Abstract
Spirit beverages are a diverse group of foodstuffs. They are very often counterfeited which cause the appearance of low quality products or wrongly labelled products on the market. It is important to find a proper quality control and botanical origin method enabling the same time preliminary check of the composition of investigated samples, which was the main goal of this work. For this purpose, the usefulness of electronic nose based on ultra-fast gas chromatography (fast GC e-nose) was verified. A set of 24 samples of raw spirits, 33 samples of vodkas, and 8 samples of whisky were analysed by fast GC e-nose. Four data analysis methods were used. The PCA was applied for the visualization of dataset, observation of the variation inside groups of samples, and selection of variables for the other three statistical methods. The SQC method was utilized to compare the quality of the samples. Both the DFA and SIMCA data analysis methods were used for discrimination of vodka, whisky, and spirits samples. The fast GC e-nose combined with four statistical methods can be used for rapid discrimination of raw spirits, vodkas, and whisky and in the same for preliminary determination of the composition of investigated samples.
1. Introduction
Electronic noses are more and more often taken into consideration as a tool used for the quality and authenticity assessment of selected products due to their numerous advantages and the principle of operation. The electronic nose is an analytical instrument used for rapid detection and differentiation between types of gaseous samples. Till now electronic nose was used for environmental monitoring (detection of air pollution, tracking of pollution pathways, and efficiency assessment of wastewater and waste gas treatment), medical sciences (identification of selected diseases, including tumors, based on odorants excreted by the infected cells and organs), the perfume industry (authentication of perfumes), the pharmaceutical industry (production control of medicines), forensic operations, and the food-processing industry [1]. This instrument mimics the principles of operation of human smell. Most of the electronic noses are based on set of sensors. Chemical sensors under the influence of the gas mixture allow for generating a characteristic odour profile, which constitutes the so-called “fingerprint” [2]. Sensors such as piezoelectric, electrochemical, and biosensors are usually used. Each chemical sensor has some limitations. For example, metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) sensors require a high working temperature, and conductive polymer (CP) sensors are susceptible to humidity. These problems can be solved by use of e-noses based on the ultra-fast gas chromatography or mass spectrometry. Example of e-nose based on the ultra-fast gas chromatography technology is Heracles II. This type of electronic nose allows for combining the features of fast gas chromatography (fast GC) with advantages of a sensor-based electronic nose. In this electronic nose system, hundreds of variables can be used to achieve reliable results. As a result of one analysis, it is possible to obtain information about the composition of investigated samples and their volatile fraction profile. In this way, complete information is obtained about the similarity of a given sample to the reference sample [3]. An electronic nose based on ultra-fast gas chromatography can be used to assess quality and authenticity and to compare samples.
Spirit beverages are a diverse group of foodstuffs, which differ in terms of their taste, odour, and appearance. Spirit beverages which are produced from grain distillates, namely vodka and whisky, belong to the most popular spirit beverages. For production of vodka and whisky is used the raw spirit which according to Regulation number 110/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council (EC) of 15 January 2008 is obtained by the distillation, after alcoholic fermentation, which does not have the characteristics of ethyl alcohol or a spirit drink but still retains the odour and flavour from the specific agricultural materials. The composition of agricultural distillates is influenced by the material, from which it is produced, and fermentation conditions [4–6]. Raw spirits may contain a lot of harmful substances, which during the production process can pass to the vodka and whiskey. Moreover, agricultural distillates can be falsified due to their botanical origin, for example, by mixing rye distillates with corn distillates [7].
Vodka is a very popular alcoholic beverage in Eastern European countries. Ethyl alcohol of agricultural origin is one of the materials used for producing vodka. Ethanol obtained during the fermentation of various agricultural materials is distilled to selectively reduce the organoleptic properties of materials [6]. By filtering alcohol several times through charcoal and by diluting it with water, an alcoholic beverage with a mild flavour is obtained [8, 9]. Whisky, just like most of the vodkas, is a grain spirit beverage produced by the distillation of a mash made from malted cereals or cereals saccharified as a result of diastasis of malt contained in them. The flavour of whisky is closely connected with the distillation process and maturation of the intermediate product in oak barrels for at least three years, which is different from vodka. Only water and pure caramel can be added to the distillate for dilution and coloring, in contrast to vodkas, to which aromas can be added; however, in this case the name of aroma should be marked on the label, for example, if it is peach aroma on the label, it should be written as “peach vodka” [10]. The composition of vodkas and whisky is usually analysed using one-dimensional gas chromatography [11–17] or two-dimensional gas chromatography [18]. If less volatile ingredients are determined, such as coumarin, it is also possible to use the HPLC technique [19]. Quality and authenticity assessments are also conducted for these matrices using infrared spectroscopy [20–22], optical spectroscopy [23], and sensory analysis [24–26] and the use of the electronic nose based on sensors [27]. None of these methods allows the simultaneous investigation of the matrix and quick differentiation of samples. Due to their diversity and popularity, spirit beverages are very often counterfeited. Lower quality products are defined as those of better quality. Raw materials on the labelling differ from those used in reality. Because of this it is important to find a method that would enable the distinction of samples because of the quality and origin and in the same time a preliminary check of the composition of the samples. Such method should be quick which would allow its introduction to the production lines.
There is a need to find equipment that quickly delivers information about composition and authenticity of spirit beverages. These requirements are fulfilled by Heracles II electronic nose based on ultra-fast gas chromatography. Two of the most popular spirit beverages, namely, vodka and whiskey, and raw spirits used for their production were selected to check the suitability of the electronic nose for quality analysis of spirit drinks. These alcoholic beverages differ significantly from each other by methods of production but they are made from similar raw materials; due to this fact it will be possible to check whether one method is good for a variety of spirits made from grains.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
A set of 24 samples of raw spirits made from different grains obtained from Destylarnia Sobieski S.A. (Poland, Pomeranian Province) were used for the research. Samples of commercially available vodkas and whisky were obtained from local stores in Gdańsk, Poland. A set of 33 samples of vodkas produced from different mixture of different type of rye were selected. Eight brands of whisky were selected from those available on the market, out of which 5 ones were produced from a mixture of barley, rye, and wheat distillates and three whiskies were produced with the addition of maize distillate.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
All samples were prepared using the same analytical procedure. To the vials of 20 mL 6.25 mL of deionised water and 1.75 mL of the alcoholic sample (vodka, whisky, or raw spirit) were added. Next, vials were incubated for 20 minutes at 40°C. Samples were dispensed using a syringe kept at 100°C.
