Abstract
Background
Carbohydrate supplements are widely used by athletes as an ergogenic aid before and during sports events. The present systematic review and meta-analysis aimed at synthesizing all available data from randomized controlled trials performed under real-life conditions.
Methods
MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched systematically up to February 2015. Study groups were categorized according to test mode and type of performance measurement. Subgroup analyses were done with reference to exercise duration and range of carbohydrate concentration. Random effects and fixed effect meta-analyses were performed using the Software package by the Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager 5.3.
Results
Twenty-four randomized controlled trials met the objectives and were included in the present systematic review, 16 of which provided data for meta-analyses. Carbohydrate supplementations were associated with a significantly shorter exercise time in groups performing submaximal exercise followed by a time trial [mean difference −0.9 min (95 % confidence interval −1.7, −0.2), p = 0.02] as compared to controls. Subgroup analysis showed that improvements were specific for studies administering a concentration of carbohydrates between 6 and 8 % [mean difference −1.0 min (95 % confidence interval −1.9, −0.0), p = 0.04]. Concerning groups with submaximal exercise followed by a time trial measuring power accomplished within a fixed time or distance, mean power output was significantly higher following carbohydrate load (mean difference 20.2 W (95 % confidence interval 9.0, 31.5), p = 0.0004]. Likewise, mean power output was significantly increased following carbohydrate intervention in groups with time trial measuring power within a fixed time or distance (mean difference 8.1 W (95 % confidence interval 0.5, 15.7) p = 0.04].
Conclusion
Due to the limitations of this systematic review, results can only be applied to a subset of athletes (trained male cyclists). For those, we could observe a potential ergogenic benefit of carbohydrate supplementation especially in a concentration range between 6 and 8 % when exercising longer than 90 min.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12970-016-0139-6) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Carbohydrate supplementation, Ergogenic effects, Exercise, Meta-analysis, Systematic review
Background
Carbohydrates are one of the two main fuels for sport activities and their importance for optimal sport performance both in training and in competition is generally undisputed among experts [1, 2].
Carbohydrates are also used by athletes as an ergogenic aid before and during sport events even when they have repleted carbohydrate reserves. The scientific background of carbohydrates as an ergogenic nutritional supplement has been the subject of numerous investigations with the majority of results indicating a performance-enhancing effect of carbohydrate supplementation shortly before and during a performance bout [3–10].
In some of these studies, subjects were competing in a fasted state. Overnight fasting may probably result in more easily reproducible outcomes due to a more balanced state of metabolism in comparison to a postprandial state [11]. However, athletes intuitively avoid a fasted state before any competition and it is not recommended in the pertinent literature. It has been indicated that during an overnight fast liver glycogen stores are reduced substantially by amounts as high as 80 % [1, 2]. Therefore, suboptimal carbohydrate stores are likely to be present when beginning an exercise in a fasted state. Furthermore, many performance studies used time-to-exhaustion tests, which asses how long subjects can exercise at a given intensity. Again, this protocol does not always reflect the conditions of a real competition because athletes, at least in elite sports, should either perform as fast as possible for a given distance (e.g., races) or as well as possible within a given time (e.g., team sports). Currell and Jeukendrup [12] assessed various performance protocols and concluded that those in which subjects were asked to complete a fixed distance/amount of work as fast as possible or to accomplish as much work/distance as possible in a given time (i.e. time trails), yielded better results with respect to validity, reliability and sensitivity as compared to time-to-exhaustion protocols [12].
In 2013, a systematic review by Colombani and co-workers [11] addressed all these aspects. Their results suggests that only 11 out of 22 investigations included in the review resulted in a significant improvement of performance following carbohydrate supplementation indicating a high amount of uncertainty concerning the benefits of carbohydrate supplementation in field experiments trying to copy a realistic performance setting.
It was the purpose of the present study to expand the approach by Colombani et al. [11] via an updated literature search in order to yield an extended number of suitable studies so that the systematic review can be combined with a statistical synthesis of the available data using a meta-analytical approach.
Methods
Search strategy
Data of the original search by Colombani et al. [11] were used as starting point. The authors performed a search in “PubMed” up to September 3, 2011 using the following combination of key words: (Exercise OR Sport OR Athlete OR Athletes) AND (Hydration OR Water OR Fluid OR Drink OR Drinks OR Beverage OR Beverages OR Glycogen OR Loading OR Carbo OR Carbohydrate OR Carbohydrates OR Glucose OR Fructose OR Maltodextrin) NOT (Mice OR Mouse OR Pig OR Pigs OR Rat OR Rats OR Horse OR Horses OR Fish OR Dog OR Dogs OR Patient OR Patients OR Disease OR Diseases OR Diabetes OR Obesity OR Obese OR “Cord injury” OR “Wheelchair).
In addition to the systematic search of Colombani and coworkers [11] we searched the electronic databases “Embase” as well as the “Cochrane Central Register Of Controlled Trials” up to February, 2016 and expanded the search in “PubMed” starting September 4th, 2011 to February, 2016 using the same combinations of search terms with the following exceptions: we used “Human” and “Adult <18 to64 years” as further limitations in the database “Embase”. Hand search was done using the reference lists of two meta-analyses [7, 8], yielding one additional article suitable for this systematic review [13].
Inclusion criteria
In accordance to Colombani et al. [11], the following inclusion criteria were defined:
Randomized, crossover, placebo-controlled and if possible blinded study design. Blinding was not feasible as an absolute criterion, as sometimes the intervention could not be fully masked;
Mean age of the subjects between 18 and 40 years, but no restriction with respect to gender;
A reported VO2max ≥ 50 mL/kg/min (for an appropriate estimation of subject’s fitness level);
Assessment of body mass;
Subjects were tested in the postprandial state (between 2 h and 4 h after ingesting last meal);
Performance test had to be either of a time trial (TT) character or a submaximal exercise followed by a time trial (S + TT);
For studies with carbohydrate intake immediately prior to and/or during exercise, we included only studies with provision of any type of carbohydrates, electrolytes and water but no further components.
Exclusion criteria
Studies with time-to-exhaustion tests or studies with insufficient methodological information to enable a check of the inclusion criteria were excluded.
Categorization of interventions
To yield more homogeneous study designs it was necessary to categorize the studies by defining comparable interventions prior to statistical analysis. Classification of groups was performed according to test mode (cycling, running, soccer), carbohydrate intervention (carboloading vs. no carboloading; carbohydrate mouth rinse vs. placebo mouth rinse; ingestion of carbohydrate containing drinks vs. drinks containing no carbohydrates), type of intervention (TT or S + TT), and outcome [performance as time needed to cover a fixed distance (or a set amount of work); distance covered within a fixed time, or power accomplished within a fixed time (or fixed distance)]. Taken together, this resulted in the following classification of groups:
Group 1: Submaximal exercise followed by a time trial measuring time needed to cover a fixed distance or a fixed set amount of work;
Group 2: Time trial measuring time needed to cover a fixed distance or a fixed set amount of work;
Group 3: Submaximal exercise followed by a time trial measuring power (W) accomplished within a fixed time or distance;
Group 4: Time trial measuring power (W) accomplished within a fixed time or distance.
