Significance
The Cheerios effect is the attraction of solid particles floating on liquids, mediated by surface tension forces. We demonstrate experimentally that a similar interaction can also occur for the inverse case, liquid particles on the surface of solids, provided that the solid is sufficiently soft. Remarkably, depending on the thickness of the solid layer, the interaction can be either purely attractive or become repulsive. A theoretical model, in excellent agreement with the experimental data, shows that the interaction requires both elasticity and capillarity. Interactions between objects on soft substrates could play an important role in phenomena of cell–cell interaction and cell adhesion to biological tissues, and be exploited to engineer soft smart surfaces for controlled drop coalescence and colloidal assembly.
Keywords: elastocapillarity, wetting, soft matter, mechanosensing, droplets
Abstract
Solid particles floating at a liquid interface exhibit a long-ranged attraction mediated by surface tension. In the absence of bulk elasticity, this is the dominant lateral interaction of mechanical origin. Here, we show that an analogous long-range interaction occurs between adjacent droplets on solid substrates, which crucially relies on a combination of capillarity and bulk elasticity. We experimentally observe the interaction between droplets on soft gels and provide a theoretical framework that quantitatively predicts the interaction force between the droplets. Remarkably, we find that, although on thick substrates the interaction is purely attractive and leads to drop–drop coalescence, for relatively thin substrates a short-range repulsion occurs, which prevents the two drops from coming into direct contact. This versatile interaction is the liquid-on-solid analog of the “Cheerios effect.” The effect will strongly influence the condensation and coarsening of drops on soft polymer films, and has potential implications for colloidal assembly and mechanobiology.
The long-ranged interaction between particles trapped at a fluid interface is exploited for the fabrication of microstructured materials via self-assembly and self-patterning (1–5) and occurs widely in the natural environment when living organisms or fine particles float on the surface of water (6, 7). In a certain class of capillary interactions, the particles deform the interface because of their shape or chemical heterogeneity (8–10). In this case, the change in interfacial area upon particle–particle approach causes an attractive capillary interaction between the particles. In the so-called Cheerios effect, the interaction between floating objects is mainly due to the change in gravitational potential energy associated to the weight of the particles, which deform the interface while being supported by surface tension (11), and the same principle applies when the interface is elastic (12–14). The name “Cheerios effect” is reminiscent of breakfast cereals floating on milk and sticking to each other or to the walls of the breakfast bowl.
Here, we consider a situation opposite to that of the Cheerios effect, liquid drops deposited on a solid. The solid is sufficiently soft to be deformed by the surface tension of the drops, resulting in a lateral interaction. Recent studies have provided a detailed view of statics of single-drop wetting on deformable surfaces (15–19). The length scale over which the substrate is deformed is set by the ratio of the droplet surface tension γ and the substrate shear modulus G. The deformation can be seen as an elastocapillary meniscus, or “wetting ridge,” around the drop (Fig. 1 A and B). Interestingly, the contact angles at the edge of the drop are governed by Neumann’s law, just as for oil drops floating on water. In contrast to the statics of soft wetting, its dynamics has only been explored recently. New effects such as stick–slip motion induced by substrate viscoelasticity (20, 21) and droplet migration due to stiffness gradients (22) have been revealed. The possibility that elastocapillarity induces an interaction between neighboring drops is of major importance for applications such as drop condensation on polymer films (23) and self-cleaning surfaces (24–27). The interaction between drops on soft surfaces might also provide insights into the mechanics of cell locomotion (28–30) and cell–cell interaction (31).
Fig. 1.
The inverse Cheerios effect for droplets on soft solids. Two liquid drops sliding down a soft gel exhibit a mutual interaction mediated by the elastic deformation of the substrate. (A) Drops sliding down a thick elastic layer attract each other, providing a new mechanism for coalescence. (B) Drops sliding down a thin elastic layer (thickness ) repel each other. (C) Measurement of the horizontal relative velocities of droplet pairs, as a function of separation distance d. This measurement quantifies the interaction strength. (D) Sliding velocity of isolated droplets on the thick layer as a function of their volume. These data are used to calibrate the relation between force (gravity) and sliding velocity.
Here, we show experimentally that long-ranged elastic deformations lead to an interaction between neighboring liquid drops on a layer of cross-linked polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The layer is sufficiently soft for significant surface tension-induced deformations to occur (Fig. 1). The interaction we observe can be thought of as the inverse Cheerios effect, because the roles of the solid and liquid phases are exchanged. Remarkably, the interaction can be either attractive or repulsive, depending on the geometry of the gel. We propose a theoretical derivation of the interaction force from a free-energy calculation that self-consistently accounts for the deformability of both the liquid drop and the elastic solid.
Experiment: Attraction Versus Repulsion
Here, the inverted Cheerios effect is observed with submillimeter drops of ethylene glycol on a PDMS gel. The gel is a reticulated polymer network formed by crosslinking small multifunctional prepolymers—contrary to hydrogels, there is no liquid phase trapped inside the network. The low shear modulus of the PDMS gel gives an elastocapillary length sufficiently large to be measurable in the optical domain.
