Abstract
Therapeutic hypothermia (TH) improves prognosis after cardiac arrest; however, thermoregulatory responses such as shivering complicate cooling. Hibernators exhibit a profound and safe reversible hypothermia without any cardiovascular side effects by lowering the shivering threshold at low ambient temperatures (Ta). Activation of adenosine A1 receptors (A1ARs) in the central nervous system (CNS) induces hibernation in hibernating species and a hibernation-like state in rats, principally by attenuating thermogenesis. Thus, we tested the hypothesis that targeted activation of the central A1AR combined with a lower Ta would provide a means of managing core body temperature (Tb) below 37 °C for therapeutic purposes. We targeted the A1AR within the CNS by combining systemic delivery of the A1AR agonist 6N-cyclohexyladenosine (CHA) with 8-(p-sulfophenyl) theophylline (8-SPT), a nonspecific adenosine receptor antagonist that does not readily cross the blood–brain barrier. Results show that CHA (1 mg/kg) and 8-SPT (25 mg/kg), administered intraperitoneally every 4 h for 20 h at a Ta of 16 °C, induce and maintain the Tb between 29 and 31 °C for 24 h in both naïve rats and rats subjected to asphyxial cardiac arrest for 8 min. Faster and more stable hypothermia was achieved by continuous infusion of CHA delivered subcutaneously via minipumps. Animals subjected to cardiac arrest and cooled by CHA survived better and showed less neuronal cell death than normothermic control animals. Central A1AR activation in combination with a thermal gradient shows promise as a novel and effective pharmacological adjunct for inducing safe and reversible targeted temperature management.
Keywords: Adenosine, hibernation, cardiac arrest, targeted temperature management, A1AR and global cerebral ischemia, CHA, 8-SPT
Graphical abstract
INTRODUCTION
Mild therapeutic hypothermia, in which the core body temperature (Tb) is reduced to 32–34 °C for ≥24 h, is becoming the standard of care for cardiac arrest patients.1 However, technical challenges may limit the use of therapeutic hypothermia. Shivering is one of the most problematic issues in targeted temperature management (TTM) and is controlled with pharmacological adjuncts, such as paralytics, narcotics, sedatives, or a combination of these such as meperidine and buspirone.2,3
Here we study 6N-cyclohexyladenosine (CHA), an A1 adenosine receptor (A1AR) agonist found to induce hibernation,4 as a novel pharmacological adjunct, to facilitate effective techniques for TTM. Tb in hibernating ground squirrels can fall to as low as −3 °C,5 through a process regulated by A1AR signaling within the central nervous system (CNS),4,6 a mechanism common to other types of torpor.7,8 Activation of the CNS A1AR suppresses shivering and nonshivering thermogenesis. 9–12 A1AR agonists protect against ischemic injury and seizure but have not been used clinically because of side effects, principally hypothermia, bradycardia, and hypotension.13 Given the central site of action for A1AR-mediated inhibition of thermogenesis, this study tests the hypotheses that (i) A1AR agonist-induced cooling can be modulated by ambient temperature (Ta), (ii) A1AR-mediated bradycardia can be managed by co-administration of an adenosine receptor antagonist that does not penetrate the blood–brain barrier, and (iii) reversal of bradycardia will occur without interfering with the cooling effects of CHA. Finally, we use a rat model of cardiac arrest to provide a proof of concept that this approach to TTM will improve survival and decrease the extent of brain injury following cardiac arrest.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
CHA Induces a Decrease in Tb and Heart Rate
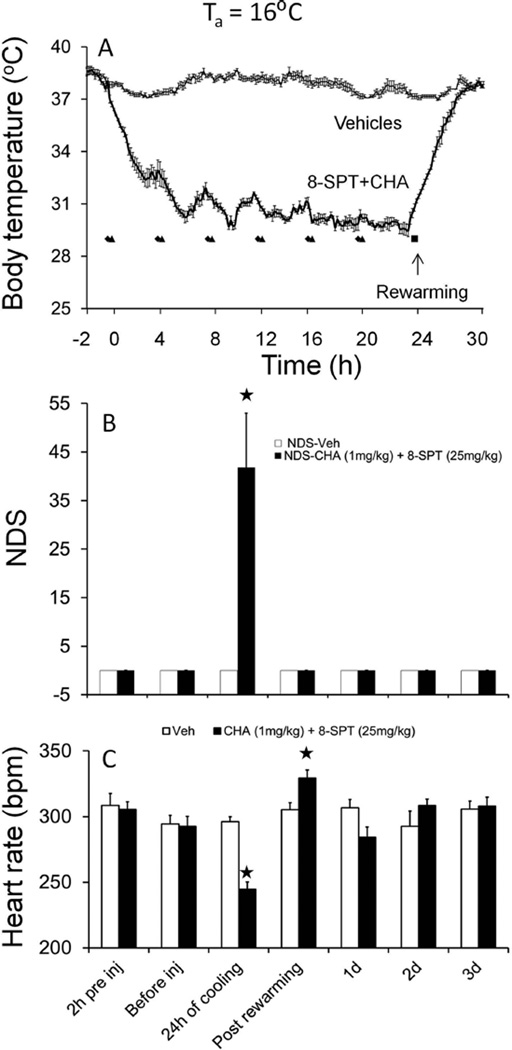
Overcoming thermoregulation is one of the most problematic issues in targeted temperature management (TTM). Shivering is controlled with pharmacological adjuncts, such as paralytics, narcotics, sedatives, or a combination of these such as meperidine and buspirone,2,3 with little regard to mechanism of action. Here we tested the concept that hypothermia in rats could be induced by mimicking the central A1AR mechanism used by hibernating species to enter hibernation. Drugs were administered systemically because this is the most feasible route of administration in a clinical setting. We report that CHA [1.0 mg/kg, intraperitoneally (IP)] decreased Tb to 33 °C within 1 h (Figure 1A). Data show that repeated injection of CHA and 8-SPT at 4 h intervals (which approximates the half-life of CHA) induces a steady minimum in Tb after the fourth injection (Figure 1A). When cold, animals show neurological deficits consistent with low Tb values (Figure 1B). All animals were rewarmed after the drug was discontinued and they were moved to a Ta of 20 °C. No adverse events were noted after rewarming from an assessment of neurological deficit (Figure 1B). At 24 h, there was evidence of a slight but statistically significant bradycardia in CHA-treated rats (Figure 1C). The heart rate remained significantly elevated 5.5 h after the last CHA and 8-SPT injections, consistent with enhanced thermogenesis following cessation of CHA administration (Figure 1C) [p < 0.0001; two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA); time × treatment; n = 6].