Furthermore, subgroups were formed in order to address two other research questions:
Whether the ergogenic effect is dependent on exercise duration (short duration < 90 min vs. long duration > 90 min);
If there is an advantage within a specified range of carbohydrate concentrations (6–8 % vs. 1–12 % vs. 12–18 %).
In the scientific literature, the different mechanisms for ergogenic effects of carbohydrates with respect to short and long lasting physical exercise was explained to be due to different carbohydrate availability. For exercise durations lasting ≤ 90 min there should be sufficient substrate without power loss given the condition of regularly filled glycogen stores [14–16]. Therefore we compared exercise durations ≤ and > than 90 min.
Statistical analyses
Data were analyzed using the Review Manager 5.3 software provided by the Cochrane Collaboration (http://tech.cochrane.org/revman). Differences in means were compared for outlining possible differences between carbohydrates and placebo with a fixed-effect meta-analysis using the inverse-variance method. However, when heterogeneity exceeded the level of 50 %, the random-effects model was used. The Cochrane Collaboration suggests to use meta-analyses in order to synthesize evidence from multiple experiments addressing the same research questions. Checking consistency of the results is of major importance in meta-analyses. Statistical heterogeneity in studies is characterized by 95 % CI that show poor overlap. We used the I2 statistic to detect heterogeneity [17]. If considerable heterogeneity is observed (I2 ≥ 50 %), fixed-effect models should be avoided, since they underperform in that context. Random effects models provide a more conservative approach yielding better estimates [18].
Descriptive data of included trials are given as mean ± SD. Pooled estimates of the effects size obtained by either comprehensive or subgroup meta-analyses are reported as mean difference together with the 95 % confidence intervals, respectively. P-values < 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. Moreover, effects sizes are given as standardized mean differences (SMD) for each analysis group as Additional files 1, 2, 3 and 4 (see corresponding Result section).
Results
Literature search
In the original literature search by Colombani et al. [11] performed in the electronic database Pubmed until September 3rd, 2011, 16,658 articles were identified. Our own updated search for literature yielded 15,105 articles (4,136 articles from PubMed published between September 4th, 2011 and February, 2016, 2,916 articles from Cochrane Central Register Of Controlled Trials, and 8,053 from Embase, respectively). Articles which contained sufficient information in the title or abstract to identify them as not eligible were discarded, if this was not the case, the full text was consulted. Furthermore, 12 reviews [3–6, 9, 10, 19–24] concerning this topic were hand-searched for eligible studies, however no additional study fulfilling the search criteria was identified. In total, the full text of 205 articles was examined yielding 24 studies that met the inclusion criteria and are displayed in the systematic review (Tables 1 and 2). 16 of these articles provided enough information to allow for a quantitative evaluation. Steps of article search and selection are summarized as a flow chart in Fig. 1.
Table 1.
General characteristics of randomized controlled trials included in the systematic review
| Reference | Type | Test | Mode | Test time | CHO content of pre-exercise meal (g/kg body weight) | Drink type during test | Drink during test per h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluid | CHO | |||||||
| Acker-Hewitt et al., 2012 [38] | CHO vs. W | S + TT | Cycle | 20 min + 44 min | 1.3 | 8 % CHO not specified | 0.7 L | 56 g |
| Angus et al., 2000 [44] | CHO vs. W | TT | Cycle | 166 min | 2.8 | 6 % CHO not specified | 1.0 L | 60 g |
| Beelen et al., 2009 [27]a | Mouth rinse | TT | Cycle | 68 min | 2.4 | 6.4 % MAL | 0.0 L | 0 g |
| Burke et al., 2000 [25]a | Carboloading | TT | Cycle | 148 min | 2 | Both trials same 7 % GLUP | 1.1 L | 72 g |
| Burke et al., 2002 [26]a | Carboloading | S + TT | Cycle | 120 + 25 min | 2 | Both trails same 6 % CHO, CHO not specified | 0.7 L | 44 g |
| Baur et al., 2014 [39] | CHO vs. W | S + TT | Cycle | 120 + 52 min | no data | a) 12 % GLU + FRU (2:1) b) 8 % GLU c) 12 % GLU |
0.8 L | a) 93 g b) 62 g c) 93 g |
| Campbell et al., 2008 [34] | CHO vs. W | S + TT | Cycle | a) 80 + 17 min b) 80 + 17 min c) 80 + 17 min |
male: 1.4 female: 1.6 |
All 5.9 % a) SUC + GLU + FRU drink b) MAL + FRU gel c) SUC + GLU sport beans |
0.7 L | 43 g |
| Clarke et al., 2011 [30]a | CHO vs. W | S + TT | Soccer | 90 + 3 min | no data | 6.6 % CHO not specified | 0.9 L | 59 g |
| Cox et al., 2008 [35] | CHO vs. W | S + TT | Cycle | 100 min + 30 min | 2.1 | 10 % GLU | 1.125 L | 112.5 g |
| Cox et al., 2010 [36] | CHO vs. W | S + TT | Cycle | 100 min + 30 min | 2.1 | 10 % GLU | 1.125 L | 112.5 g |
| Desbrow et al., 2004 [45] | CHO vs. W | TT | Cycle | 63 min | 2 | 6 % CHO not specified | 1.0 L | 61 g |
| El-Sayed et al., 1995 [33]a | CHO vs. W | S + TT | Cycle | 60 + 10 min | no data | 7.5 % GLU | 0.7 L | 54 g |
| El-Sayed et al., 1997 [47] | CHO vs. W | TT | Cycle | 60 min | no data | 8 % GLU | 0.3 L | 25 g |
| Flynn et al., 1989 [32]a | CHO vs. W | S + TT | Cycle | 105 + 15 min | 3.5 | 7.7 % GLUP & SUC | 0.7 L | 58 g |
| Ganio et al., 2010 [31] | CHO vs. W | S + TT | Cycle | 120 + 15 min | no data | 6 % CHO not specified | 0.9 L | 53 g |
| Hulston et al., 2009 [37] | CHO vs. W | S + TT | Cycle | 120 + 59 min | no data | 6 % GLU & FRU (2:1) | 0.8 L | 45 g |
| Hunter et al., 2002 [46] | CHO vs. W | TT | Cycle | 150 min | no data | 7 % CHO not specified | 0.6 L | 42 g |
| Jeukendrup et al., 2008 [22] | CHO vs. W | TT | Cycle | 26 min | no data | 6 % SUC & GLU (3:2) | 1.2 L | 70 g |
| Langenfeld et al., 1994 [40] | CHO vs. W | TT | Cycle | 241 min | no data | 7 % MAL & FRU (5:2) | 0.5 L | 37 g |
| McGawley et al., 2012 [29]a | CHO vs. W | S + TT | Run | 88 min + 40 min | no data | 14.4 % MAL + FRU (2:1) | 0.8 L | 115 g |
| Mitchell et al., 1989 [13] | CHO vs. W | S + TT | Cycle | 105 + 15 min | 0.7 | a) 6 % GLUP & SUC (2:1) b) 12 % GLUP & FRU (2.4:1) c) 18 % GLUP & FRU (4.1:1) |
0.6 L | a) 37 g b) 75 g c) 111 g |
| Nassif et al., 2014 [41] | CHO vs. W | TT | Cycle | 135 min | no data | 6 % CHO not specified | 0.63 L | 38 g |
| Rollo et al., 2010 [28]a | CHO vs. W | TT | Run | 60 min | 2.5 | 6.4 % CHO not specified | 0.4 L | 28 g |
| van Essen et al., 2006 [42] | CHO vs. W | TT | Cycle | 135 min | no data | 6 % SUC | 1.0 L | 60 g |
CHO carbohydrates, GLU glucose, GLUP glucose polymer, FRU fructose, MAL maltodextrin, SUC sucrose, S + TT submaximal exercise + time trial, TT time trial, W water
anot suitable for meta-analyses
Table 2.
