Abstract
Fragile X tremor ataxia syndrome (FXTAS) is a late-onset disorder manifesting in a proportion of FMR1 premutation individuals (PM: 55-199 CGG triplet expansions). FXTAS is associated with elevated levels of FMR1 mRNA which are toxic. In this study, relationships between neurocognitive and intra-step gait variability measures with mRNA levels, measured in blood samples, were examined in 35 PM and 35 matched control females. The real-time PCR assays measured FMR1 mRNA, and previously used internal control genes: β-Glucuronidase (GUS), Succinate Dehydrogenase 1 (SDHA) and Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4A (EI4A2). Although there was significant correlation of gait variability with FMR1 mRNA levels (p = 0.004) when normalized to GUS (FMR1/GUS), this was lost when FMR1 was normalized to SDHA and EI4A2 (2IC). In contrast, GUS mRNA level normalized to 2IC showed a strong correlation with gait variability measures (p < 0.007), working memory (p = 0.001) and verbal intelligence scores (p = 0.008). PM specific changes in GUS mRNA were not mediated by FMR1 mRNA. These results raise interest in the role of GUS in PM related disorders and emphasise the importance of using appropriate internal control genes, which have no significant association with PM phenotype, to normalize FMR1 mRNA levels.
A number of overlapping mechanisms have been proposed to cause Fragile X-spectrum disorders (FXSD)1 involving CGG trinucleotide expansion in the 5′UTR of FMR12. These include reduced FMR1 protein expression (FMRP), elevated levels of non-coding RNA (FMR4, FMR5, FMR6)3,4, mitochondrial dysfunction5, CGG repeat-associated non-AUG-initiation6, and gain-of-function RNA toxicity7. The “gain of function” toxicity8 has been one of the more prominent hypotheses used to explain FXSD, where two to eight fold increase in FMR1 mRNA expression and in levels of its antisense transcript ASFMR1 have been positively correlated with CGG triplet expansion size2. Specifically, RNA from the expanded allele is thought to bind to and sequester mRNA binding proteins from their pre-determined role, leading to dysregulation of multiple neuronal pathways. The primary CGG triplet expansion class associated with this toxicity is known as FMR1 premutation (PM), ranging between 55 and 199 CGG triplet repeats. This allele class is usually unmethylated within the FMR1 promoter, is common in the general population (~1 in 150 females and ~1 in 450 males)9 and had been associated with two important clinical conditions. Up to 40% of PM males and ~8–16% of PM females develop fragile X-tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS) - a neurodegenerative tremor and ataxia, late-onset adult disorder10. An additional ~20% of PM females also develop fragile X-primary ovarian insufficiency (FXPOI), characterised by premature ovarian failure prior to the age of 4011.
Furthermore, FMR1 mRNA silencing and loss of FMRP have been linked to hypermethylated FMR1 full mutation expansions (FM: >200 CGG triplet repeats), leading to fragile X syndrome - a common neurodevelopmental disorder found ~1 in 4000 in the general population12. Up to 40% of all FM individuals have been reported to be either mosaic for methylation and/or CGG size13. Because these mosaic individuals have some cells that carry unmethylated FM or PM expansion that over-express FMR1 and other cells that have methylated FM alleles and under-express FMR1, they are also susceptible to disorders associated with FMR1 mRNA “gain of function” toxicity and FMRP deficiency. In addition, rare cases of males with completely unmethylated FM alleles have been reported that do not have typical FXS (as they express FMRP), but develop a FXTAS phenotype associated with the FMR1 mRNA toxicity14. Therefore, accurate quantification of FMR1 mRNA levels is of importance for studies of both fragile X syndrome and of other Fragile X-associated Disorders in PM and FM individuals.
Since increase in CGG triplet expansion has been associated with an increase in FMR1 mRNA toxicity, mitochondrial dysfunction and elevated apoptosis8, it is not unreasonable to postulate that CGG triplet repeat size has an impact on the expression profile of many genes. This is consistent with genome wide gene expression analysis showing that multiple pathways are affected by a PM expansion, including glycoprotein biosynthesis, which is mediated through the β-glucuronidase (GUS) pathway15. An additional interest in investigating GUS mRNA expression in this context is that previous PM studies using reverse transcription real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) have used this as a single gene for normalisation of FMR1 mRNA expression (described in Supplementary Table S1).
We postulated that normalising FMR1 mRNA to GUS mRNA levels in blood should impact the correlation that is understood to exist between FMR1 mRNA levels and PM specific phenotypes, as opposed to the correlation with FMR1 mRNA expression when normalised to that of other internal control genes. This study, therefore, examined relationships of FMR1 and GUS mRNA levels in blood samples (with reverse transcription real-time quantitative RT-PCR [RT-qPCR] normalized to different internal controls) and gait stepping and working memory measures previously described to reflect PM-specific neurocognitive phenotypes16.
Methods
Participants
The data for molecular, working memory and gait analyses was collected from 35 PM females and 35 age- and IQ-matched control females previously16,17, with different components re-analysed to answer questions specific to this study. Groups were matched on height, BMI, age and Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI) Full Scale IQ score (see details in Table 1). Participants were English speaking with no history of epilepsy or of a serious head injury and had normal (or corrected) vision and hearing, and no sign of colour blindness or intellectual disability (as assessed using the WASI Full Scale IQ score <70). The FXTAS Rating Scale was used to screen all participants for features of FXTAS - that is, tremor, ataxia or parkinsonism - or any other neuromotor disorder. A total of 6 PM and 3 control females in this study were taking anti-depressants at the time of testing. One female PM was additionally taking anti-psychotic medication and one other was taking both anti-psychotic and stimulant medication. We did not find any pattern of medication or dietary supplement use by PM or control participants in the first or third quartiles for GUS mRNA level (see details in Supplementary Tables S3 and S4). The PM cohort included 28 different pedigrees, including four families of two full blood related sisters, one with three blood related sisters and one with two half-sisters (paternal inheritance). All study participants provided signed informed consent and the study procedures were consistent with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Southern Health Ethics Committee (project 10147B).
