Figure 3. Catalytic mechanism and peptide binding site of hNaa60.
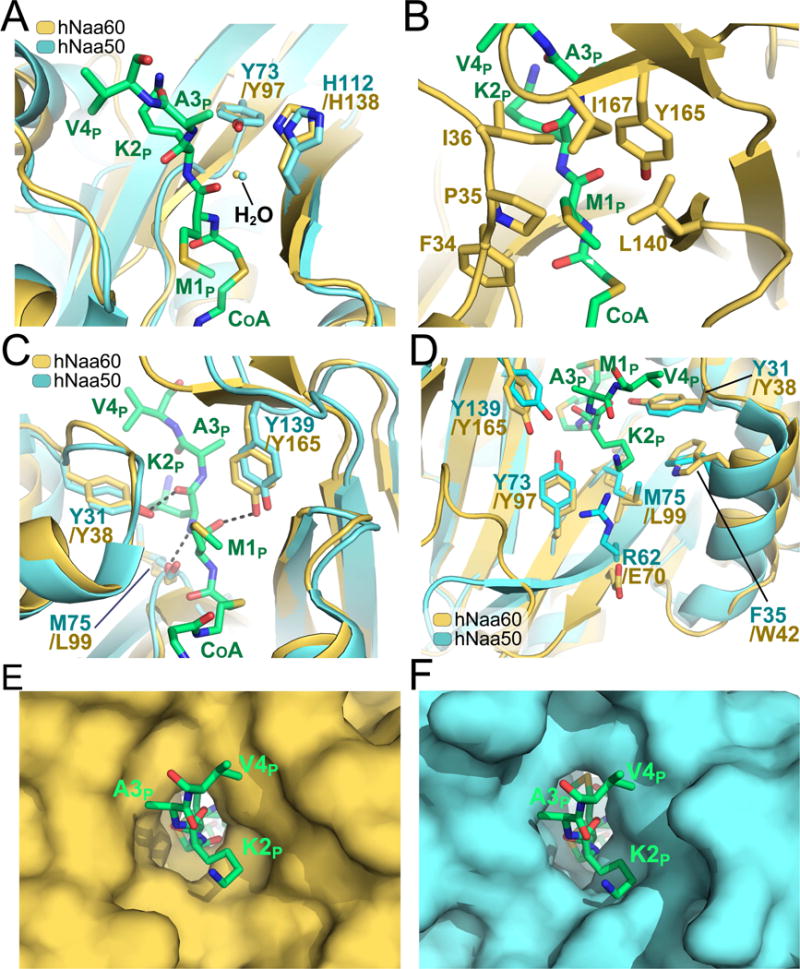
A) Superimposition of the hNaa60 and hNaa50 active site (shown in yellow and cyan respectively). Residues associated with catalysis (Y97, H138 of hNaa60 and Y73, H112 of Naa50) are shown in sticks. An ordered water molecule involved in catalysis is shown in yellow and cyan for the hNaa60 and hNaa50 structure respectively. The bisubstrate analogue CoA-Ac-MKAV7 is shown in green sticks in all figures (A–F). B) Residues F34, P35 I36, L140, Y165 and I167 (yellow sticks) are forming a hydrophobic pocket surrounding the substrate peptide M1p side chain. C) Structural alignment of hNaa60 and hNaa50 active sites. Residues L99, Y38, and Y165 of hNaa60 that plays important roles in peptide anchoring and which are structurally conserved between hNaa60 and hNaa50 are shown as yellow sticks. D) Superimposition of the cavity surrounding the hNaa60 and hNaa50 peptide binding site. E) Active site surface representation of hNaa60. F) Active site surface representation of hNaa50.