Characteristics of participants in studies eligible for systematic review
| Reference | Number of subjects | Gender | Age | VO2max (mL/kg body mass/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acker-Hewitt et al., 2012 [38] | 10 | Males | 28 | 66 |
| Angus et al., 2000 [44] | 8 | Males | 22 | 65 |
| Beelen et al., 2009 [27]a | 14 | Males | 24 | 68 |
| Burke et al., 2000 [25]a | 7 | Males | 28 | 64 |
| Burke et al., 2002 [26]a | 8 | Males | 28 | 69 |
| Baur et al., 2014 [39] | 8 | Males | 25 | 62 |
| Campbell et al., 2008 [34] | 16 | 8 males/8 females | 35/32 | 59/50 |
| Clarke et al., 2011 [30]a | 12 | Males | 25 | 61 |
| Cox et al., 2008 [35] | 16 | Males | 31 | 65 |
| Cox et al., 2010 [36] | 16 | Males | 31 | 65 |
| Desbrow et al., 2004 [45] | 9 | Males | 30 | 65 |
| El-Sayed et al., 1995 [33]a | 9 | Males | 24 | 61 |
| El-Sayed et al., 1997 [47] | 8 | Males | 25 | 67 |
| Flynn et al., 1989 [32]a | 7 | Males | 29 | 62 |
| Ganio et al., 2010 [31] | 14 | Males | 27 | 60 |
| Hulston et al., 2009 [37] | 10 | Males | 28 | 62 |
| Hunter et al., 2002 [46] | 8 | Males | 24 | 65 |
| Jeukendrup et al., 2008 [22] | 12 | Males | 19 | 66 |
| Langenfeld et al., 1994 [40] | 14 | Males | 21 | 56 |
| McGawley et al., 2012 [29]a | 10 | 6 males/4 females | 26/24 | 63/62 |
| Mitchell et al., 1989 [13] | 10 | Males | 24 | 63 |
| Nassif et al., 2014 [41] | 10 | Males | 26 | 71 |
| Rollo et al., 2010 [28]a | 10 | Males | 34 | 62 |
| van Essen et al., 2006 [42] | 10 | Males | 24 | 63 |
anot suitable for meta-analyses
Fig. 1.
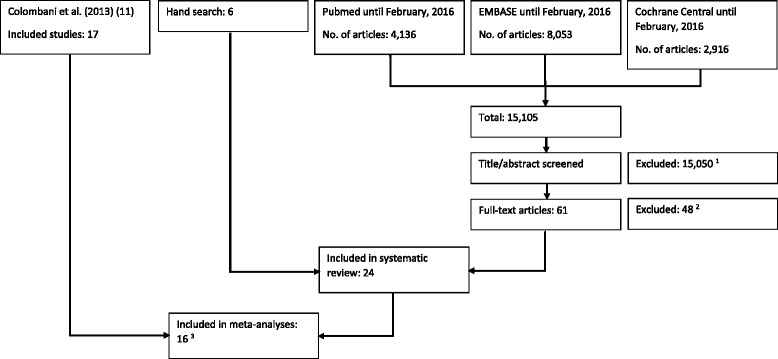
Flow diagram of article selection process. 1 Exclusion of duplicates. 2 not randomized controlled trials, different age group, no time trial or submaximal exercise followed by time trial. 3 Considerable differences with respect to type of exercise: McGawley et al., [29]; Rollo et al., [28]. Soccer-specific protocol: Clarke et al., [30]. Considerable differences with respect to carbohydrate intervention: Burke et al., [25]; Burke et al., [26]; Beelen et al., [27]. Inoperable presentation of data: El-Sayed et al., [33]; Flynn et al., [32]
Types of studies
Carbohydrate intervention
Two studies were carboloading interventions, one [25] using a TT as the performance test, the other one [26] a submaximal exercise followed by a TT.
We found one eligible study [27] with a mouth-rinse intervention, the remaining 21 studies compared the effect of a carbohydrate-containing drink versus a non-carbohydrate placebo. In eight of these interventions, the carbohydrate type was not specified with only the total amount of carbohydrate being reported. In the remaining 13 studies, either glucose, a glucose-polymer, maltodextrin, fructose, and/or sucrose was used as carbohydrate sources with a concentration ranging between 5.9 and 18 %.
Test mode
Most studies used cycling as their exercise mode with three exceptions: Rollo and Williams [28] measured performance while running a distance within a fixed time using a submaximal exercise followd by a TT, McGawley et al. [29] measured performance via running-time needed to cover a fixed distance using only TT, and Clarke et al. [30] investigated the ergogenic effect of carbohydrates with a soccer-specific mode.
Eleven studies used a TT as their performance test with test durations between 26 min to 241 min.
The remaining 13 investigations used a submaximal exercise followed by a TT with test durations between 20 + 44 min-120 + 59 min. Intervention and test modes for all studies are summarized in Tables 1 and 2, respectively.
All of the 16 studies provided enough information for a quantitative evaluation used cycling as their exercise mode. For reason of a better comparability, these studies were assigned to one of four different groups as described in the Methods section. Study designs with both time and power outcomes where assigned to all applicable groups. Two articles presented their outcomes as work [13, 31], which was converted into power prior to analyses by dividing work by the required time.