The interaction between two neighboring liquid drops is quantified by tracking their positions while they are sliding under the effect of gravity along the surface of a soft solid held vertically. The interaction can be either attractive (Fig. 1A) or repulsive (Fig. 1B): drops on relatively thick gel layers attract each other, whereas drops on relatively thin layers experience a repulsion.
The drop–drop interaction induces a lateral motion that can be quantified by measuring the horizontal component of the relative droplet velocity, ( implies repulsion). In Fig. 1C, we report as a function of the separation d, defined as the shortest distance between the surfaces of the drops. The drops () exhibit attraction when sliding down a thick layer (, black curve), whereas they repel on a thin layer (, red curve). The value of is larger at close proximity, signaling an increase in the interaction force. Spontaneous merging occurs where drops come into direct contact. Importantly, these interactions provide a new mechanism for droplet coarsening (or ordering) by coalescence (or its suppression) that has no counterpart on rigid surfaces.
The interaction force F can be inferred from the relative velocities between the drops, by using an effective “drag law”, where the drag is due to sliding on the gel. We first calibrate this drag law by considering drops that are sufficiently separated, so that they do not experience any mutual interaction. The motion is purely downward and driven only by a gravitational force (inertia is negligible). Fig. 1D shows that the droplet velocity approximately scales as . This force–velocity calibration curve is in good agreement with viscoelastic dissipation in the gel, based on which one expects the scaling law (21):
| [1] |
Here, n is the rheological exponent that emerges from the scale invariance of the gel network (32–34), and τ is a characteristic timescale. The parameter values and are calibrated in a rheometer (SI Materials and Methods). Eq. 1 is valid for v below the characteristic rheological speed, . Our approach is justified here because for the silicone gel, whereas the reported speeds reach at most . The large viscoelastic dissipation in the gel exceeds the dissipation within the drop by orders of magnitude, and explains these extremely slow drop velocities observed experimentally (21, 35). In this case, it was also shown that all of the dissipation occurs in a very narrow region around the wetting ridge (21). Therefore, the dynamic substrate deformation approaches the corresponding static deformation beyond a distance from the contact line. The force–distance relation for the inverse Cheerios effect can now be measured directly using the independently calibrated force–velocity relation (Fig. 1D and Eq. 1). By monitoring how the trajectories are deflected with respect to the downward motion of the drops, we obtain F (see Materials and Methods for additional details). Despite the different origins of calibration and interaction forces, both are balanced by the same dissipative mechanism because the dissipative viscoelastic force is nearly perfectly localized at the contact line (21), which corroborates the validity of our calibration routine.
The key result is shown in Fig. 2, where we report the interaction force F as a function of distance d. Fig. 2A shows experimental data for the attractive force () between drops on thick layers (black dots), together with the theoretical prediction outlined below. Movie S1 shows an example of attractive drop–drop interaction. The attractive force is of the order of micronewtons, which is comparable to both the capillary force scale and the elastic force scale . The force decreases for larger distance and its measurable influence was up to .
Fig. 2.
Measured interaction force F (symbols) as a function of their separation d, compared with the 3D theory (red lines, no adjustable parameters). (A) Attraction on a thick elastic layer (). (B) Repulsion and attraction on a thin layer (). Each data point represents an average over ∼10 realizations, with the error bars giving the SD. Measurements are based on pairs of ethylene glycol drops whose radii are in the range . The elastic substrate has a static shear modulus of .
Fig. 2B shows the interaction force between drops on thin layers. The dominant interaction is now repulsive () (Movie S2). Intriguingly, we find that the interaction is not purely repulsive, but displays an attractive range at very small distance. It is possible to access this range experimentally in case the motion of the individual drops are sufficiently closely aligned (Movie S3). The “neutral” distance for which the interaction force changes sign appears when the separation is comparable to the substrate thickness , suggesting that the key parameter governing whether the drops attract or repel is the thickness of the gel.
Mechanism of Interaction: Rotation of Elastic Meniscus
We explain the attraction versus repulsion of neighboring drops by computing the total free energy of drops on gel layers of different thicknesses. The interaction force between the drops is equal to the energy gradient with respect to the separation, , which in the experiment is balanced by the forces due to viscoelastic dissipation in the vicinity of the contact line. In contrast to the normal Cheerios effect, which involves two rigid particles, both the droplet and the elastic substrate are deformable, and their shapes will change upon varying the distance d. Hence, the interaction force involves both the elastic and the surface tension contributions to the free energy. The free energy emerges from self-consistently computed shapes of the drops and elastic deformations.