2.2.2. Instrumentation
The Heracles II electronic nose based on ultra-fast gas chromatography by Alpha MOS (Toulouse, France) was used for the research. It is equipped with a sorption trap, a dispenser allowing the introduction of a gas or liquid sample, two Flame Ionisation Detectors (FID), dedicated AlphaSoft V12 software with implemented modules for chromatographic, chemometric, and sensory analysis of characteristics of detected chemical compounds, the Arochembase V4 library, an HS100 autosampler, and a set of independent chromatographic columns with different polarity (nonpolar MXT-5 and medium polar MXT-1701, length 10 m each). Parameters of operation of the electronic nose used for the analysis of spirit beverages are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Parameters of electronic nose operation.
| Parameter | Conditions |
|---|---|
| Dispenser operation conditions | |
| Dispensing volume | 2.5 mL |
| Dispensing time | 15 s |
| Dispenser temperature | 200°C |
| Volumetric intensity of carrier gas flow | 30 mL/min |
|
| |
| Parameters of sorption trap operation | |
| Trap temperature | 40°C |
| Retention time | 20 s |
|
| |
| Conditions for chromatographic analysis | |
| Temperature programme | 40°C (2 s) - 3°C/s - 270°C (18 s) |
| Carrier gas | Hydrogen |
| Dispenser temperature | 270°C |
|
| |
| Detector operation conditions | |
| Detector temperature | 270°C |
3. Results and Discussion
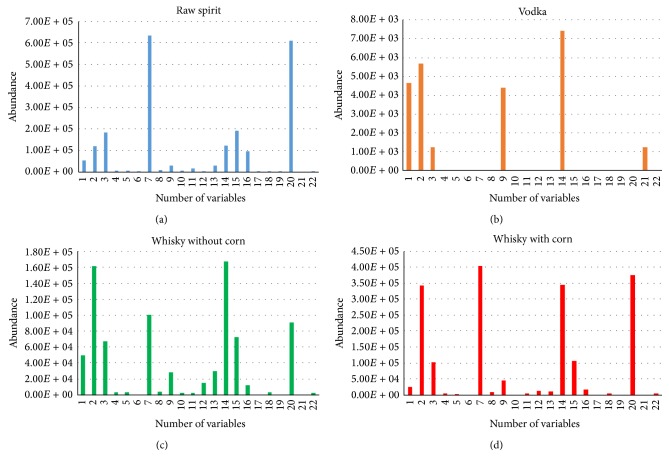
Following chemometric analysis PCA (Principal Component Analysis), DFA (Discriminant Function Analysis), SIMCA classification (SIMCA (Soft Independent Modeling of Class Analogies)), and SQC (Statistical Quality Control) were used for data analysis. For all analyses, sensors (area of the peaks) with the highest discrimination power were used. At the first stage, PCA was used. Principal Component Analysis is one of the most popular chemometric methods used for modelling, compression, and visualization of multidimensional data [28, 29]. Because of that, this method was checked for visualization of the obtained data. All beverages listed in point 2.1 were used for data analysis (Figure 1). PCA allowed for distinguishing between all the three groups of samples. However, this analysis is not typically used to distinguish between groups; it allows spotting the differences between the analysed samples. For example, in Figure 1(a), how diversified the studied groups are can be seen. Groups were created due to the type of spirit drinks (raw spirits, vodka, and whisky). On the basis of the distance between the samples, it can be concluded that the group of whisky comprises two substantially different groups of samples. In the case of raw spirit samples, the relatively low precision of results is caused by the fact that all samples were made from unknown mixture of grains. All vodkas were made from the same type of grain, namely, rye. In the case of whisky, the information about botanical origin of samples was available. Three of them were made not only from barley, wheat, and rye, but also from corn. Because of that, two separate groups of whisky of different botanical origin were created (Figure 1(b)). The variables chosen for PCA, namely, the most discriminant peak areas of specific compounds, were treated as an input dataset for statistical analysis. This dataset was presented in Figure 2 and the names of selected substances were listed in Table 2. Due to satisfactory discrimination of sample groups after application of PCA method, chosen variables were also used as input data in other utilized chemometric methods.
Figure 1.
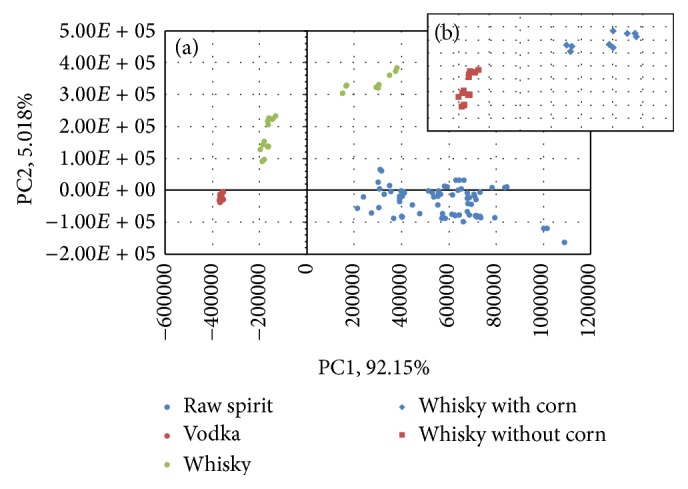
(a) PCA results for vodkas, whiskies, and raw spirits; (b) PCA results for vodkas, whiskies made from corn, whisky made without corn, and raw spirits.
Figure 2.
Mean bar graphs of selected peak areas used as raw data in chemometrics representing key chemical compounds, which are important for discrimination of (a) raw spirit, (b) vodka, (c) whisky without corn, and (d) whisky with corn.
Table 2.
Key chemical compounds (variables), which are important for sample discrimination.
| Number of variables from – 1 or 2 column | Name of the compound | Type of sample (raw spirit, vodka, whisky without corn, and whisky with corn) |
|---|---|---|
| 1—1 | tert-Butylmethylether | All |
| 2—1 | Ethyl acetate | All |
| 3—1 | 2-Methyl-1-butanol | All |
| 4—1 | 2-Methyl-1-propanol | Raw spirit, whisky without corn, and whisky with corn |
| 5—1 | n-Butanol | Raw spirit, whisky without corn, and whisky with corn |
| 6—1 | 2,3-Pentanedione | Raw spirit |
| 7—1 | Methyl butanoate | Raw spirit, whisky without corn, and whisky with corn |
| 8—1 | Pentanol | Raw spirit, whisky without corn, and whisky with corn |
| 9—1 | 1-Hexanol | All |
| 10—1 | (Z)-4-Heptenal | Raw spirit and whisky without corn |
| 11—2 | Diethyl ether | Raw spirit, whisky without corn, and whisky with corn |
| 12—2 | 2-Methylfuran | Raw spirit, whisky without corn, and whisky with corn |
| 13—2 | 2-Methyl-1-propanol | Raw spirit, whisky without corn, and whisky with corn |
| 14—2 | Ethyl acetate | All |
| 15—2 | Methyl butanoate | Raw spirit, whisky without corn, and whisky with corn |
| 16—2 | Propyl acetate | Raw spirit, whisky without corn, and whisky with corn |
| 17—2 | 1-Hydroxy-2-propanone | Raw spirit |
| 18—2 | 1-Hexen-3-ol | Raw spirit, whisky without corn, and whisky with corn |
| 19—2 | 2-Methylthiophene | Raw spirit |
| 20—2 | Pentanol | Raw spirit, whisky without corn, and whisky with corn |
| 21—2 | 3-Methylbut-2-en-1-ol | Vodka |
| 22—2 | (Z)-3-Hexen-1-ol | Raw spirit, whisky without corn, and whisky with corn |
Discriminant Function Analysis is one of the most commonly methods used to decide which variables allow correct classification of a set of objects [30, 31]. DFA was used for discrimination of the data obtained from e-nose analysis of spirit beverages. In Figure 3 the results of DFA analysis for groups of vodkas, whiskies, and raw spirits are shown, and in Figure 4 the results of DFA for vodkas, whiskies made from corn, whisky made without corn, and raw spirits are shown. Both DFA allowed for distinguishing between all groups of samples. As opposed to PCA, DFA is used to distinguish groups not to make the actual data visualization. In Figure 3 it can be seen that points belonging to group of whiskies are definitely more concise than in the case of PCA. The groups of samples were not divided. Using DFA data analysis method the differentiation between groups of samples is more unambiguous. On the other hand differences between individial samples are disappearing when a grup of whiskey samples is defined as a one coherent group. When two groups of whiskies are created (groups which were showed on the PCA graph (Figure 1(b)) it can be seen that the groups are distinguished very well (Figure 4). In the case of DFA, spirit beverages can be distinguishing due to the general type (raw spirits, vodka, and whisky) and due to the botanical origin if the information about their origin is known as in the case of whisky produced with and without corn. In the case of the PCA the differences between the samples within the selected groups cannot be neglected.