Results for group 1 and 3 were subdivided based on the administered carbohydrate concentrations, results for group 2 and 4 were subdivided based on exercise duration.
Exclusion of studies
Two studies tested the advantage of carbohydrates during a running exercise and were not included into one of the four groups because of considerable physiological differences between this and the other types of exercise [28, 29]. In addition, the study by Clarke et al. [30] was the only eligible study using a soccer-specific protocol and could therefore not be included in the meta-analysis. Other studies had to be excluded due to either different carbohydrate intervention [mouth rinse [27], carboloading [25, 26]], or presentation of data in an inoperable unit (N/m) [32], or presentation of results only via graphics, respectively [33].
Characteristics of subjects
Subjects were male with the exception of two studies [29, 34] enrolling both genders. Sample size varied between seven and 16 volunteers, mean age ranged between 19 and 35 years, and mean VO2max ranged between 50 and 71 ml/kg body weight/min.
Performance outcomes
For each of the four groups, results of both comprehensive as well as subgroup meta-analyses are given in Figs. 2, 3, 4 and 5, respectively. Please note that classification into subgroups was performed for every group independent of resulting numbers of studies.
Fig. 2.
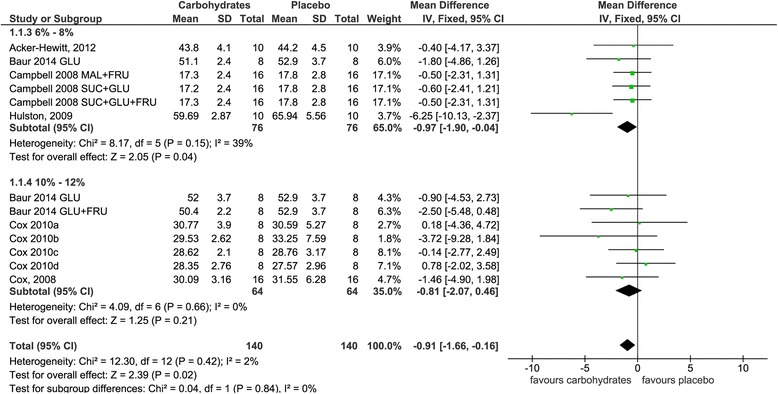
Effects of carbohydrate interventions as compared to placebo on time required to finish a time trial. Forest plot shows pooled mean differences with 95 % confidence intervals (CI) for 6 randomized controlled trials. Subgroup analyses show the results for carbohydrate concentrations ranging between 6–8 % and 10–12 %, respectively. The diamond at the bottom of the graph and the subgroups represents the pooled mean difference with the 95 % CI for all trials following fixed effect meta-analyses. GLU = glucose; FRU = fructose; MAL = maltodextrin; SUC = sucrose
Fig. 3.
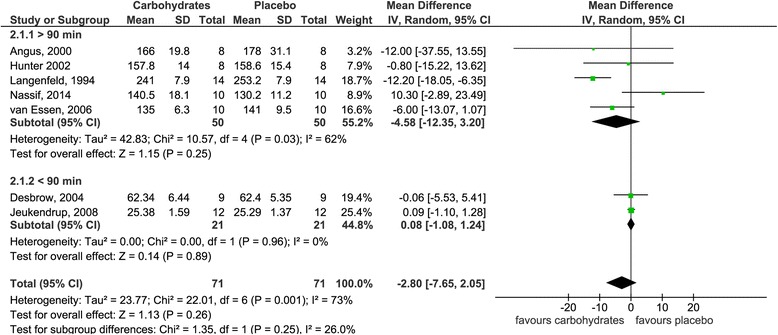
Effects of carbohydrate interventions as compared to placebo on time required to finish a time trial. Forest plot shows pooled mean differences with 95 % confidence intervals (CI) for 7 randomized controlled trials. Subgroup analyses show the results for exercise duration shorter than 90 min or longer than 90 min, respectively. The diamond at the bottom of the graph and the subgroups represents the pooled mean difference with the 95 % CI for all trials following random effects meta-analyses
Fig. 4.
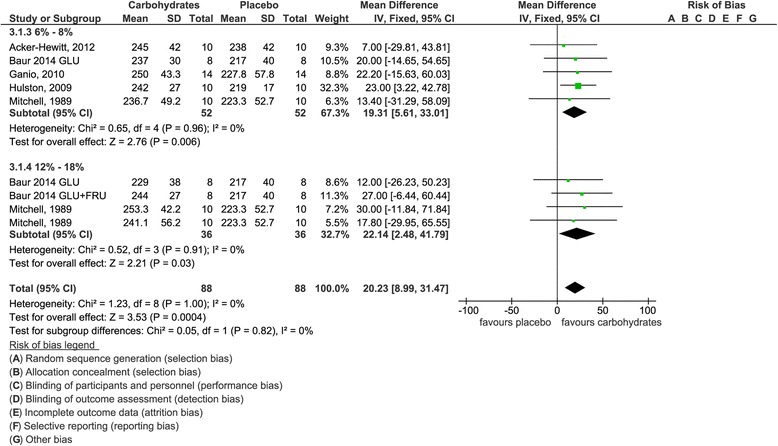
Effects of carbohydrate interventions as compared to placebo on mean power output. Forest plot shows pooled mean differences with 95 % confidence intervals (CI) for 5 randomized controlled trials. Subgroup analyses show the results for carbohydrate concentrations ranging between 6–8 % and 12–18 %, respectively. The diamond at the bottom of the graph and the subgroups represents the pooled mean difference with the 95 % CI for all trials following fixed effect meta-analyses. GLU = glucose; FRU = fructose
Fig. 5.
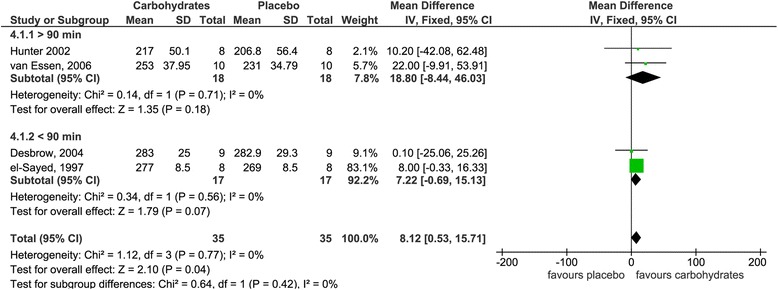
Effects of carbohydrate interventions as compared to placebo on mean power output. Forest plot shows pooled mean differences with 95 % confidence intervals (CI) for 4 randomized controlled trials. Subgroup analyses show the results for exercise duration shorter than 90 min or longer than 90 min, respectively. The diamond at the bottom of the graph and the subgroups represents the pooled mean difference with the 95 % CI for all trials following fixed effect meta-analyses
Group 1 included six studies [34–39] with 13 interventions in total. Pooled estimates of the effects size for the effects of carbohydrate interventions as compared to placebo on time required to finish a TT are presented in Fig. 2 (forest plot showing pooled SMD is given as Additional file 1). Carbohydrate interventions were associated with a significantly lower amount of time [mean differences −0.9 min (95 % CI −1.7, −0.2), p = 0.02]. Following subgroup analyses, significant performance improvements remained only for those studies administering a concentration of carbohydrates between 6 and 8 % [MD = −1.0 min (95 % CI −1.9, −0.0), p = 0.04].
