Abstract
Background:
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has emerged as a new marker of inflammation associated with the severity of several respiratory and cardiac diseases.
Materials and Methods:
We investigated whether the degree of systemic inflammation in sarcoidosis patients as measured by the NLR is associated with pulmonary hypertension (PH).
Results:
A NLR > 3.5 occurred with a significantly higher frequency in sarcoidosis patients with PH (50% vs. 24%, P=0.016) yielding a sensitivity of 50%, specificity of 78%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 41.9% and negative predictive value (NPV) of 81.4% and remained independently associated with PH in multivariate analysis (OR: 3.254, 95% CI: 1.094–9.678, P=0.034).
Conclusion:
We conclude that level of inflammation in sarcoidosis patients may be associated with the development of PH. Owing to the relatively good specificity and NPV, NLR may be a good negative test, which is a simple, inexpensive and widely available in office-based setting to predict the risk of PH in sarcoidosis patients.
Keywords: Sarcoidosis, Pulmonary hypertension, Blood, Marker, Diagnosis
INTRODUCTION
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio has been recently emerged as a new marker of inflammation and was found to be associated with the severity and prognosis of several respiratory and cardiac diseases (1–4). Sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory disease characterized by formation of granulomas in different affected organs (5,6). Pulmonary hypertension is a feared complication in patients with sarcoidosis as it is an important negative prognostic factor, which is reflected in the added priority given to these subjects for orthotopic lung transplantation (7,8). Pulmonary hypertension is considered a vasculopathy caused by excessive vascular cell growth with inflammation playing a major role (8). Previous studies showed that NLR was significantly elevated in PH patients compared with healthy volunteers (9) and may be useful for the assessment of disease severity (10). The increased prevalence of PH in systemic inflammatory diseases such as sarcoidosis is well known (7,8). Although the gold standard in diagnosing PH is the direct measurement of the pulmonary artery pressure with right heart catheterization (RHC), RHC needs highly skilled personnel and advanced technology that are not available in many settings with limited resources (11). Instead, echocardiography is widely used to estimate pulmonary artery systolic pressure (12). Echocardiography is not a simple and easy tool to be considered as a point-of-care test in primary care setting. We hypothesized that the degree of systemic inflammation (as measured by NLR) would be significantly higher in sarcoidosis subjects with PH compared to those without PH and could be an appropriate test for primary care setting. Herein, we aimed to assess the relationship between NLR and PH in sarcoidosis patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
An IRB-approved retrospective chart review (approval number 20130195001) was conducted at University of Illinois in Chicago from January 2010 through January 2015 on adult patients diagnosed with sarcoidosis. Cases were divided into two groups based on presence or absence of PH, which was diagnosed when the pulmonary artery systolic pressure was >25 mmHg using transthoracic echocardiogram. Patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction (EF≤40 mmHg) were excluded. In subjects with more than one complete blood count during hospitalization, the average of the highest and lowest absolute neutrophil and lymphocyte counts was used.
Continuous variables were compared using Student t-test and categorical variables were compared using the Chi-square test. To determine the ideal cutoff value of NLR, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used. To assess whether NLR was independently associated with PH in sarcoidosis patients, multivariate regression analysis with backward stepwise elimination was performed.
RESULTS
A total of 107 cases diagnosed with sarcoidosis were included in the study, among which 28 patients (26%) had PH. The mean age of the study population was 53.4±9.4 years; 76.9% were females, 70% were African Americans and the average duration of sarcoidosis was 12 years.