Figure 3.
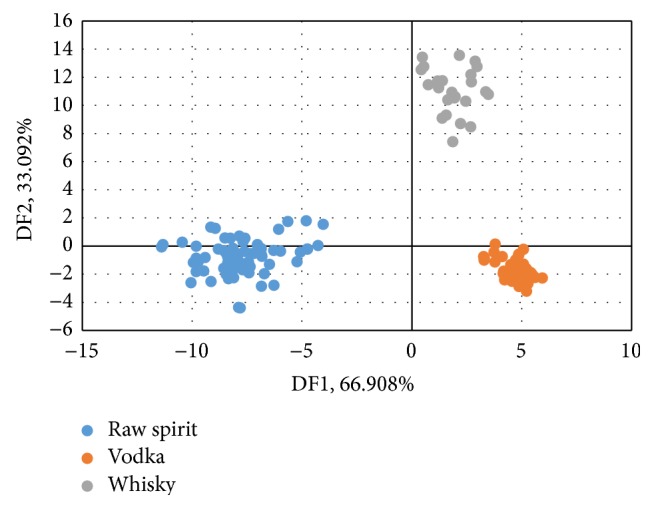
DFA of vodkas, whiskies, and raw spirits.
Figure 4.
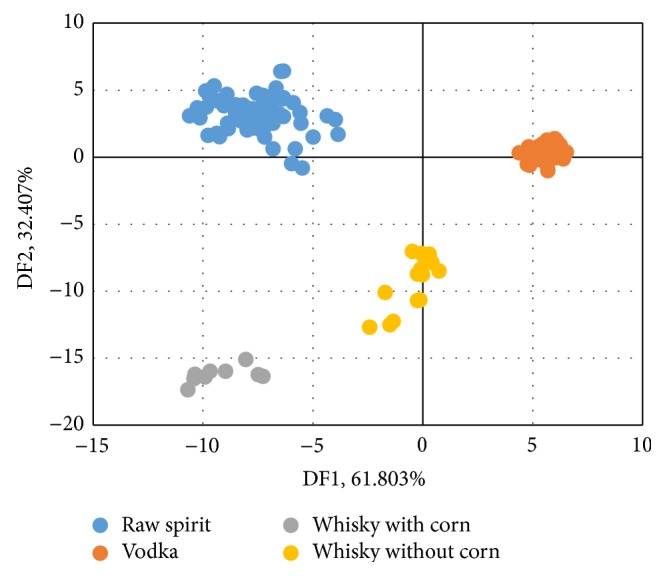
DFA results for vodkas, whiskies made from corn, whisky made without corn, and raw spirits.
In SIMCA classification, a separate model is created for each class based on the principal component method. Next, the so-called “confidence envelope” (a certain volume) is created around the model. It should include with defined probability all elements belonging to a given class [1, 32]. SIMCA analysis is method typically used for classification of the samples. It was used for classification samples into four groups. SIMCA analysis was made for each reference group: vodka (Figure 5), raw spirit (Figure 6), whisky without corn (Figure 7), and whisky with corn (Figure 8). In all cases with one exception points belonging to the reference group were located in the blue area in the confidence envelope. In the case of exception one sample was not classified properly to the reference group in case of vodka classification. This analysis is similar to DFA and it is used to distinguish the groups. In contrast to DFA, SIMCA graph is created for each group separately. It is therefore more time-consuming than DFA. On the other hand, discrimination between different groups is more visible. Due to the envelope of confidence the boundaries of analysed groups are determined. Therefore, the identification of unknown samples is unambiguous.
Figure 5.
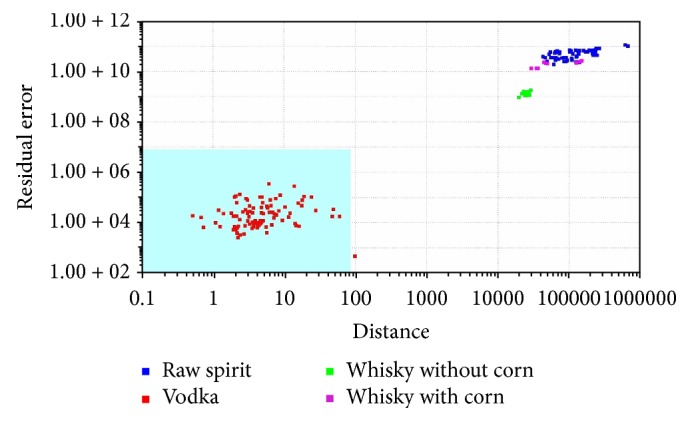
SIMCA analysis for vodkas, whiskies, and raw spirits: vodka, reference group.
Figure 6.
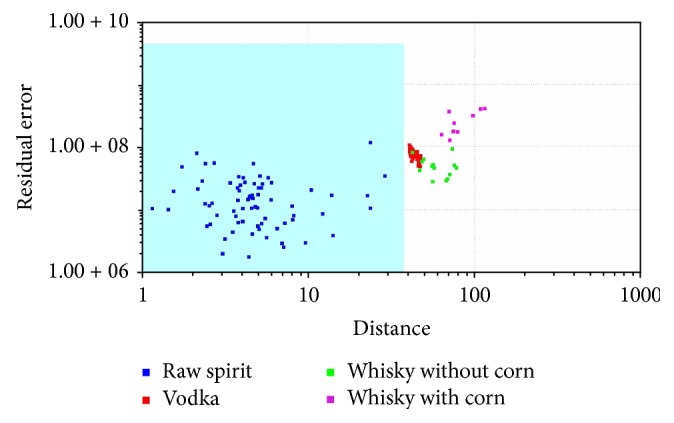
SIMCA analysis for vodkas, whiskies, and raw spirits: raw spirit, reference group.