Group 2 included seven studies [40–46] with seven interventions in total. Figure 3 summarizes the pooled estimates for effect size obtained by a random effects model due to the considerable heterogeneity between studies (I2 = 73 %; P = 0.001) (forest plot showing pooled SMD is given as Additional file 2). Average cycling time was faster in subjects ingesting carbohydrates as compared to placebo, however, without being statistically significant [mean difference 2.8 min (95 % CI −7.7, 2.1), p = 0.26]. Subgroup analysis including only studies with an exercise duration shorter than 90 min revealed a marginally higher average cycling time in the carbohydrate groups [mean difference 0.1 min (95 % CI −1.1, 1.2), p = 0.89]. In contrast, subgroup analysis taking into account studies with an exercise duration longer than 90 min resulted in a decreased average cycling time following carbohydrate ingestion when compared to placebo [mean difference −4.6 min (95 % CI −12.4, 3.2), p = 0.25].
Group 3 included five studies [13, 31, 37–39] with nine interventions in total, results of which are summarized in Fig. 4 (forest plot showing pooled SMD is given as Additional file 3). Mean power output was significantly more pronounced in participants subjected to a carbohydrate load as compared to placebo [mean difference 20.2 W (95 % CI 9.0, 31.5, p = 0.0004]. Comparable results could be obtained following subgroup analyses subclassifying carbohydrate interventions into ranges of 6–8 % [mean difference 19.3 W (95 % CI 5.6, 33.0), p = 0.006] and 12–18 % [mean difference 22.1 W (95 % CI 2.5, 41.8), p = 0.03], respectively.
Group 4 included four studies [42, 45–47] with four interventions in total. Meta-analytical data are depicted in Fig. 5 (forest plot showing pooled SMD is given as Additional file 4). Mean power output turned out to be significantly increased in volunteers following a carbohydrate intervention [mean difference 8.1 W (95 % CI 0.5, 15.7), p = 0.04]. Concerning subgroup analysis, performance tended to be higher in both studies with an exercise duration greater than 90 min [mean difference 18.8 W (95 % CI −8.4, 46.0), p = 0.18] and shorter than 90 min [mean difference 7.2 W (95 % CI −0.6, 15.1), p = 0.07] without yielding statistically significant results.
Discussion
Based upon the recent systematic review by Colombani et al. [11], it was the purpose of the present study to synthesize all available data from randomized controlled trials investigating the potential ergogenic effects of carbohydrate supplementation via meta-analysis. Due to the in-between heterogeneity of trials with respect to study design, we decided to evaluate only studies choosing cycling as the mode of exercise. Moreover, four groups of carbohydrate interventions with respect to test and performance measurement were classified in order to achieve a better comparability of results. Taken together, all four groups indicated an improved performance following carbohydrate intervention as compared to placebo with differences being statistically significant in group 1 (submaximal exercise followed by a time trial measuring time needed to cover a fixed distance or a fixed set amount of work), group 3 (submaximal exercise followed by a time trial measuring power (W) accomplished within a fixed time or distance), and group 4 (time trial measuring power (W) accomplished within a fixed time or distance), respectively.
Subgroups duration
Duration of exercise ≤ 90 min did not result in statistically significant differences between carbohydrate interventions and placebo either in group 2 or in group 4. These findings seem to be in contrast with studies reporting an improved performance via carbohydrate mouth rinsing [10, 48–54]. It has been suggested that oral receptors within the mouth and the digestive tract sense carbohydrates and activate brain regions associated with reward and pleasure which may lead to enhanced performance [5, 10, 48]. However, most mouth rinse studies were conducted in a fasted state [48, 50, 52, 53] or had other limitations such as lack of or improper randomization [51, 54] or uncertain time of last ingested meal [49]. In our systematic review, three studies [27, 33, 38] with an exercise duration less than 90 min could not be included in either groups 2 or group 4. Beelen et al. [27] demonstrated a non-significant performance decline when testing a carbohydrate mouth rinse. Likewise, Acker-Hewitt et al. [38] did not find a significantly better performance subsequent to a carbohydrate solution when compared to placebo, while El-Sayed et al. [33] could detect an increase in performance capacity. Therefore, it seems premature to finally evaluate the potential benefit of ingesting carbohydrates in short-term exercises (less than 90 min), further trials reflecting realistic conditions are necessary.
Subgroup analysis of five trials with a duration time higher than 90 min in group 2 resulted in a trend towards a decreased time needed to cover a fixed distance or a fixed set amount of work. A similar trend could be observed in group 4, albeit with only two trials included in the subgroup. Taking all results under consideration, a performance benefit through carbohydrates might be possible when exercise duration exceeds 90 min. However, similar to subgroups with ≤ 90 min, additional studies are required for evidence-based recommendations.
Subgroups carbohydrate concentration
Irrespective of specific carbohydrate concentrations, meta-analytical results of both groups 1 and 3 yielded statistically significant benefits for carbohydrate supplementation. In general, this might be due to multiple factors including maintenance of blood glucose [55–57] and high levels of carbohydrate oxidation especially towards the end of exercise [58, 59], thus sparing liver glycogen [60–63], as well as a central effect of carbohydrates [48, 52].