Figure 1.
(A) CHA at a Ta of 16 °C induces hypothermia and heart rate changes. CHA injected every 4 h induces and maintains moderate hypothermia for 24 h. 8-SPT was administered 15 min prior to CHA: (◆) time of 8-SPT injection and (▲) time of CHA injection. Vehicle injections [saline and phosphate buffer (PB)] had no effect. (B) Neurological deficit scores (NDSs) increase during hypothermia. (C) Heart rate decreases during cooling and increases after rewarming. Data shown are means ± the standard error of the mean. ★p < 0.05 vs veh [saline and phosphate buffer (PB)] (Tukey test; n = 6 per group).
The CHA-Induced Decrease in Tb Depends on Ta
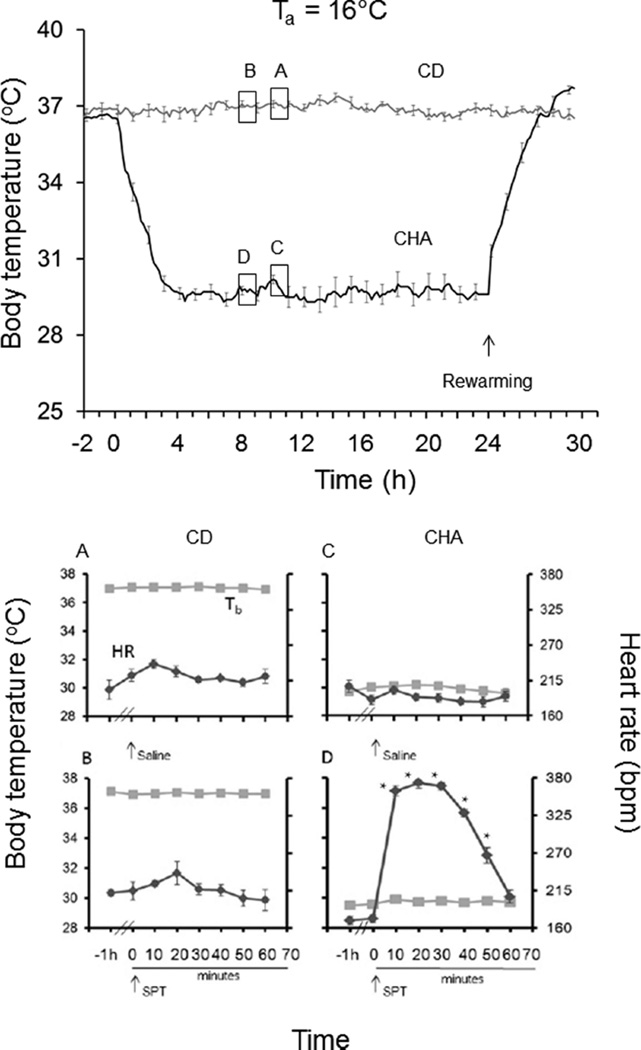
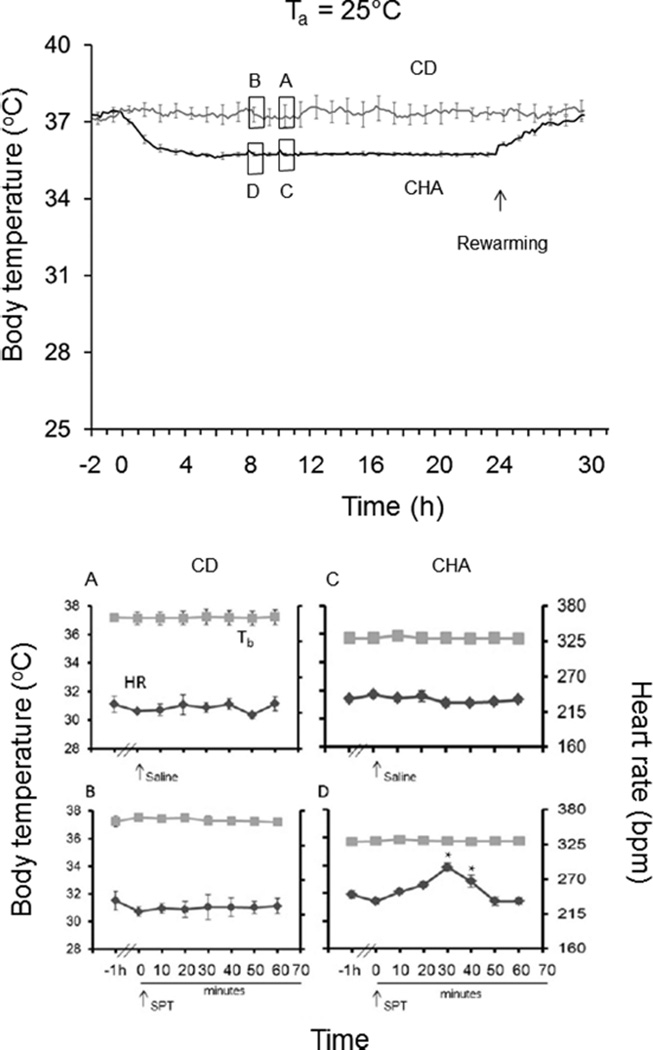
If CHA-induced cooling is due to inhibition of thermogenesis, we predicted that the magnitude of cooling should depend on the thermal gradient, i.e., the difference between Tb and Ta, as seen during hibernation. To address this question, we employed programmable minipumps to deliver CHA continuously for 24 h to rats housed at a Ta of 16 or 25 °C. Results show that continuous administration of CHA at Ta values of 16 and 25 °C decreases Tb (p < 0.0001) and heart rate {p < 0.01; three-way ANOVAs, main effects of group [CD vs CHA (Figures 2 and 3)]} with no effect on hemoglobin oxygen saturation (sO2) (not shown). Moreover, Tb was lowest at a Ta of 16 °C. At a Ta of 16 °C, the mean minimum Tb was 29.3 ± 0.3 °C (Figure 2), and at a Ta of 25 °C, the mean minimum Tb was 35.6 ± 0.1 °C. CHA is thought to facilitate the onset of torpor by suppressing thermogenesis via activation of the A1AR within the CNS.11,14 Core heat then dissipates at rates governed by Ta and thermal conductance. These results are consistent with this mechanism of action because the magnitude of CHA-induced cooling increased with a decrease in Ta. Although systemic administration is more likely to translate to a clinical scenario than ICV administration, direct stimulation of the A1AR on the heart produces profound bradycardia.11,15
Figure 2.
Continuous CHA delivery (30 µL/h) via a SQ minipump at a dose equivalent to 1.0 mg/kg every 4 h at a Ta of 16 °C produces stable hypothermia (top). 8-SPT (25 mg/kg, IP) delivered 8 h after the onset of CHA delivery (B and D) increases heart rate without affecting body temperature. 8-SPT vehicle (saline) delivered 1 h later had no effect (A and C) (★p < 0.05 vs an analogous time point shown in panel C; Tukey test; n = 5 per group). The symbol and line style defined as Tb in panel A denotes Tb in panels B–D. The symbol and line style defined as HR in panel A denotes HR in panels B–D.
