Abstract
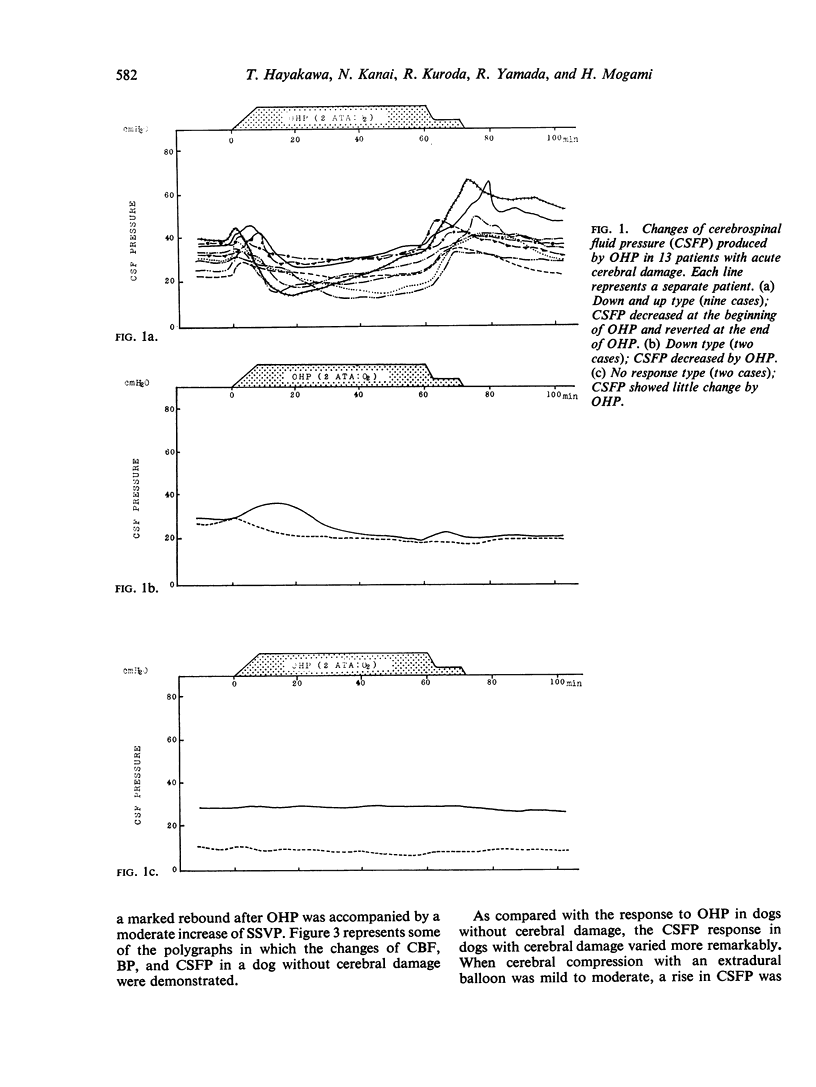
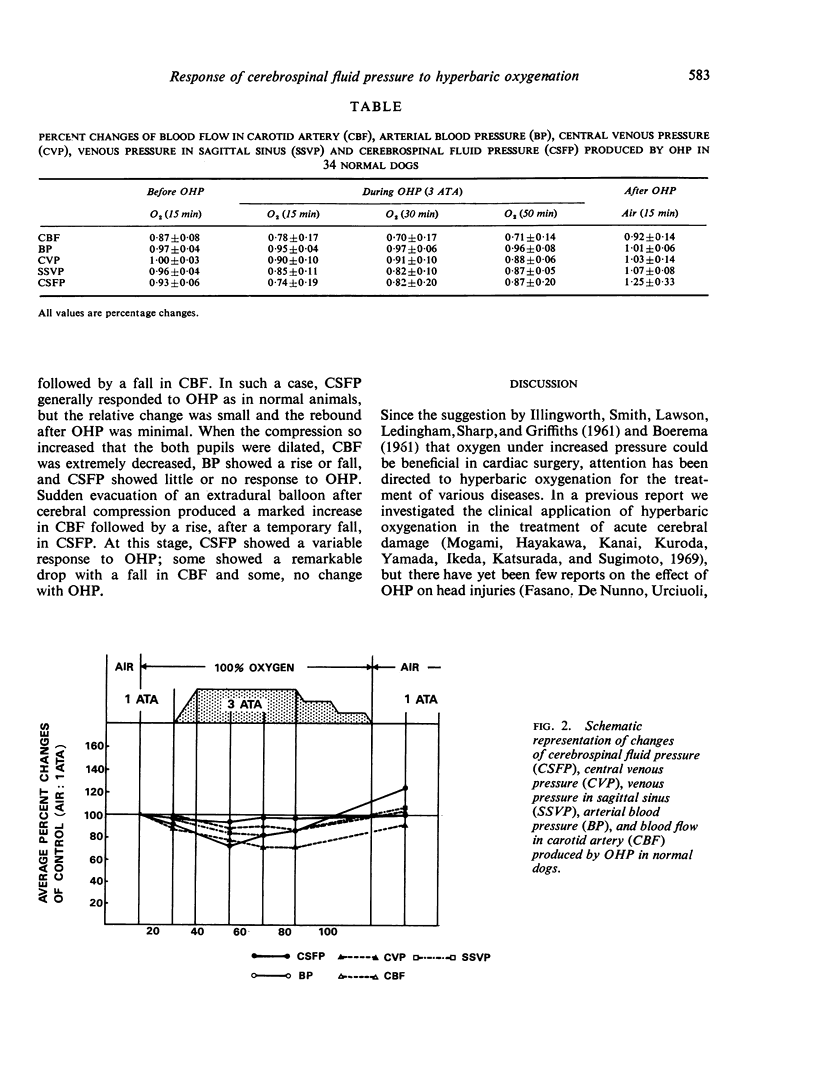
The response of cerebrospinal fluid pressure (CSFP) to hyperbaric oxygenation (OHP) was investigated in 13 patients with acute cerebral damage and in dogs with or without experimentally produced cerebral damage. To elucidate the mechanism of the CSFP response, continuous measurements of carotid blood flow, arterial blood pressure, central venous pressure, and superior sagittal sinus pressure and CSFP were made before, during and after OHP. There was considerable variation in the response of CSFP to OHP in the patients, but three main patterns emerged; type I (nine cases), CSFP decreased at the beginning and rose again at the end of OHP, type II (two cases), CSFP fell with OHP and remained significantly lower than pretreatment level after it, and type III (two cases), CSFP showed little change with OHP. An animal without cerebral damage commonly showed a type I response of CSFP to OHP; the changes of CSFP at the beginning and end of OHP are mainly due to the changes of the cerebral blood flow. There may be two different actions of OHP on cerebral oedema, one decreasing cerebral oedema and another (mainly affecting the normal brain) producing cerebral oedema. Information obtained from the response of CSFP to OHP may be useful in judging the severity and pathophysiological state of cerebral damage.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARACH A. L. HYPERBARIC OXYGEN AND CURRENT MEDICAL USES OF OXYGEN. N Y State J Med. 1963 Oct 1;63:2775–2782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coe J. E., Hayes T. M. Treatment of experimental brain injury by hyperbaric oxygenation. Preliminary report. Am Surg. 1966 Jul;32(7):493–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGVAR D. H., LASSEN N. A. TREATMENT OF FOCAL CEREBRAL ISCHEMIA WITH HYPERBARIC OXYGEN. REPORT OF 4 CASES. Acta Neurol Scand. 1965;41:92–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1965.tb04282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON I., HARPER A. M., MCDOWALL D. G. THE EFFECTS OF OXYGEN UNDER PRESSURE ON CEREBRAL BLOOD-FLOW AND CEREBRAL VENOUS OXYGEN TENSION. Lancet. 1963 Sep 14;2(7307):549–549. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92644-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMBERTSEN C. J., DOUGH R. H., COOPER D. Y., EMMEL G. L., LOESCHCKE H. H., SCHMIDT C. F. Oxygen toxicity; effects in man of oxygen inhalation at 1 and 3.5 atmospheres upon blood gas transport, cerebral circulation and cerebral metabolism. J Appl Physiol. 1953 Mar;5(9):471–486. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1953.5.9.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG N. Continuous recording and control of ventricular fluid pressure in neurosurgical practice. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1960;36(149):1–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langfitt T. W., Kassell N. F. Acute brain swelling in neurosurgical patients. J Neurosurg. 1966 Jun;24(6):975–983. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.24.6.0975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langfitt T. W., Tannanbaum H. M., Kassell N. F. The etiology of acute brain swelling following experimental head injury. J Neurosurg. 1966 Jan;24(1):47–56. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.24.1.0047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg N., Troupp H., Lorin H. Continuous recording of the ventricular-fluid pressure in patients with severe acute traumatic brain injury. A preliminary report. J Neurosurg. 1965 Jun;22(6):581–590. doi: 10.3171/jns.1965.22.6.0581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogami H., Hayakawa T., Kanai N., Kuroda R., Yamada R., Ikeda T., Katsurada K., Sugimoto T. Clinical application of hyperbaric oxygenation in the treatment of acute cerebral damage. J Neurosurg. 1969 Dec;31(6):636–643. doi: 10.3171/jns.1969.31.6.0636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukoff M. H., Hollin S. A., Espinosa O. E., Jacobson J. H., 2nd The protective effect of hyperbaric oxygenation in experimental cerebral edema. J Neurosurg. 1968 Sep;29(3):236–241. doi: 10.3171/jns.1968.29.3.0236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. C., Brooks J. R., Goldthwait J. C., Adams R. D. CHANGES IN BRAIN VOLUME AND BLOOD CONTENT AFTER EXPERIMENTAL CONCUSSION. Ann Surg. 1943 Oct;118(4):619–633. doi: 10.1097/00000658-194310000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



