Abstract
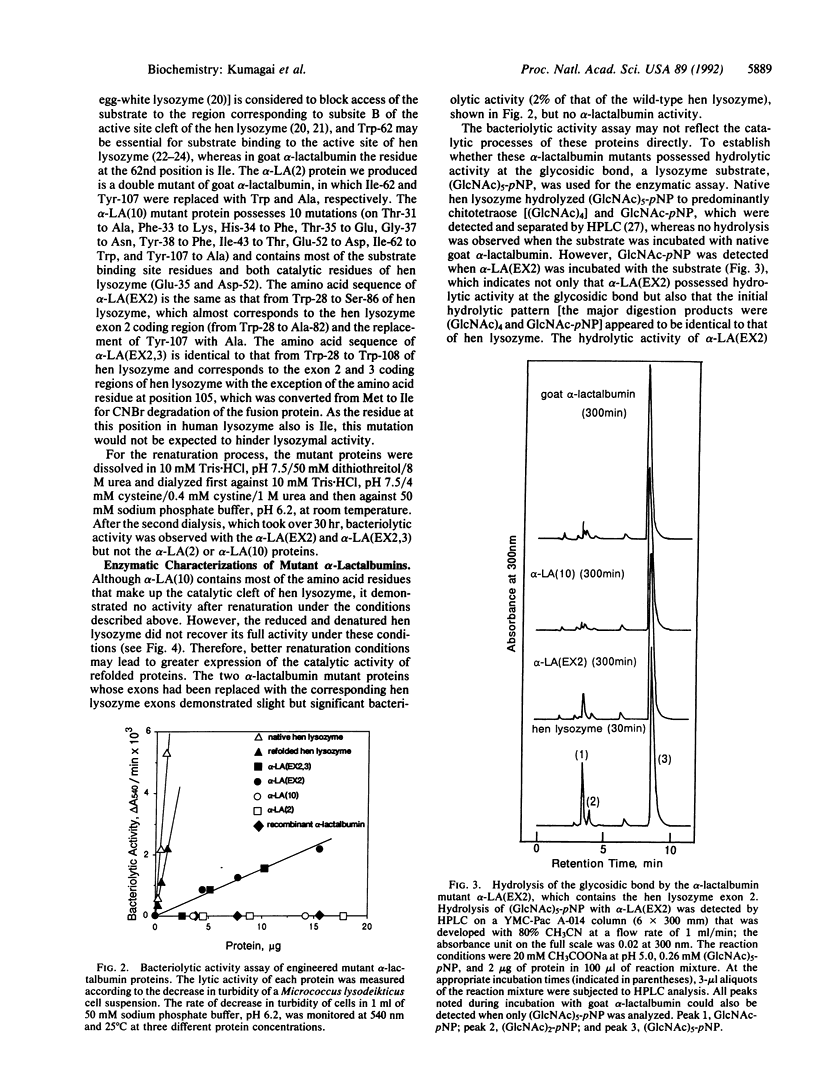
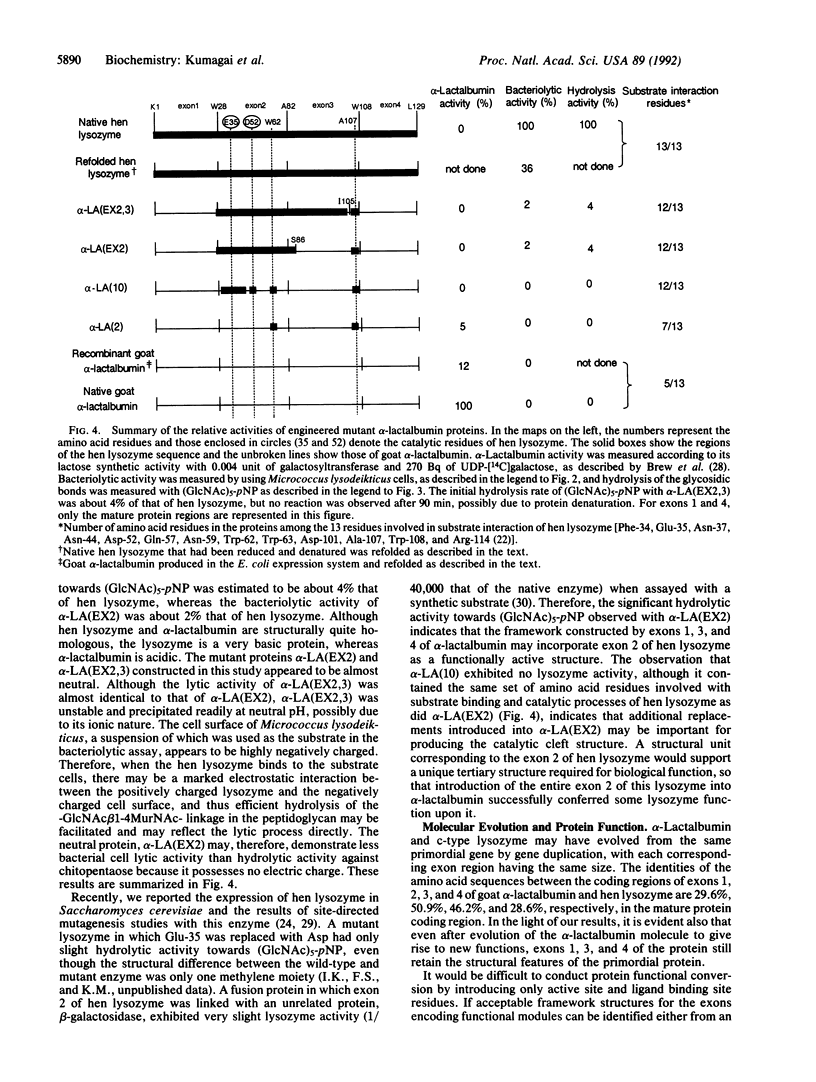
Exons of eukaryotic genes that encode proteins frequently appear to encode structural and/or functional protein units [Gilbert, W. (1978) Nature (London) 271, 501; Blake, C.C.F. (1979) Nature (London) 277, 598]. alpha-Lactalbumin and c-type lysozyme are functionally quite different but structurally highly homologous proteins. Their gene organizations have been shown to be virtually the same and their exon structures are identical. The exon 2 region of hen lysozyme contains most of the amino acid residues that make up its catalytic cleft. In this study, we engineered a hybrid protein in which the exon 2 region of goat alpha-lactalbumin was replaced with that of hen lysozyme. This conferred catalytic activity on the alpha-lactalbumin, which is a nonenzymatic protein in its native structural form.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acharya K. R., Ren J. S., Stuart D. I., Phillips D. C., Fenna R. E. Crystal structure of human alpha-lactalbumin at 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):571–581. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acharya K. R., Stuart D. I., Walker N. P., Lewis M., Phillips D. C. Refined structure of baboon alpha-lactalbumin at 1.7 A resolution. Comparison with C-type lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 5;208(1):99–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C. Exons encode protein functional units. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):598–598. doi: 10.1038/277598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Johnson L. N., Mair G. A., North A. C., Phillips D. C., Sarma V. R. Crystallographic studies of the activity of hen egg-white lysozyme. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Apr 18;167(1009):378–388. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew K., Hill R. L. Lactose biosynthesis. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1975;72:105–158. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew K., Vanaman T. C., Hill R. L. Comparison of the amino acid sequence of bovine alpha-lactalbumin and hens egg white lysozyme. J Biol Chem. 1967 Aug 25;242(16):3747–3749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew K., Vanaman T. C., Hill R. L. The role of alpha-lactalbumin and the A protein in lactose synthetase: a unique mechanism for the control of a biological reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):491–497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne W. J., North A. C., Phillips D. C., Brew K., Vanaman T. C., Hill R. L. A possible three-dimensional structure of bovine alpha-lactalbumin based on that of hen's egg-white lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):65–86. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90487-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L., Emery D. C., Davies M. S., Parker D., Craig R. K. Organization and sequence of the human alpha-lactalbumin gene. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 15;242(3):735–742. doi: 10.1042/bj2420735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka Y., Segawa T., Kuwajima K., Sugai S., Murai N. alpha-Lactalbumin: a calcium metalloprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 14;95(3):1098–1104. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91585-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jollès P., Jollès J. What's new in lysozyme research? Always a model system, today as yesterday. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984 Sep;63(2):165–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00285225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung A., Sippel A. E., Grez M., Schütz G. Exons encode functional and structural units of chicken lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchinke W. 50 residues coded by exon 2 of chicken lysozyme carry residual catalytic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):927–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92197-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai I., Kojima S., Tamaki E., Miura K. Conversion of Trp 62 of hen egg-white lysozyme to Tyr by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biochem. 1987 Oct;102(4):733–740. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai I., Miura K. Enhanced bacteriolytic activity of hen egg-white lysozyme due to conversion of Trp62 to other aromatic amino acid residues. J Biochem. 1989 Jun;105(6):946–948. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai I., Takeda S., Hibino T., Miura K. Expression of goat alpha-lactalbumin in Escherichia coli and its refolding to biologically active protein. Protein Eng. 1990 Apr;3(5):449–452. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.5.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird J. E., Jack L., Hall L., Boulton A. P., Parker D., Craig R. K. Structure and expression of the guinea-pig alpha-lactalbumin gene. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 15;254(1):85–94. doi: 10.1042/bj2540085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanjo F., Sakai K., Usui T. p-nitrophenyl penta-N-acetyl-beta-chitopentaoside as a novel synthetic substrate for the colorimetric assay of lysozyme. J Biochem. 1988 Aug;104(2):255–258. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta K., Sugai S. The evolution of lysozyme and alpha-lactalbumin. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jun 1;182(1):111–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prager E. M., Wilson A. C. Ancient origin of lactalbumin from lysozyme: analysis of DNA and amino acid sequences. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(4):326–335. doi: 10.1007/BF02101195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qasba P. K., Safaya S. K. Similarity of the nucleotide sequences of rat alpha-lactalbumin and chicken lysozyme genes. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):377–380. doi: 10.1038/308377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewale J. G., Sinha S. K., Brew K. Evolution of alpha-lactalbumins. The complete amino acid sequence of the alpha-lactalbumin from a marsupial (Macropus rufogriseus) and corrections to regions of sequence in bovine and goat alpha-lactalbumins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4947–4956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilotte J. L., Soulier S., Printz C., Mercier J. C. Sequence of the goat alpha-lactalbumin-encoding gene: comparison with the bovine gene and evidence of related sequences in the goat genome. Gene. 1991 Feb 15;98(2):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90185-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warme P. K., Momany F. A., Rumball S. V., Tuttle R. W., Scheraga H. A. Computation of structures of homologous proteins. Alpha-lactalbumin from lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):768–782. doi: 10.1021/bi00701a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