Table 1. Comparisons between control and PM groups using generalised estimating equations.
| Control (N = 35) |
PM (N = 35) |
p-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Characteristics | |||||
| Age | 41.11 | 8.636 | 41.14 | 8.335 | 0.989 |
| BMI | 27.28 | 6.421 | 27.61 | 6.338 | 0.761* |
| Height | 1.652 | 0.086 | 1.646 | 0.072 | 0.739 |
| IQ test | |||||
| FSIQ | 111.9 | 9.541 | 110.3 | 10.936 | 0.506 |
| PIQ | 113.9 | 11.15 | 110.9 | 11.136 | 0.260 |
| VIQ | 108.1 | 11.36 | 106.6 | 13.900 | 0.619 |
| Molecular | |||||
| AR | 0.575 | 0.060 | 0.577 | 0.053 | 0.963 |
| FMR1/3IC | 1.129 | 0.285 | 1.655 | 0.540 | 10−9** |
| FMR1/2IC | 1.422 | 0.316 | 2.197 | 0.751 | 10−11** |
| FMR1/GUS | 0.867 | 0.259 | 1.190 | 0.398 | 10−5* |
| GUS/2IC | 1.919 | 0.429 | 2.033 | 0.480 | 0.318 |
| SDHA/EIF4A2 | 1.342 | 0.207 | 1.371 | 0.315 | 0.803 |
| FMR1/3IC/AR | 1.978 | 0.514 | 2.811 | 0.923 | 0.964** |
| FMR1/2IC/AR | 2.478 | 0.528 | 3.758 | 1.329 | 10−6 |
| FMR1/GUS/AR | 1.523 | 0.477 | 2.009 | 0.664 | 0.013 |
| GUS/2IC/AR | 3.346 | 0.687 | 3.613 | 1.012 | 0.219 |
| SDHA/EIF4A2/AR | 2.375 | 0.504 | 2.358 | 0.608 | 0.938 |
| Working memory | |||||
| LNS | 13.89 | 3.206 | 12.60 | 3.474 | 0.112 |
| Gait step time variability | |||||
| DTC Finger tapping | 0.425 | 26.56 | 4.298 | 38.76 | 0.601 |
| DTC Counting by 3 | 23.36 | 48.00 | 40.30 | 70.16 | 0.203 |
| DTC Counting by 7 | 51.52 | 97.65 | 66.42 | 99.64 | 0.468 |
| Gait step length variability | |||||
| DTC Finger tapping | −2.681 | 32.17 | 7.216 | 41.25 | 0.259 |
| DTC Counting by 3 | 1.905 | 33.32 | 23.51 | 54.49 | 0.036 |
| DTC Counting by 7 | 27.50 | 58.34 | 38.09 | 51.92 | 0.453 |
Note: Mean and SD were presented for raw data; p-values computed using *log and **reciprocal transformed. Significant values (p < 0.05) in bold.
AR = FMR1 activation ratio; BMI = Body Mass Index; DTC = Dual Task Cost; EIF4A2 = Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-2 mRNA; FSIQ = WASI Full Scale IQ; LNS = Letter number sequencing working memory test; PIQ = WASI Performance IQ; SDHA = succinate dehydrogenase complex, subunit A, flavoprotein (Fp) mRNA; VIQ = WASI Verbal IQ.
Molecular analyses
CGG sizing and methylation analysis, used to determine activation ratio (AR) were performed on DNA extracted from whole blood. The CGG sizing was performed using the Asuragen AmplideX™ FMR1 PCR Kit (Asuragen: Austin, TX, USA)18. PCR products were assessed via capillary electrophoresis on an Applied Biosytems 3130 Genetic Analyzer with electropherogram analysis conducted using GeneMapper software (Applied Biosystems; Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Methylation sensitive Southern Blot was used to determine AR by targeting a NruI restriction site within the FMR1 CpG island, as previously described19. RNA was extracted from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) isolated from whole blood using Ficoll gradient separation8. For the FMR1 mRNA analysis, RT-qPCR on a ViiA™ 7 System (Life Technologies, Global) was used to quantify FMR1-5′, FMR1-3′, GUS, and two internal control genes, EIF4A2 and SDHA, as previously described20. The samples were quantified in arbitrary units in relationship to the standard curves performed on each plate. The mean FMR1 mRNA levels were normalized to: (i) GUS alone (FMR1/GUS); (ii) mean of EIF4A2, and SDHA mRNA levels (FMR1/2IC); (iii) mean of GUS, EIF4A2, and SDHA mRNA levels (FMR1/3IC). Other outputs included GUS mRNA levels normalized to mean of EIF4A2 and SDHA mRNA levels (GUS/2IC), and EIF4A2 mRNA normalized to SDHA mRNA levels (EIF4A2/SDHA). EIF4A2 and SDHA were chosen as alternative internal control genes as these were the most stably expressed of the gene panel tested using the geNorm approach in another cohort (Supplementary Figure S1).
RNA from each sample was reverse-transcribed in two separate cDNA reactions, with each cDNA analyzed in two separate RT-PCR reactions. The mean of the four arbitrary unit outputs was used as a summary measure for mRNA expression for each participant. Of the 70 blood samples, there were no FMR1 mRNA results obtained for two PM females and five control females because there was either insufficient RNA extracted or because the results failed the 5′ and 3′ FMR1 mRNA quality control step21.