Figure 3.
Continuous CHA delivery via a SQ minipump at a rate equivalent to 1.0 mg/kg every 4 h at a Ta of 25 °C produces stable hypothermia (top). 8-SPT (25 mg/kg, IP) delivered 8 h after the onset of CHA delivery (B and D) increases heart rate without affecting body temperature (D). 8-SPT vehicle (saline) delivered 1 h later had no effect (A and C) (★p < 0.05; n = 5). The symbol and line style defined as Tb in panel A denotes Tb in panels B–D. The symbol and line style defined as HR in panel A denotes HR in panels B–D.
A1AR Antagonist 8-SPT Reverses Bradycardia during Therapeutic Hypothermia without Affecting Tb
Knowing that CHA induces torpor via effects on the brain suggested that an A1AR antagonist with poor blood–brain barrier permeability might reverse bradycardia while sparing the decrease in Tb. CHA lowered Tb when 8-SPT was administered 15 min prior to CHA in the preceding experiment. However, the short half-life of 8-SPT (45 min in rabbit16) suggested that heart rate measured 4 h after the last 8-SPT injection under-reported the full effect of 8-SPT because the drug would have been cleared by this time. Thus, during the 24 h period of continuous CHA administration, 8-SPT (or saline vehicle) was delivered, and heart rate and sO2 were monitored at 10 min intervals for 60 min. At a Ta of 16 °C, in control (CD-treated) animals, both 8-SPT and saline vehicle increased heart rate. The increase in HR in both of these groups was interpreted as an effect of the injection because the effect of 8-SPT did not differ from the effect of saline [p = 0.0434; two-way ANOVA; main effect of time (Figure 2A,B)]. By contrast, in animals treated with CHA, 8-SPT (and not the vehicle saline) produced a 2-fold increase in heart rate (p < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA; time × treatment) with no influence on Tb (Figure 2C,D). As expected because of the short half-life of 8-SPT, the effects on heart rate subsided within 60 min of drug administration. Bradycardia at −1 h is not apparent in Figure 2C most likely because of random error in heart rate measurement. Bradycardia is evident in Figure 1C after the subjects had been cooled for 24 h and in Figure 2D during continuous CHA administration.