Figure 7.
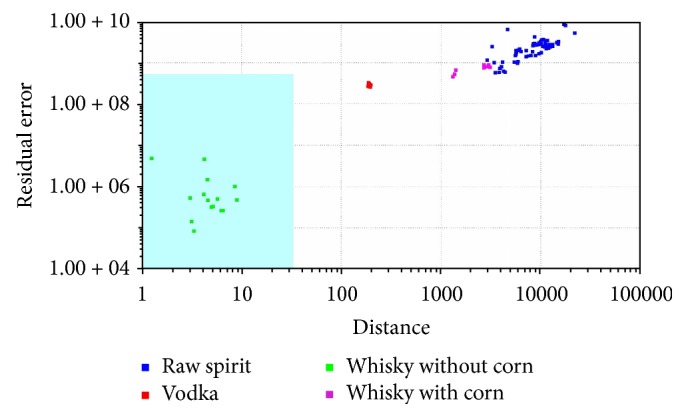
SIMCA analysis for vodkas, whiskies, and raw spirits: whisky without corn, reference group.
Figure 8.
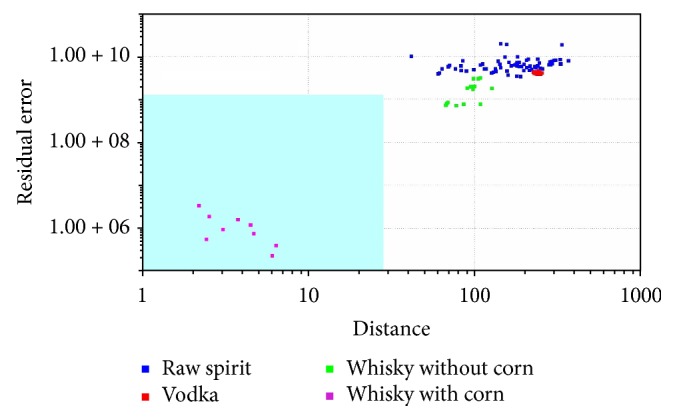
SIMCA analysis for vodkas, whiskies, and raw spirits: whisky with corn, reference group.
The SQC analysis is used for process quality control. Samples, which belong to one group, should be situated in the area designated using parameters on the y-axis of the graph [33, 34]. It can be used for quality analysis of samples on production lines. SQC analysis was performed for four groups of samples, namely, for vodkas, whiskies without corn, whiskies with corn, and raw spirits to show capabilities of this method. SQC analysis allows seeing the differences between individual samples and excluding those that differ from others. It is the proper method for assessing the quality of products, because it is rapid and easy to use and the discrete differences in the studied group of samples can be determined. This method allows observing which sample is statistically different from the other ones in a given batch. It enables the possibility of exclusion of a sample during the final control of ready products. In Figure 9 it can be seen that the differences between the points assigned to a group of vodkas are small. In contrast, the differences between the points belonging to the group of whiskies without corn in Figure 10 are more noticeable. It can be noticed that the area in which points belong to the reference group should be located depending on the deviation between the samples in certain group. The greater the differences between the samples in the group, the greater the tolerance range for the whole group.
Figure 9.
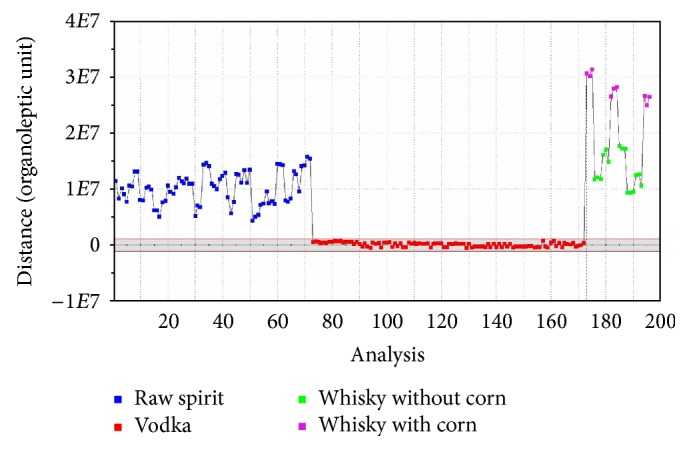
SQC analysis for unflavoured vodkas, raw spirits, and whiskies: vodka, reference group.
Figure 10.
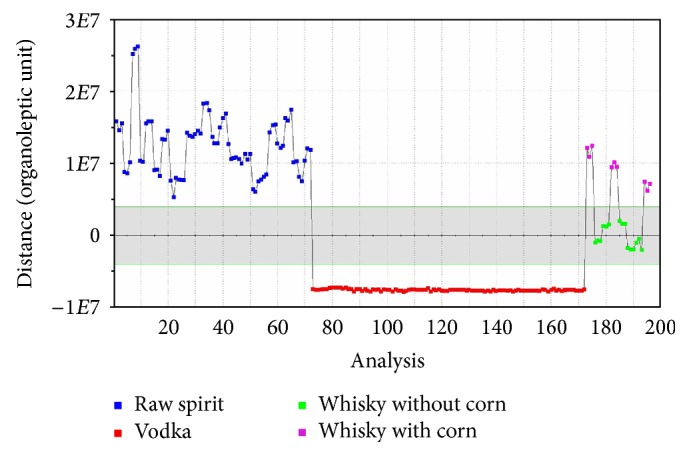
SQC analysis for unflavoured vodkas, raw spirits, and whiskies: whisky without corn, reference group.
Due to the presence of two chromatographic columns of different polarity, it is possible to obtain two different chromatograms and identify individual compounds included in the samples. This is the difference between electronic nose based on sensors and electronic nose based on fast GC. Figures 11 and 12 present chromatograms obtained from the analysis of vodka and whisky. It can be noticed that they differ considerably from each other. As compared to vodka, the odour profile of whiskey is much richer. Nearly twice as many compounds were detected for whisky compared to vodka. Some of chemical compounds detected in vodka, whisky, and raw spirits samples are presented in Tables 3, 4, and 5, respectively. Criterion for the selection of compounds was the similarity parameter set at 90%. Compounds present in the sample were identified on the basis of comparison of calculated linear temperature-programmed retention indices (LTPRI) for compounds from both columns with indices provided in the literature. Apart from LTPRI, the tables also include approximate retention times for the detected chemical compounds and odour descriptions contained in literature sources, which can be found in Arochembase V4 library. Compounds present in the volatile fraction of vodka can be characterized by fewer descriptors than those found in whisky and raw spirits. Mostly, the aroma of compounds identified in vodka matrix was defined as fruity or green, but some of them were also described as sulphurous, winey, alcoholic, bread, straw, corn, or alkane one. In the case of whisky, compounds are mostly characterized as fruity, green, and woody. Other compounds were described as spicy, winey, earthy, sweet, smoky, alcoholic, or pine. Regarding the aroma of raw spirits most of the constituents of this matrix were determined as fruity, fusel, and anise one. Some of the compounds were described as a green, woody, minty, floral, sweet, and solvent one. As it can be noticed the decryption of compounds present in the whisky samples was more connected with aroma of barrels, forest, and sweet fruits than in the case of vodka and raw spirit samples.