Gait and working memory analysis
Spatiotemporal gait characteristics were assessed by a 593 cm long × 89 cm wide instrumented walkway (GAITRite, CIR Systems Inc., Clifton, NJ, USA), as previously described16. The GAITRite is a valid and reliable method for assessing spatial and temporal parameters of gait22. It has also demonstrated high validity when compared to the ‘gold standard’ 3-dimensional motion analysis system23. In accordance with published recommendations, participants traversed the GAITrite walkway across six walking trials per condition (>30 steps per condition), with minimal interruption between walks24. Participants initiated and ended walking 1.5 m before and after the mat to reduce the effects of acceleration and deceleration during each walk. A dual-task paradigm that pairs walking with concurrent performance of a cognitive task was employed. This approach induces capacity interference and is commonly used to investigate subtle changes in motor control associated with vulnerabilities in subcortical structures of the brain that would normally be compensated for by higher cortical structures25. Gait was assessed under three different dual-task walking conditions: (1) counting backward aloud by 3′s; (2) counting backward aloud by 7′s; (3) finger tapping (i.e., repeating sequence of thumb to finger tapping, moving in the direction from second to fifth digit). Participants were instructed to walk at their preferred speed during all conditions, to not prioritise one task over the other and to keep walking even if they were struggling to identify new word items. The GAITRite computer software recorded average step length and step time for each walk. Step-to-step variability for both variables were calculated as coefficient of variation1. Dual-task costs (henceforth referred to as DTCs) were defined as a change in step length variability and step time variability from baseline to dual-task condition. DTC was determined using the following published formula: DTC = [(dual-task score – single-task score)/single-task score] × 100 where a higher value indicated an increase in variability from single to dual-task condition, and a lower value indicated a decrease in variability26. The Letter-Number Sequencing (LNS) subtest from the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS-IV) was selected to assess central executive working memory performance.
Statistical analyses
For comparison between control and PM groups the distribution of the tested variable was first checked for normal distribution using Shapiro-Wilk test statistics at 5% significance level. All variables that did not satisfy this distribution were transformed using either log or reciprocal function. Generalised estimating (GEE) method was then for the inter-group comparison, taking into account correlation within a family in the PM cohort. Relationship between each molecular variable (outcome) and age or BMI (predictor) in the controls data was assessed using robust regression. This method down weighted effects of outliers that can distort the estimates of regression coefficients. The same method was also used to examine relationships between WASI Full Scale IQ, LNS, DTC step time and length variability (outcome) with each molecular variable. For PM molecular data we initially screened for unusual observations by visual inspection of the scatter plot for outliers, and then performed least square regression and checked observation for high influence and leverage27. The outliers were then excluded from analysis using the GEE estimation method. We used p-value < 0.05 as significant level. All analyses were performed using STATA software (version 13.1, StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA).
Results
GUS mRNA changes in blood are significantly correlated with gait step length variability in PM females
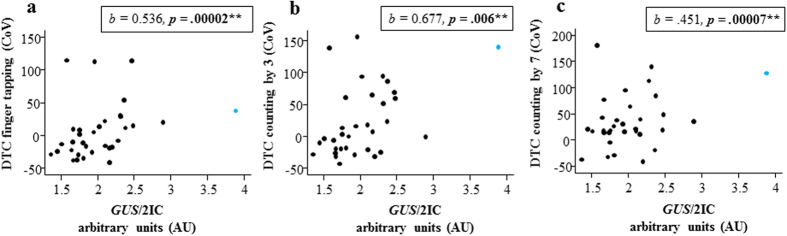
In PM females, GUS/2IC was significantly correlated with WASI verbal intelligence (p = 0.008), working memory (p = 0.001) and step length variability DTC for all three conditions: finger tapping (p = 0.00002), counting backwards by 3′s (p = 0.006) and 7′s (p = 0.00007) (Fig. 1, Tables 2 and 3). The ratio between the mRNA levels of two internal control genes used to normalize GUS (SDHA/EIF4A2) was also significantly correlated with working memory (p = 0.006) in the PM group (Table 3), indicating that the correlation between working memory and GUS/2IC is also affected by changes in expression of the chosen internal control genes SDHA and EIF4A2. However, there were no correlations between the ratio of these internal control genes (SDHA/EIF4A2) and step length variability (Tables 2 and 3), which indicated that GUS/2IC correlations with the step length variability measure were in fact only due to changes in GUS mRNA, and not the internal control genes.
Figure 1. Relationships between GUS mRNA normalized to mean expression of EIF4A2 and SHDA (GUS/2IC) and different step length variability dual-task cost (DTC) measures in PM females.
Scatter plot between GUS/2IC and the gait step length variability DTC for (a) the finger tapping condition, (b) the count by 3′s condition and (c) the count by 7′s condition. Note: The PM female found to be an outlier for the above relationships is indicated in blue.
Table 2. PM group p-values indicating the strength of correlation between step length variability and molecular parameters using regression method estimated by generalised estimating equations.
| Step length variability DTC Finger tapping |
Step length variability DTC Counting by 3 |
Step length variability DTC Counting by 7 |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | s.e | p-value | b | s.e | p-value | b | s.e | p-value | |
| FMR1/3IC | −0.139 | 0.077 | 0.070 | −0.104 | 0.125 | 0.407 | 0.074 | 0.081 | 0.362 |
| FMR1/2IC | 0.044 | 0.082 | 0.590 | 0.050 | 0.155 | 0.749 | 0.154 | 0.111 | 0.166 |
| FMR1/GUS | −0.164 | 0.057 | 0.004 | −0.251 | 0.130 | 0.054 | −0.005 | 0.099 | 0.959 |
| GUS/2IC | 0.536 | 0.126 | 0.00002 | 0.677 | 0.246 | 0.006 | 0.451 | 0.113 | 0.00007 |
| SDHA/EIF4A2 | 0.139 | 0.158 | 0.377 | 0.062 | 0.199 | 0.756 | 0.139 | 0.170 | 0.415 |
| AR | −0.033 | 0.168 | 0.843 | −0.226 | 0.181 | 0.212 | −0.193 | 0.169 | 0.252 |
| FMR1/3IC /AR | −0.009 | 0.116 | 0.935 | 0.140 | 0.158 | 0.378 | 0.177 | 0.107 | 0.100 |
| FMR1/2IC /AR | 0.252 | 0.141 | 0.074 | 0.529 | 0.156 | 0.001 | 0.416 | 0.128 | 0.001 |
| GUS/2IC/AR | 0.396 | 0.141 | 0.005 | 0.427 | 0.124 | 0.001 | 0.325 | 0.144 | 0.024 |
| SDHA/EIF4A2/AR | 0.066 | 0.175 | 0.704 | 0.100 | 0.230 | 0.665 | 0.136 | 0.196 | 0.489 |
Note: b = standardised regression coefficient. Significant values in bold.
