREBRAL BLOOD-FLOW AND CEREBRAL VENOUS OXYGEN TENSION. Lancet. 1963 Sep 14;2(7307):549–549. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92644-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON I., LAWSON D. D. THE EFFECT OF HYPERBARIC OXYGEN ON EXPERIMENTAL CEREBRAL INFARCTION IN THE DOG. WITH PRELIMINARY CORRELATIONS OF CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AT 2 ATMOSPHERES OF OXYGEN. J Neurosurg. 1963 Oct;20:849–859. doi: 10.3171/jns.1963.20.10.0849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLATZO I., PIRAUX A., LASKOWSKI E. J. The relationship between edema, blood-brain-barrier and tissue elements in a local brain injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1958 Oct;17(4):548–564. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195810000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kety S. S., Schmidt C. F. THE EFFECTS OF ALTERED ARTERIAL TENSIONS OF CARBON DIOXIDE AND OXYGEN ON CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND CEREBRAL OXYGEN CONSUMPTION OF NORMAL YOUNG MEN. J Clin Invest. 1948 Jul;27(4):484–492. doi: 10.1172/JCI101995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMBERTSEN C. J., DOUGH R. H., COOPER D. Y., EMMEL G. L., LOESCHCKE H. H., SCHMIDT C. F. Oxygen toxicity; effects in man of oxygen inhalation at 1 and 3.5 atmospheres upon blood gas transport, cerebral circulation and cerebral metabolism. J Appl Physiol. 1953 Mar;5(9):471–486. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1953.5.9.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGFITT T. W., KASSELL N. F., WEINSTEIN J. D. CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW WITH INTRACRANIAL HYPERTENSION. Neurology. 1965 Aug;15:761–773. doi: 10.1212/wnl.15.8.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGFITT T. W., WEINSTEIN J. D., KASSELL N. F. CEREBRAL VASOMOTOR PARALYSIS PRODUCED BY INTRACRANIAL HYPERTENSION. Neurology. 1965 Jul;15:622–641. doi: 10.1212/wnl.15.7.622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSEN N. A., INGVAR D. H. The blood flow of the cerebral cortex determined by radioactive krypton. Experientia. 1961 Jan 15;17:42–43. doi: 10.1007/BF02157946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall W. J., Jackson J. L., Langfitt T. W. Brain swelling caused by trauma and arterial hypertension. Hemodynamic aspects. Arch Neurol. 1969 Nov;21(5):545–553. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480170117012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowall D. G., Ledingham I. M., Tindal S. Alveolar-arterial gradients for oxygen at 1, 2, and 3 atmospheres absolute. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Mar;24(3):324–329. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.24.3.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. D., Fitch W., Cameron B. D. Regional cerebral blood flow measurement in the presence of raised intracranial pressure: a comparison between thermal and krypton-85 beta clearance. J Surg Res. 1969 Jul;9(7):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(69)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. D., Fitch W., Ledingham I. M., Jennett W. B. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen on experimentally increased intracranial pressure. J Neurosurg. 1970 Sep;33(3):287–296. doi: 10.3171/jns.1970.33.3.0287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody R. A., Mead C. O., Ruamsuke S., Mullan S. Therapeutic value of oxygen at normal and hyperbaric pressure in experimental head injury. J Neurosurg. 1970 Jan;32(1):51–54. doi: 10.3171/jns.1970.32.1.0051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pálvölgyi R. Regional cerebral blood flow in patients with intracranial tumors. J Neurosurg. 1969 Aug;31(2):149–163. doi: 10.3171/jns.1969.31.2.0149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSOMOFF H. L. Experimental brain injury during hypothermia. J Neurosurg. 1959 Mar;16(2):177–187. doi: 10.3171/jns.1959.16.2.0177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowan J. O., Harper A. M., Miller J. D., Tedeschi G. M., Jennett W. B. Relationship between volume flow and velocity in the cerebral circulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Dec;33(6):733–738. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.6.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinghaus J. W. Blood gas calculator. J Appl Physiol. 1966 May;21(3):1108–1116. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.3.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloway M., Nadel W., Albin M. S., White R. J. The effect of hyperventilation on subsequent cerebral infarction. Anesthesiology. 1968 Sep-Oct;29(5):975–980. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196809000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukoff M. H., Hollin S. A., Espinosa O. E., Jacobson J. H., 2nd The protective effect of hyperbaric oxygenation in experimental cerebral edema. J Neurosurg. 1968 Sep;29(3):236–241. doi: 10.3171/jns.1968.29.3.0236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L. EQUATIONS FOR MEASURING BLOOD FLOW BY EXTERNAL MONITORING OF RADIOISOTOPES. Circ Res. 1965 Apr;16:309–321. doi: 10.1161/01.res.16.4.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]