To reveal the mechanism of interaction, we first consider 2D drops, for which the free energy can be written as follows:
| [2] |
The geometry is sketched in Fig. 3 B and C, and further details are given in Supporting Information and Fig. S1. The elastic energy is a functional of the profile describing the shape of the elastic solid: the functional explicitly depends on the layer thickness and is ultimately responsible for the change from attraction to repulsion. The function represents the shape of the liquid–vapor interface. The integrals in Eq. 2 represent the interfacial energies; they depend on the surface tensions γ, , associated with the liquid–vapor, solid–liquid, and solid–vapor interfaces, respectively. For the sake of simplicity, we ignore here the possibility of a dependence of surface energy on the elastic strain. In absence of the Shuttleworth effect (36), surface stress and surface energy are equal.
Fig. 3.
Mechanism of interaction between two liquid drops on a soft solid. (A) Deformation induced by a single droplet on a thick substrate. The zoom near the contact line illustrates that the contact angles satisfy the Neumann condition. (B) A second drop placed on a thick substrate experiences a background profile due to the deformation induced by the neighboring drop on the right. This background profile is shown in red. As a consequence, the solid angles near the elastic meniscus rotate by an angle φ (see zoom). This rotation perturbs the Neumann balance, yielding an attractive force f. In the experiment, this force is balanced by the dissipative force due to the viscoelastic deformation of the wetting ridge. (C) On a thin substrate the single-drop profile yields a nonmonotonic elastic deformation. The zoom illustrates a rotation φ of the Neumann triangle in the opposite direction, leading to a repulsive interaction.
Fig. S1.
Problem setup. Two liquid droplets on an elastic half space. Energy is to be minimized with respect to , , , , and . The liquid angles and follow from the minimization. The distance d between the adjacent contact lines is enforced with a Lagrange multiplier f acting on .
At equilibrium, the droplet shapes can be found by analyzing the changes in the free energy upon variations of the functions and . The variation of the contact line positions provide the relevant boundary conditions (19). However, when two drops are separated by a finite distance d, the drops are not at equilibrium: the gradient in free energy results into an overdamped motion in which changes in free energy are dissipated in the solid. To compute the interaction force f (per unit length in the 2D model), one therefore needs to consider the work done by the dissipative force −f that we can assume to be localized near the inner contact line. This allows one to determine the interaction force , with the convention that attractive forces correspond to (see Supporting Information and Fig. S2 for details).
Fig. S2.
Force–distance curve for 2D droplets on elastic half space (log–log scale), for , . The Inset shows solid profiles at the indicated distances.
The energy minimization reveals the mechanism of drop–drop interaction: the interaction force f appears in the boundary condition for the contact angles,
| [3] |
where the angles are defined in Fig. 3. Eq. 3 can be thought of as an “imbalance” of the static Neumann boundary condition. The resulting interaction force due to the elastocapillary energy gradient is balanced by the dissipation due to the viscoelastic nature of the substrate. For a single droplet, the contact angles satisfy Neumann’s law, which is Eq. 3 with (Fig. 3A). On a thick elastic layer, the overall shape of the wetting ridge is of the following form (18, 19):
| [4] |
where the horizontal scale is set by the elastocapillary length based on the solid surface tension . The origin of f can be understood from the principle of superposition. Due to the substrate deformation of a single drop, a second drop approaching the first one will see a surface that is locally rotated by an angle . The elastic meniscus near the inner contact line of this approaching drop will correspondingly be rotated by an angle φ (Fig. 3B). Importantly, changes in the liquid angle θ scale as , which for large drops can be ignored. As a consequence, this meniscus rotation induces a net resultant surface tension forces according to Eq. 3, which is balanced by the dissipative force f due to the viscoelastic nature of the substrate (21). For small rotations, one obtains , where φ follows from the single-drop deformation (Eq. 4). There is no resultant interaction force from the stress below the drop, which, due to deformability of the drop, results only in a uniform pressure on the solid-liquid interface.
The inverted Cheerios effect is substantially different from the Cheerios effect between two particles floating at the surface of a liquid. Apart from the drop being deformable, we note that the energy driving the interaction is different in the two cases: whereas the liquid interface shape is determined by the balance between gravity and surface tension in the Cheerios effect, the solid shape is determined by elastocapillarity in the inverted Cheerios effect. Another difference is the mechanism by which the interaction is mediated. The Cheerios effect is primarily driven by a change in gravitational potential energy, which implies a vertical displacement of particles: a heavy particle slides downward, like a bead on a string, along the deformation created by a neighboring particle (11). A similar interaction was recently discussed for rigid cylinders that deform an elastic surface due to gravity (14). In contrast, the inverted Cheerios effect discussed here does not involve gravity and can be totally ascribed to elastocapillary tilting of the solid interfaces, as shown in Fig. 3.
The rotation of contact angles explains why the drop–drop interaction can be either attractive or repulsive. On a thick substrate, the second drop experiences solid contact angles that are rotated counterclockwise, inducing an attractive force (Fig. 3B). In contrast, on a thin substrate, the elastic deformation induced by the second drop has a nonmonotonic profile . This is due to volume conservation of the substrate: lifting the gel near the contact line creates a depression at larger distances (Fig. 3C). The rotation of the contact angles thus changes sign, and, accordingly, the interaction force changes from attractive to repulsive. The relevant length scale for this phenomenon is set by the layer thickness .