AR = FMR1 activation ratio; DTC = Dual Task Cost; EIF4A2 = Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-2 mRNA; SDHA = succinate dehydrogenase complex, subunit A, flavoprotein (Fp) mRNA. The FMR1 mRNA levels were normalized to: (i) GUS alone (FMR1/GUS); (ii) mean of EIF4A2, and SDHA mRNA levels (FMR1/2IC); (iii) mean of GUS, EIF4A2, and SDHA mRNA levels (FMR1/3IC); (iv) mean of EIF4A2, and SDHA mRNA levels divided by AR (FMR1/2IC/AR); (v) mean of GUS, EIF4A2, and SDHA mRNA levels divided by AR (FMR1/3IC/AR). The GUS mRNA levels were normalized to: (i) mean of EIF4A2, and SDHA mRNA levels (GUS/2IC); (ii) mean of EIF4A2, and SDHA mRNA levels divided by AR (FMR1/2IC/AR). Other outputs included AR used alone, and EIF4A2 mRNA normalized to SDHA mRNA levels (EIF4A2/SDHA).
Table 3. PM group p-values indicating the strength of correlation between phenotype and molecular parameters using regression method estimated by generalised estimating equations.
| Variable | FMR1/3IC | FMR1/2IC | FMR1/GUS | GUS/2IC | SDHA/EIF4A2* | AR | FMR1/3IC/AR | FMR1/2IC/AR | FMR1/GUS/AR | GUS/2IC/AR | SDHA/EIF4A2/AR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | |||||||||||
| Age | 0.642 | 0.630 | 0.447 | 0.702 | 0.472 | 0.883 | 0.614 | 0.607 | 0.452 | 0.735 | 0.456 |
| BMI | 0.476 | 0.487 | 0.443 | 0.570 | 0.031 | 0.366 | 0.154 | 0.181 | 0.124 | 0.666 | 0.077 |
| IQ | |||||||||||
| FSIQ | 0.794 | 0.309 | 0.873 | 0.683 | 0.061 | 0.128 | 0.280 | 0.401 | 0.769 | 0.260 | 0.080 |
| VIQ | 0.770 | 0.237 | 0.714 | 0.008 | 0.222 | 0.988 | 0.588 | 0.882 | 0.680 | 0.010 | 0.189 |
| PIQ | 0.935 | 0.534 | 0.638 | 0.227 | 0.058 | 0.030 | 0.338 | 0.056 | 0.851 | 0.200 | 0.060 |
| Working memory | |||||||||||
| LNS | 0.264 | 0.492 | 0.109 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.090 | 0.441 | 0.753 | 0.915 | 0.105 | 0.018 |
| Step time variability | |||||||||||
| DTC Finger tapping | 0.254 | 0.562 | 0.190 | 0.156 | 0.794 | 0.223 | 0.818 | 0.908 | 0.585 | 0.752 | 0.911 |
| DTC Counting by 3 | 0.496 | 0.952 | 0.196 | 0.104 | 0.762 | 0.129 | 0.538 | 0.220 | 0.961 | 0.309 | 0.996 |
| DTC Counting by 7 | 0.555 | 0.415 | 0.577 | 0.406 | 0.458 | 0.123 | 0.847 | 0.465 | 0.836 | 0.678 | 0.188 |
| Step length variability | |||||||||||
| DTC Finger tapping | 0.070 | 0.734 | 0.004 | 0.00002 | 0.377 | 0.843 | 0.935 | 0.074 | 0.107 | 0.005 | 0.704 |
| DTC Counting by 3 | 0.407 | 0.749 | 0.054 | 0.006 | 0.756 | 0.212 | 0.378 | 0.001 | 0.545 | 0.001 | 0.665 |
| DTC Counting by 7 | 0.362 | 0.166 | 0.959 | 0.00007 | 0.415n | 0.252 | 0.100 | 0.001 | 0.552 | 0.024 | 0.489 |
Significant values (p < 0.05) in bold. *SDHA/EIF4A2 was adjusted for BMI in the regression by taking residuals of the regression of EIF4A2 on BMI.
AR = FMR1 activation ratio; BMI = Body Mass Index; DTC = Dual Task Cost; EIF4A2 = Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-2 mRNA; FSIQ = WASI Full Scale IQ; LNS = Letter number sequencing working memory test; PIQ = WASI Performance IQ; SDHA = succinate dehydrogenase complex, subunit A, flavoprotein (Fp) mRNA; VIQ = WASI Verbal IQ.
FMR1 mRNA level correlations with phenotypic measures depend on choice of control genes
Six different methodologies for normalization of FMR1 mRNA levels in blood were used: FMR1/GUS; FMR1/2IC; FMR1/3IC; FMR1/GUS normalized by AR (FMR1/GUS/AR); FMR1/2IC normalized by AR (FMR1/2IC/AR); FMR1/3IC normalized by AR (FMR1/3IC/AR). The choice of the normalization method significantly impacted the correlation between FMR1 mRNA output and clinical outcome variables.