Figure 11.
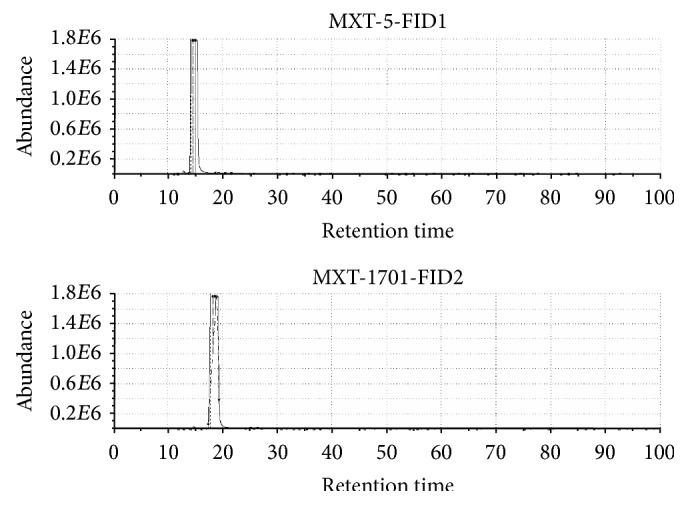
An example of a vodka sample presented in a chromatogram.
Figure 12.
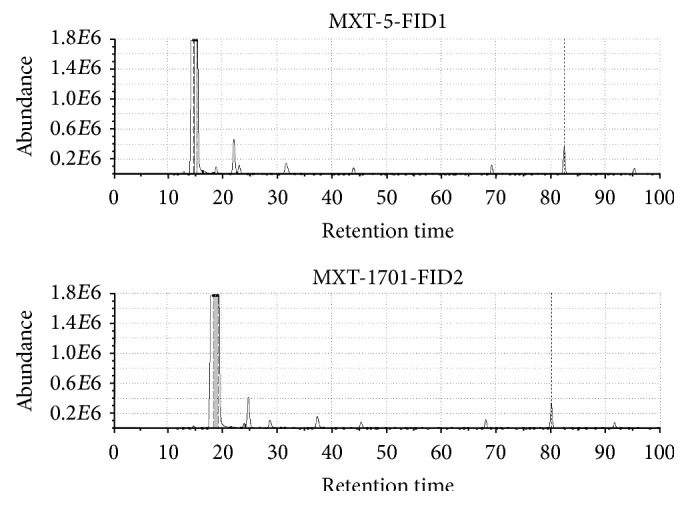
An example of a whisky sample presented in a chromatogram.
Table 3.
Compounds detected in vodka samples.
| Name | RT1/LTPRI1 | RT1/LTPRI2 | LTPRI1 LIT | LTPRI2 LIT | Descriptor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (E)-2-Heptenal | 50.41/950 | 53.00/1049 | 960 | 1062 | Sulfurous, earthy, grossy, and almond |
| (E)-2-Octene | 38.55/813 | 34.72/816 | 815 | 819 | — |
| (Z)-2-Nonenal | 64.94/1134 | 66.97/1251 | 1148 | 1254 | Cucumber, geranium and green |
| 1-Hexanol | 42.59/875 | 45.73/991 | 870 | 980 | Dry, floral, grossy, green, woody, and fruity |
| 1-Octen-3-one | 52.82/979 | 54.96/1075 | 979 | 1066 | Herbaceous |
| 2-Methyl-1-butanol | 32.07/739 | 37.35/848 | 739 | 852 | Winey, buttery, and malty |
| 3-Methylbut-2-en-1-ol | 35.22/775 | 38.53/863 | 778 | 863 | Fruity and green |
| 3-Methylfuran | 22.07/614 | 37.44/849 | 614 | 856 | — |
| Ethanol | 14.91/426 | 18.55/575 | 437 | 564 | Alcoholic |
| Ethyl acetate | 21.00/600 | 24.68/682 | 609 | 673 | Acidic, etheral, fruity, and orange |
| Ethyl butyrate | 37.31/799 | 38.42/861 | 799 | 864 | Fruity and acetone |
| Furfural | 38.49/812 | 46.80/967 | 827 | 972 | Almond and bread |
| Hexyl butyrate | 69.28/1193 | 68.24/1271 | 1191 | 1257 | Apple, fruity, and green |
| Limonene | 58.06/1044 | 54.82/1074 | 1033 | 1061 | Citrus, fruity, and minty |
| Methanol | 14.63/418 | 16.67/516 | 419 | 507 | — |
| Methylnonanedione | 73.97/1261 | 75.92/1396 | 1253 | 1397 | Fruity and straw |
| Propenal | 15.24/435 | 18.11/561 | 450 | 566 | — |
| Pyrazine | 31.11/728 | 35.94/831 | 738 | 822 | Corn and nutty |
| Tert-butylmethylether | 19.31/551 | 19.24/596 | 546 | 600 | — |
| Tetradecane | 82.64/1393 | 75.83/1395 | 1400 | 1400 | Alkane, sweet, and mildly herbaceous |
| Undecane | 62.56/1101 | 56.14/1091 | 1100 | 1100 | Alkane and fusel |
RT1: retention time in column 1 (MXT-5);
LTPRI1: linear temperature-programmed retention index for compounds from column 1;
RT2: retention time in column 2 (MXT-1701);
LTPRI2: linear temperature-programmed retention index for compounds from column 2;
LTPRI1 LIT: linear temperature-programmed retention index for compounds from column 1 from literature;
LTPRI2 LIT: linear temperature-programmed retention index for compounds from column 2 from literature.
The positive identification of selected compounds was highlighted in bold font.
Table 4.
