Abstract
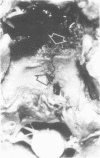
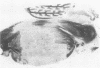
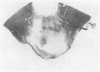
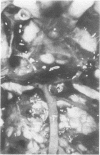
The neuropathological findings at necropsy are described in three cases of basilar artery injuries and their consequences after head trauma and the mechanism of injuries is discussed. The first case was that of massive pontine infarct due to an occlusion of the basilar artery trapped in the fracture of the clivus, 13 days before death. The second case, also with a pontine infarct, survived for two and two-thirds months; the trauma was probably similar, but the presence of the basal skull fracture and the occlusion of the basilar artery can be surmised only in retrospect. The third case was one of delayed rupture of the basilar artery occurring three to four weeks after the injury, which caused aneurysmal formation in the left posterior cerebral artery.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOTS G. T., KRAMER W. TRAUMATIC THROMBOSIS OF INTRACRANIAL ARTERIES AND EXTENSIVE NECROSIS OF THE BRAIN DEVELOPED DURING REANIMATION. Acta Neuropathol. 1964 May 5;3:416–427. doi: 10.1007/BF00688452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton C., Velasco F., Dorman J. Traumatic aneurysm of a peripheral cerebral artery. Review and case report. J Neurosurg. 1968 May;28(5):468–474. doi: 10.3171/jns.1968.28.5.0468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARMICHAEL R. The pathogenesis of noninflammatory cerebral aneurysms. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1950 Jan;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1002/path.1700620102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARPENTER S. Injury of neck as cause of vertebral artery thrombosis. J Neurosurg. 1961 Nov;18:849–853. doi: 10.3171/jns.1961.18.6.0849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHATRIAN G. E., WHITE L. E., Jr, SHAW C. M. EEG PATTERN RESEMBLING WAKEFULNESS IN UNRESPONSIVE DECEREBRATE STATE FOLLOWING TRAUMATIC BRAIN-STEM INFARCT. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1964 Mar;16:285–289. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(64)90111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE P. R., DICKSON J., SMITH B. J. Traumatic thrombosis of the internal carotid artery following a non-penetrating injury and leading to infraction of the brain. Br J Surg. 1955 Sep;43(178):215–216. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004317816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD F. R., CLARK D. Thrombosis of the basilar artery with softenings in the cerebellum and brain stem due to manipulation of the neck; a report of two cases with one post-mortem examination, reasons are given to prove that damage to the vertebral arteries is responsible. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1956 Jan;98(1):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GURDJIAN E. S., HARDY W. G., LINDNER D. W., THOMAS L. M. CLOSED CERVICAL CRANIAL TRAUMA ASSOCIATED WITH INVOLVEMENT OF CAROTID AND VERTEBRAL ARTERIES. J Neurosurg. 1963 May;20:418–427. doi: 10.3171/jns.1963.20.5.0418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. F., DAVID M., SACHS M. [Traumatic intracranial arterial aneurysms]. Neurochirurgie. 1962 Apr-Jun;8:189–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOCKADAY T. D. Traumatic thrombosis of the internal carotid artery. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1959 Aug;22:229–231. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.22.3.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUCK W. S., JACKSON J. R., ODOM G. L., YOUNG W. G. OCCLUSION OF THE INTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY IN THE NECK SECONDARY TO CLOSED TRAUMA TO THE HEAD AND NECK: A REPORT OF TWO CASES. Ann Surg. 1964 Feb;159:219–221. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196402000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. G., NEWTON T. H. Internal carotid artery occlusion in young adults. Brain. 1960 Dec;83:565–578. doi: 10.1093/brain/83.4.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. T., Brownell B. Traumatic thrombosis of the internal carotid artery in the neck. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Aug;31(4):307–314. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.4.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKLE E. C., MULLER J. C., ODOM G. L. Traumatic brain-stem thrombosis: report of a case and analysis of the mechanism of injury. Ann Intern Med. 1952 May;36(5):1329–1335. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-36-5-1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDENBERG R. Compression of brain arteries as pathogenetic factor for tissue necroses and their areas of predilection. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1955 Jul;14(3):223–243. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195507000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOOP J. W., WHITE L. E., Jr, SHAW C. M. TRAUMATIC OCCLUSION OF THE BASILAR ARTERY WITHIN A CLIVUS FRACTURE. Radiology. 1964 Jul;83:36–40. doi: 10.1148/83.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenberg R. Incarceration of a vertebral artery in the cleft of a longitudinal fracture of the skull. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1966 May;24(5):908–910. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.24.5.0908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locksley H. B. Natural history of subarachnoid hemorrhage, intracranial aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations. Based on 6368 cases in the cooperative study. J Neurosurg. 1966 Aug;25(2):219–239. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.25.2.0219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY D. S. Post-traumatic thrombosis of the internal carotid and vertebral arteries after non-penetrating injuries of the neck. Br J Surg. 1957 May;44(188):556–561. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004418803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastaglia F. L., Savas S., Kakulas B. A. Intracranial thrombosis of the internal carotid artery after closed head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1969 Oct;32(5):383–388. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.32.5.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. D., Ayers T. N. Post-traumatic changes in the internal carotid artery and its branches: an arteriographic study. Radiology. 1967 Jul;89(1):95–100. doi: 10.1148/89.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitner S. E. Carotid thrombosis due to intraoral trauma. An unusual complication of a common childhood accident. N Engl J Med. 1966 Apr 7;274(14):764–767. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196604072741403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER R. C., LEMMEN L. J. Traumatic internal carotid artery thrombosis secondary to nonpenetrating injuries to the neck; a problem in the differential diagnosis of craniocerebral trauma. J Neurosurg. 1952 Sep;9(5):495–507. doi: 10.3171/jns.1952.9.5.0495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEDZIMIR C. B. Head injury as a cause of internal carotid thrombosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1955 Nov;18(4):293–296. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.18.4.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. M., Foltz E. L. Traumatic dissecting aneurysm of middle cerebral artery and carotid-cavernous fistula with massive intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1968 May;28(5):475–479. doi: 10.3171/jns.1968.28.5.0475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sights W. P., Jr Incarceration of the basilar artery in a fracture of the clivus. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1968 Jun;28(6):588–591. doi: 10.3171/jns.1968.28.6.0588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMSON J. L. TRAUMATIC THROMBOSIS OF THE INTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY IN THE CAROTID CANAL. Br J Radiol. 1963 Nov;36:840–842. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-36-431-840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOAKLEY G., MCCAFFREY J. TRAUMATIC THROMBOSIS OF THE INTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY. Aust N Z J Surg. 1965 May;34:261–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1965.tb04371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]