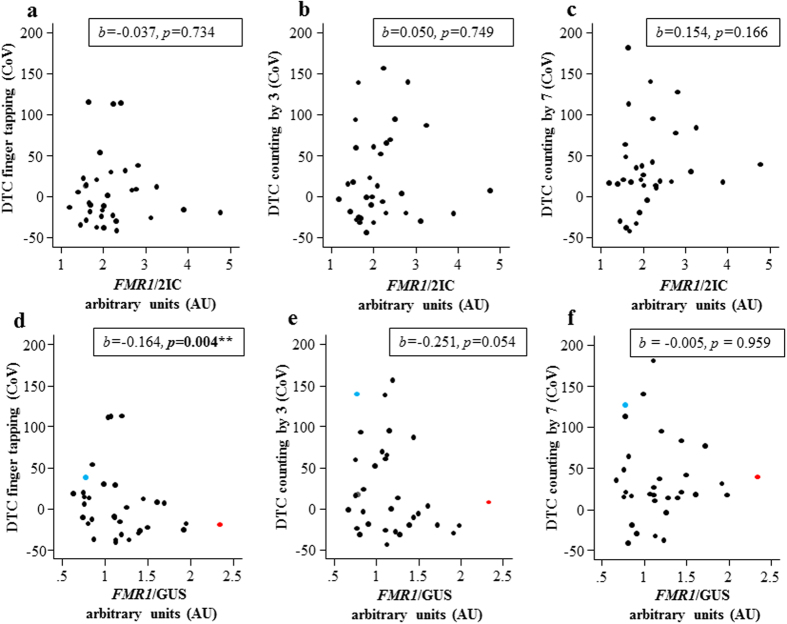
Correlations between FMR1/GUS (where GUS was the sole internal control) and step length variability were significant for step length variability during the finger tapping condition (p = 0.004) and of borderline significance for the counting by 3′s condition (p = 0.054) (Fig. 2, Tables 2 and 3). Adjusting for IQ increased the strength of the correlation between FMR1/GUS and step length variability finger tapping (p = 0.005) and counting by 3′s (p = 0.022). FMR1 /GUS adjusted for FSIQ was also significantly correlated with poorer performance on the working memory test in PM females (p = 0.049) (Table 4). These significant correlations were specific to the PM group, as they were not found in the control group (Supplementary Table S2).
Figure 2.
Relationships between GUS and FMR1 mRNA normalized to expression of different internal control genes in PM females. Scatter plot between FMR1/2IC and the gait step length variability dual-task cost (DTC) for (a) the finger tapping condition, (b) the count by 3′s condition and (c) the count by 7′s condition. Correlation between FMR1/GUS and the gait step length variability DTC for (d) the finger tapping condition, (e) the count by 3′s condition and (f) the count by 7′s condition. Note: The PM female found to be an outlier for the relationship between gait step length variability DTC and the GUS/2IC variable in Fig. 1 is indicated in blue. A PM participant who was an outlier for the relationships between gait step length variability DTC and the FMR1/GUS variable is highlighted in red.
Table 4. PM group p-values indicating the strength of correlation between phenotype and molecular parameters adjusted for FSIQ using regression method estimated by generalised estimating equations.
| Variable | FMR1/3IC | FMR1/2IC | FMR1/GUS | GUS/2IC | SDHA/EIF4A2* | AR | FMR1/3IC/AR | FMR1/2IC/AR | FMR1/GUS/AR | GUS/2IC/AR | SDHA/EIF4A2/AR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working memory | |||||||||||
| LNS | 0.147 | 0.955 | 0.049 | 0.061 | 0.032 | 0.612 | 0.098 | 0.610 | 0.011 | 0.205 | 0.021 |
| Step time variability | |||||||||||
| DTC Finger tapping | 0.154 | 0.207 | 0.188 | 0.759 | 0.761 | 0.432 | 0.446 | 0.791 | 0.403 | 0.999 | 0.465 |
| DTC Counting by 3 | 0.271 | 0.466 | 0.196 | 0.696 | 0.187 | 0.476 | 0.530 | 0.533 | 0.398 | 0.636 | 0.939 |
| DTC Counting by 7 | 0.687 | 0.706 | 0.528 | 0.300 | 0.386 | 0.197 | 0.700 | 0.668 | 0.993 | 0.419 | 0.344 |
| Step length variability | |||||||||||
| DTC Finger tapping | 0.056 | 0.552 | 0.005 | 0.00003 | 0.556 | 0.750 | 0.854 | 0.115 | 0.119 | 0.001 | 0.809 |
| DTC Counting by 3 | 0.275 | 0.821 | 0.022 | 0.012 | 0.725 | 0.267 | 0.703 | 0.001 | 0.473 | 0.003 | 0.919 |
| DTC Counting by 7 | 0.572 | 0.348 | 0.984 | 0.154 | 0.625 | 0.184 | 0.215 | 0.001 | 0.717 | 0.023 | 0.529 |
Significant values (p < 0.05) in bold. *SDHA/EIF4A2 was adjusted for BMI in the regression by taking residuals of the regression of EIF4A2 on BMI.
AR = FMR1 activation ratio; BMI = Body Mass Index; DTC = Dual Task Cost; EIF4A2 = Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-2 mRNA; FSIQ = WASI Full Scale IQ; LNS = Letter number sequencing working memory test; PIQ = WASI Performance IQ; SDHA = succinate dehydrogenase complex, subunit A, flavoprotein (Fp) mRNA; VIQ = WASI Verbal IQ.
In contrast to FMR1/GUS, FMR1/2IC and FMR1/3IC outcomes were not significantly correlated with any gait outcome measures in PM females, suggesting that all positive correlations with FMR1/GUS were solely driven by changes in GUS mRNA levels, rather than that of FMR1 mRNA. This was also consistent with significant negative spearman’s rank correlation between FMR1/GUS and GUS/2IC, and GUS/2IC showing significant correlations with the step length variability measures that were not significantly correlated with FMR1/2IC (Fig. 1, Tables 2 and 3). Importantly, FMR1/2IC vs GUS/2IC outcomes were not significantly correlated with one another (Supplementary Figure S2), suggesting that PM specific changes in GUS mRNA were not dependent on PM specific changes in FMR1 mRNA.