Compounds detected in whiskey samples.
| Name | RT/LTPRI1 | RT/LTPRI2 | LTPRI1 LIT | LTPRI2 LIT | Descriptor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (E)-2-Decanal | 73.93/1260 | 74.36/1370 | 1262 | 1371 | Green, orange, and tallowy |
| (E)-2-Heptenal | 51.87/967 | 54.44/1068 | 960 | 1062 | Almond, earthy, grossy, and sulfurous |
| (Z)-3-Hexen-1-ol | 41.95/851 | 45.39/949 | 852 | 960 | Mossy, green, and fresh |
| (Z)-3-Hexen-1-ol, butanoate | 62.83/1173 | 67.05/1252 | 1187 | 1256 | Banana, green, and winey |
| (Z)-3-Hexenyl isobutyrate | 64.91/1133 | 64.39/1211 | 1144 | 1208 | Apple, etheral, sweet, and winey |
| (Z)-4-Heptenal | 46.43/903 | 48.33/986 | 900 | 988 | Creamy, sweet, and boiled potato |
| (Z)-Whisky lactone | 76.94/1305 | 84.64/1550 | 1316 | 1548 | Coconut |
| 1-Hexanol | 44.01/875 | 48.67/991 | 870 | 980 | Dry, floral, grossy, green, woody, and fruity |
| 1-Hexen-3-ol | 34.00/772 | 38.82/865 | 775 | 850 | Green |
| 2, 4, 5-Trimethylthiazole | 54.21/995 | 54.50/1069 | 996 | 1073 | Earthy, hazelnut, moldy, and chocolate |
| 2-Methyl-1-butanol | 31.68/735 | 37.41/849 | 739 | 852 | Fruity and malty |
| 2-Methyl-1-propanol | 23.13/628 | 28.76/740 | 628 | 735 | Alcoholic, bitter, and winey |
| 2-Methylfuran | 21.06/601 | 22.64/652 | 602 | 639 | Burnt, solvent, metallic, and musty |
| 2-Methylphenol | 57.98/1043 | 69.35/1288 | 1054 | 1283 | Phenolic |
| 3, 5-Octadien-2-one | 61.96/1093 | 64.00/1205 | 7092 | 1203 | Fruity and mushroom |
| 3-Heptanone | 45.39/891 | 46.91/968 | 888 | 969 | Cinnamon, green, spicy, and sweet |
| 4-Ethylguaiacol | 74.66/1271 | 77.35/1421 | 1282 | 1430 | Floral, spicy, and phenolic |
| 6-Decenal | 70.20/1206 | 70.60/1308 | 1203 | 1294 | Green |
| Benzaldehyde | 50.37/950 | 55.86/1088 | 959 | 1086 | Almond, woody, and burnt sugar |
| Beta-ionone | 88.65/1487 | 88.71/1623 | 1490 | 1627 | Floral, woody, and raspberry |
| Beta-phellandrene | 56.63/1026 | 52.75/1045 | 1030 | 1059 | Fruity, minty, and herbaceous |
| Beta-pinene | 52.71/977 | 48.79/992 | 979 | 994 | Green, pine, sweet, and resin |
| Butanoic acid | 38.50/812 | 46.84/967 | 816 | 970 | Rancid, sweaty, and butter |
| Carvone | 73.14/1249 | 75.94/1397 | 1253 | 1386 | Minty and peppermint |
| Diethyl ether | 16.70/476 | 16.90/524 | 491 | 532 | — |
| Ethanol | 15.14/432 | 18.28/566 | 437 | 564 | Alcoholic |
| Ethyl acetate | 22.16/615 | 24.05/675 | 609 | 673 | Acidic, etheral, fruity, and orange |
| Ethyl butyrate | 37.34/799 | 38.92/867 | 799 | 864 | Banana, fruity, sweet, and acetonic |
| Furfural | 40.86/839 | 47.61/977 | 827 | 972 | Almond, bread, and sweet |
| Geosmin | 85.91/1444 | 83.15/1523 | 1430 | 1513 | Beet and earthy |
| Hexyl acetate | 55.27/1009 | 55.80/1087 | 1011 | 1082 | Citrus, fruity, green, and spicy |
| Hexyl butyrate | 69.27/1193 | 68.18/1270 | 1191 | 1257 | Apple, fruity, and green |
| Indole | 76.04/1291 | 84.64/1550 | 1295 | 1549 | Burnt, earthy, floral, and jasmine |
| Limonene | 56.63/1026 | 53.13/1051 | 1033 | 1061 | Citrus, fruity, minty, and peely |
| Methyl butanoate | 29.59/711 | 31.73/778 | 717 | 784 | Ester, etheral, green, and sweet |
| n-Butanol | 26.00/655 | 31.69/774 | 651 | 778 | Fermented and fruity |
| p-Cresol | 60.18/1071 | 71.60/1325 | 1072 | 1312 | Phenolic and smoky |
| Pentanol | 33.68/757 | 38.87/867 | 767 | 879 | Anise, fruity, and green |
| Propyl acetate | 28.76/701 | 31.38/774 | 708 | 775 | Fruity, ketonic, sweet, and solvent |
| Terpinolene | 61.36/1086 | 58.04/1118 | 1088 | 1112 | Fruity, pine, herbaceous, and sweet |
| tert-Butylmethylether | 20.35/551 | 20.28/596 | 546 | 600 | — |
RT1: retention time in column 1 (MXT-5);
LTPRI1: linear temperature-programmed retention index for compounds from column 1;
RT2: retention time in column 2 (MXT-1701);
LTPRI2: linear temperature-programmed retention index for compounds from column 2;
LTPRI1 LIT: linear temperature-programmed retention index for compounds from column 1 from literature;
LTPRI2 LIT: linear temperature-programmed retention index for compounds from column 2 from literature.
The positive identification of selected compounds was highlighted in bold font.
Table 5.
Compounds detected in raw spirit samples.