At a Ta of 25 °C, 8-SPT and saline vehicle delivered to control (CD treated) animals had no effect on heart rate or Tb (Figure 3A,B). However, when 8-SPT was delivered to CHA-treated animals, this adenosine receptor antagonist produced a small but significant increase in heart rate (p < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA; time × treatment) with no influence on Tb (Figure 3C,D). Under these conditions, CHA induced only a slight decrease in Tb and no significant decrease in HR, showing that cooling is more effective at producing bradycardia than this dose of CHA. Importantly, the magnitude of the effect of 8-SPT on heart rate was greater in animals housed at a Ta of 16 °C than on those housed at a Ta of 25 °C (Figures 2 and 3). These results show that both hypothermia and CHA contribute to an adenosine receptor-mediated bradycardia, both of which can be managed with 8-SPT without compromising hypothermia.
The time to target temperature may influence outcome. Thus, control over time to target Tb is desired even though optimal timing remains an area of active research.17 Here we show that pharmacological intervention with adjustments in the temperature differential can be used to manage the rate of cooling and maintenance of hypothermia; animals were cooled faster and to a lower Tb at the colder Ta. In addition, continuous administration of CHA produced a faster decline and a steadier minimum Tb when compared to intermittent injections. A1AR agonists applied too soon after the ischemic event, however, could be detrimental. An increased level of adenosine signaling immediately after traumatic brain injury contributes to respiratory depression and death such that caffeine, a nonselective adenosine receptor antagonist, prevents acute mortality when administered immediately after traumatic brain injury.18 Other studies show that a longer time lag between the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) and target Tb is associated with a more favorable neurologic outcome in patients after cardiac arrest when compared to patients with a shorter time lag between ROSC and target Tb.17 Nonetheless, because the rate of CHA-induced cooling and minimum Tb depend on the temperature differential, one is able to adjust the timing and depth of hypothermia through control of the temperature differential, i.e., the heat sink. The temperature differential may be achieved through surface cooling, intravascular cooling,19,20 or Ta. Moreover, the ability to control the rate and depth of cooling with Ta is consistent with other evidence that CHA produces a decrease in Tb by inhibiting thermogenesis.9
CHA-Induced Therapeutic Hypothermia following Cardiac Arrest Decreases the Extent of Brain Damage
