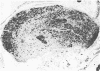
Abstract
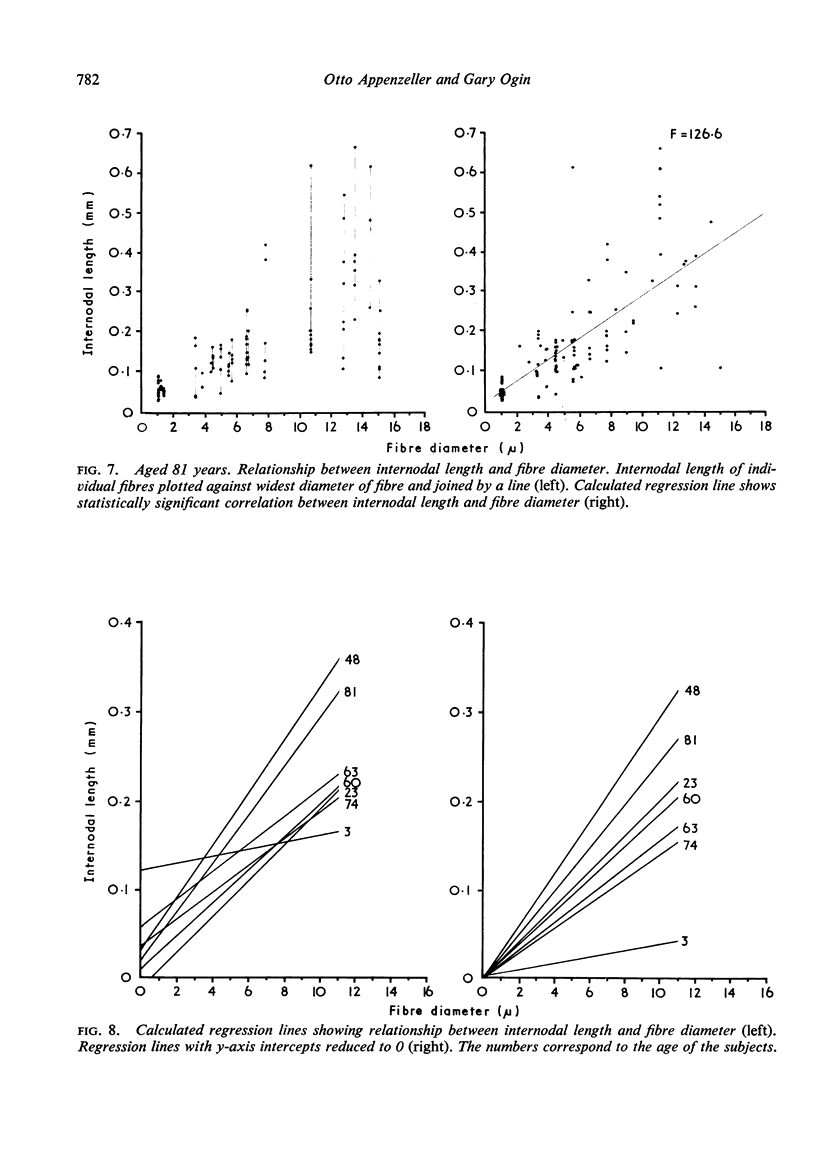
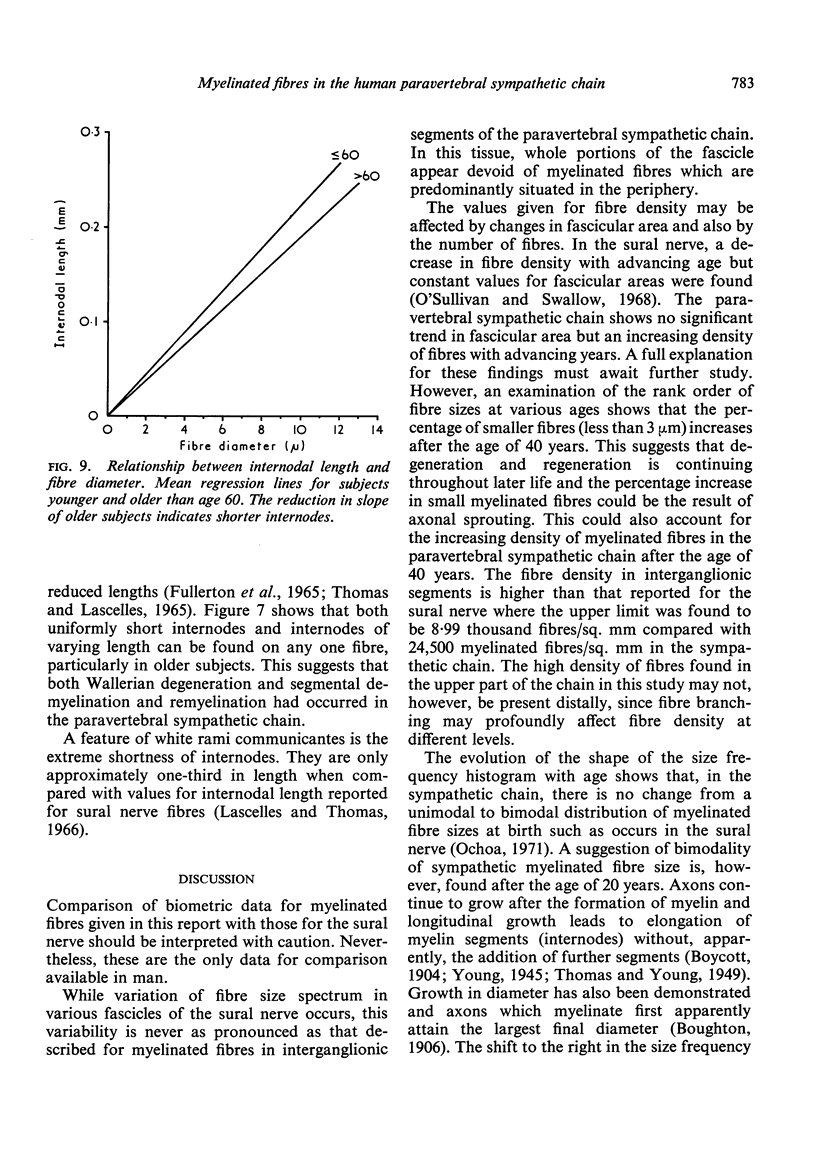
Myelinated fibres in the human sympathetic paravertebral chain were examined histologically and in single teased fibre preparations in various age groups in subjects dying from disorders not affecting primarily the autonomic nervous system. An increase in fibre density predominantly due to an increase in the number of small fibres was found in older subjects. A correlation between internodal length and fibre diameter was found but the internodes of sympathetic myelinated fibres are shorter for any given diameter than those found on fibres of comparable size in the sural nerve. A reduction in internodal lengths with advancing years was demonstrated. These observations are interpreted to show that Wallerian degeneration and segmental demyelination occur with increasing frequency in old age and that regeneration does not keep pace with successive degenerative events. The deterioration in function of the autonomic nervous system with advancing years may be attributed in part to the changes found in myelinated fibres in the paravertebral sympathetic chain.
