Abstract
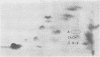
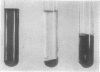
Whereas the addition of four moles of zinc acetate to one of normal human haemoglobin at pH 7.4 results in a clear solution, addition to unstable haemoglobin results in precipitate formation. Within certain limits no false-positive results are obtained with methaemoglobin, and with fetal haemoglobin. With excess zinc, normal haemoglobin also precipitates, but this process is reversible and can be used for a rapid concentration of dilute solutions of normal haemoglobin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANASZAK L. J., WATSON H. C., KENDREW J. C. THE BINDING OF CUPRIC AND ZINC IONS TO CRYSTALLINE SPERM WHALE MYOGLOBIN. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:130–137. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Kay R. A simple method for the detection of unstable haemoglobins. Br J Haematol. 1972 Nov;23(5):615–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb07096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey R., Kynoch P. A., Lang A., Lehmann H., Nozari G., Shinton N. K. Double heterozygosity for two unstable haemoglobins: Hb Sydney (beta67[E11] Val leads to Ala) and Hb Coventry (beta141[H19] Leu deleted). Br J Haematol. 1978 Feb;38(2):195–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb01036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacie J. V., Shinton N. K., Gaffney P. J., Jr, Lehmann H. Haemoglobin Hammersmith (beta-42 (CDI) Phe replaced by ser). Nature. 1967 Nov 18;216(5116):663–665. doi: 10.1038/216663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. V., Grimes A. J., Carrell R. W., Lehmann H. Köln haemoglobinopathy. Further data and a comparison with other hereditary Heinz body anaemias. Br J Haematol. 1967 May;13(3):394–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb08754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann H. Factors influencing the formation of Robison ester. Biochem J. 1939 Aug;33(8):1241–1244. doi: 10.1042/bj0331241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelshlegel F. J., Jr, Brewer G. J., Knutsen C., Prasad A. S., Schoomaker E. B. Studies on the interaction of zinc with human hemoglobin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Aug;163(2):742–748. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90536-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelshlegel F. J., Jr, Brewer G. J., Prasad A. S., Knutsen C., Schoomaker E. B. Effect of zinc on increasing oxygen affinity of sickle and normal red blood cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jul 17;53(2):560–566. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90698-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]