Hypothermia is well-known to enhance survival after cardiac arrest.21 To ensure that CHA or 8-SPT did not interfere with the documented benefits of TH, we next sought to test if CHA-induced TH in conscious rats would improve survival and decrease the extent of brain damage following global cerebral ischemia using a model of asphyxial cardiac arrest (CA). With this model, in our hands, asphyxia for 6 and 8 min produces a similar loss of CA1 neurons 8 days after ROSC.16
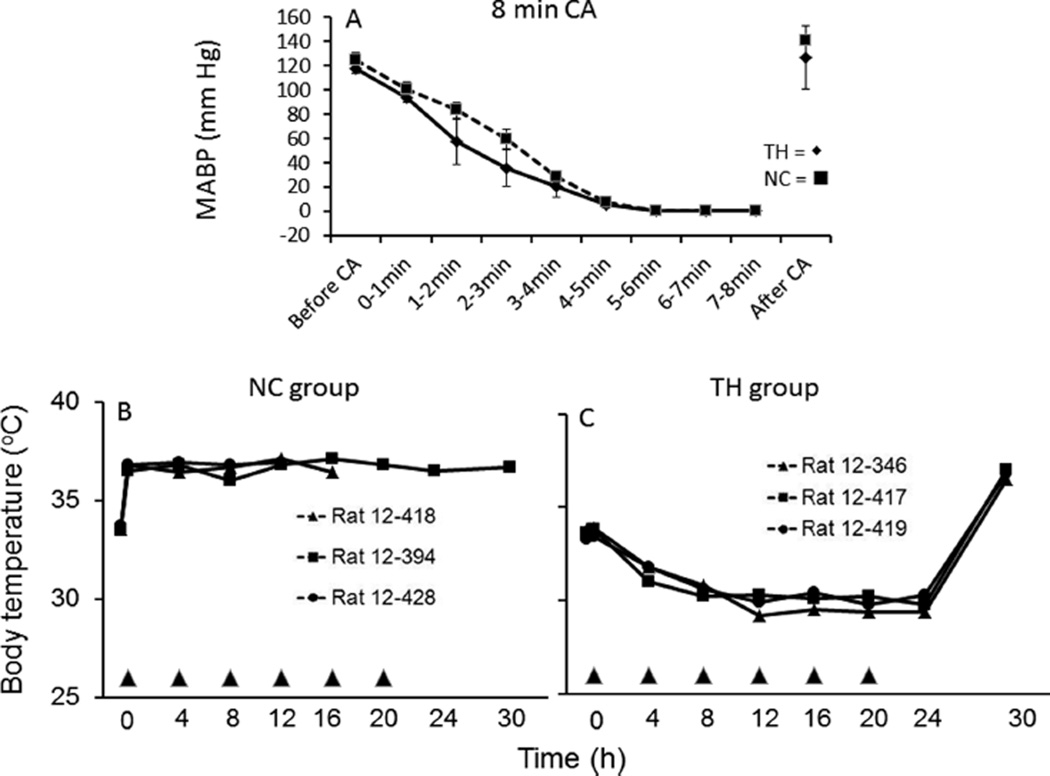
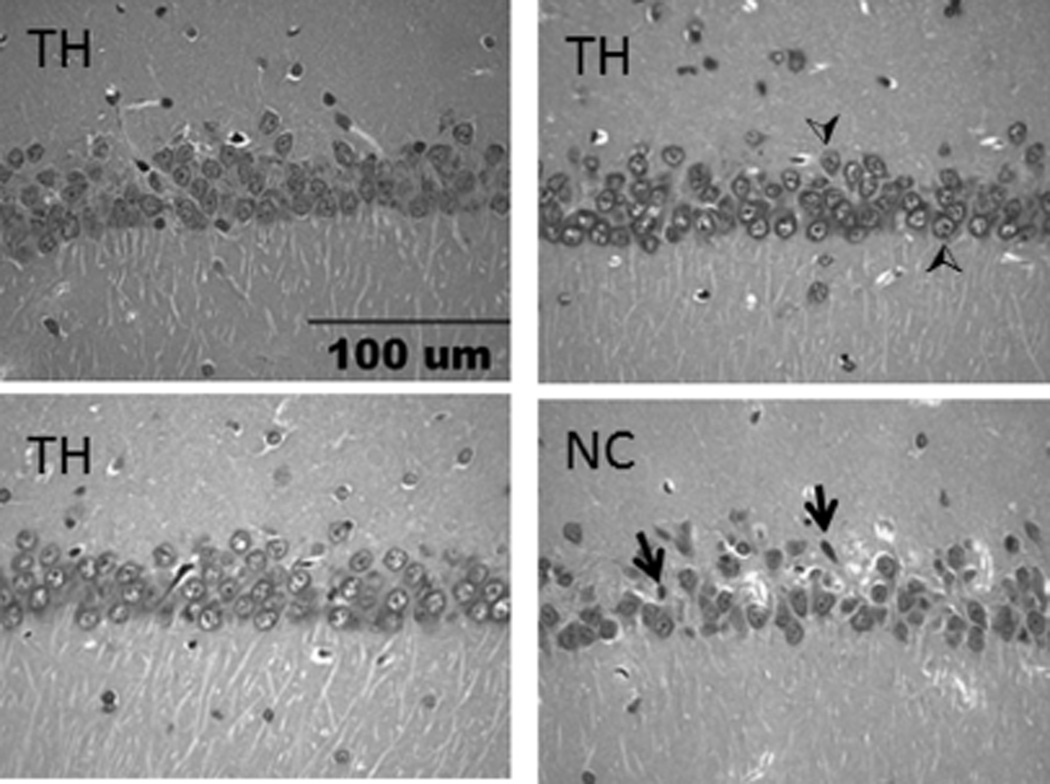
Rats subjected to CA for 8 min and treated with 8-SPT and CHA at a Ta of 16 °C survived better than the normothermic control (NC) group. At the onset of treatment, Tb was 33.5 ± 0.1 and 33.5 ± 0.1 °C in the NC and TH groups, respectively. Tb in all three NC rats increased to 36.5–36.8 °C within 15 min of placement at 29 °C and remained between 36.2 and 37.3 °C until death. Only one rat in the NC group survived to 8 days. The two remaining rats died between 13 and 18 h after ROSC (Figure 4). Tb in the three rats treated with TH decreased to 31.0–31.6 °C within 3 h of CHA injection and remained between 31.8 and 29.2 °C for 24 h before the rats were rewarmed; the mean of individual Tb minima was 29.7 ± 0.3 °C. Rats were rewarmed without intervention within 5 h of transfer to a Ta of 20 °C. Transfer occurred 4 h after the last injection of CHA. All three rats treated with TH survived for 8 days despite a CA-induced decrease in MABP similar to that of the NC group (Figure 4). Histopathology showed ischemia-induced cell death of CA1 neurons in the hippocampus of the one normothermic control animal that survived for 8 days (Figure 5). The number of healthy neurons per millimeter of CA1 (mean ± standard error of the mean) was 135.5 ± 4.6 for the TH group (n = 3) and 47.8 for the normothermic control group (n = 1). This compares to the value of 180.8 ± 12.3 for naïve rats (n = 5) reported previously.16 The hypothermic group showed better survival but was also exposed to a lower Ta. A lowered Ta is unlikely to have improved survival unless it also affected core Tb. This is because, without CHA, a lowered Ta stimulates thermogenesis, and the greater metabolic demand would be expected to worsen the outcome.
Figure 4.
(A) Mean arterial blood pressure (MABP) before, during, and after induction of asphyxial cardiac arrest for 8 min was similar in rats subsequently assigned to therapeutic hypothermia (TH, ◆) (n = 3) or normothermic control (NC, ■) (n = 3) groups. (B) Tb in NC and (C) Tb in TH-treated rats. Only one rat in the NC group survived for 7 days.
Figure 5.
Representative images showing the histopathology of pyknotic (ischemic, arrows) and healthy (normal, arrowheads) neurons in the CA1 hippocampal region of rats 8 days after asphyxial CA for 8 min in TH and NC groups. The scale bar is 100 µm.
