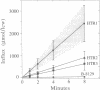
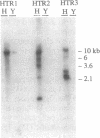
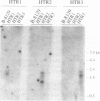
Abstract
A human cDNA library in lambda-yes plasmid was used to transform a strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with defects in histidine biosynthesis (his4-401) and histidine permease (hip1-614) and with the general amino acid permease (GAP) repressed by excess ammonium. We investigated three plasmids complementing the transport defect on a medium with a low concentration of histidine. Inserts in these plasmids hybridized with human genomic but not yeast genomic DNA, indicating their human origin. mRNA corresponding to the human DNA insert was produced by each yeast transformant. Complementation of the histidine transport defect was confirmed by direct measurement of histidine uptake, which was increased 15- to 65-fold in the transformants as compared with the parental strain. Competitive inhibition studies, measurement of citrulline uptake, and lack of complementation in gap1- strains indicated that the human cDNA genes code for proteins that prevent GAP repression by ammonium. The amino acid sequence encoded by one of the cDNA clones is related to T-complex proteins, which suggests a "chaperonin"-like function. We suggest that the human chaperonin-like protein stabilizes the NPR1 gene product and prevents inactivation of GAP.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton L. M., Tseng L., Scadden D., Cunningham J. M. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker D. M., Fikes J. D., Guarente L. A cDNA encoding a human CCAAT-binding protein cloned by functional complementation in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1968–1972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty K. M., Brandriss M. C., Valle D. Cloning human pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase cDNA by complementation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):871–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Mulligan J. T., Ramer S. W., Spottswood M., Davis R. W. Lambda YES: a multifunctional cDNA expression vector for the isolation of genes by complementation of yeast and Escherichia coli mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1731–1735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Spottswood M. R. A new human p34 protein kinase, CDK2, identified by complementation of a cdc28 mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is a homolog of Xenopus Eg1. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2653–2659. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07808.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J., Hemmingsen S. M. Molecular chaperones: proteins essential for the biogenesis of some macromolecular structures. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Aug;14(8):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J. Molecular chaperones: the plant connection. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):954–959. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenson M. Inactivation-reactivation process and repression of permease formation regulate several ammonia-sensitive permeases in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):135–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenson M. Study of the positive control of the general amino-acid permease and other ammonia-sensitive uptake systems by the product of the NPR1 gene in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):141–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07439.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S. Sequence and structural homology between a mouse T-complex protein TCP-1 and the 'chaperonin' family of bacterial (GroEL, 60-65 kDa heat shock antigen) and eukaryotic proteins. Biochem Int. 1990;20(4):833–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauniaux J. C., Grenson M. GAP1, the general amino acid permease gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleotide sequence, protein similarity with the other bakers yeast amino acid permeases, and nitrogen catabolite repression. Eur J Biochem. 1990 May 31;190(1):39–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. W., Closs E. I., Albritton L. M., Cunningham J. M. Transport of cationic amino acids by the mouse ecotropic retrovirus receptor. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):725–728. doi: 10.1038/352725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhoff C., Willison K. Nucleotide and amino-acid sequence of human testis-derived TCP1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4247–4247. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. At least six nucleotides preceding the AUG initiator codon enhance translation in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):947–950. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Dulić V., Reed S. I. Isolation of three novel human cyclins by rescue of G1 cyclin (Cln) function in yeast. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1197–1206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90042-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minet M., Lacroute F. Cloning and sequencing of a human cDNA coding for a multifunctional polypeptide of the purine pathway by complementation of the ade2-101 mutant in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1990 Nov;18(4):287–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00318209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya-Tsuji J., Nomoto S., Yasuda H., Reed S. I., Matsumoto K. Cloning of a human cDNA encoding a CDC2-related kinase by complementation of a budding yeast cdc28 mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North G. Cell biology. A cytoplasmic chaperonin? Nature. 1991 Dec 12;354(6353):434–435. doi: 10.1038/354434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxender D. L., Collarini E. J., Shotwell M. A., Lobaton C. D., Moreno A., Campbell G. S. Regulation and genetics of amino acid transport. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;456:404–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb14892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytka J. Positive selection of general amino acid permease mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):562–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.562-570.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild D., Brake A. J., Kiefer M. C., Young D., Barr P. J. Cloning of three human multifunctional de novo purine biosynthetic genes by functional complementation of yeast mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2916–2920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segel G. B., Cokelet G. R., Lichtman M. A. The measurement of lymphocyte volume: importance of reference particle deformability and counting solution tonicity. Blood. 1981 May;57(5):894–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segel G. B., Simon W., Lichtman M. A. Multicomponent analysis of amino acid transport in human lymphocytes. Diminished L-system transport in chronic leukemic B lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):17–24. doi: 10.1172/JCI111398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver L. M., White M. A gene product of the mouse t complex with chemical properties of a cell surface-associated component of the extracellular matrix. Dev Biol. 1982 Jun;91(2):423–430. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka J., Fink G. R. The histidine permease gene (HIP1) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. D., Nimmesgern E., Wall J. S., Hartl F. U., Horwich A. L. A molecular chaperone from a thermophilic archaebacterium is related to the eukaryotic protein t-complex polypeptide-1. Nature. 1991 Dec 12;354(6353):490–493. doi: 10.1038/354490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbol M., Jauniaux J. C., Grenson M. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae NPR1 gene required for the activity of ammonia-sensitive amino acid permeases encodes a protein kinase homologue. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jul;222(2-3):393–399. doi: 10.1007/BF00633845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbol M., Jauniaux J. C., Vissers S., Grenson M. Isolation of the NPR1 gene responsible for the reactivation of ammonia-sensitive amino-acid permeases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. RNA analysis and gene dosage effects. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 4;164(3):607–612. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainer S. R., Boveris A., Ramos E. H. Control of leucine transport in yeast by periplasmic binding proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 May 1;262(2):481–490. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90399-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Kavanaugh M. P., North R. A., Kabat D. Cell-surface receptor for ecotropic murine retroviruses is a basic amino-acid transporter. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):729–731. doi: 10.1038/352729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willison K. R., Dudley K., Potter J. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of a haploid expressed gene encoding t complex polypeptide 1. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):727–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90839-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward J. R., Cirillo V. P. Amino acid transport and metabolism in nitrogen-starved cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):714–723. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.714-723.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]