Abstract
The hammerhead ribozyme, as engineered by J. Haseloff and W. L. Gerlach [(1988) Nature (London) 334, 585-591], is an RNA molecule containing two regions of conserved nucleotides, a double helix, called helix II, which connects the two conserved regions, and flanking arms of variable sequence, which hybridize the ribozyme to its specific target. Here we show that this ribozyme may be reduced in size and still retain cleavage activity by replacing helix II with just a few nucleotides that cannot form Watson-Crick base pairs between themselves. Furthermore, the nucleotides replacing helix II and the nucleotides in the flanking arms may be substituted with DNA, and this small, DNA-containing ribozyme is fully as active as the original, full-size ribozyme. Cleavage activity of the minimized ribozyme depends on the number and sequence of the few nucleotides that replace helix II; optimal activity, thus far, is achieved by four or five deoxyribopyrimidines. The minimized ribozyme, or "minizyme," is active as a monomer, as shown by its nearly constant activity over a concentration range varying 25,000-fold, by the mobility of the minizyme-substrate complex in nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels as compared with other nucleic acid molecules of known size, and by other observations. These minizymes provide an excellent model system for studying the structure and mechanism of catalytic RNA; they might also be useful in a variety of biological applications.
Full text
PDF
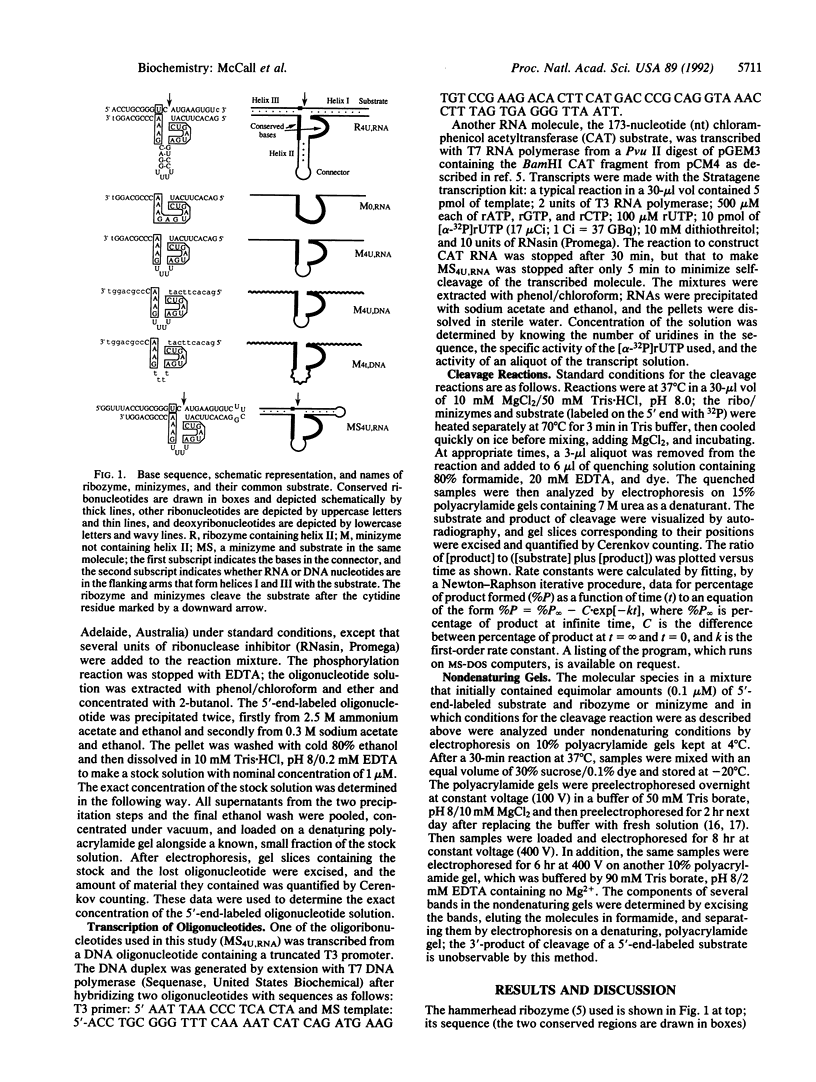
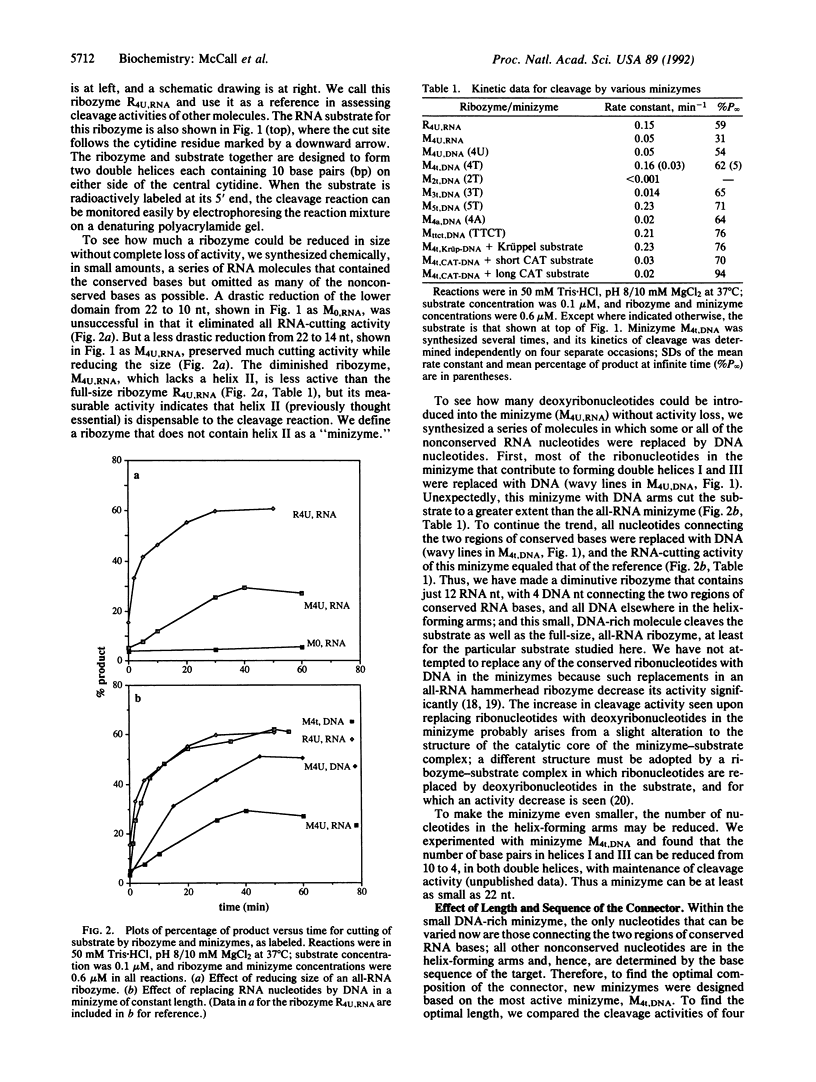
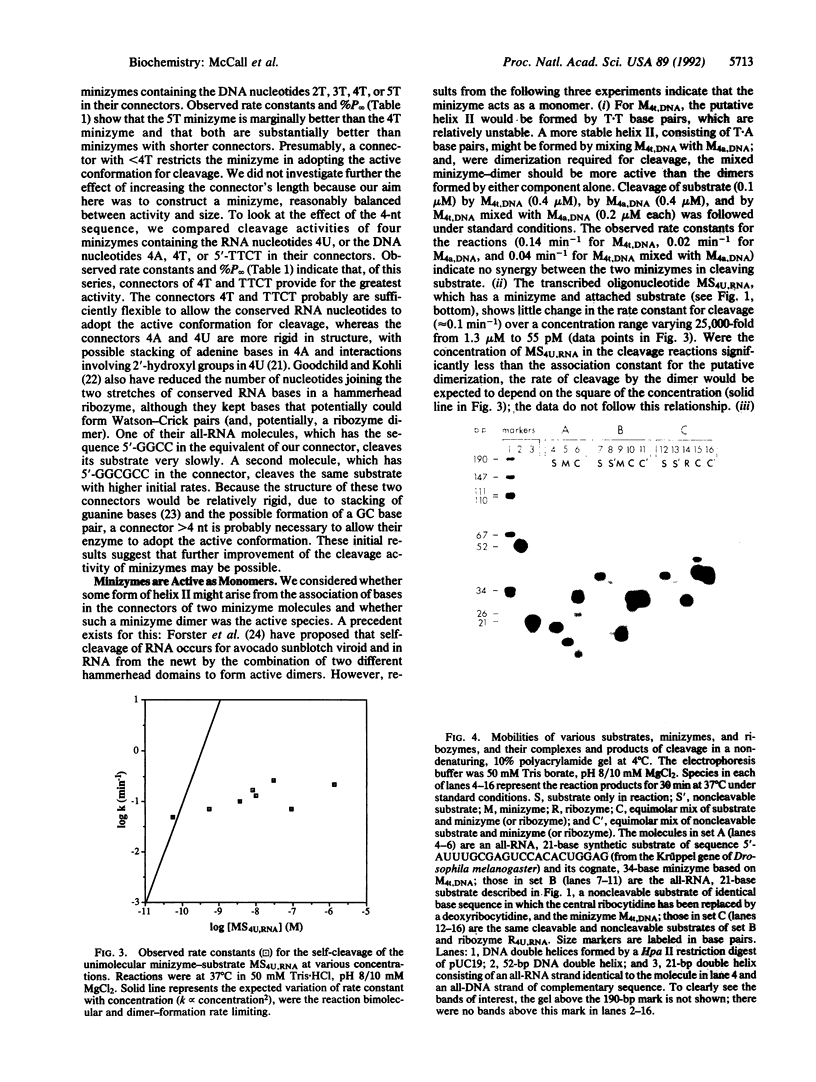

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calladine C. R., Collis C. M., Drew H. R., Mott M. R. A study of electrophoretic mobility of DNA in agarose and polyacrylamide gels. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 5;221(3):981–1005. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80187-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron F. H., Jennings P. A. Specific gene suppression by engineered ribozymes in monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9139–9143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Bass B. L. Biological catalysis by RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:599–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Birnstiel M. L. Ribozyme mediated destruction of RNA in vivo. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3861–3866. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., Wang J. C. On the sequence determinants and flexibility of the kinetoplast DNA fragment with abnormal gel electrophoretic mobilities. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Davies C., Sheldon C. C., Jeffries A. C., Symons R. H. Self-cleaving viroid and newt RNAs may only be active as dimers. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):265–267. doi: 10.1038/334265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Symons R. H. Self-cleavage of plus and minus RNAs of a virusoid and a structural model for the active sites. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90562-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Symons R. H. Self-cleavage of virusoid RNA is performed by the proposed 55-nucleotide active site. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90657-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gast F. U., Hagerman P. J. Electrophoretic and hydrodynamic properties of duplex ribonucleic acid molecules transcribed in vitro: evidence that A-tracts do not generate curvature in RNA. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 30;30(17):4268–4277. doi: 10.1021/bi00231a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild J., Kohli V. Ribozymes that cleave an RNA sequence from human immunodeficiency virus: the effect of flanking sequence on rate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Feb 1;284(2):386–391. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90313-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseloff J., Gerlach W. L. Simple RNA enzymes with new and highly specific endoribonuclease activities. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):585–591. doi: 10.1038/334585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries A. C., Symons R. H. A catalytic 13-mer ribozyme. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1371–1377. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi M., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E. Cleavage of specific sites of RNA by designed ribozymes. FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 7;239(2):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80935-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perreault J. P., Labuda D., Usman N., Yang J. H., Cedergren R. Relationship between 2'-hydroxyls and magnesium binding in the hammerhead RNA domain: a model for ribozyme catalysis. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 23;30(16):4020–4025. doi: 10.1021/bi00230a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perreault J. P., Wu T. F., Cousineau B., Ogilvie K. K., Cedergren R. Mixed deoxyribo- and ribo-oligonucleotides with catalytic activity. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):565–567. doi: 10.1038/344565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prody G. A., Bakos J. T., Buzayan J. M., Schneider I. R., Bruening G. Autolytic processing of dimeric plant virus satellite RNA. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1577–1580. doi: 10.1126/science.231.4745.1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffner D. E., Stormo G. D., Uhlenbeck O. C. Sequence requirements of the hammerhead RNA self-cleavage reaction. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10695–10702. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Cantin E. M., Chang P. S., Zaia J. A., Ladne P. A., Stephens D. A., Rossi J. J. Ribozymes as potential anti-HIV-1 therapeutic agents. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1222–1225. doi: 10.1126/science.2107573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena S. K., Ackerman E. J. Ribozymes correctly cleave a model substrate and endogenous RNA in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17106–17109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C. A small catalytic oligoribonucleotide. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):596–600. doi: 10.1038/328596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. H., Perreault J. P., Labuda D., Usman N., Cedergren R. Mixed DNA/RNA polymers are cleaved by the hammerhead ribozyme. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 25;29(51):11156–11160. doi: 10.1021/bi00503a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]