Three-Dimensional Theory
The extension of the theory to three dimensions is straightforward and allows for a quantitative comparison with the experiments. For the 3D case, we compute the shape of the solid numerically, by first solving for the deformation field induced by a single drop using an axisymmetric elastic Green's function (18). Adding a second drop on this deformed surface gives an intricate deformation that is shown in Fig. 4 and Fig. S3. The imbalance of the Neumann law applies everywhere around the contact line: the background deformation induces a rotation of the solid contact angles around the drop. According to Eq. 3, these rotations result into a distribution of force per unit length contact line , where is the radial unit vector and β is the azimuthal angle (Fig. 4). The resultant interaction force is obtained by integration along the contact line, (see Supporting Information and Fig. S4 for details). By symmetry, this force is oriented along the line connecting the two drops.
Fig. 4.
Three-dimensional calculation of interface deformation for a pair of axisymmetric drops. The elastocapillary meniscus between the two drops is clearly visible, giving a rotation of the contact angle around the drop. The total interaction force is obtained by integration of the horizontal force (indicated in red) and is related to the free-energy gradient associated with a change in separation between the drops. Parameter values are , .
Fig. S3.
Problem setup for axisymmetric drops on an elastic half space. The solid shape is shown for a distance between the droplets and . x and y are in units of R, and z is in units of .
Fig. S4.
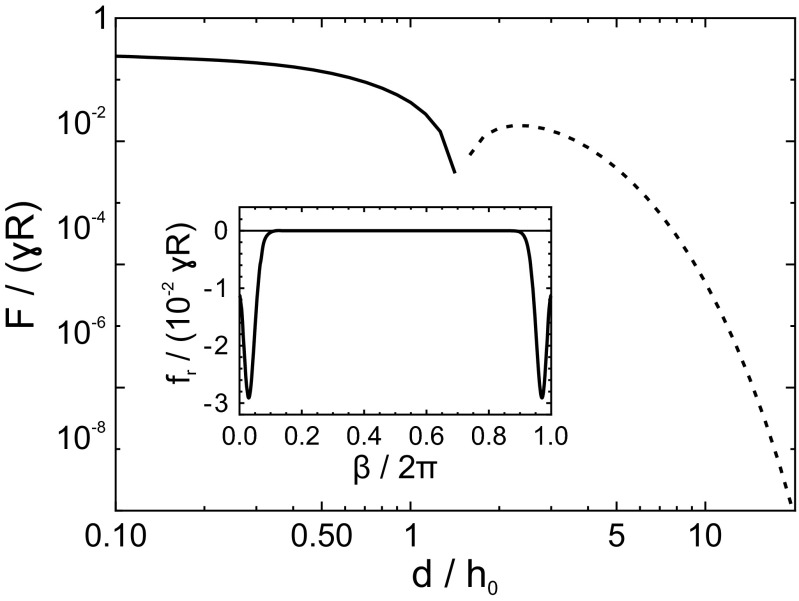
Force–distance curve for axisymmetric droplets on a thin elastic layer. (Inset) at the contact line of a droplet on a thin layer in the presence of a second droplet at . , , .
The interaction force obtained by the 3D theory is indicated by the red curves in Fig. 2 A and B. The theory gives an excellent description of the experimental data without adjustable parameters. The quantitative agreement indicates that the interaction mechanism is indeed caused by the rotation of the elastic meniscus.
Discussion
In summary, we have shown that liquid drops can exhibit a mutual interaction when deposited on soft surfaces. The interaction is mediated by substrate deformations, and its direction (repulsive versus attractive) can be tuned by varying the thickness of the layer. The measured force/distance relation is in quantitative agreement with the proposed elastocapillary theory. The current study reveals that multiple “pinchings” of an elastic layer by localized tractions γ lead to an interaction having a range comparable to . The key insight is that interaction emerges from the rotation of the elastic surface, providing a generic mechanism that should be applicable to a wide range of objects interacting on soft media.
Our model provides general concepts that are applicable to a wide range of experimental settings, whenever objects exert dipolar or quadrupolar forces on their substrate [the integral force must vanish in this case, however, as is the case, e.g., for cells (37)]. The length scale of interaction is governed by the ratio of two quantities: the force (per unit length) γ, and the substrate shear modulus G. This can range from nanometers for small forces or stiff substrates, to hundreds of microns for strong forces or soft substrates. In biological settings, elastocapillary interactions may play a role in cell–cell interactions, which are known to be sensitive to substrate stiffness (31). One example would be stem cell aggregates that interact with their extracellular matrix (38). In addition, the elastic interaction could also play a role in cell–extracellular matrix interactions, as a purely passive force promoting aggregation between anchor points on the surface of adhered biological cells. For example, it has been demonstrated that a characteristic distance of about 70 nm between topographical features enables the clustering of integrins. These transmembrane proteins are responsible for cell adhesion to the surrounding matrix, mediating the formation of strong anchor points when cells adhere to substrates (39, 40). Assuming that the topographical features “pinch” the cell with a force likely comparable to the cell’s cortical tension, which takes values in the range 0.1–1 mN/m (41–44), and an elastic modulus of 103–104 Pa in the physiological range of biological tissues (45), one predicts a range of interaction consistent with observations.