In addition to effects on thermogenesis, A1AR agonists are neuroprotective in animal models of cardiac arrest22 and attenuate seizure activity.23 These direct effects within the CNS may have contributed to enhanced survival in this study and contribute to the therapeutic efficacy of these drugs if used as pharmacological adjuncts for TH. Importantly in this study, enhanced survival was observed relative to a NC group where Tb varied between 33.5 and 37.1 °C. In no case did Tb exceed 37.1 °C in the NC group at any of the times measured. Thus, enhanced survival is not due to the absence of hyperthermia, an issue emphasized in a recent clinical study that questions the value of cooling.24
These results show that A1AR agonist CHA, combined with a decrease in Ta, is an effective adjunct for inducing TH. Decreasing Ta to 16 °C and administering CHA intermittently or continuously produces a rapid and sustained decrease in core Tb with minimal effects on heart rate. Moreover, slight bradycardia is readily reversed with 8-SPT, which has no effect on Tb. We, and others, have shown that activation of CNS adenosine A1 receptors (A1ARs) is necessary and sufficient to induce hibernation and torpor in mice.4,7,8 These results suggest that some of the torpor-inducing effects of CHA may translate to refined methods of facilitating hypothermia for therapeutic purposes. Pharmacological management of shivering and nonshivering thermogenesis is necessary to counteract normal thermoregulatory mechanisms, especially shivering.2 Cold infusions alone do not keep patients cool.25 In comatose cardiac arrest patients, shivering may be controlled by a number of pharmacological adjuncts, including sedatives, narcotics, and paralytics.2 Surface cooling can cause skin lesions when shivering is not adequately controlled.26 More importantly, shivering can prevent the attainment of the target temperature and contribute to adverse effects of TH. Shivering is especially difficult to manage in conscious patients,3 which may limit the benefit of TH in stroke patients.27 A recent study in rats9 shows that CHA acts, in part, within the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) to produce effects that closely resemble the suite of thermoregulatory and autonomic nervous system changes that accompany the onset of hibernation.14,28,29 These data suggest that A1AR agonists are promising pharmacological adjuncts for TH for the treatment of stroke, cardiac arrest, and other conditions.30 The data shown here with CHA complement prior work using 5′AMP as an A1AR agonist to induce TH, an approach found to reduce infarct size following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats.12
METHODS
Sustained Hypothermia in Conscious Rats
Experiments were performed in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th Edition (National Research Council, National Academies Press, 2010), and protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Alaska Fairbanks. Male Sprague-Dawley rats (2–3 months old, 375–400 g; obtained directly or derived from breeders obtained from Simonson Laboratories, Gilroy, CA) were housed in pairs at 20 °C on a 12L:12D photoperiod, fed ad libitum, and allowed at least 2 weeks to acclimate before being used.
Implantation of Data Loggers and a Programmable Pump
Baytril [5 mg/kg, subcutaneously (SC)] began 24 h before surgery and continued BID for 3 days. On the day of surgery, isoflurane anesthesia mixed with medical grade O2, delivered at a rate of 1.5 L/min, was induced at 5% and maintained at ≤2% depending on respiratory frequency. Surgery was followed by 10–14 days of postoperative recovery. iButton data loggers (Maxim Integrated, San Jose, CA) were implanted IP alone or in combination with an iPRECIO pump (Data Sciences International, St. Paul, MN). Pumps were implanted SC at the back of the neck. The outlet tube on the pump was tunneled subcutaneously from the dorsal pocket to the incision site on the neck and secured. Prior to implantation, the pumps were programmed to deliver at a rate of 1.0 µL/h except on the two experimental days, during which the flow rate increased to 30.0 µL/h for 24 h. CHA or vehicle delivery commenced just after residual saline was withdrawn and the 900 µL reservoir filled with CHA or vehicle. Delivery ended after 24 h when residual CHA or vehicle was withdrawn and the reservoir refilled with saline.
Drugs
N6-Cyclohexyladenosine (CHA) and 8-(p-sulfophenyl)-theophylline hydrate (8-SPT) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (CD) was purchased from TCI America (Portland, OR).