| Name | RT/LTPRI1 | RT/LTPRI2 | LTPRI1 LIT | LTPRI2 LIT | Descriptor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Z)-3-Hexen-1-ol | 42.63/859 | 46.74/966 | 852 | 960 | Mossy, green, and fresh |
| (Z)-4-Heptenal | 46.13/899 | 48.66/991 | 900 | 988 | Creamy, sweet, and boiled potato |
| 1,2-Benzenediol | 77.77/1318 | 78.44/1440 | 1324 | 1455 | — |
| 1-Hexanol | 44.12/876 | 48.66/991 | 870 | 980 | Dry, floral, grossy, green, woody, and fruity |
| 1-Hexen-3-ol | 34.53/770 | 38.32/860 | 775 | 850 | Green |
| 1-Hydroxy-2-propanone | 25.24/655 | 35.08/820 | 643 | 810 | Caramelized and sweet |
| 1-Octen-3-one | 52.11/970 | 54.49/1069 | 979 | 1066 | Herbaceous |
| 2,3-Pentanedione | 28.79/702 | 33.61/802 | 698 | 788 | Creamy, fresh, fruity, and sweet |
| 2-Methyl-1-butanol | 31.92/737 | 37.55/857 | 739 | 852 | Fruity and malty |
| 2-Methyl-1-propanol | 23.26/629 | 28.83/741 | 628 | 735 | Alcoholic, bitter, and winey |
| 2-Methylfuran | 21.06/601 | 22.64/652 | 602 | 639 | Burnt, solvent, metallic, and musty |
| 2-Methylphenol | 58.18/1045 | 69.44/1290 | 1054 | 1283 | Phenolic |
| 2-Methylthiophene | 35.16/774 | 35.92/831 | 775 | 827 | Sulphurous |
| 2-Undecanal | 80.83/1365 | 82.07/1504 | 1368 | 1503 | Fruity, geranium, green and metallic |
| Alpha-pinene | 49.46/939 | 45.49/941 | 937 | 945 | Green, pine, camphor, and sweet |
| Benzaldehyde | 50.53/951 | 54.90/1075 | 959 | 1086 | Almond, woody, and burnt sugar |
| Beta-ionone | 88.68/1487 | 88.30/1615 | 1490 | 1627 | Floral, woody, and raspberry |
| Butanoic acid | 39.77/827 | 46.74/966 | 816 | 970 | Butter, rancid, and sweaty |
| Carvone | 73.57/1255 | 74.52/1373 | 1253 | 1386 | Minty and peppermint |
| Decanal | 70.67/1212 | 69.44/1290 | 1206 | 1293 | Aldehydic, burnt, floral, and green |
| Decanoic acid | 78.58/1330 | 80.10/1469 | 1323 | 1476 | Fatty, rancid, and soapy |
| Diethyl ether | 16.77/479 | 16.98/526 | 491 | 532 | — |
| Ethanol | 14.85/424 | 18.47/572 | 437 | 564 | Alcoholic |
| Ethyl acetate | 21.56/607 | 24.14/676 | 609 | 673 | Acidic, etheral, fruity, and orange |
| Ethyl hexanoate | 54.39/997 | 52.80/1046 | 995 | 1061 | Anise, apple, fruity, and sweet |
| Ethyl octanoate | 69.45/1195 | 68.26/1271 | 1196 | 1260 | Anise, floral, fresh, and leafy |
| Ethyl phenylacetate | 71.81/1229 | 73.79/1361 | 1243 | 1370 | Anise, cinnamon, floral, and spicy |
| Furfural | 40.93/840 | 46.94/966 | 827 | 972 | Almond, bread, and sweet |
| Geosmin | 85.79/1442 | 83.14/1523 | 1430 | 1513 | Beet and earthy |
| Geranial | 74.70/1272 | 76.83/1412 | 1270 | 1416 | Citrus, floral, lemon, and minty |
| Hexadecane | 96.54/1605 | 87.18/1595 | 1600 | 1600 | Alkane, fusel, fruity, and sweet |
| Hexanal | 36.62/791 | 41.31/897 | 795 | 883 | Grassy, green, herbaceous, and leafy |
| Hexanoic acid | 52.84/979 | 62.10/1177 | 990 | 1186 | Fatty, rancid, and sweaty |
| Hexyl acetate | 55.56/1012 | 56.21/1092 | 1011 | 1083 | Citrus, fruity, green, and spicy |
| Hexyl butyrate | 68.38/1180 | 67.11/1253 | 1191 | 1257 | Apple, fruity, and green |
| Hexyl isobutyrate | 65.11/1136 | 63.90/1203 | 1150 | 1208 | Green |
| Indole | 76.44/1297 | 85.12/1558 | 1295 | 1549 | Burnt, earthy, floral, and jasmine |
| Limonene | 56.84/1028 | 54.49/1069 | 1033 | 1061 | Citrus, fruity, minty, and peely |
| Linalool | 62.89/1106 | 62.96/1189 | 1099 | 1195 | Floral, fruity, green, and lavender |
| Methyl butanoate | 31.22/729 | 31.74/778 | 717 | 784 | Ester, etheral, green, and sweet |
| Methyl-2-propenoate | 22.20/616 | 24.82/687 | 611 | 680 | — |
| n-Butanol | 26.04/666 | 29.84/754 | 651 | 778 | Fermented and fruity |
| Nonane | 46.49/903 | 41.31/897 | 900 | 900 | Alkane and fusel |
| P-Cresol | 60.39/1073 | 71.49/1323 | 1072 | 1312 | Phenolic and smoky |
| Pentadecane | 90.40/1514 | 82.07/1504 | 1500 | 1500 | Alkane, fusel, and mild green |
| Pentanol | 34.68/766 | 39.87/873 | 767 | 879 | Anise, fruity, and green |
| Propenal | 15.61/446 | 18.18/563 | 450 | 566 | — |
| Propyl acetate | 29.52/710 | 31.36/773 | 708 | 775 | Fruity, ketonic, sweet, and solvent |
| Terpinolene | 61.46/1087 | 58.14/1120 | 1088 | 1112 | Fruity, pine, herbaceous, and sweet |
| tert-Butylmethylether | 19.08/545 | 19.79/607 | 546 | 600 | — |
| Tridecane | 77.16/1308 | 70.34/1304 | 1300 | 1300 | Alkane, citrus, fruity, and fusel |
| Undecane | 62.24/1097 | 57.03/1104 | 1100 | 1100 | Alkane and fusel |
RT1: retention time in column 1 (MXT-5);
LTPRI1: linear temperature-programmed retention index for compounds from column 1;
RT2: retention time in column 2 (MXT-1701);
LTPRI2: linear temperature-programmed retention index for compounds from column 2;
LTPRI1 LIT: linear temperature-programmed retention index for compounds from column 1 from literature;
LTPRI2 LIT: linear temperature-programmed retention index for compounds from column 2 from literature.
The positive identification of selected compounds was highlighted in bold font.
4. Conclusion
In this paper the usefulness of the electronic nose using ultra-fast gas chromatography for the qualitative analysis of selected spirit beverages was checked. Four chemometric methods were used to interpret obtained results. PCA and SQC analysis were used to check deviations of individual samples from groups to which they belong. PCA enables the visualization of results. As a result, it was possible to quickly determine that the group of whiskies includes two different groups of samples. Through an SQC analysis, it is possible to check the quality of the samples. Samples of vodka had a similar composition and method of production, due to this fact they are located in one line in Figures 9 and 10. The differences in composition between whisky samples are more significant due to their different method of production and different raw materials used, which was presented in Figures 9 and 10. DFA and SIMCA analysis, on the other hand, were used to group vodka, whisky, and spirits samples and to compare them. Furthermore, in contrast to traditional electronic nose based on the sensors, the electronic nose based on a fast gas chromatography allows determining the compounds included in the sample. This is possible thanks to the presence of two chromatographic columns of different polarity and well-equipped database that allows comparison of retention indexes and retention times. Additionally, each compound can be attributed to the smell which has been previously described in the literature. Summing up, the use of electronic nose based on ultra-fast gas chromatography and four applied statistical methods can be used to distinguish groups of spirit beverages. It also allows finding the differences between individual samples in one group and to determine the composition of the investigated samples. By using Arochembase V4 library it was possible to make an assignment of the odours described in the literature to the individual components present in the samples.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support for this study by Grant no. 2012/05/B/ST4/01984 from National Science Centre of Poland.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Śliwińska M., Wiśniewska P., Dymerski T., Namieśnik J., Wardencki W. Food analysis using artificial senses. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2014;62(7):1423–1448. doi: 10.1021/jf403215y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dymerski T. M., Chmiel T. M., Wardencki W. Invited Review Article: an odor-sensing system-powerful technique for foodstuff studies. Review of Scientific Instruments. 2011;82(11) doi: 10.1063/1.3660805.111101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Alpha MOS. HERACLES Flash Gas Chromatography Electronic Nose. 2014. http://www.alpha-mos.com/analytical-instruments/heracles-electronic-nose.php. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tarko T. Komponenty aromatu napojów alkoholowych. Laboratorium. 2006;11:39–42. [Google Scholar]
- 5. The Act of 13 September 2002. Of spirit beverages (Polish Regulation No. 166, item. 1362)
- 6. REGULATION (EC) No 110/2008 of the European Parliament and the Council of 15 January 2008 on the definition, description, presentation, labelling and protection of geographical indications of spirit beverages and repealing Council Regulation (EEC) No 1576/89.