Full text
PDF

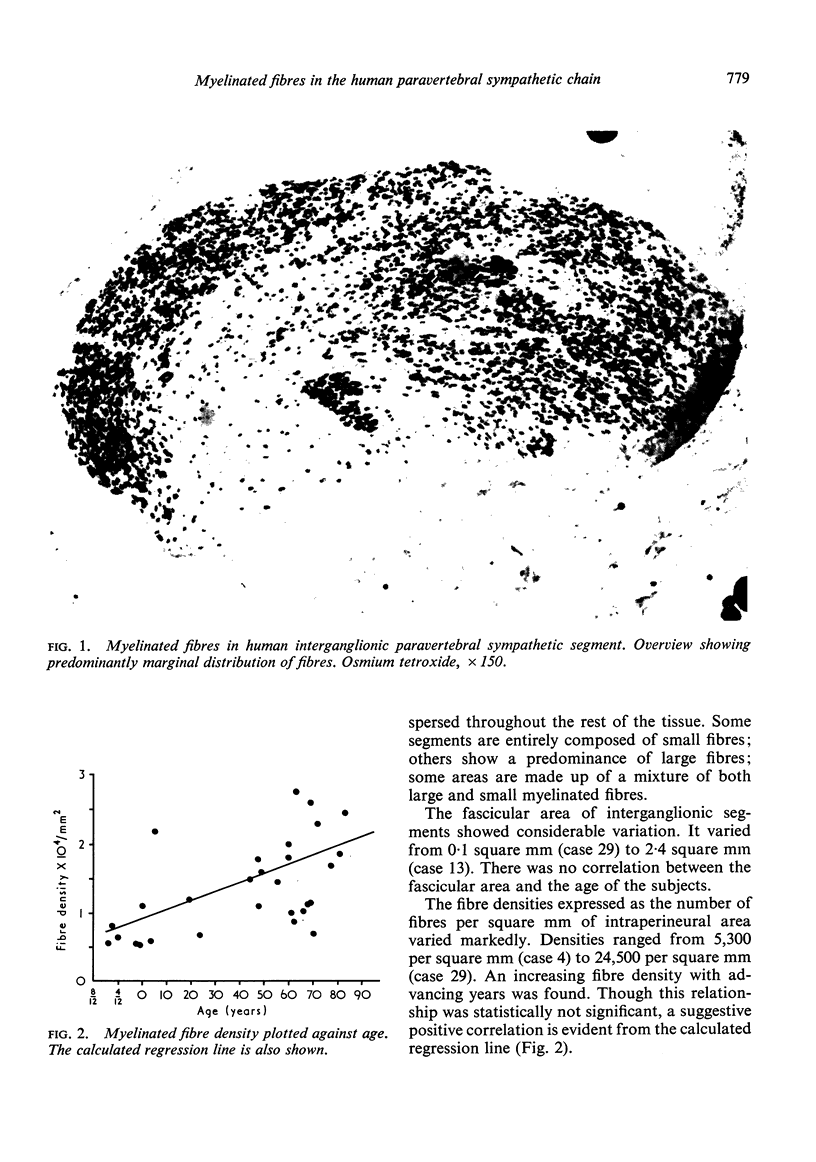
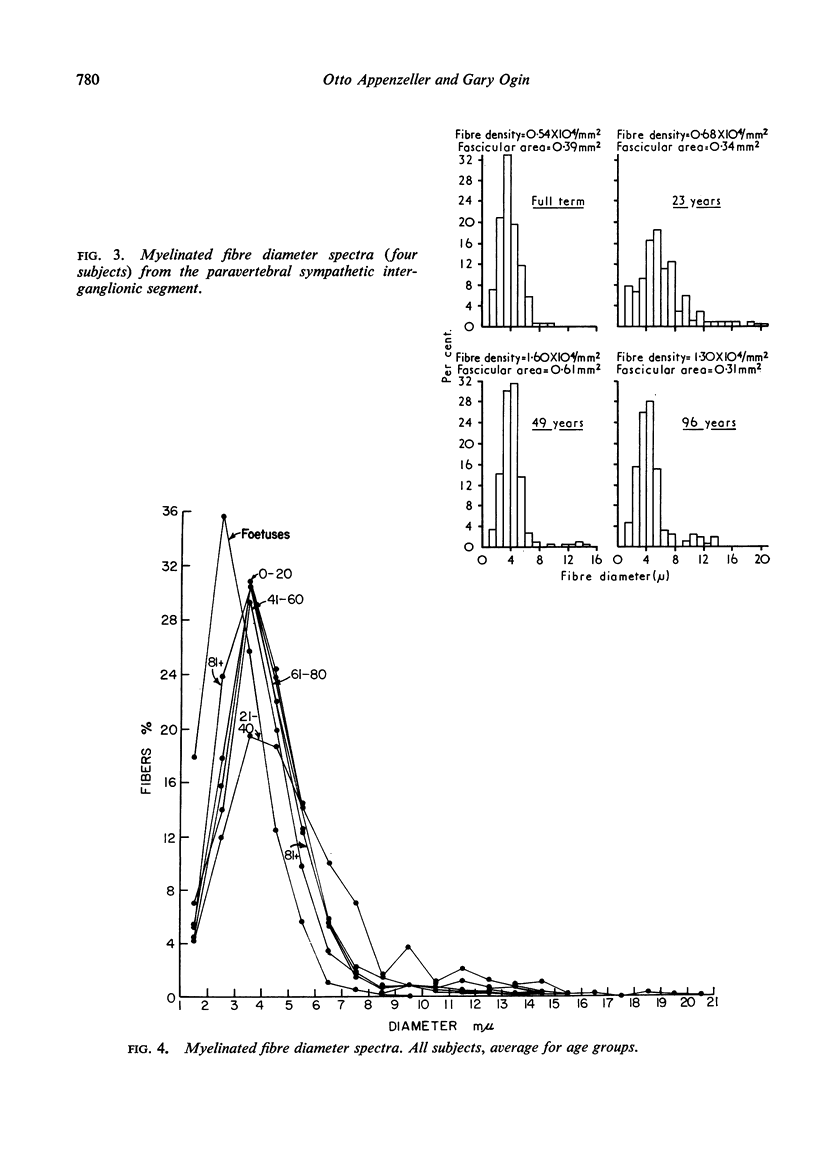
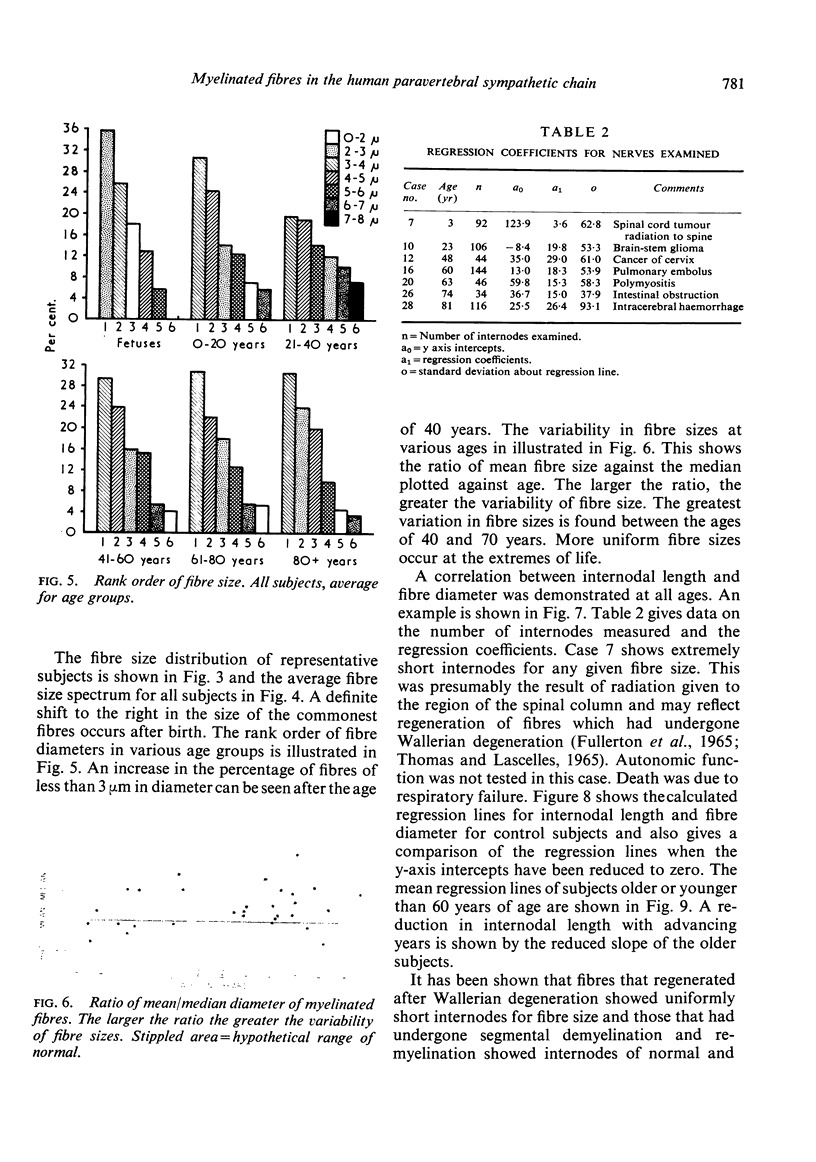


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPENZELLER O., DESCARRIES L. CIRCULATORY REFLEXES IN PATIENTS WITH CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASE. N Engl J Med. 1964 Oct 15;271:820–823. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196410152711604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appenzeller O., Kornfeld M., MacGee J. Neuropathy in chronic renal disease. A microscopic, ultrastructural, and biochemical study of sural nerve biopsies. Arch Neurol. 1971 May;24(5):449–461. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00480350083009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appenzeller O., Richardson E. P., Jr The sympathetic chain in patients with diabetic and alcoholic polyneuropathy. Neurology. 1966 Dec;16(12):1205–1209. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.12.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold N., Harriman D. G. The incidence of abnormality in control human peripheral nerves studied by single axon dissection. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Feb;33(1):55–61. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boycott A. E. On the number of nodes of Ranvier in different stages of the growth of nerve fibres in the frog. J Physiol. 