Drug Delivery via Sequential IP Injections
Animals were instrumented with IP iButton data loggers (Maxim Integrated) programmed to record body temperature (Tb) every 10 min and allowed 14 days postoperative recovery prior to drug testing. 6N-Cyclohexyladenosine (CHA) (A1AR agonist) was dissolved in 0.01 M phosphate buffer (PB); 8-(p-sulfophenyl)theophylline (8-SPT) (non-selective adenosine receptor antagonist) was dissolved in 0.9% saline and filter sterilized on the day of administration. PB for CHA and saline for 8-SPT were administered as vehicle controls where indicated. The day before the experiment, animals in both treatment and control groups were moved to a Ta of 16 °C and remained at this Ta until they were returned to a Ta of 20 °C, 4 h after the last injection. Animals in the treatment group received a total of six injections of CHA (1.0 mg/kg, IP) every 4 h and a total of six injections of 8-SPT (25 mg/kg, IP), administered 15 min prior to each CHA injection. The control group received the same number of injections, with 8-SPT replaced by saline and CHA replaced by PB. Treatment and control conditions were tested in all animals with at least 1 week between experiments using a balanced crossover design such that one-half of the animals received CHA and 8-SPT during the first experiment and the other half received CHA and 8-SPT during the second experiment. Except for moving rats to a Ta of 20 °C 4 h after the last injection, no other means were used to facilitate rewarming. Neurological deficits, heart rate, and sO2 were measured 2 h and immediately before injection, at 24 h, after the rats had been rewarmed and daily for the next 3 days using a pulse oximeter applied to the hind paw (Vet/Ox TM 4402L, Sensor Devices, Waukesha, WI). The total neurological deficit score (NDS) consists of five components: consciousness and respiration, cranial nerve function, motor function, sensory function and coordination (leg/tail movement, cleaning, depth perception, and righting reflex), and motor and sensory function as described previously.31 NDS ranges between 0 (no neurological deficiency, normal function) and 100 (maximal neurological deficiency). Healthy neurons in CA1 were counted as described previously.16
Drug Delivery through iPRECIO Pumps
To determine if the effects of CHA on heart rate were due to direct effects of CHA on the heart or the effects of tissue temperature, we employed programmable peristaltic minipumps to deliver CHA continuously for 24 h at Ta values of 25 and 16 °C. During constant delivery of agonist, we also tested the effects of 8-SPT on heart rate and hemoglobin saturation (sO2) at 10 min intervals appropriate for the short half-life of the drug. For these experiments, rats were instrumented with programmable iPRECIO pumps (Data Sciences International). CHA was dissolved in 25% (w/v) hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (CD) in sterile water, and 8-SPT was dissolved in 0.9% saline. Pumps delivered the same mass of CHA as in the first experiment (6 mg/kg over a 24 h period); however, in this case, CHA was delivered at a constant rate of 30 µL/h. HR and sO2 were monitored using a pulse oximeter every 10 min for 1 h following a single injection of 8-SPT (25 mg/kg, IP) or vehicle as indicated. As before, animals in both treatment and control groups were moved to a Ta of 16 or 25 °C the day before the experiment and remained at this Ta until they were returned to a Ta of 20 °C, 4 h after the end of drug delivery. Drug and vehicle treatments were administered to all animals using a balanced crossover design. At least 1 week separated CHA and vehicle (CD) treatment, and 1 h separated 8-SPT and vehicle (saline) injections.
Therapeutic Benefit of Sustained Hypothermia in Conscious Rats Subjected to Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest
Rats 68–75 days of age were subjected to asphyxial cardiac arrest for 8 min, and animals that were resuscitated within 120 s and met additional inclusion criteria 60 min after ROSC (Table 1) were randomly allocated to a therapeutic hypothermia (TH) or a normothermic control (NC) group using a computer-generated randomization schedule (http://www.jerrydallal.com). Treatment commenced 70 min after ROSC. Animals assigned to the TH group were moved to 16 °C and CHA and 8-SPT delivered as described above for Drug Delivery via Sequential IP Injections. Animals assigned to the NC group were moved to a neonatal incubator set to 29 °C and vehicles (PB and saline) delivered as described above for the control group (see Drug Delivery via Sequential IP Injections). At the end of 24 h, all rats were moved to and housed at an Ta of 20 °C for 7 days until they were euthanized for tissue collection. Body temperature was monitored prior to each injection throughout the treatment and daily thereafter using SC IPTT-300 transponders (BioMedic Data Systems, Inc., Seaford, DE).
Table 1.
| time from ROSC (min) |
criteria for inclusion |
|---|---|
| 2 | ROSC within 120 s |
| 30 | blood gases stable and within normal ranges, base excess of >0 |
| 30–40 | MABP ≥ 80 mmHg |
| 60–70 | Tb ≥ 33 °C |
| 70 | comatose (unresponsive to toe pinch) |
Statistics
Data are reported as means ± the standard error of the mean unless otherwise indicated. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with repeated measures over time and Tukey post hoc comparisons (SAS, version 9.1.3) or a t test (Excel 2010) where indicated.
Acknowledgments
Funding
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke of the National Institutes of Health via Grant R15NS070779.
We thank Lori Bogren, Saurav Bhowmick, Zac Carlson, and Jeanette Moore for technical assistance.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Arrich J, Holzer M, Herkner H, Mullner M. Hypothermia for neuroprotection in adults after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Cochrane Database System Review. 2009:CD004128. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004128.pub2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Logan A, Sangkachand P, Funk M. Optimal management of shivering during therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest. Critical Care Nursing. 2011;31:e18–e30. doi: 10.4037/ccn2011618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Testori C, Sterz F, Behringer W, Spiel A, Firbas C, Jilma B. Surface cooling for induction of mild hypothermia in conscious healthy volunteers: A feasibility trial. Critical Care. 2011;15:R248. doi: 10.1186/cc10506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jinka TR, Toien O, Drew KL. Season primes the brain in an arctic hibernator to facilitate entrance into torpor mediated by adenosine A1 receptors. J. Neurosci. 2011;31:10752–10758. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1240-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Barnes BM. Freeze avoidance in a mammal: Body temperatures below 0 °C in an arctic hibernator. Science. 1989;244:1593–1595. doi: 10.1126/science.2740905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Olson JM, Jinka TR, Larson LK, Danielson JJ, Moore JT, Carpluck J, Drew KL. Circannual rhythm in body temperature, torpor, and sensitivity to A1 adenosine receptor agonist in Arctic ground squirrels. J. Biol. Rhythms. 