More generally, substrate-mediated interactions could be dynamically programmed using the responsiveness of many gels to external stimuli (pH, temperature, electric fields). Possible applications range from fog harvesting and cooling to self-cleaning or anti-fouling surfaces, which rely on controlling drop migration and coalescence. The physical mechanisms revealed here, in combination with the fully quantitative elastocapillary theory we propose, pave the way for new design strategies for smart soft surfaces.
Materials and Methods
Supporting Information provides further technical information, the derivation underlying Eq. 3, and the numerical scheme used for the calculations of Figs. 2 and 4. Movies S1–S3 show typical experiments of drop–drop interactions.
Substrate Preparation.
The two prepolymer components (Dow Corning; CY52-276 A and B) were mixed in a ratio of 1.3:1 (A:B). Thick elastic layers (∼8 mm) were prepared in Petri dishes (diameter, ∼90 mm). Thin layers (∼40 μm) were prepared by spin-coating the gel onto silicon wafers. The thickness was determined by color interferometry. See SI Materials and Methods for details on substrate curing and rheology (Fig. S5).
Fig. S5.
Spectra of storage () and loss modulus () of the substrates. Curves for −10 °C and 80 °C were shifted to obtain a room temperature master curve.
Determining the Interaction Between Drops.
Droplets of ethylene glycol (V ∼ 0.3–0.8 μL) were pipetted onto a small region near the center of the cured substrate. The sample was then mounted vertically so that gravity acts along the surface ( direction; compare Fig. 1 A and B). The droplets were observed in transmission (thick layers) or reflection (thin layers) with collimated illumination, using a telecentric lens (JenMetar 1×) and a digital camera (pco 1200). Images were taken every 10 s. The contours of the droplets were determined by a standard correlation technique.
At large separation, droplets move downward due to gravity. The gravitational force on each droplet is proportional to its volume. The relation between force and velocity follows the same power law as the rheology, as was explained recently (21).
Individual droplets have different volumes and move with different velocities. Thus their distances change with time. Whenever two droplets approach each other, their trajectories change due to their interaction. Drops on thick substrates (Fig. 1C, black) attract and eventually merge. On a rigid surface, these droplets would not have merged. The opposite holds for droplets on thin layers (red): the droplets repel each other, which prevents coalescence.
To determine the interaction forces, we first evaluate the velocity vector of each individual droplet. The droplets move in a quasi-stationary manner, and the total force vector acting on each droplet is aligned with its velocity vector. The magnitude of the total force is obtained through calibration from the data shown in Fig. 1D. The interaction force is obtained by subtracting the gravitational force from the total force. Fig. 2A shows data from nine individual droplet pairs, corresponding to different times and different locations on the substrate. Fig. 2B shows data from 18 different droplet pairs. The raw data have been averaged over distance bins, taking the SD as error bar.
Supporting Information describes technical details of the theory by which we compute the drop–drop interaction as well as experimental information. We first discuss the 2D variational problem and numerical solution, and the scheme is then extended to axisymmetric 3D droplets. SI Materials and Methods describe details of the experiment, including the rheological calibration.
Interaction of 2D Droplets
Free Energy.
The problem setup is shown in Fig. S1. Two liquid drops of radius R sit on a soft, elastic substrate with shear modulus G. The distance between liquid drops is d. The soft substrate has surface free energies (dry part) and (wet part). γ is the liquid surface tension. The proximal contact lines of the two drops are at and , whereas the distal contact lines are at and . and . and are the inner and outer liquid contact angles and are unknown at this point. The deformed profile of the substrate is defined by and , for wet and dry parts, respectively.
Due to the extremely slow motion of the droplets, all dissipative effects are localized at the contact line (21). We use a quasistationary approximation and incorporate the total dissipative force into a Lagrange multiplier f, acting on the contact line distance between the drops.
Owing to the left–right symmetry, we use the energy of the right half of the system, so that the total free energy of the system is :
| [S1] |
The first term, , describes the elastic energy. Its explicit form will be discussed later. Terms with prefactors γ, , and are the surface energies of the drop and the dry and the wet part of the solid, respectively. This form is presented as Eq. 2 in the main text.
The remaining terms are Lagrange multipliers to enforce the various boundary conditions on the three phase contact lines:
• to enforce contact between the three interfaces , , and at and , and thereby also the continuity of the substrate surface.
• f enforces the distance d between the inner contact lines of the two droplets. Hence, f quantifies the interaction force. Positive value of f corresponds to a repulsive interaction.
• P is the Laplace pressure inside the drop, which enforces a drop volume V.
We solve for stationary at fixed d. The variation of d gives , which implies that f is indeed the interaction force (the factor 1/2 drops out because is only one-half of total free energy of the system).