Regarding range of carbohydrate concentrations, results were statistically significant in favour of the lower range of 6–8 % of carbohydrate supplementation both in groups 1 and 3, while corresponding results for the higher range was only significant in group 3 (12–18 %), but not in group 1 (10–12 %). However, in both groups, the respective higher concentration range resulted in greater statistical variance when compared to the 6–8 % range. Therefore, one might speculate an impact of the administered carbohydrate type becoming more effective at higher concentrations. A high dose of ingested carbohydrates while exercising may cause gastrointestinal discomfort [64] which subsequently may decrease performance [65]. The maximal rate at which a single type of ingested carbohydrate can be oxidized is 60–70 g/h and ingesting more than this amount will not augment the oxidation rate but rather increases the chance for gastrointestinal discomfort [22]. It has been suggested that the ingestion of carbohydrates that use different, not competing, transporters increases the maximal carbohydrate oxidation rate (up to 105 g/h) [66], which has been verified by numerous studies [24, 39, 67–69]. In the study by Baur and co-workers [39], three different carbohydrate solutions were examined (8 % glucose solution, 12 % glucose solution, 12 % glucose–fructose (2:1) solution). The glucose-fructose solution achieved the greatest performance improvement, while the 12 % glucose solution did not affect performance significantly. Likewise, three different carbohydrate solutions (a 6 % glucose polymer-sucrose-solution (2:1, 37 g/h), a 12 % glucose polymer-fructose solution (2.4:1, 75 g/h), and an 18 % (4.1:1, 111 g/h) glucose polymer-fructose solution) were comparatively investigated in the trial by Mitchell et al. [13]. The best performance outcome was found with the 12 % glucose polymer-fructose solution. Despite no direct measurement of gastrointestinal symptoms, the authors concluded that the 18 % solution caused gastrointestinal distress and therefore the performance enhancement was not as high as with the 12 % solution [13].
Thus, the carbohydrate concentration resulting in optimal performance seems to be dependent on many factors, although our data suggests a more consistent benefit with carbohydrate solutions ranging between 6 and 8 %.
Strengths and limitations
The protocol of the present systematic review was designed to summarize the available evidence on the ergogenic effects of carbohydrate supplementation as an expansion of the results by Colombani et al. [11] focusing on randomized controlled trials investigating the outcomes of their interventions under real-life conditions (no overnight fasting, no time-to-exhaustion tests). Moreover, we decided to categorize trials with respect to types of test and performance measurements. This rigid protocol allows for better comparison between the different trials, it is associated with a number of limitations as well. First of all, the number of studies suitable for meta-analyses turned out to be rather low. All of the 16 trials providing extractable data for meta-analyses used cycling as their exercise mode. Although this might be another aspect increasing the homogeneity of the results, it is not possible to draw any conclusions for other types of exercise such as running. Data on the content of the last meal prior to trials suggest heterogeneous pre-exercise carbohydrate intake between studies. Another common limitation of performance studies is the only low to average power with respect to the number of participants ranging between 16 and 32 volunteers in the present meta-analyses. Since only one trial [39] enrolled subjects with a mean VO2max that would classify them as elite endurance athletes, the results are most likely not affected by heterogeneity between baseline capacities of study participants. In addition, with the exception of References [29] and [34], all trials were performed with male volunteers hampering transfer of results to female athletes. Following conversion of absolute values into percentage data, results were widely spread yielding improvements in assessed outcomes between 0.2 % [45] –13 % [13] as well as declines ranging between −0.6 % [22] and −7.3 % [41], respectively. This may serve as a potential indicator for the heterogeneous study designs.
Conclusions
In conclusion there may be a benefit for trained male cyclists when ingesting carbohydrates in a concentration range of 6–8 % just before and/or while exercising longer than 90 min. Due to lack of sufficient data, it is difficult to extrapolate this result to elite or generally female athletes. Moreover, further research is needed to gain additional information on exercise durations lower than 90 min and in a wider variety of types of exercise.
Abbreviations
CHO, carbohydrates; CI, confidence interval; FRU, fructose; GLU, glucose; GLUP, glucose polymers; MAL, maltodextrin; MD, mean difference; S + TT, submaximal exercise followed by time trial; SUC, sucrose; TT, time trial
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
This article was supported by the Open Access Publication Fund of the University of Vienna. No other sources of funding to be declared.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional files.
Authors’ contributions
PCC acquired part of the data (up to 9-3-2013). GH and LS developed the idea for this systematic review, GH prepared the protocol. Literature search was performed by MP and LS, while data extraction, analyses, and synthesis was done by all authors. GH prepared the first draft of the manuscript. Disagreements were resolved by consensus, all authors read and approved of the final manuscript.
Competing interests
PCC has received honoraria and free products from several companies producing and/or selling carbohydrate-containing sport drinks for diverse purposes (e.g., product development consultations, sponsorships of conferences organized by the authors, talks given to or for the companies). All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional files
Effects of carbohydrate interventions as compared to placebo on time required to finish a time trial. Forest plot shows pooled standardized mean differences with 95 % confidence intervals (CI) for 6 randomized controlled trials. Subgroup analyses show the results for carbohydrate concentrations ranging between 6–8 % and 10–12 %, respectively. The diamond at the bottom of the graph and the subgroups represents the pooled mean difference with the 95 % CI for all trials following fixed effect meta-analyses. GLU = glucose; FRU = fructose; MAL = maltodextrin; SUC = sucrose. Title: File format: tiff (TIF 7950 kb)
Effects of carbohydrate interventions as compared to placebo on time required to finish a time trial. Forest plot shows pooled standardized mean differences with 95 % confidence intervals (CI) for 7 randomized controlled trials. Subgroup analyses show the results for exercise duration shorter than 90 min or longer than 90 min, respectively. The diamond at the bottom of the graph and the subgroups represents the pooled mean difference with the 95 % CI for all trials following random effects meta-analyses. (TIF 6850 kb)
Effects of carbohydrate interventions as compared to placebo on mean power output. Forest plot shows pooled standardized mean differences with 95 % confidence intervals (CI) for 5 randomized controlled trials. Subgroup analyses show the results for carbohydrate concentrations ranging between 6–8 % and 12–18 %, respectively. The diamond at the bottom of the graph and the subgroups represents the pooled mean difference with the 95 % CI for all trials following fixed effect meta-analyses. GLU = glucose; FRU = fructose. (TIF 7339 kb)
Effects of carbohydrate interventions as compared to placebo on mean power output. Forest plot shows pooled standardized mean differences with 95 % confidence intervals (CI) for 4 randomized controlled trials. Subgroup analyses show the results for exercise duration shorter than 90 min or longer than 90 min, respectively. The diamond at the bottom of the graph and the subgroups represents the pooled mean difference with the 95 % CI for all trials following fixed effect meta-analyses. (TIF 5891 kb)
References
