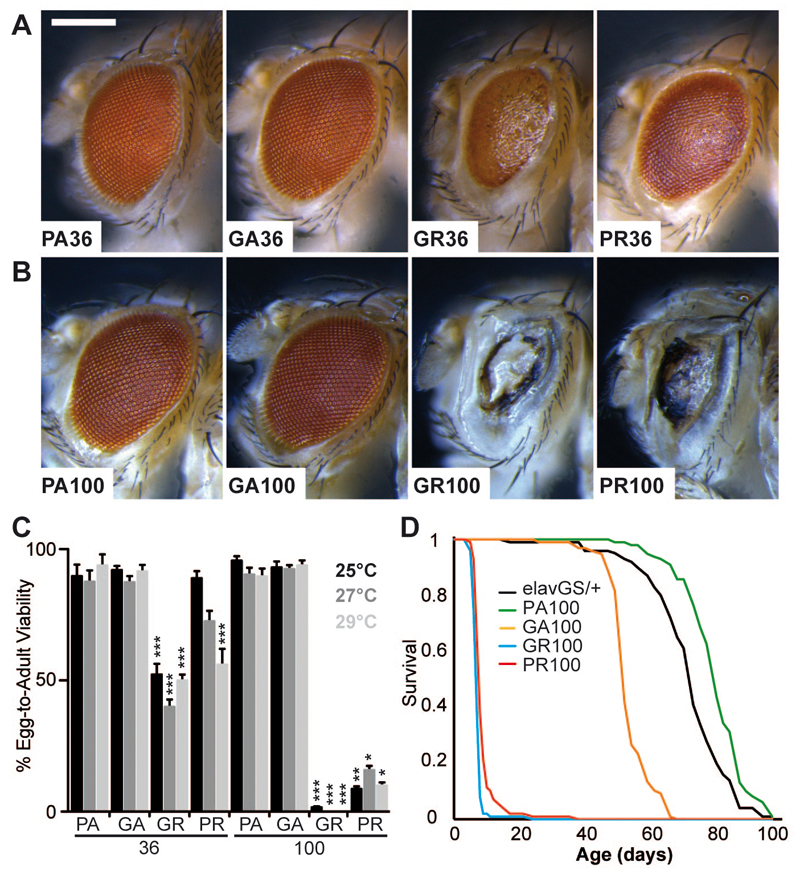
Fig. 3. DPR toxicity was caused by poly-GR and poly-PR proteins.
“Protein-only” constructs for individual DPR proteins were expressed in the Drosophila eye (A-C), and the adult nervous system (D). (A) (GR)36 and (PR)36 caused eye degeneration, while (GA)36 and (PA)36 had no effect. Genotypes were: w; UAS-PA36/GMR-Gal4, w; UAS-GA36/GMR-Gal4, w; UAS-GR36/GMR-Gal4, w; UAS-PR36/GMR-Gal4. Scale bar represents 200 µm. (B) (GR)100 and (PR)100 caused extensive eye degeneration, while (GA)100 and (PA)100 had no effect. Genotypes were: w; UAS-PA100/GMR-Gal4, w; UAS-GA100/GMR-Gal4, w; UAS-GR100/GMR-Gal4, w; UAS-PR100/GMR-Gal4. (C) Quantification of egg-to-adult viability showed (GR)100 and (PR)100 caused a substantial reduction in survival, whereas (GA)100 and (PA)100 had no effect (Kruskal Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison, selected pairs, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, error bars represent SEM). Genotypes were as in (A) and (B). (D) Expression of (GR)100 and (PR)100 in adult neurons using the elav-GeneSwitch (elavGS) driver caused a substantial decrease in viability (p<0.001, log-rank test); (GA)100 caused a late-onset decrease in survival, and (PA)100 or elavGS driver alone had no effect. Genotypes were: w; elavGS/+, w; UAS-PA100/+; elavGS/+, w; UAS-GA100/+; elavGS/+, w; UAS-GR100/+; elavGS/+, w; UAS-PR100/+; elavGS/+.