Variation of .
| [S2] |
Because is arbitrary, and at equilibrium, we obtain the following relations for the Lagrange multipliers to :
| [S3] |
In addition, the integrand in Eq. S2 should vanish in the domain , which gives the differential equation for the drop shape:
| [S4] |
Variation of and .
The Lagrange multipliers enforce the continuity of the solid profile at and . With
| [S5] |
we can write for the elastic free energy:
| [S6] |
where is the normal stress at the surface of the elastic medium. The variation gives the following:
| [S7] |
Due to symmetry, . In addition, we impose that the deformation (and thus its variation ) shall vanish for . Hence, the elastic problem is defined by the normal stress as follows:
| [S8] |
In analogy to ref. 19, the elastic stress consists of a solid Laplace pressure term proportional to the curvature of the deformed substrate; inside the drop, there is in addition the capillary pressure P.
As before, the boundary terms give the following:
| [S9] |
Combined with Eq. S3, this gives the vertical boundary conditions at the two contact lines,
| [S10] |
Variation of and .
The key equation that provides the interaction force, Eq. 3 of the main text, is obtained from the variation of :
| [S11] |
The last term drops out as the interfaces meet at the contact lines. Now using Eq. S9 to express and , the equilibrium condition gives the following:
| [S12] |
This is Eq. 3 of the main text, which demonstrates that f emerges as an imbalance in the horizontal Neumann condition of the contact angles at .
For the variation of , we obtain the following:
| [S13] |
Again, with Eq. S9 and :
| [S14] |
This is the horizontal Neumann condition at the outer contact line at .
Numerical Solution.
This variations of and the contact line positions define the problem of two interacting drops. As usual, the constrained minimization (i.e., imposing the distance between the inner contact lines) only admits solutions for a particular value of the Lagrange multiplier f. By determining numerically the solutions consistent with the boundary conditions, we thus find a unique interaction force f for a given distance.
The spherical cap solution for , together with elementary geometry, allows to express the drop pressure in terms of the contact angles as follows:
| [S15] |
This appears as a traction to the elastic layer. The substrate shape is solved using linear elasticity and a Green’s function approach, , where is the Green’s function for the elastic medium. The resulting equation is best solved in Fourier space (15). We use the following convention:
| [S16] |
to obtain in the limit of small slopes and assuming :
| [S17] |
Here, is the Fourier transform of Green’s function:
| [S18] |
| [S19] |
where corresponds to an elastic half-space, and to elastic layers with finite thickness . is the traction that the two droplets exert onto the elastic medium given by Eq. S8. Following the same steps as for the single-drop problem (19), we find the explicit form
| [S20] |
where we made use of Eq. S15 to eliminate the pressure inside the drop. Note that, within this formulation, the vertical Neumann balance is automatically ensured.
The solution for the elastic layer is now fully specified in terms of and . These need to satisfy the two horizontal Neumann conditions (Eqs. S12 and S14), but this introduces another unknown f. The problem is closed by the requirement that the heights match at the contact lines, , which selects a solution with unique and f for each distance d. These solutions are determined numerically.
Fig. S2 shows a force distance curve for typical parameters, together with solid profiles (Inset) at given distances.
Interaction of Axisymmetric Droplets
According to ref. 18, the Green’s functions for axisymmetric loads on elastic media are as follows:
| [S21] |
| [S22] |
for half-space and thin layers, respectively. The displacements due to the traction exerted by a droplet at the origin reads in Fourier space (18):
| [S23] |
Real-space profiles are obtained by numerical Hankel transformation according to the following:
| [S24] |
Two Droplets.
In the presence of a second droplet, the slope of the wetting ridge of the second droplet will rotate the solid angles at the contact line of the first drop. Therefore, two droplets nearby will not be the equilibrium configuration, but attract or repel, depending on the relative strengths of the forces acting on the contact line. To keep two droplets with circular footprints of radius 1 at a distance d, we impose a constraint on the radial coordinate of the contact line. Associated with this is a continuous Lagrange multiplier that depends on the azimuthal angle β. can be interpreted as a virtual traction that fixes the contact line position. The horizontal force balance becomes the following:
| [S25] |
Let be the solid shape for the case of two droplets a and b, where drop a shall be located at the origin of the coordinate system, and drop b shall be located to the right of drop a, centered at (Fig. S3). The full shape is composed as the superposition of two individual droplets as follows:
| [S26] |
In polar coordinates, this becomes the following:
| [S27] |
where .
In small-slope approximation, the horizontal force balance for drop a becomes the following:
| [S28] |
where the superscripts + and − indicate the slopes on the dry and the wet side of the contact line, respectively. Again, this can be decomposed into a slope discontinuity and a rotation. The discontinuity equals , and the rotational part can be obtained by evaluating the backward transform exactly at the position of the discontinuity (46), and the force balance becomes the following:
| [S29] |
The interaction force between the droplets is given by the integral of the projection of onto :
| [S30] |
The calculation for axisymmetric droplets on thin elastic layers is identical except for the convolution kernel. As in the 2D case, the “dimple” in the profile causes a sign change in the slope, which results in a repulsive regime for distances . However, now the contact line of one droplet always crosses the dimple of the other droplet. Therefore, the rotation of the solid angle and the net radial force on the contact line may change sign when plotted against the azimuthal angle (compare Fig. S4, Inset). This leads to a different compared with the 2D model: the sign change in the 3D model appears at smaller distances because a significant fraction of the contact line remains in the repulsive range.