- 1.Rodriguez NR, Di Marco NM, Langley S. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Nutrition and athletic performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41:709–31. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e31890eb86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Burke L, Deakin V. Clinical sports nutrition. 4. McGraw-Hill Medical: Sydney; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Correia-Oliveira CR, Bertuzzi R, Dal'Molin Kiss MAP, Lima-Silva AE. Strategies of dietary carbohydrate manipulation and their effects on performance in cycling time trials. Sports Med. 2013;43:707–19. doi: 10.1007/s40279-013-0054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ormsbee MJ, Bach CW, Baur DA. Pre-exercise nutrition: the role of macronutrients, modified starches and supplements on metabolism and endurance performance. Nutrients. 2014;6:1782–808. doi: 10.3390/nu6051782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Burke LM, Maughan RJ. The Governor has a sweet tooth - Mouth sensing of nutrients to enhance sports performance. Eur J Sport Sci. 2015;15:29–40. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2014.971880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Stellingwerff T, Cox GR. Systematic review: Carbohydrate supplementation on exercise performance or capacity of varying durations. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2014;39:998–1011. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2014-0027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Vandenbogaerde TJ, Hopkins WG. Effects of acute carbohydrate supplementation on endurance performance: a meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2011;41:773–92. doi: 10.2165/11590520-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Temesi J, Johnson NA, Raymond J, Burdon CA, O'Connor HT. Carbohydrate ingestion during endurance exercise improves performance in adults. J Nutr. 2011;141:890–7. doi: 10.3945/jn.110.137075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cermak NM, van Loon LJC. The use of carbohydrates during exercise as an ergogenic aid. Sports Med. 2013;43:1139–55. doi: 10.1007/s40279-013-0079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.de Ataide e Silva T, de Di Cavalcanti Alves Souza ME, Amorim JF, Stathis CG, Leandro CG, Lima-Silva AE. Can carbohydrate mouth rinse improve performance during exercise? A systematic review. Nutrients. 2014;6:1–10. doi: 10.3390/nu6010001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Colombani PC, Mannhart C, Mettler S. Carbohydrates and exercise performance in non-fasted athletes: a systematic review of studies mimicking real-life. Nutr J. 2013;12:16. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-12-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Currell K, Jeukendrup AE. Validity, reliability and sensitivity of measures of sporting performance. Sports Med. 2008;38:297–316. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200838040-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mitchell JB, Costill DL, Houmard JA, Fink WJ, Pascoe DD, Pearson DR. Influence of carbohydrate dosage on exercise performance and glycogen metabolism. J Appl Physiol. 1989;67:1843–9. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.5.1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jeukendrup A, Brouns F, Wagenmakers AJ, Saris WH. Carbohydrate-electrolyte feedings improve 1 h time trial cycling performance. Int J Sports Med. 1997;18:125–9. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-972607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hawley JA, Schabort EJ, Noakes TD, Dennis SC. Carbohydrate-loading and exercise performance. An update. Sports Med. 1997;24:73–81. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199724020-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Carter JM, Jeukendrup AE, Mann CH, Jones DA. The effect of glucose infusion on glucose kinetics during a 1-h time trial. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36:1543–50. doi: 10.1249/01.MSS.0000139892.69410.D8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brockwell SE, Gordon IR. A comparison of statistical methods for meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2001;20(6):825–40. doi: 10.1002/sim.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Coggan AR, Coyle EF. Carbohydrate ingestion during prolonged exercise: effects on metabolism and performance. Exerc Sports Sci Rev. 1991;19:1–40. doi: 10.1249/00003677-199101000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jeukendrup AE. Carbohydrate intake during exercise and performance. Nutrition. 2004;20:669–77. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2004.04.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schubert MM, Astorino TA. A systematic review of the efficacy of ergogenic aids for improving running performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2013;27:1699–707. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e31826cad24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jeukendrup AE. Carbohydrate feeding during exercise. Eur J Sport Sci. 2008;8:77–86. doi: 10.1080/17461390801918971. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Coombes JSHKL. The effectiveness of commercially available sports drinks. Sports Med. 2000;29:181–209. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200029030-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wallis GA, Wittekind A. Is there a specific role for sucrose in sports and exercise performance? Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2013;23:571–83. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.23.6.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Burke LM, Hawley JA, Schabort EJ, St Clair Gibson A, Mujika I, Noakes TD. Carbohydrate loading failed to improve 100-km cycling performance in a placebo-controlled trial. J Appl Physiol. 2000;88:1284–90. doi: 10.1152/jappl.2000.88.4.1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Burke LM, Hawley JA, Angus DJ, Cox GR, Clark SA, Cummings NK, et al. Adaptations to short-term high-fat diet persist during exercise despite high carbohydrate availability. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34:83–91. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200201000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Beelen M, Berghuis J, Bonaparte B, Ballak SB, Jeukendrup AE, van Loon LJC. Carbohydrate mouth rinsing in the fed state: lack of enhancement of time-trial performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2009;19:400–9. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.19.4.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rollo I, Williams C. Influence of ingesting a carbohydrate-electrolyte solution before and during a 1-hour run in fed endurance-trained runners. J Sports Sci. 2010;28:593–601. doi: 10.1080/02640410903582784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.McGawley K, Shannon O, Betts J. Ingesting a high-dose carbohydrate solution during the cycle section of a simulated Olympic-distance triathlon improves subsequent run performance. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2012;37:664–71. doi: 10.1139/h2012-040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Clarke ND, Maclaren DPM, Reilly T, Drust B. Carbohydrate ingestion and pre-cooling improves exercise capacity following soccer-specific intermittent exercise performed in the heat. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011;111:1447–55. doi: 10.1007/s00421-010-1771-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ganio MS, Klau JF, Lee EC, Yeargin SW, McDermott BP, Buyckx M. Effect of various carbohydrate-electrolyte fluids on cycling performance and maximal voluntary contraction. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2010;20:104–14. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.20.2.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Flynn MG, Michaud TJ, Rodriguez-Zayas J, Lambert CP, Boone JB, Moleski RW. Effects of 4- and 8-h preexercise feedings on substrate use and performance. J Appl Physiol. 1989;67:2066–71. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.5.2066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.el-Sayed MS, Rattu AJ, Roberts I. Effects of carbohydrate feeding before and during prolonged exercise on subsequent maximal exercise performance capacity. Int J Sport Nutr. 1995;5:215–24. doi: 10.1123/ijsn.5.3.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Campbell C, Prince D, Braun M, Applegate E, Casazza GA. Carbohydrate-supplement form and exercise performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2008;18:179–90. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.18.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cox AJ, Pyne DB, Cox GR, Callister R, Gleeson M. Pre-exercise carbohydrate status influences carbohydrate-mediated attenuation of post-exercise cytokine responses. Int J Sports Med. 2008;29:1003–9. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1038753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cox GR, Clark SA, Cox AJ, Halson SL, Hargreaves M, Hawley JA, et al. Daily training with high carbohydrate availability increases exogenous carbohydrate oxidation during endurance cycling. J Appl Physiol. 2010;109:126–34. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00950.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hulston CJ, Jeukendrup AE. No placebo effect from carbohydrate intake during prolonged exercise. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2009;19:275–84. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.19.3.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Acker-Hewitt TL, Shafer BM, Saunders MJ, Goh Q, Luden ND. Independent and combined effects of carbohydrate and caffeine ingestion on aerobic cycling performance in the fed state. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2012;37:276–83. doi: 10.1139/h11-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Baur DA, Schroer AB, Luden ND, Womack CJ, Smyth SA, Saunders MJ. Glucose-fructose enhances performance versus isocaloric, but not moderate, glucose. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014;46:1778–86. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000000284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Langenfeld ME, Seifert JG, Rudge SR, Bucher RJ. Effect of carbohydrate ingestion on performance of non-fasted cyclists during a simulated 80-mile time trial. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 1994;34:263–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nassif C, Gomes AR, Peixoto GHC, Chagas MH, Soares DD, Silami-Garcia E, et al. The effect of double--blind carbohydrate ingestion during 60 km of self-paced exercise in warm ambient conditions. PloS One. 2014;9:e104710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.van Essen M, Gibala MJ. Failure of protein to improve time trial performance when added to a sports drink. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006;38:1476–83. doi: 10.1249/01.mss.0000228958.82968.0a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jeukendrup AE, Hopkins S, Aragon-Vargas LF, Hulston C. No effect of carbohydrate feeding on 16 km cycling time trial performance. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2008;104:831–7. doi: 10.1007/s00421-008-0838-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Angus DJ, Hargreaves M, Dancey J, Febbraio MA. Effect of carbohydrate or carbohydrate plus medium-chain triglyceride ingestion on cycling time trial performance. J Appl Physiol. 2000;88:113–9. doi: 10.1152/jappl.2000.88.1.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Desbrow B, Anderson S, Barrett J, Rao E, Hargreaves M. Carbohydrate-electrolyte feedings and 1 h time trial cycling performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2004;14:541–9. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.14.5.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hunter AM, St Clair Gibson A, Collins M, Lambert M, Noakes TD. Caffeine ingestion does not alter performance during a 100-km cycling time-trial performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2002;12:438–52. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.12.4.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.el-Sayed MS, Balmer J, Rattu AJ. Carbohydrate ingestion improves endurance performance during a 1 h simulated cycling time trial. J Sports Sci. 1997;15:223–30. doi: 10.1080/026404197367506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chambers ES, Bridge MW, Jones DA. Carbohydrate sensing in the human mouth: effects on exercise performance and brain activity. J Physiol. 2009;587:1779–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.164285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Pottier A, Bouckaert J, Gilis W, Roels T, Derave W. Mouth rinse but not ingestion of a carbohydrate solution improves 1-h cycle time trial performance. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2010;20:105–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2008.00868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rollo I, Cole M, Miller R, Williams C. Influence of mouth rinsing a carbohydrate solution on 1-h running performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42:798–804. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181bac6e4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lane SC, Bird SR, Burke LM, Hawley JA. Effect of a carbohydrate mouth rinse on simulated cycling time-trial performance commenced in a fed or fasted state. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2013;38:134–9. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2012-0300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Carter JM, Jeukendrup AE, Jones DA. The effect of carbohydrate mouth rinse on 1-h cycle time trial performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36:2107–11. doi: 10.1249/01.MSS.0000147585.65709.6F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rollo I, Williams C, Gant N, Nute M. The influence of carbohydrate mouth rinse on self-selected speeds during a 30-min treadmill run. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2008;18:585–600. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.18.6.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sinclair J, Bottoms L, Flynn C, Bradley E, Alexander G, McCullagh S, et al. The effect of different durations of carbohydrate mouth rinse on cycling performance. Eur J Sport Sci. 2014;14:259–64. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2013.785599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Erickson MA, Schwarzkopf RJ, McKenzie RD. Effects of caffeine, fructose, and glucose ingestion on muscle glycogen utilization during exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1987;19:579–83. doi: 10.1249/00005768-198712000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Pirnay F, Crielaard JM, Pallikarakis N, Lacroix M, Mosora F, Krzentowski G, et al. Fate of exogenous glucose during exercise of different intensities in humans. J Appl. Physiol. 1982;53:1620–4. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.6.1620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Costill DL, Bennett A, Branam G, Eddy D. Glucose ingestion at rest and during prolonged exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1973;34:764–9. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.34.6.764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Coggan AR, Coyle EF. Metabolism and performance following carbohydrate ingestion late in exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1989;21:59–65. doi: 10.1249/00005768-198902000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Coyle EF, Coggan AR, Hemmert MK, Ivy JL. Muscle glycogen utilization during prolonged strenuous exercise when fed carbohydrate. J Appl Physiol. 1986;61:165–72. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Jeukendrup AE, Raben A, Gijsen A, Stegen JH, Brouns F, Saris WH, Wagenmakers AJ. Glucose kinetics during prolonged exercise in highly trained human subjects: effect of glucose ingestion. J Physiol. 1999;515(Pt 2):579–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.579ac.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Howlett K, Angus D, Proietto J, Hargreaves M. Effect of increased blood glucose availability on glucose kinetics during exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1998;84:1413–7. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1998.84.4.1413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.van Handel PJ, Fink WJ, Branam G, Costill DL. Fate of 14 C Glucose ingested during prolonged exercise. Int J Sports Med. 1980;1:127–31. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1034647. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Bosch AN, Dennis SC, Noakes TD. Influence of carbohydrate ingestion on fuel substrate turnover and oxidation during prolonged exercise. J Appl Physiol. (Bethesda, MD) 1994;76:2364–72. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1994.76.6.2364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Brouns F, Beckers E. Is the gut an athletic organ? Digestion, absorption and exercise. Sports Med. 1993;15:242–57. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199315040-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Rowlands DS, Swift M, Ros M, Green JG. Composite versus single transportable carbohydrate solution enhances race and laboratory cycling performance. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2012;37:425–36. doi: 10.1139/h2012-013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Jentjens RL, Jeukendrup AE. High rates of exogenous carbohydrate oxidation from a mixture of glucose and fructose ingested during prolonged cycling exercise. Br J Nutr. 2005;93:485–92. doi: 10.1079/BJN20041368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Triplett D, Doyle JA, Rupp JC, Benardot D. An isocaloric glucose-fructose beverage’s effect on simulated 100-km cycling performance compared with a glucose-only beverage. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2010;20:122–31. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.20.2.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Wallis GA, Rowlands DS, Shaw C, Jentjens RLPG, Jeukendrup AE. Oxidation of combined ingestion of maltodextrins and fructose during exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37:426–32. doi: 10.1249/01.MSS.0000155399.23358.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Currell K, Jeukendrup AE. Superior endurance performance with ingestion of multiple transportable carbohydrates. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008;40:275–81. doi: 10.1249/mss.0b013e31815adf19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional files.


