Abstract
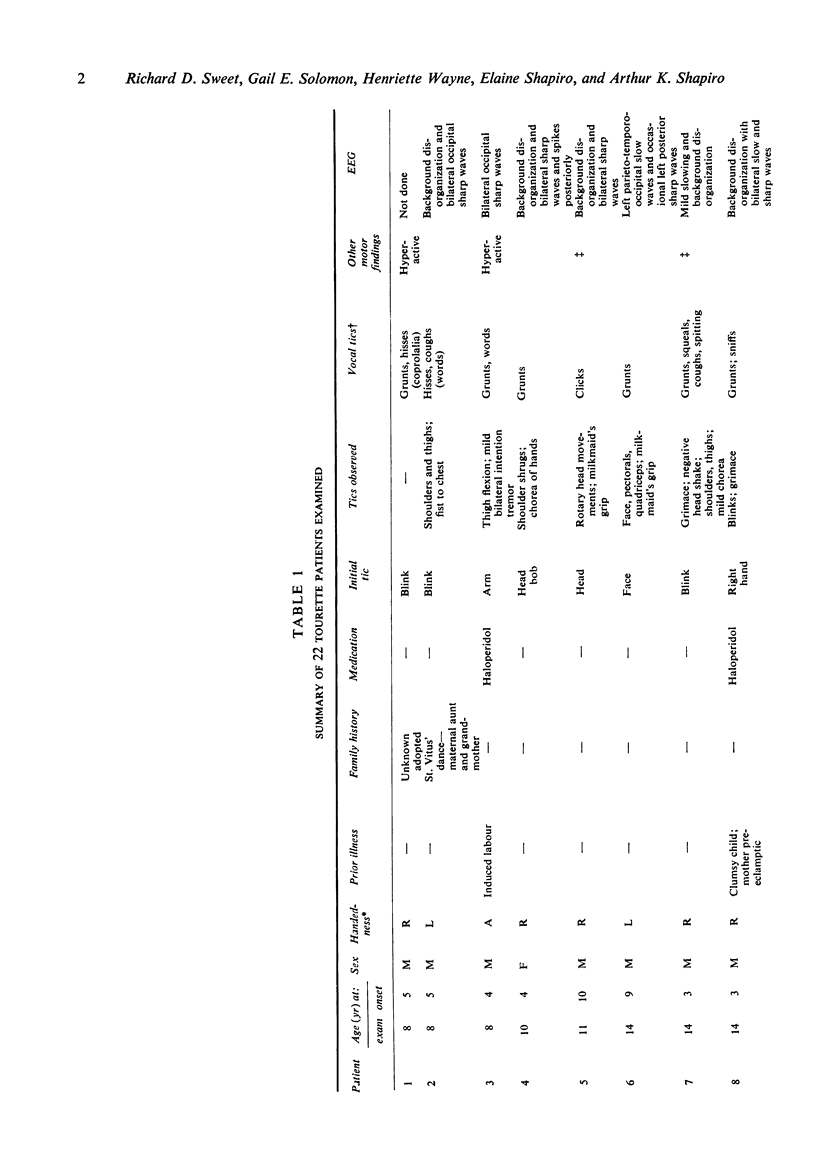
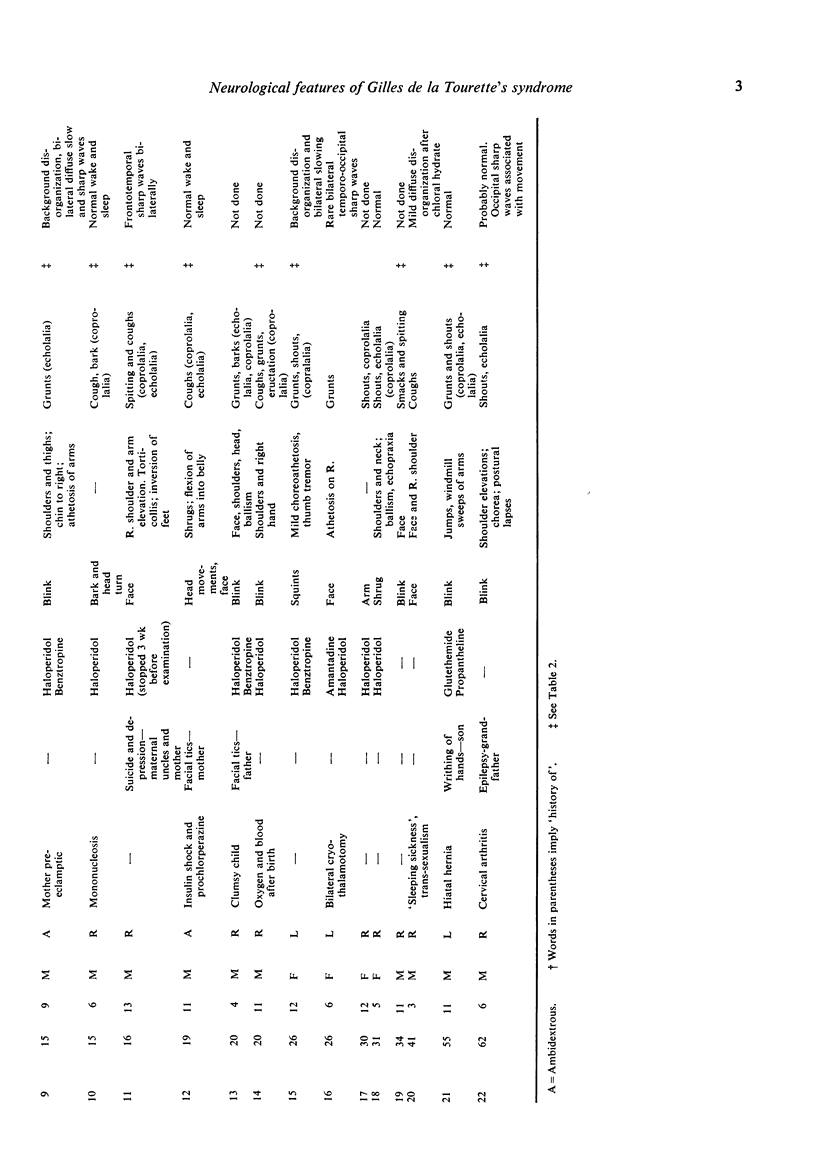
Clinical neurological examinations of 22 patients with Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome and written reports of examinations of seven other patients are reported. Half the personally examined patients had minor motor asymmetries in addition to the typical motor and vocal tics found in all the patients. Thirty-six per cent of patients were left handed or ambidextrous. Electroencephalograms performed on 17 of the 22 patients showed non-specific abnormalities in 12 of them. These findings suggest that a neurological disorder underlies Tourette's syndrome, but they do not clarify its nature.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON W. W. THE HYPERKINETIC CHILD: A NEUROLOGICAL APPRAISAL. Neurology. 1963 Nov;13:968–973. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.11.968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTHASAR K. Uber das anatomische Substrat der generalisierten Tic-Krank-heit (maladie des tics, Gilles de la Tourette): Entwicklungshemmung des corpus striatum. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr Z Gesamte Neurol Psychiatr. 1957;195(6):531–549. doi: 10.1007/BF00343129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPEL J. L., BROWN N., JENKINS R. L. TOURETTE'S DISEASE: SYMPTOMATIC RELIEF WITH HALOPERIDOL. Am J Psychiatry. 1964 Dec;121:608–610. doi: 10.1176/ajp.121.6.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORBIN H. P., BICKFORD R. G. Studies of the electroencephalogram of normal children: comparison of viscal and automatic frequency analyses. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1955 Feb;7(1):15–28. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(55)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapel J. L. Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome. Latah, myriachit, and jumpers revisited. N Y State J Med. 1970 Sep 1;70(17):2201–2204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Mathews A. M., Connell P. H., Shapiro D. A. Tics and Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome: a follow-up study and critical review. Br J Psychiatry. 1969 Nov;115(528):1229–1241. doi: 10.1192/bjp.115.528.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley E. M., Nicholson J. T., Betts J. J., Weatherall D. J. Acanthocytosis, normolipoproteinaemia and multiple tics. Postgrad Med J. 1970 Dec;46(542):698–701. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.46.542.698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGiacomo J. N., Fahn S., Glass J. B., Westlake R. J. A case with Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome: recurrent refractoriness to haloperidol, and unsuccessful treatment with L-dopa. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1971 Feb;152(2):115–117. doi: 10.1097/00005053-197102000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feild J. R., Corbon K. B., Goldstein N. P., Klass D. W. Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome. Neurology. 1966 May;16(5):453–462. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.5.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando S. J. Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome. A report on four cases and a review of published case reports. Br J Psychiatry. 1967 Jun;113(499):607–617. doi: 10.1192/bjp.113.499.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itil T. M., Gannon P., Hsu W., Klingenberg H. Digital computer analyzed sleep and resting EEG during haloperidol treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 1970 Oct;127(4):462–471. doi: 10.1176/ajp.127.4.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A. R. Gilles de la Tourette's disease. An overview. N Y State J Med. 1970 Sep 1;70(17):2197–2200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messiha F. S., Knopp W., Vanecko S., O'Brien V., Corson S. A. Haloperidol therapy in Tourette's syndrome: neurophysiological, biochemical and behavioral correlates. Life Sci I. 1971 Apr 15;10(8):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90110-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morphew J. A., Sim M. Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome: a clinical and psychopathological study. Br J Med Psychol. 1969 Dec;42(4):293–301. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8341.1969.tb02083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINE R. S. Minimal chronic brain syndromes in children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1962 Feb;4:21–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1962.tb03094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRECHTL H. F., STEMMER J. The choreiform syndrome in children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1962 Apr;4:119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1962.tb03120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. K., Shapiro E. Treatment of Gilles de la Tourette's Syndrome with haloperidol. Br J Psychiatry. 1968 Mar;114(508):345–350. doi: 10.1192/bjp.114.508.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Taylor K. M., Coyle J. T., Meyerhoff J. L. The role of brain dopamine in behavioral regulation and the actions of psychotropic drugs. Am J Psychiatry. 1970 Aug;127(2):199–207. doi: 10.1176/ajp.127.2.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOHLFART G., INGVAR D. H., HELLBERG A. M. Compulsory shouting (Benedek's "klazomania") associated with oculogyric spasms in chronic epidemic encephalitis. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1961;36:369–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1961.tb01051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh B. K., McNay J. L., Goldberg L. I. Attenuation of dopamine renal and mesenteric vasodilation by haloperidol: evidence for a specific dopamine receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Aug;168(2):303–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