SI Materials and Methods
Experiments were performed using ethylene glycol (Sigma; purity, ) drops on a silicone gel (Dow Corning; CY52-276). Typical droplet radii were R ∼ 500–800 μm. The two prepolymer components were mixed in a ratio of 1.3:1 (A:B), stirred thoroughly, degassed, and poured into Petri dishes (diameter, ∼90 mm) to make thick (∼8 mm) elastic layers. Thin layers (∼40 μm) were prepared by spin-coating the gel onto silicon wafers. Thicknesses were determined by color interferometry. To ascertain smooth and flat gel surfaces, substrates were cured in two steps: first, the sample was kept for 48 h at room temperature on a stabilized optical table in a dust-free environment. After that, the gels were slowly heated to 90 °C in an oven and cured for 2 h at that temperature. To determine the substrate rheology, part of the mixed prepolymers was cured simultaneously (with the same temperature profile) in a parallel plate geometry () of a rheometer (Anton Paar MCR502 with Peltier bottom plate and hood). After curing, frequency sweeps with small strains were performed at 20 °C. Measurements are accurately fitted by the following form:
| [S31] |
with exponent , a timescale s, and a long-time shear modulus Pa. Combined with N/m, this provides the magnitude for elastic deformations dictated by the elastocapillary length . Fig. S5 shows the measured rheology of the substrates used in the experiments. High- and low-temperature measurements are shifted to give a room temperature master curve.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
L.B. acknowledges useful discussion on mechanobiology with Dr. Nuria Gavara, and financial support from European Union Grant CIG 618335. S.K. acknowledges financial support from NWO through VIDI Grant 11304. A.P. and J.H.S. acknowledge financial support from European Research Council Consolidator Grant 616918.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission. K.D.-V. is a guest editor invited by the Editorial Board.
See Commentary on page 7294.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1601411113/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Tessier PM, et al. Structured metallic films for optical and spectroscopic applications via colloidal crystal templating. Adv Mater. 2001;13(6):396–400. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Furst EM. Directing colloidal assembly at fluid interfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(52):20853–20854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1118441109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cavallaro M, Jr, et al. Exploiting imperfections in the bulk to direct assembly of surface colloids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(47):18804–18808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1313551110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bowden N, Terfort A, Carbeck J, Whitesides GM. Self-assembly of mesoscale objects into ordered two-dimensional arrays. Science. 1997;276(5310):233–235. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5310.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ershov D, Sprakel J, Appel J, Cohen Stuart MA, van der Gucht J. Capillarity-induced ordering of spherical colloids on an interface with anisotropic curvature. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(23):9220–9224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222196110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Loudet JC, Pouligny B. How do mosquito eggs self-assemble on the water surface? Eur Phys J E Soft Matter. 2011;34(8):76. doi: 10.1140/epje/i2011-11076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Peruzzo P, Defina A, Nepf HM, Stocker R. Capillary interception of floating particles by surface-piercing vegetation. Phys Rev Lett. 2013;111(16):164501. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.164501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Danov KD, Kralchevsky PA, Naydenov BN, Brenn G. Interactions between particles with an undulated contact line at a fluid interface: Capillary multipoles of arbitrary order. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2005;287(1):121–134. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2005.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Botto L, Lewandowski EP, Cavallaro M, Stebe KJ. Capillary interactions between anisotropic particles. Soft Matter. 2012;8(39):9957–9971. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kumar A, Park BJ, Tu F, Lee D. Amphiphilic Janus particles at fluid interfaces. Soft Matter. 2013;9(29):6604–6617. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vella D, Mahadevan L. The Cheerios effect. Am J Phys. 2005;73(9):817–825. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chakrabarti A, Chaudhury MK. Surface folding-induced attraction and motion of particles in a soft elastic gel: Cooperative effects of surface tension, elasticity, and gravity. Langmuir. 2013;29(50):15543–15550. doi: 10.1021/la402527r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chakrabarti A, Chaudhury MK. Elastocapillary interaction of particles on the surfaces of ultrasoft gels: A novel route to study self-assembly and soft lubrication. Langmuir. 2014;30(16):4684–4693. doi: 10.1021/la5007988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chakrabarti A, Ryan L, Chaudhury M, Mahadevan L. Elastic cheerios effect: Self-assembly of cylinders on a soft solid. Europhys Lett. 2015;112(5):54001. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jerison ER, Xu Y, Wilen LA, Dufresne ER. Deformation of an elastic substrate by a three-phase contact line. Phys Rev Lett. 2011;106(18):186103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.186103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Limat L. Straight contact lines on a soft, incompressible solid. Eur Phys J E Soft Matter. 