Characteristics of sarcoidosis patients with and without PH are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Baseline demographic, clinical and laboratory characteristics among sarcoidosis cases with and without pulmonary hypertension
| All (n=107) | Sarcoidosis with PHTN (n=28) | Sarcoidosis without PHTN (n=79) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 53.4 ± 9.4 | 57.1 ± 8.8 | 51.9 ± 9.3 | 0.011 |
| Female sex % (n) | 76.6% (82) | 82.1% (23) | 74.7% (59) | 0.425 |
| BMI (mean ±SD) | 31.9 ± 8 | 32.2 ± 7.2 | 31.9 ± 8.3 | 0.836 |
| Duration of sarcoidosis (y, mean± SD) | 12.2 ± 9.1 | 14.3 ± 10.7 | 11.5 ± 8.5 | 0.18 |
| African American % (n) | 70.1% (75) | 82.1% (23) | 65.8% (52) | 0.112 |
| Diabetes % (n) | 31.4% (33) | 17.9% (5) | 36.4% (28) | 0.077 |
| Dyslipidemia % (n) | 24.5% (26) | 25% (7) | 24.4% (19) | 0.946 |
| CKD % (n) | 3.7% (4) | 3.6% (1) | 3.8% (3) | 0.957 |
| PCI or CABG % (n) | 1.9% (2) | 0% (0) | 2.5% (2) | 0.543 |
| Atrial fibrillation % (n) | 5.6% (6) | 10.7% (3) | 3.8% (3) | 0.190 |
| Pulmonary sarcoidosis % (n) | 91.9% (91) | 96.3% (26) | 90.3% (65) | 0.347 |
| Extrapulmonary sarcoidosis % (n) | 64.5% (69) | 60.7% (17) | 65.8% (52) | 0.628 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis % (n) | 3.7% (4) | 0% (0) | 5.1% (4) | 0.291 |
| Asthma % (n) | 26.4% (28) | 28.6% (8) | 25.6% (20) | 0.763 |
| OSA % (n) | 24.5% (26) | 29.6% (8) | 22.8% (18) | 0.477 |
| Bronchiectasis % (n) | 9.3% (10) | 21.4% (6) | 5.1% (4) | 0.018 |
| FVC % (mean ±SD) | 93.2 ±20.9 | 84.1 ± 24.8 | 96.4 ± 18.4 | 0.014 |
| FEV1 % (mean ±SD) | 88 ± 24.9 | 74.5 ± 27.9 | 92.8 ± 22 | 0.002 |
| TLC % (mean ±SD) | 89.1 ±15.6 | 84.7 ± 16.8 | 90.7 ± 15 | 0.114 |
| RV % (mean ±SD) | 99.4 ±26.7 | 102.2 ± 29.8 | 98.3 ± 25.7 | 0.605 |
| FRC % (mean ±SD) | 97.4 ±22.1 | 102.5 ± 20.2 | 95.6 ± 22.7 | 0.291 |
| DLCO % (mean ±SD) | 67 ± 20.3 | 60.8 ± 18.2 | 69.3 ± 20.7 | 0.088 |
| PASP (mmHg, mean ±SD) | 35.1 ±17.4 | 41.1 ± 17.7 | 21.2 ± 2.3 | 0.000 |
| EF (mean ±SD) | 57.8 ± 4.8 | 57.5 ± 5 | 58 ± 4.7 | 0.672 |
| Neutrophil (mean ±SD) | 4.9 ± 2 | 5.5 ± 2.4 | 4.7 ± 1.8 | 0.098 |
| Lymphocyte (mean ±SD) | 1.76 ± 0.7 | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 1.8 ± 0.8 | 0.221 |
| Neutrophil/Lymphocyte ratio (mean± SD) | 3.4 ± 2.5 | 4.1 ± 2.9 | 3.2 ± 2.4 | 0.120 |
| Neutrophil/Lymphocyte ratio > 3.5 % (n) | 30.7% (31) | 50% (13) | 24% (18) | 0.016 |
| CRP (mean ±SD) | 2.5 ± 4.2 | 3 ± 4.1 | 2.4 ± 4.2 | 0.562 |
| ESR (mean ±SD) | 35.2 ±33.4 | 45.8 ± 32.6 | 32.6 ± 33.3 | 0.160 |
| Oral steroid % (n) | 83.3% (85) | 88.9% (24) | 81.3% (61) | 0.372 |
| DMARD % (n) | 44.3% (47) | 32.1% (9) | 48.7% (38) | 0.133 |
| Methotrexate % (n) | 29.9% (32) | 17.9% (5) | 34.2% (27) | 0.112 |
| Azathioprine% (n) | 4.7%(5) | 7.1% (2) | 3.8%(3) | 0.478 |
| Sildenafil% (n) | 7.5%(8) | 14.3% (4) | 5.1% (4) | 0.126 |
| Warfarin% (n) | 2.8%(3) | 7.1% (2) | 1.3% (1) | 0.150 |
PHTN: Pulmonary hypertension, BMI: Body mass index, CKD: Chronic kidney disease, PCI: Percutaneous coronary intervention, CABG: Coronary artery bypass graft, OSA: Obstructive sleep apnea, PASP: Pulmonary artery systolic pressure, EF: Ejection fraction, ESR: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, CRP: C-reactive protein, DMARD: Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug, y: Year, m: Mean, SD: Standard deviation.
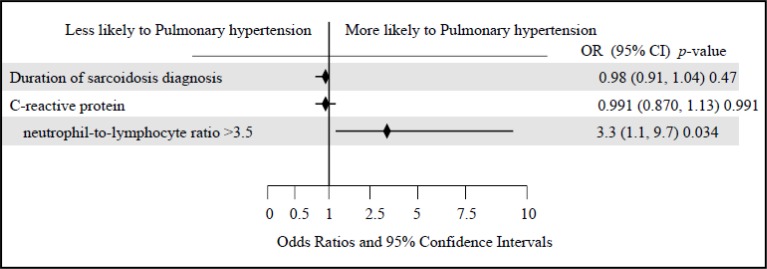
Compared to sarcoidosis patients without PH, those with PH were significantly older (57.1±8.8 vs. 51.9±9.3 years, P=0.011), had a higher frequency of bronchiectasis (21.4% vs. 5.1%, P=0.012), lower FVC% (84.1±24.8% vs. 96.4±18.4%, P=0.014), lower FEV1% (74.5±27.9% vs. 92.8±22%, P=0.002) and a trend towards lower DLCO% (60.8±18.2% vs. 69.3±20.7%, P=0.088). Also, sarcoidosis patients with PH had a trend towards higher neutrophil count (5.5±2.4 vs. 4.7±1.8, P=0.098), lower lymphocyte count (1.6±0.6 vs. 1.8±0.8, P=0.221) and higher NLR (4.1±2.9 vs. 3.2±2.4, P=0.120). A NLR > 3.5 occurred with significantly higher frequency in sarcoidosis patients with PH (50% vs. 24%, P=0.016). The value of 3.5 was determined as the most appropriate cutoff value for NLR for distinction between sarcoidosis patients with and without PH, which yielded a sensitivity of 50%, specificity of 78%, PPV of 41.9% and NPV of 81.4% with an area under curve of 0.619. In the multivariate model, NLR >3.5 remained independently associated with PH (OR 3.254, 95% CI 1.094–9.678, P=0.034). We found no significant association between PH and CRP or ESR. Figure 1 is a forest plot of the variables used in the multivariate model.