2013;28:201–207. doi: 10.1177/0748730413490667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Iliff BW, Swoap SJ. Central adenosine receptor signaling is necessary for daily torpor in mice. Am. J. Physiol. 2012;303:R477–R484. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00081.2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tamura Y, Shintani M, Nakamura A, Monden M, Shiomi H. Phase-specific central regulatory systems of hibernation in syrian hamsters. Brain Res. 2005;1045:88–96. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.03.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tupone D, Madden CJ, Morrison SF. Central activation of the A1 adenosine receptor (A1AR) induces a hypothermic, torpor-like state in the rat. J. Neurosci. 2013;33:14512–14525. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1980-13.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tse SY, Wei ET. Inhibition of the shake response in rats by adenosine and 2-chloroadenosine. Psychopharmacology. 1986;90:322–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00179184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Anderson R, Sheehan MJ, Strong P. Characterization of the adenosine receptors mediating hypothermia in the conscious mouse. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1994;113:1386–1390. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Muzzi M, Blasi F, Chiarugi A. Amp-dependent hypothermia affords protection from ischemic brain injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33:171–174. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2012.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bischofberger N, Jacobson KA, von Lubitz DK. Adenosine A1 receptor agonists as clinically viable agents for treatment of ischemic brain disorders. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1997;825:23–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1997.tb48411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Heller HC, Colliver GW, Beard J. Thermoregulation during entrance into hibernation. Pfluegers Arch. 1977;369:55–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00580810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cheung JW, Lerman BB. Cvt-510: A selective A1 adenosine receptor agonist. Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. 2003;21:277–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2003.tb00122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Combs VM, Crispell HD, Drew KL. d-Cycloserine 24 and 48 h after asphyxial cardiac arrest has no effect on hippocampal ca1 neuropathology. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014;34:1720. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2014.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Haugk M, Testori C, Sterz F, Uranitsch M, Holzer M, Behringer W, Herkner H. Relationship between time to target temperature and outcome in patients treated with therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest. Critical Care. 2011;15:R101. doi: 10.1186/cc10116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lusardi TA, Lytle NK, Szybala C, Boison D. Caffeine prevents acute mortality after tbi in rats without increased morbidity. Exp. Neurol. 2012;234:161–168. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.12.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lyden PD, Allgren RL, Ng K, Akins P, Meyer B, Al-Sanani F, Lutsep H, Dobak J, Matsubara BS, Zivin J. Intravascular cooling in the treatment of stroke (ictus): Early clinical experience. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases. 2005;14:107–114. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2005.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Faridar A, Bershad EM, Emiru T, Iaizzo PA, Suarez JI, Divani AA. Therapeutic hypothermia in stroke and traumatic brain injury. Front. Neurol. 2011;2:80. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2011.00080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bernard SA, Gray TW, Buist MD, Jones BM, Silvester W, Gutteridge G, Smith K. Treatment of comatose survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with induced hypothermia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;346:557–563. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa003289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Xu K, Puchowicz MA, Lust WD, LaManna JC. Adenosine treatment delays postischemic hippocampal ca1 loss after cardiac arrest and resuscitation in rats. Brain Res. 2006;1071:208–217. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.11.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Unearthing the naked mole-rat. Lab. Anim. 2012;41:305. doi: 10.1038/laban.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nielsen N, Wetterslev J, Cronberg T, Erlinge D, Gasche Y, Hassager C, Horn J, Hovdenes J, Kjaergaard J, Kuiper M, Pellis T, Stammet P, Wanscher M, Wise MP, Aneman A, Al-Subaie N, Boesgaard S, Bro-Jeppesen J, Brunetti I, Bugge JF, Hingston CD, Juffermans NP, Koopmans M, Kober L, Langorgen J, Lilja G, Möller JE, Rundgren M, Rylander C, Smid O, Werer C, Winkel P, Friberg H Investigators TTMT. Targeted temperature management at 33 °C versus 36 °C after cardiac arrest. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013;369:2197–2206. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1310519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kliegel A, Janata A, Wandaller C, Uray T, Spiel A, Losert H, Kliegel M, Holzer M, Haugk M, Sterz F, Laggner AN. Cold infusions alone are effective for induction of therapeutic hypothermia but do not keep patients cool after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2007;73:46–53. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2006.08.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Uray T, Malzer R. Out-of-hospital surface cooling to induce mild hypothermia in human cardiac arrest: A feasibility trial. Resuscitation. 2008;77:331–338. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2008.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zgavc T, Ceulemans AG, Sarre S, Michotte Y, Hachimi-Idrissi S. Experimental and clinical use of therapeutic hypothermia for ischemic stroke: Opportunities and limitations. Stroke Res. Treat. 2011;2011:689290. doi: 10.4061/2011/689290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Harris MB, Milsom WK. Parasympathetic influence on heart rate in euthermic and hibernating ground squirrels. J. Exp. Biol. 1995;198:931–937. doi: 10.1242/jeb.198.4.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lyman CP, O’Brien RC. Autonomic control of circulation during the hibernating cycle in ground squirrels. J. Physiol. 1963;168:477–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Peretti D, Bastide A, Radford H, Verity N, Molloy C, Martin MG, Moreno JA, Steinert JR, Smith T, Dinsdale D, Willis AE, Mallucci GR. Rbm3 mediates structural plasticity and protective effects of cooling in neurodegeneration. Nature. 2015;518:236–239. doi: 10.1038/nature14142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Katz L, Ebmeyer U, Safar P, Radovsky A, Neumar R. Outcome model of asphyxial cardiac arrest in rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1995;15:1032–1039. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1995.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]