2012;35(12):9811. doi: 10.1140/epje/i2012-12134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Marchand A, Das S, Snoeijer JH, Andreotti B. Contact angles on a soft solid: From Young’s law to Neumann’s law. Phys Rev Lett. 2012;109(23):236101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.236101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Style RW, Dufresne ER. Static wetting on deformable substrates, from liquids to soft solids. Soft Matter. 2012;8(27):7177–7184. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lubbers LA, et al. Drops on soft solids: Free energy and double transition of contact angles. J Fluid Mech. 2014;747:R1. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kajiya T, et al. A liquid contact line receding on a soft gel surface: Dip-coating geometry investigation. Soft Matter. 2014;10(44):8888–8895. doi: 10.1039/c4sm01609b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Karpitschka S, et al. Droplets move over viscoelastic substrates by surfing a ridge. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7891. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Style RW, et al. Patterning droplets with durotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(31):12541–12544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307122110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sokuler M, et al. The softer the better: Fast condensation on soft surfaces. Langmuir. 2010;26(3):1544–1547. doi: 10.1021/la903996j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schellenberger F, et al. Direct observation of drops on slippery lubricant-infused surfaces. Soft Matter. 2015;11(38):7617–7626. doi: 10.1039/c5sm01809a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rykaczewski K, et al. Dropwise condensation of low surface tension fluids on omniphobic surfaces. Sci Rep. 2014;4:4158. doi: 10.1038/srep04158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kim P, et al. Liquid-infused nanostructured surfaces with extreme anti-ice and anti-frost performance. ACS Nano. 2012;6(8):6569–6577. doi: 10.1021/nn302310q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Subramanyam SB, Rykaczewski K, Varanasi KK. Ice adhesion on lubricant-impregnated textured surfaces. Langmuir. 2013;29(44):13414–13418. doi: 10.1021/la402456c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Discher DE, Janmey P, Wang YL. Tissue cells feel and respond to the stiffness of their substrate. Science. 2005;310(5751):1139–1143. doi: 10.1126/science.1116995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lo CM, Wang HB, Dembo M, Wang YL. Cell movement is guided by the rigidity of the substrate. Biophys J. 2000;79(1):144–152. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76279-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhang R, Ni L, Jin Z, Li J, Jin F. Bacteria slingshot more on soft surfaces. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5541. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guo WH, Frey MT, Burnham NA, Wang YL. Substrate rigidity regulates the formation and maintenance of tissues. Biophys J. 2006;90(6):2213–2220. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.070144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Winter H, Chambon F. Analysis of linear viscoelasticity of a cross-linking polymer at the gel point. J Rheol (NYNY) 1986;30(2):367–382. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Long D, Ajdari A, Leibler L. Static and dynamic wetting properties of thin rubber films. Langmuir. 1996;12(21):5221–5230. [Google Scholar]
- 34.de Gennes PG. Soft adhesives. Langmuir. 1996;12(19):4497–4500. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Carre A, Gastel J, Shanahan M. Viscoelastic effects in the spreading of liquids. Nature. 1996;379(6564):432–434. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Andreotti B, Snoeijer JH. Soft wetting and the Shuttleworth effect, at the crossroads between thermodynamics and mechanics. Europhys Lett. 2016;113(6):66001. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Henry S, Chen C, Crocker J, Hammer D. Dynamic traction forces of human neutrophil adhesion. Biophys J. 2015;108(2):495a. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Przybyla L, Lakins JN, Sunyer R, Trepat X, Weaver VM. Monitoring developmental force distributions in reconstituted embryonic epithelia. Methods. 2016;94:101–113. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Huang J, et al. Impact of order and disorder in RGD nanopatterns on cell adhesion. Nano Lett. 2009;9(3):1111–1116. doi: 10.1021/nl803548b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dalby MJ, Gadegaard N, Oreffo RO. Harnessing nanotopography and integrin-matrix interactions to influence stem cell fate. Nat Mater. 2014;13(6):558–569. doi: 10.1038/nmat3980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Krieg M, et al. Tensile forces govern germ-layer organization in zebrafish. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(4):429–436. doi: 10.1038/ncb1705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tinevez JY, et al. Role of cortical tension in bleb growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(44):18581–18586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903353106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fischer-Friedrich E, Hyman AA, Jülicher F, Müller DJ, Helenius J. Quantification of surface tension and internal pressure generated by single mitotic cells. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6213. doi: 10.1038/srep06213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sliogeryte K, Thorpe SD, Lee DA, Botto L, Knight MM. Stem cell differentiation increases membrane-actin adhesion regulating cell blebability, migration and mechanics. Sci Rep. 2014;4:7307. doi: 10.1038/srep07307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Swift J, et al. Nuclear lamin-A scales with tissue stiffness and enhances matrix-directed differentiation. Science. 2013;341(6149):1240104. doi: 10.1126/science.1240104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sneddon IN. Fourier Transforms. McGraw-Hill; New York: 1951. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.