- 7.Wiśniewska P., Śliwińska M., Dymerski T., Wardencki W., Namieśnik J. The analysis of raw spirits-a review of methodology. Journal of the Institute of Brewing. 2016;122(1):5–10. doi: 10.1002/jib.288. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Christoph N., Bauer-Christoph C. Vodka. In: Berger R. G., editor. Flavours and Fragrances Chemistry, Bioprocessing and Sustainability. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ng L.-K., Hupé M., Harnois J., Moccia D. Characterisation of commercial vodkas by solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 1996;70(3):380–388. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0010(199603)70:3<380::AID-JSFA517>3.0.CO;2-M. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rhodes C. N., Heaton K., Goodall I., Brereton P. A. Gas chromatography carbon isotope ratio mass spectrometry applied to the detection of neutral alcohol in Scotch whisky: an internal reference approach. Food Chemistry. 2009;114(2):697–701. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.059. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pereira E. V. S., Oliveira S. P. A., Nóbrega I. C. C., et al. Brazilian vodkas have undetectable levels of ethyl carbamate. Quimica Nova. 2013;36(6):822–825. doi: 10.1590/S0100-40422013000600014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lachenmeier D. W., Anh P. T. H., Popova S., Rehm J. The quality of alcohol products in Vietnam and its implications for public health. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2009;6:2090–2101. doi: 10.3390/ijerph6082090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Siríštová L., Prinosilová Š., Riddellová K., Hajšlová J., Melzoch K. Changes in quality parameters of vodka filtered through activated charcoal. Czech Journal of Food Sciences. 2012;30(5):474–482. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Martí M. P., Boqué R., Busto O., Guasch J. Electronic noses in the quality control of alcoholic beverages. TrAC—Trends in Analytical Chemistry. 2005;24(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2004.09.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ng L.-K. Analysis by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry of fatty acids and esters in alcoholic beverages and tobaccos. Analytica Chimica Acta. 2002;465(1-2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(01)01497-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Barbeira P. J. S., Stradiotto N. R. Anodic stripping voltammetric determination of Zn, Pb and Cu traces in whisky samples. Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry. 1998;361(5):507–509. doi: 10.1007/s002160050935. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Garcia J. S., Vaz B. G., Corilo Y. E., et al. Whisky analysis by electrospray ionization-Fourier transform mass spectrometry. Food Research International. 2013;51(1):98–106. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.11.027. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cardeal Z. L., Marriott P. J. Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis and comparison of volatile organic compounds in Brazilian cachaça and selected spirits. Food Chemistry. 2009;112(3):747–755. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.06.057. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sproll C., Ruge W., Andlauer C., Godelmann R., Lachenmeier D. W. HPLC analysis and safety assessment of coumarin in foods. Food Chemistry. 2008;109(2):462–469. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.12.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Adam T., Duthie E., Feldmann J. Investigations into the use of copper and other metals as indicators for the authenticity of scotch whiskies. Journal of the Institute of Brewing. 2002;108(4):459–464. doi: 10.1002/j.2050-0416.2002.tb00576.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Aylott R. I., Clyne A. H., Fox A. P., Walker D. A. Analytical strategies to confirm Scotch whisky authenticity. The Analyst. 1994;119(8):1741–1746. doi: 10.1039/AN9941901741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sujka K., Koczoń P. Zastosowanie spektroskopii FT-IR do oceny zawartości alkoholu etylowego w komercyjnych wódkach. Zeszyty Problemowe Postępów Nauk Rolniczych. 2012;571:107–114. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mignani A. G., Ciaccheri L., Gordillo B., et al. Identifying the production region of single-malt Scotch whiskies using optical spectroscopy and pattern recognition techniques. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. 2012;171-172:458–462. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2012.05.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sujka K., Koczoń P., Górska A., Wirkowska M., Reder M. Sensory and spectral characteristics of selected freeze-dried spirit beverages. Food.Science.Technology.Quality. 2013;4(89):184–194. doi: 10.15193/zntj/2013/89/184-198. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lee K.-Y. M., Paterson A., Piggott J. R., Richardson G. D. Sensory discrimination of blended Scotch whiskies of different product categories. Food Quality and Preference. 2001;12(2):109–117. doi: 10.1016/S0950-3293(00)00037-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Parker I. G., Kelly S. D., Sharman M., Dennis M. J., Howie D. Investigation into the use of carbon isotope ratios (13C/12C) of Scotch whisky congeners to establish brand authenticity using gas chromatography-combustion-isotope ratio mass spectrometry. Food Chemistry. 1998;63(3):423–428. doi: 10.1016/s0308-8146(98)00010-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ragazzo-Sanchez J. A., Chalier P., Chevalier D., Ghommidh C. Electronic nose discrimination of aroma compounds in alcoholised solutions. Sensors and Actuators, B: Chemical. 2006;114(2):665–673. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2005.05.032. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wilson D. M., Dunman K., Roppel T., Kalim R. Rank extraction in tin-oxide sensor arrays. Sensors and Actuators, B: Chemical. 2000;62(3):199–210. doi: 10.1016/S0925-4005(99)00386-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Merkisz J., Barczak A., Pielecha J. Badanie zmiennosci emisji zanieczyszczen z zastosowaniem metody PCA. Logistyka. 2011;3:1835–1844. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stat Soft. Discriminant Function Analysis, http://www.statsoft.com/Textbook/Discriminant-Function-Analysis.
- 31.McGarigal K., Cushman S., Stafford S. Multivariate Statistics for Wildlife and Ecology Research. New York, NY, USA: Springer; 2000. Discriminant analysis; pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mazerski J. Podstawy Chemometrii. Gdańsk, Poland: Wydaw. Politechniki Gdańskiej; 2000. Klasyfikacja; pp. 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- 33. Alpha MOS. Data Treatment: More About Quality Control Models, http://www.alpha-mos.com/pdf/en/data_treatment/quality_control_models.pdf.
- 34.Hubbard M. R. Statistical Quality Control for the Food Industry. Berlin, Germany: Springer Science & Business Media; 2012. Control charts; pp. 49–70. [Google Scholar]