1903 Dec 14;30(3-4):370–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1903.sp001001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAGH J. B., JACOBS J. M. SOME QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF DIPHTHERITIC NEUROPATHY. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Jun;45:309–322. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M. The effect of posture on subjects with cerebrovascular disease. Q J Med. 1970 Oct;39(156):485–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutrecht J. A., Dyck P. J. Segmental demyelinization in peroneal muscular atrophy: nerve fibers teased from sural nerve biopsy specimens. Mayo Clin Proc. 1966 Nov;41(11):775–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL T. H. Senile deterioration of the central nervous system; a clinical study. Br Med J. 1949 Jan 8;1(4592):56–58. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4592.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lascelles R. G., Thomas P. K. Changes due to age in internodal length in the sural nerve in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Feb;29(1):40–44. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRIS A. H., SHOCK N. W., WAGMAN I. H. Age changes in the maximum conduction velocity of motor fibers of human ulnar nerves. J Appl Physiol. 1953 Apr;5(10):589–593. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1953.5.10.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan D. J., Swallow M. The fibre size and content of the radial and sural nerves. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):464–470. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa J., Mair W. G. The normal sural nerve in man. II. Changes in the axons and Schwann cells due to ageing. Acta Neuropathol. 1969;13(3):217–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00690643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa J. The sural nerve of the human foetus: electron microscope observations and counts of axons. J Anat. 1971 Feb;108(Pt 2):231–245. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi O., Perri V. Effetti della piritiamina e dell'ossitiamina sull'ampiezza del potenziale d'azione e la velocità di conduzione delle fibre del tronco simpatico cervicale del ratto. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1969 Dec 31;45(24):1597–1601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K., LASCELLES R. G. SCHWANN-CELL ABNORMALITIES IN DIABETIC NEUROPATHY. Lancet. 1965 Jun 26;1(7400):1355–1357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K., YOUNG J. Z. Internode lengths in the nerves of fishes. J Anat. 1949 Oct;83(4):336-50, pl. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIZOSO A. D. The relationship between internodal length and growth in human nerves. J Anat. 1950 Oct;84(4):342–353. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizoso A. D., Young J. Z. Internode length and fibre diameter in developing and regenerating nerves. J Anat. 1948 Apr;82(Pt 1-2):110–134.1. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]