Interestingly, FMR1/2IC/AR was significantly correlated with step length variability counting by 3 (p = 0.001) and 7 (p = 0.001) (Table 3), while FMR1/2IC output was not correlated with these measures. Furthermore, the above correlations were not affected after adjustment for FSIQ (Table 4).
Discussion
GUS has been commonly used as an internal control gene for investigations of inter-relationships between gene expression and phenotype due to its stable expression during brain development28,29 and similar levels of expression in blood to FMR130. However, recent studies have found that β-glucuronidase activity can change in response to inflammatory processes, increased body mass index (BMI), older age, gender and insecticide-related neurotoxicity31,32,33. Thus it appears that GUS may not be an ideal gene for normalization of FMR1 mRNA levels, especially if used on its own, as phenotype correlations might be incorrectly attributed solely to changes in FMR1 mRNA and not GUS mRNA levels. Many of the previous studies examining relationships between FMR1 mRNA toxicity (normalized to GUS) and clinical parameters have been based on cohorts with late-onset neurodegenerative disorders or other medical health conditions (e.g. autoimmune disorders) in which GUS mRNA changes could be relevant (Supplementary Table S1).
Supplementary Table S1 demonstrates potential significance of the problem, where out of 28 studies examining FMR1 mRNA levels in FXSD in males and females, 82% (23 out of 28) used GUS as a sole internal control, one study had not stated a normalization strategy used, while only 14% (4 out of 28) used multiple internal control genes to normalize FMR1 mRNA output data. Some inconsistencies reported include presence of correlations between FMR1 mRNA levels and FXDs severity measures in only 46% of the included studies (13 out of 28), with 50% of the studies (14 out of 23) not reporting significant correlations between these measures, and 4% (1 study) examining these relationships, but not stating if they were significant. While the approach to FMR1 mRNA normalisation is one factor to consider, it must also be highlighted that other issues may be at play. For example, differences in expression of FMR1 mRNA and internal control genes between tissues, over time and between medications regimes could affect the results. Cohort effects such as recruitment bias, and gender and age differences across studies as well as different phenotype measurements/methodologies are other possibilities.
In this study, while FMR1 mRNA levels normalized to two internal control genes (EIF4A2 and SDHA) and AR were significantly correlated with step length variability, FMR1 mRNA levels normalized to only the two internal control genes, and not AR, were not correlated with any clinical variables. This suggests that the significant correlations for FMR1 mRNA output when normalized for AR in this study are driven solely by changes in AR, that may represent X chromosome inactivation skewing, rather than changes in FMR1 mRNA.
Importantly, this study demonstrates that changes in GUS mRNA levels are positively and significantly correlated with gait intra-step variability in adult PM females, and to a lesser degree with poorer performance on working memory and verbal intelligence tests. As expected, this study found that the results of FMR1 mRNA-phenotype investigations depend on the selection of internal control genes. Most importantly, when FMR1 mRNA was controlled only by GUS, PM females with the highest GUS mRNA levels were found to have significantly underestimated FMR1 mRNA levels. For example, the PM case with the highest GUS mRNA level of 3.89 had a low value for FMR1/GUS (0.78) compared to a moderate value for FMR1/2IC (no GUS) (2.82) and FMR1/3IC (GUS and two other genes) (1.48) (Figs 1 and 2). Moreover, GUS/2IC was significantly negatively correlated with FMR1/GUS which again suggests that using GUS as a sole internal control gene for the quantification of FMR1 mRNA introduces variability into the data that is not consistent with changes in FMR1 mRNA levels. As recently highlighted, this is not a problem unique to the FXSD field, and there is growing recognition that other factors, such as inflammation, can significantly influence expression of internal control genes across various tissues, cell types and clinical manifestations34. Indeed, the present study identified that working memory performance in PM females was significantly correlated with both GUS mRNA levels and the ratio between the mRNA levels of EIF4A2 and SDHA used to normalize GUS, indicating that GUS is not likely to be the only gene dysregulated in PM females with working memory deficits.
Abnormal GUS mRNA could itself contribute to PM related phenotypes as it encodes the β-glucuronidase enzyme involved in catabolism of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) within the lysosome35. Thus any neuropathology that increases lysosomal activity could also indirectly impact GUS transcription. GUS mRNA levels may be predictive of FXTAS in PM females, as high gait variability, which has been previously observed in FXTAS, strongly correlated with GUS mRNA levels36. Furthermore, the scaling and timing of stepping associated with intra-step gait variability is strongly dependent on the same cerebellar structures significantly affected by FMR1 mRNA toxicity in individuals with the FXTAS phenotype10. For this reason, it has previously been argued that PM carriers demonstrating high gait variability could have cerebellar dysfunction and may therefore be either in a pre-clinical stage of FXTAS or have a phenotype that is stable yet reminiscent of the more severe FXTAS16.
This study suggests that PM females with high gait variability may also have elevated GUS mRNA levels. Furthermore, the lack of significant correlation between GUS and FMR1 mRNA in the present PM group, when normalized to the same internal control genes (SDHA and EIF4A2) suggests that the PM specific changes in GUS expression are not directly mediated by FMR1 mRNA toxicity. Future studies should explore this lack of association through examining alternative mechanisms/relationships between GUS and RAN translation and related sequestration that may occur independent of elevated FMR1 mRNA transcription. RAN initiated translation of the CGG repeat has been linked to production of a toxic polyglycine protein called FMRpolyG that is associated with activity within the protein degradation pathways37, and this may indirectly implicate lysosome enzymes via the process of autophagy previously associated in other settings with abnormal GUS expression and neuropathology38.
