Abstract
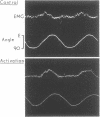
The stretch reflexes and shortening reactions evoked in six normal subjects during reinforcement were compared with those recorded from patients with Parkinson's disease. Although the responses to stretch and shortening of triceps were similar in both groups, they differed in the biceps muscle. In Parkinson's disease increasing muscle stretch of biceps was associated with increasing reflex activity, whereas the reverse relationship occurred in the activated normal subjects. The biceps EMG during sinusoidal stretching comprised two peaks in the activated normal group, a phenomenon not seen in Parkinson's disease. It is postulated that this response in the activated normal group is due to activation or reinforcement engaging long-loop reflexes. It is concluded that the rigidity of Parkinson's disease is not simply an exaggeration of the stretch reflexes found in normal man but differs in that the effects of flexor reflex afferent nerve fibres are submerged by group Ia afferent activity, and that some long-loop reflex pathways are no longer operative in Parkinson's disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews C. J., Burke D., Lance J. W. The response to muscle stretch and shortening in Parkinsonian rigidity. Brain. 1972;95(4):795–812. doi: 10.1093/brain/95.4.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby P., Burke D. Stretch reflexes in the upper limb of spastic man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Dec;34(6):765–771. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.6.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Andrews C. J., Gillies J. D. The reflex response to sinusoidal stretching in spastic man. Brain. 1971;94(3):455–470. doi: 10.1093/brain/94.3.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Gillies J. D., Lance J. W. Hamstrings stretch reflex in human spasticity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Jun;34(3):231–235. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.3.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Gillies J. D., Lance J. W. The quadriceps stretch reflex in human spasticity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Apr;33(2):216–223. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.2.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASSEL M. M., DIAMANTOPOULOS E. THE JENDRASSIK MANEUVER. I. THE PATTERN OF REINFORCEMENT OF MONOSYNAPTIC REFLEXES IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND PATIENTS WITH SPASTICITY OF RIGIDITY. Neurology. 1964 Jun;14:555–560. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.6.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau W. M., Struppler A., Mehls O. A comparative electromyographic study of the reactions to passive movement in parkinsonism and in normal subjects. Neurology. 1966 Jan;16(1):34–48. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARK R. F. TONIC STRETCH REFLEXES IN THE CALF MUSCLES OF NORMAL HUMAN SUBJECTS. Nature. 1963 Jul 6;199:50–52. doi: 10.1038/199050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson P. D. Frequency-response characteristics of the tonic stretch reflexes of biceps brachii muscle in intact man. Med Biol Eng. 1972 Jul;10(4):460–472. doi: 10.1007/BF02474194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]