Figure 1.
Forest plot of the variables used in the multivariate model among sarcoidosis cases with and without pulmonary hypertension
DISCUSSION
In this retrospective study, we were able to show an independent relationship between NLR, a marker of inflammation, and PH in sarcoidosis patients. It is obvious that patients with a systemic inflammatory disease such as sarcoidosis will have an elevated NLR, and this was in fact demonstrated by Iliaz and colleagues who found a NLR of 2.48±1.1 in sarcoidosis patients compared with 1.73±0.7 in the control group (P<0.001)(13). Nonetheless, as we speculated, a higher NLR (>3.5) in sarcoidosis patients signifies a more intense inflammatory response, which may be the underlying subset and pathophysiological basis for development of PH. These results raise hope and provoke further research to study the utility of this promising marker in sarcoidosis-associated PH. This test is a good negative test owing to the relatively good specificity (78%) and NPV (81.4%). Compared to other inflammatory markers, the NLR is a simple, inexpensive and widely available test that is routinely measured in office-based settings and adds no extra cost. Our study limitations included the single center retrospective design and the relatively small cohort due to rarity of the disease.
We conclude that level of inflammation in sarcoidosis patients may be associated with development of PH. Also, NLR has low sensitivity and PPV for diagnosis of PH in sarcoidosis patients and therefore it is not an ideal screening tool. However, its high NPV makes it an interesting tool to exclude PH in patients with sarcoidosis. Larger studies are required to evaluate the value of NLR in predicting sarcoidosis-associated PH and confirm our findings before being used in the primary care setting.
REFERENCES
- 1. Uthamalingam S, Patvardhan EA, Subramanian S, Ahmed W, Martin W, Daley M, et al. Utility of the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in predicting long-term outcomes in acute decompensated heart failure. Am J Cardiol 2011; 107 (3): 433– 8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Korkmaz A, Yildiz A, Gunes H, Duyuler S, Tuncez A. Utility of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting Troponin Elevation in the Emergency Department Setting. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2015; 21 (7): 667– 71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Tasal A, Erturk M, Uyarel H, Karakurt H, Bacaksiz A, Vatankulu MA, et al. Utility of the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio for predicting in-hospital mortality after levosimendan infusion in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. J Cardiol 2014; 63 (6): 418– 23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Kayrak M, Erdoğan HI, Solak Y, Akilli H, Gül EE, Yildirim O, et al. Prognostic value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: a restrospective study. Heart Lung Circ 2014; 23 (1): 56– 62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Mortaz E, Sereshki HA, Abedini A, Kiani A, Mirsaeidi M, Soroush D, et al. Association of serum TNF-α, IL-8 and free light chain with HLA-DR B alleles expression in pulmonary and extra-pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Inflamm (Lond) 2015; 12: 21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Mirsaeidi M, Machado RF, Schraufnagel D, Sweiss NJ, Baughman RP. Racial difference in sarcoidosis mortality in the United States. Chest 2015; 147 (2): 438– 49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Baughman RP, Engel PJ, Meyer CA, Barrett AB, Lower EE. Pulmonary hypertension in sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 2006; 23 (2): 108– 16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Baughman RP. Pulmonary hypertension associated with sarcoidosis. Arthritis Res Ther 2007; 9 Suppl 2: S8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Yıldız A, Kaya H, Ertaş F, Oylumlu M, Bilik MZ, Yüksel M, et al. Association between neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars 2013; 41 (7): 604– 9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Özpelit E, Akdeniz B, Özpelit ME, Tas S, Bozkurt S, Tertemiz KC, et al. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Int Med Res 2015; 43 (5): 661– 71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Keusch S, Bucher A, Müller-Mottet S, Hasler E, Maggiorini M, Speich R, et al. Experience with exercise right heart catheterization in the diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension: a retrospective study. Multidiscip Respir Med 2014; 9 (1): 51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Bossone E, D'Andrea A, D'Alto M, Citro R, Argiento P, Ferrara F, et al. Echocardiography in pulmonary arterial hypertension: from diagnosis to prognosis. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2013; 26 (1): 1– 14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Iliaz S, Iliaz R, Ortakoylu G, Bahadir A, Bagci BA, Caglar E. Value of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in the differential diagnosis of sarcoidosis and tuberculosis. Ann Thorac Med 2014; 9 (4): 232– 5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]