Another mediator that could link changes in GUS mRNA with PM size expansion may be mitochondrial dysfunction, which is itself related to: (i) increased levels of oxidative stress in PM carrier males with FXTAS as well as those with a Parkinsonism phenotype, (ii) elevated ASFMR1 expression8. These findings are relevant to the β-glucuronidase pathway because mitochondrial derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ongoing oxidate stress are known putative mechanisms behind abnormal permeability of lysosomal membranes, which has been shown to indirectly effect activity of lysosomal enzymes such as β-glucuronidase39.
However, while current disease models for PM-related neurotoxicity provide an indirect link to GUS gene expression, more research is needed in this area, especially since there are a number of other biological or environment factors that can also effect activity of the β-glucuronidase enzyme40,41.
The main strength of this study is that it uses previously validated clinical data (working memory and gait analyses) in both PM females and age- and IQ-matched control females16,17 to shed new light on the PM specific role of FMR1 expression when normalized to different internal controls. Previous studies, commonly used a single FMR1 normalization strategy that masked contribution of GUS, and this could explain often conflicting evidence on the relationship between FMR1 mRNA levels and the phenotype (Supplementary Table S1). Another strength is that this study confirms using multiple lines of evidence that measuring mRNA levels with qRT-PCR in PM related disorders requires an improved approach to the internal control methodology that is using at least two or three internal control genes determined to be stably expressed. One important limitation, and the direction for future studies, however, is that, a better approach would be through absolute quantification of mRNA using methods that do not rely on internal control normalization such as competitive PCR42 or Droplet Digital PCR43, demonstrated to be effective for gene expression analysis in other settings. Other limitations include the relatively small sample size, the need to reproduce these findings in an independent cohort of PM females, and to explore contribution of GUS to the phenotype in PM males where FXTAS is more prevalent. Future studies should also examine: (i) GUS expression at both mRNA and protein levels in adults with FXSD including FXS, to rule out any associations with FMRP deficit; and (ii) to compare SDHA and EIF4A2 normalization strategy as well as the ratio between the two internal controls across FXSD including FXS.
In summary, this study showed that GUS is not an ideal control gene for assessing relationships of FMR1 mRNA and the PM phenotypes examined in this study. Indeed, previously unrecognised effects from GUS may also have played a role in the inconsistencies of previously reported inter-correlations between FMR1 mRNA and phenotype in PM carriers. The correlations of GUS mRNA levels with PM phenotype prompt further investigation of the β-glucuronidase pathway in the pathology of FMR1 PM-related disorders.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Kraan, C. M. et al. β-glucuronidase mRNA levels are correlated with gait and working memory in premutation females: understanding the role of FMR1 premutation alleles. Sci. Rep. 6, 29366; doi: 10.1038/srep29366 (2016).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by an Australian Research Council (ARC) Discovery grant (DP110103346) to K.M.C, and a National Fragile X Foundation Rosen Summer Student Fellowship award, Australian Postgraduate Award Scholarship and Monash University Faculty of Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences Bridging Postdoctoral Fellowship to C.M.K; and by the Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Program, with the salaries for the molecular component supported by an NHMRC project grant (no. 104299 to H.R.S and D.E.G); and NHMRC project grant (no. 1103389 to H.R.S and D.E.G); Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, Royal Children’s Hospital Foundation (D.E.G.). The authors thank the Fragile X Association of Australia and Fragile X Alliance for supporting recruitment. They also sincerely thank all the women who participated in this research.
Footnotes
Author Contributions C.M.K., K.M.C. and D.E.G. conceptualized and designed the study, provided intellectual input into the interpretation of the data, and co-wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Q.M.B. conducted statistical analyses and provided intellectual input into drafts of the manuscript. D.E.G. performed and supervised sample processing, FMR1 mRNA, Southern blot. X.L. performed FMR1 mRNA and Southern blot molecular data analyses, and was involved in drafting of the manuscript. H.R.S. co-supervised Southern blot - based analyses and was involved in drafting of the manuscript.
References
- Lozano R., Martinez-Cerdeno V. & Hagerman R. J. Advances in the Understanding of the Gabaergic Neurobiology of FMR1 Expanded Alleles Leading to Targeted Treatments for Fragile X Spectrum Disorder. Curr Pharm Des 21, 4972–4979 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin P. et al. RNA-mediated neurodegeneration caused by the fragile X premutation rCGG repeats in Drosophila. Neuron 39, 739–747 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastori C. et al. Comprehensive analysis of the transcriptional landscape of the human FMR1 gene reveals two new long noncoding RNAs differentially expressed in Fragile X syndrome and Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome. Hum Genet 133, 59–67, 10.1007/s00439-013-1356-6 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesch D. Z. et al. Evidence for the toxicity of bidirectional transcripts and mitochondrial dysfunction in blood associated with small CGG expansions in the FMR1 gene in patients with parkinsonism. Genet Med 13, 392–399, 10.1097/GIM.0b013e3182064362 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hukema R. K. et al. Induced expression of expanded CGG RNA causes mitochondrial dysfunction in vivo. Cell Cycle 13, 2600–2608, 10.4161/15384101.2014.943112 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd P. K. et al. CGG repeat-associated translation mediates neurodegeneration in fragile X tremor ataxia syndrome. Neuron 78, 440–455, 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.03.026 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. & Hagerman R. J. Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1338, 58–70, 10.1111/nyas.12693 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesch D. Z. et al. Evidence for the toxicity of bidirectional transcripts and mitochondrial dysfunction in blood associated with small CGG expansions in the FMR1 gene in patients with parkinsonism. Genet Med 13, 392–399 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer M. M. et al. Prevalence of CGG expansions of the FMR1 gene in a US population-based sample. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 159B, 589–597, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.32065 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman R. J. et al. Intention tremor, parkinsonism, and generalized brain atrophy in male carriers of fragile X. Neurology 57, 127–130 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L. Premature ovarian failure in the fragile X syndrome. Am J Med Genet 97, 189–194 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman R. J., Des-Portes V., Gasparini F., Jacquemont S. & Gomez-Mancilla B. Translating molecular advances in fragile X syndrome into therapy: a review. J Clin Psychiatry 75, e294–307, 10.4088/JCP.13r08714 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolin S. L., Glicksman A., Houck G. E. Jr., Brown W. T. & Dobkin C. S. Mosaicism in fragile X affected males. Am J Med Genet 51, 509–512, 10.1002/ajmg.1320510444 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santa Maria L. et al. FXTAS in an unmethylated mosaic male with fragile X syndrome from Chile. Clin Genet 86, 378–382, 10.1111/cge.12278 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa V. et al. Long CGG-repeat tracts are toxic to human cells: implications for carriers of Fragile X premutation alleles. FEBS Lett 579, 2702–2708 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraan C. M. et al. Age and CGG-repeat length are associated with neuromotor impairments in at-risk females with the FMR1 premutation. Neurobiol Aging 35, 2179 e2177–2113, 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.03.018 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraan C. M. et al. Impaired response inhibition is associated with self-reported symptoms of depression, anxiety, and ADHD in female FMR1 premutation carriers. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 26, 32203 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. et al. An information-rich CGG repeat primed PCR that detects the full range of fragile X expanded alleles and minimizes the need for southern blot analysis. J Mol Diagn 12, 589–600 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish K. M. et al. Novel methylation markers of the dysexecutive-psychiatric phenotype in FMR1 premutation females. Neurology 84(16), 1631–8 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesch D. Z. et al. White matter changes in basis pontis in small expansion FMR1 allele carriers with parkinsonism. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 156B, 502–506, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.31189 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godler D. E. et al. Improved methodology for assessment of mRNA levels in blood of patients with FMR1 related disorders. BMC Clin Pathol 9, 1472–6890 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menz H. B., Latt M. D., Tiedemann A., Mun San Kwan M. & Lord S. R. Reliability of the GAITRite walkway system for the quantification of temporo-spatial parameters of gait in young and older people. Gait Posture 20, 20–25 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster K. E., Wittwer J. E. & Feller J. A. Validity of the GAITRite walkway system for the measurement of averaged and individual step parameters of gait. Gait Posture 22, 317–321, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2004.10.005 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galna B., Lord S. & Rochester L. Is gait variability reliable in older adults and Parkinson’s disease?Towards an optimal testing protocol. Gait Posture 37, 580–585 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord S., Galna B. & Rochester L. Moving forward on gait measurement: toward a more refined approach. Mov Disord 28, 1534–1543 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. E., Delbaere K., Mikolaizak A. S., Lord S. R. & Close J. C. Gait parameter risk factors for falls under simple and dual task conditions in cognitively impaired older people. Gait Posture 37, 126–130, 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2012.06.024 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseeuw P. J. & Leroy A. M. Robust Regression and Outlier Detection (John Wiley and Sons, 2003). [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo A., Caimi L., Marchesini S., Goi G. C. & Tettamanti G. Enzymes of lysosomal origin in human plasma and serum: assay conditions and parameters influencing the assay. Clin Chim Acta 108, 337–346 (1980). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Bader M. D. & Al-Sarraf H. A. Housekeeping gene expression during fetal brain development in the rat-validation by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. Brain research. Developmental brain research 156, 38–45, 10.1016/j.devbrainres.2005.01.010 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassone F. et al. Elevated levels of FMR1 mRNA in carrier males: a new mechanism of involvement in the fragile-X syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 66, 6–15 (2000). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo A. et al. Plasma lysosomal glycohydrolases in a general population. Clin Chim Acta 247, 39–49 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobben N. A. et al. Serum beta-glucuronidase activity in a population of ex-coalminers. Clinical biochemistry 32, 659–664 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueyama J. et al. Beta-glucuronidase activity is a sensitive biomarker to assess low-level organophosphorus insecticide exposure. Toxicology letters 193, 115–119, 10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.12.009 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennani-Baiti B. et al. Inflammation Modulates RLIP76/RALBP1 Electrophile-Glutathione Conjugate Transporter and Housekeeping Genes in Human Blood-Brain Barrier Endothelial Cells. PLoS ONE 10, e0139101, 10.1371/journal.pone.0139101 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy B., Galvin N., Vogler C., Birkenmeier E. H. & Sly W. S. Neuropathology of murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII. Acta Neuropathol 92, 562–568 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Keefe J. A., Robertson-Dick E. E., Hall D. A. & Berry-Kravis E. Gait and Functional Mobility Deficits in Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome. Cerebellum, 14(6), 650–62, 10.1007/s12311-015-0714-4 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S. Y. et al. RAN translation at CGG repeats induces ubiquitin proteasome system impairment in models of fragile X-associated tremor ataxia syndrome. Hum Mol Genet, 24(15), 4317–26, 10.1093/hmg/ddv165 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parente M. K., Rozen R., Cearley C. N. & Wolfe J. H. Dysregulation of gene expression in a lysosomal storage disease varies between brain regions implicating unexpected mechanisms of neuropathology. PLoS One 7, e32419, 10.1371/journal.pone.0032419 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boya P. Lysosomal function and dysfunction: mechanism and disease. Antioxidants & redox signaling 17, 766–774, 10.1089/ars.2011.4405 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tappel A. L. & Dillard C. J. Inhibition of beta-glucuronidase by cholesterol and retinol. J Biol Chem 242, 2463–2469 (1967). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez A. et al. The flavonoid quercetin induces acute vasodilator effects in healthy volunteers: correlation with beta-glucuronidase activity. Pharmacological research 89, 11–18, 10.1016/j.phrs.2014.07.005 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godler D. E., Stein A. N., Bakharevski O., Lindsay M. M. & Ryan P. F. Parathyroid hormone-related peptide expression in rat collagen-induced arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 44, 1122–1131 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindson C. M. et al. Absolute quantification by droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR. Nature methods 10, 1003–1005, 10.1038/nmeth.2633 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.